Featured
-
-
Article |
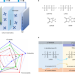 Stable non-corrosive sulfonimide salt for 4-V-class lithium metal batteries
Stable non-corrosive sulfonimide salt for 4-V-class lithium metal batteries
Lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide is used as a conducting salt for rechargeable lithium metal batteries because of its stability, but corrosion with aluminium current collectors is an issue. A non-corrosive sulfonimide salt is shown to suppress anodic dissolution of an Al current collector at high potentials while improving cycling.
- Lixin Qiao
- , Uxue Oteo
- & Heng Zhang
-
News & Views |
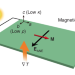 Anisotropy boosts transverse thermoelectrics
Anisotropy boosts transverse thermoelectrics
Despite its tiny magnetization, the non-collinear antiferromagnet YbMnBi2 is shown to possess exceptional transverse thermoelectric performance owing to its anisotropic transport properties.
- Ken-ichi Uchida
-
Article |
 Tandem catalysis with double-shelled hollow spheres
Tandem catalysis with double-shelled hollow spheres
Metal oxide–zeolite bifunctional catalysts allow coupling of reactions and so enhance catalytic processes, but structure and reactivity control is difficult. Here, a general synthesis is presented for metal oxide–zeolite double-shelled hollow spheres, which outperform other catalysts for petroleum production.
- Jiadong Xiao
- , Kang Cheng
- & Bert M. Weckhuysen
-
Article |
 Suspension electrolyte with modified Li+ solvation environment for lithium metal batteries
Suspension electrolyte with modified Li+ solvation environment for lithium metal batteries
Stable solid–electrolyte interphases on Li anodes are crucial for reliable Li metal batteries. A suspension electrolyte design that modifies the Li+ solvation environment in liquid electrolytes and creates inorganic-rich interphases on Li is now reported.
- Mun Sek Kim
- , Zewen Zhang
- & Yi Cui
-
Article |
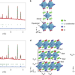 Hydride-ion-conducting K2NiF4-type Ba–Li oxyhydride solid electrolyte
Hydride-ion-conducting K2NiF4-type Ba–Li oxyhydride solid electrolyte
Although using proton (H+) conductors is attractive for energy applications, practical conductivity at intermediate temperatures (200–400 °C) remains a challenge. A K2NiF4-type Ba–Li oxyhydride is shown to exhibit a temperature-independent hydrogen conductivity of more than 0.01 S cm–1 above 315 °C.
- Fumitaka Takeiri
- , Akihiro Watanabe
- & Genki Kobayashi
-
Article |
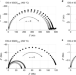 Photo-enhanced ionic conductivity across grain boundaries in polycrystalline ceramics
Photo-enhanced ionic conductivity across grain boundaries in polycrystalline ceramics
Grain boundary conductivity limitations are ubiquitous in material science. Illumination with above-bandgap light is now shown to decrease grain boundary resistance in a model gadolinium-doped ceria solid ionic conductor.
- Thomas Defferriere
- , Dino Klotz
- & Harry L. Tuller
-
Article
| Open Access A smart and responsive crystalline porous organic cage membrane with switchable pore apertures for graded molecular sieving
A smart and responsive crystalline porous organic cage membrane with switchable pore apertures for graded molecular sieving
The separation of multicomponent mixtures is performed by distillation, as multiple-membrane cascades are too complex. Here, a porous organic cage composite undergoes solid-state transformation in solvent; this alters pore size, enabling graded separation of three dyes with a single membrane.
- Ai He
- , Zhiwei Jiang
- & Andrew I. Cooper
-
Article |
 Inter-facet junction effects on particulate photoelectrodes
Inter-facet junction effects on particulate photoelectrodes
In anisotropically shaped photocatalyst particles different constituent facets may form inter-facet junctions at their adjoining edges. Using multimodal functional imaging, inter-facet junction effects on anisotropically shaped bismuth vanadate particles are revealed.
- Xianwen Mao
- & Peng Chen
-
Comment |
 Flexible automation accelerates materials discovery
Flexible automation accelerates materials discovery
Automated experiments can accelerate research and development. ‘Flexible automation’ enables the cost- and time-effective design, construction and reconfiguration of automated experiments. Flexible automation is empowering researchers to deploy new science and technology faster than ever before.
