Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Electrochemomechanical failure in layered oxide cathodes caused by rotational stacking faults
Electrochemomechanical failure in layered oxide cathodes caused by rotational stacking faults
Degradation is one of the most common causes of capacity deterioration in high-energy-density cathodes. Rotational stacking faults in layered lithium transition-metal oxides are shown to play a critical role in determining their structural and electrochemical stabilities.
- Donggun Eum
- , Sung-O Park
- & Kisuk Kang
-
Article |
 Effect of pre-intercalation on Li-ion diffusion