- Benjamin P. MacLeod
- , Fraser G. L. Parlane
- & Curtis P. Berlinguette
-
Article |
 Effect of crystallite geometries on electrochemical performance of porous intercalation electrodes by multiscale operando investigation
Effect of crystallite geometries on electrochemical performance of porous intercalation electrodes by multiscale operando investigation
Designing electrode architectures for Li-ion batteries that can be reversibly accessible for ion storage can be challenging. Using operando techniques the mechanistic origin of lithiation-induced phase transformations in a V2O5 model cathode is now clarified.
- Yuting Luo
- , Yang Bai
- & Sarbajit Banerjee
-
News & Views |
 Confined water controls capacitance
Confined water controls capacitance
By using a battery of experimental and theoretical methods, it is shown that ion intercalation into the electrode material birnessite is mediated by structural water.
- Patrice Simon
- & Yury Gogotsi
-
Article
| Open Access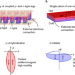 Giant anomalous Nernst signal in the antiferromagnet YbMnBi2
Giant anomalous Nernst signal in the antiferromagnet YbMnBi2
The anomalous Nernst effect (ANE) in topological materials with large Berry curvature shows great potential for transverse thermoelectrics, but antiferromagnets typically show small ANEs. The antiferromagnet YbMnBi2 has an ANE thermopower of 3 μV K−1, similar to ferromagnets, and a larger ANE conductivity.
- Yu Pan
- , Congcong Le
- & Claudia Felser
-
Article |
 Zwitterionic materials with disorder and plasticity and their application as non-volatile solid or liquid electrolytes
Zwitterionic materials with disorder and plasticity and their application as non-volatile solid or liquid electrolytes
The tunability of covalently bound cationic and anionic moieties of zwitterionic materials makes them attractive for potential applications. A family of zwitterions exhibiting molecular disorder and plasticity allows their use as a solid-state conductive matrix.
- Faezeh Makhlooghiazad
- , Luke A. O’Dell
- & Jennifer M. Pringle
-
Article |
 Electronic screening using a virtual Thomas–Fermi fluid for predicting wetting and phase transitions of ionic liquids at metal surfaces
Electronic screening using a virtual Thomas–Fermi fluid for predicting wetting and phase transitions of ionic liquids at metal surfaces
Ionic and dipolar liquids display unexpected behaviours, especially in confinement, that are relevant to energy storage, electrochemistry and catalysis. An approach that involves electronic screening while capturing molecular aspects of interfacial fluids is now proposed.
- Alexander Schlaich
- , Dongliang Jin
- & Benoit Coasne
-
Review Article |
 High-performance thermoelectrics and challenges for practical devices
High-performance thermoelectrics and challenges for practical devices
Thermoelectric materials can generate energy from a heat differential. This Review provides an overview of mid- to high-temperature thermoelectrics, their application in modules, and the issues that need to be addressed to enable commercial implementation of state-of-the-art materials.
- Qingyu Yan
- & Mercouri G. Kanatzidis
-
Review Article |
 Strain analysis and engineering in halide perovskite photovoltaics
Strain analysis and engineering in halide perovskite photovoltaics
This Review provides an outlook on current understanding of the role of strain on the performance and stability of perovskite solar cells, as well as on tools to characterize strain in halide perovskite films and on strain management strategies.
- Dongtao Liu
- , Deying Luo
- & Wei Zhang
-
News & Views |
 Breaking thermoelectric performance limits
Breaking thermoelectric performance limits
Through meticulous care for detail, researchers have now shattered the ceiling on thermoelectric performance, achieving a figure of merit above 3 for bulk SnSe polycrystalline powder.
- Bo Brummerstedt Iversen
-
Article
| Open Access Polycrystalline SnSe with a thermoelectric figure of merit greater than the single crystal
Polycrystalline SnSe with a thermoelectric figure of merit greater than the single crystal
SnSe has a very high thermoelectric figure of merit ZT, but uncommonly polycrystalline samples have higher lattice thermal conductivity than single crystals. Here, by controlling Sn reagent purity and removing SnOx impurities, a lower thermal conductivity is achieved, enabling ZT of 3.1 at 783 K.
- Chongjian Zhou
- , Yong Kyu Lee
- & In Chung
-
Article |
 Extending insertion electrochemistry to soluble layered halides with superconcentrated electrolytes
Extending insertion electrochemistry to soluble layered halides with superconcentrated electrolytes
Insertion compounds in layered oxide or sulfide electrodes provide the fundamental basis of current commercialized Li-ion batteries. The feasibility of reversibly intercalating Li+ electrochemically into halide compounds via the use of superconcentrated electrolytes is now demonstrated.
- Nicolas Dubouis
- , Thomas Marchandier
- & Alexis Grimaud
-
Editorial |
 Controlling and capturing emissions
Controlling and capturing emissions
Technological civilization often depends on processes that have a significant environmental impact, but emissions control catalysts or porous adsorbent materials can ameliorate these risks.
-
Review Article |
 Porous materials for carbon dioxide separations
Porous materials for carbon dioxide separations
Porous materials can selectively and reversibly adsorb large quantities of gas. This Review highlights progress made in using this class of materials for CO2 capture processes and discusses key gaps that the materials community can address to accelerate greater adoption of adsorptive carbon capture technologies.
- Rebecca L. Siegelman
- , Eugene J. Kim
- & Jeffrey R. Long
-
Article |
 Chemical vapour deposition of Fe–N–C oxygen reduction catalysts with full utilization of dense Fe–N4 sites
Chemical vapour deposition of Fe–N–C oxygen reduction catalysts with full utilization of dense Fe–N4 sites
Replacing platinum with metal–nitrogen–carbon catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction in proton exchange membrane fuel cells has been impeded by low activity. These limitations have now been overcome by the trans-metalation of Zn–N4 sites into Fe–N4 sites.
- Li Jiao
- , Jingkun Li
- & Qingying Jia
-
Letter |
 Local electronic structure variation resulting in Li ‘filament’ formation within solid electrolytes
Local electronic structure variation resulting in Li ‘filament’ formation within solid electrolytes
Solid electrolytes are promising for enabling the use of Li metal anodes but Li infiltration along grain boundaries can lead to battery failure. Li infiltration in a model solid oxide electrolyte is now found to be strongly associated with local electronic band structure.
- Xiaoming Liu
- , Regina Garcia-Mendez
- & Miaofang Chi
-
Article |
 Revealing the role of the cathode–electrolyte interface on solid-state batteries
Revealing the role of the cathode–electrolyte interface on solid-state batteries
Interfaces play crucial, but still poorly understood, roles in the performance of secondary solid-state batteries. Using crystallographically oriented and highly faceted thick cathodes, the impact of cathode crystallography and morphology on long-term performance is investigated.
- Beniamin Zahiri
- , Arghya Patra
- & Paul V. Braun
-
Article |
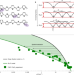 Quantifying charge carrier localization in chemically doped semiconducting polymers
Quantifying charge carrier localization in chemically doped semiconducting polymers
A model describing the behaviour of charge carriers in semiconducting polymers both in the hopping-like and metal-like regimes is developed, and used to quantify charge carrier localization and other transport parameters in organic semiconductors.
- Shawn A. Gregory
- , Riley Hanus
- & Shannon K. Yee
-
Matters Arising |
Reply to: On the observation of photo-excitation effects in molecules using muon spin spectroscopy
- M. Jingliang
- , K. Wang
- & A. J. Drew
-
Article |
 Solid-state rigid-rod polymer composite electrolytes with nanocrystalline lithium ion pathways
Solid-state rigid-rod polymer composite electrolytes with nanocrystalline lithium ion pathways
Developing safe electrolytes compatible with high-energy-density electrodes is key for the next generation of lithium-based batteries. Stable solid-state rigid-rod polymer composite electrolytes with nanocrystalline lithium ion pathways are now proposed.
- Ying Wang
- , Curt J. Zanelotti
- & Louis A. Madsen
-
News & Views |
 Hydrogen freedom linked to perovskite efficiency
Hydrogen freedom linked to perovskite efficiency
First-principles calculations on a prototypical hybrid organic–inorganic perovskite reveal an unexpected role for hydrogen defects in the optoelectronic properties of this material.
- Leeor Kronik
- & Andrew M. Rappe
-
Article |
 Minimizing hydrogen vacancies to enable highly efficient hybrid perovskites
Minimizing hydrogen vacancies to enable highly efficient hybrid perovskites
First-principles calculations reveal that hydrogen vacancies induce non-radiative losses in methylammonium lead iodide perovskites synthesized under iodine-poor conditions, whereas they are less detrimental in formamidinium-based hybrid perovskites.
- Xie Zhang
- , Jimmy-Xuan Shen
- & Chris G. Van de Walle
-
News & Views |
 Towards practical organic batteries
Towards practical organic batteries
Conjugated sulfonamides have been demonstrated as cathodes with high redox potentials and exceptional atmospheric stability, providing a sustainable alternative to traditional inorganic materials used in commercial lithium-ion batteries.
- Jing Xie
- & Yi-Chun Lu
-
Article |
 Visualizing plating-induced cracking in lithium-anode solid-electrolyte cells
Visualizing plating-induced cracking in lithium-anode solid-electrolyte cells
Lithium dendrite propagation through ceramic electrolytes can prevent the realization of high-energy-density all-solid-state lithium-anode batteries. The propagation of cracks and lithium dendrites through a solid electrolyte has now been tracked as a function of charge.
- Ziyang Ning
- , Dominic Spencer Jolly
- & Peter G. Bruce
-
Article |
 High-rate nanofluidic energy absorption in porous zeolitic frameworks
High-rate nanofluidic energy absorption in porous zeolitic frameworks
Porous materials can absorb energy by water infiltration, but studies at industrially relevant high-rate intrusions are rare. Here, high-rate experiments are performed on ZIFs showing high energy storage capacity, while molecular simulations allow design rules to be formulated for absorption materials.
- Yueting Sun
- , Sven M. J. Rogge
- & Jin-Chong Tan
-
Why it Matters |
 Building on trust and vision
Building on trust and vision
Olga Malinkiewicz, founder of Saule Technologies, discusses her transition from academia to industry.
- Olga Malinkiewicz
-
Article |
 Extraction of mobile charge carrier photogeneration yield spectrum of ultrathin-film metal oxide photoanodes for solar water splitting
Extraction of mobile charge carrier photogeneration yield spectrum of ultrathin-film metal oxide photoanodes for solar water splitting
Although the photogeneration yield spectrum is a key property for photoabsorbers in photovoltaic and photoelectrochemical cells, its characterization remains challenging. An empirical method to extract this parameter through quantum efficiency measurements of ultrathin films is proposed.
- Daniel A. Grave
- , David S. Ellis
- & Avner Rothschild
-
Perspective |
 The changing state of porous materials
The changing state of porous materials
Highly ordered crystalline porous solids are useful for many applications. This Perspective explores the evolution of these systems from the ordered state to the glassy and liquid states, discusses the different types of porous liquid and considers possible applications of these disordered systems.
- Thomas D. Bennett
- , François-Xavier Coudert
- & Andrew I. Cooper
-
Article |
 Development of a photoelectrochemically self-improving Si/GaN photocathode for efficient and durable H2 production
Development of a photoelectrochemically self-improving Si/GaN photocathode for efficient and durable H2 production
Development of efficient yet durable photoelectrodes is of paramount importance for deployment of solar-fuel production. The photoelectrochemically self-improving behaviour of a silicon/gallium nitride photocathode highly efficient for hydrogen production is now reported.
- Guosong Zeng
- , Tuan Anh Pham
- & Francesca M. Toma
-
Article |
 High-performance organic pseudocapacitors via molecular contortion
High-performance organic pseudocapacitors via molecular contortion
Pseudocapacitors exhibit charge-storage mechanisms leading to high-capacity and rapidly cycling devices. An organic system designed via molecular contortion is now shown to exhibit unprecedented electrochemical performance and stability.
- Jake C. Russell
- , Victoria A. Posey
- & Samuel R. Peurifoy
-
Article |
 Microstructural origin of locally enhanced CO2 electroreduction activity on gold
Microstructural origin of locally enhanced CO2 electroreduction activity on gold
Although bulk defects can influence the performance of electrocatalysts used for energy conversion, their structural origins are still unclear. The effects of bulk defects on CO2 electroreduction and H2 evolution activity on Au electrodes are now elucidated.
- Ruperto G. Mariano
- , Minkyung Kang
- & Matthew W. Kanan
-
Article |
 Two-dimensional overdamped fluctuations of the soft perovskite lattice in CsPbBr3
Two-dimensional overdamped fluctuations of the soft perovskite lattice in CsPbBr3
Neutron and X-ray scattering measurements provide further insight into the anharmonic behaviour of lead halide perovskites, revealing that rotations of PbBr6 octahedra in CsPbBr3 crystals occur in a correlated fashion along two-dimensional planes.
- T. Lanigan-Atkins
- , X. He
- & O. Delaire
-
Article |
 Fictitious phase separation in Li layered oxides driven by electro-autocatalysis
Fictitious phase separation in Li layered oxides driven by electro-autocatalysis
Although layered oxides electrodes in lithium-ion batteries are designed under conditions avoiding phase transitions, phase separation during delithiation has been observed. This apparent phase separation is shown to be a dynamical artefact occurring in a many-particle system driven by autocatalytic electrochemical reactions.
- Jungjin Park
- , Hongbo Zhao
- & William C. Chueh
-
Article |
 Electrolyte melt infiltration for scalable manufacturing of inorganic all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries
Electrolyte melt infiltration for scalable manufacturing of inorganic all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries
All-solid-state lithium-ion batteries provide improved safety but typically suffer from high cost and low volumetric energy density. An electrolyte melt-infiltration approach offering reduced manufacturing costs and improved volumetric energy density in all solid cells is proposed.
- Yiran Xiao
- , Kostiantyn Turcheniuk
- & Gleb Yushin
-
Obituary |
 John Meurig Thomas (1932–2020)
John Meurig Thomas (1932–2020)
Sir John Meurig Thomas, who was one of the leading materials and catalytic scientists of his generation, sadly died in November 2020, aged 87.
- Richard Catlow
- & Graham Hutchings
-
Article |
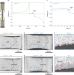 Linking void and interphase evolution to electrochemistry in solid-state batteries using operando X-ray tomography
Linking void and interphase evolution to electrochemistry in solid-state batteries using operando X-ray tomography
Understanding electrochemical behaviour and stability at solid–solid interfaces remains challenging. Operando synchrotron X-ray computed microtomography loss reveals that reconfiguration of interfacial contact is critical to explain cell failure during solid-state battery cycling.
- John A. Lewis
- , Francisco Javier Quintero Cortes
- & Matthew T. McDowell
-
News & Views |
 Making large single crystals of 2D MOFs
Making large single crystals of 2D MOFs
Linking π-conjugated, electron-deficient ligands into atomically precise large single crystals of conducting 2D metal–organic frameworks can allow the determination of intrinsic electrical conductivity and charge transport mechanism.
- Renhao Dong
- & Xinliang Feng
-
Article |
 Revisiting metal fluorides as lithium-ion battery cathodes
Revisiting metal fluorides as lithium-ion battery cathodes
Metal-fluoride-based lithium-ion battery cathodes are typically classified as conversion materials because reconstructive phase transitions are presumed to occur upon lithiation. Metal fluoride lithiation is now shown to be dominated instead by diffusion-controlled displacement mechanisms.
- Xiao Hua
- , Alexander S. Eggeman
- & Clare P. Grey
-
News & Views |
 Magic clusters are better together
Magic clusters are better together
Hybrid materials constructed from the assembly of inorganic building blocks and organic linkers have shown unique properties and applications. Superstructures of semiconductor magic-sized nanoclusters linked by diamines now join this class of materials.
- Raffaella Buonsanti
-
News & Views |
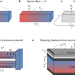 Twisting the thermoelectric potential
Twisting the thermoelectric potential
A multifunctional device produces a much-improved thermoelectric-driven transverse voltage by exploiting a thermoelectric current to drive an anomalous Hall effect in a ferromagnet.
- Andrew F. May
- & Brian C. Sales
-
Article |
 Highly luminescent and catalytically active suprastructures of magic-sized semiconductor nanoclusters
Highly luminescent and catalytically active suprastructures of magic-sized semiconductor nanoclusters
Assembly of magic-sized nanoclusters into suprastructures leads to enhanced luminescence and catalytic activity for CO2 conversion while substantially extending their ambient stability.
- Woonhyuk Baek
- , Megalamane S. Bootharaju
- & Taeghwan Hyeon
-
Letter |
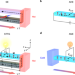 Seebeck-driven transverse thermoelectric generation
Seebeck-driven transverse thermoelectric generation
Transverse thermeoelectrics can simplify devices as the electric field and heat gradient are perpendicular, but the power output is much less than in standard devices. Here, by forming a closed circuit of thermoelectric and magnetic materials, a much larger transverse thermopower is generated.
- Weinan Zhou
- , Kaoru Yamamoto
- & Yuya Sakuraba

 Tunable metal hydroxide–organic frameworks for catalysing oxygen evolution
Tunable metal hydroxide–organic frameworks for catalysing oxygen evolution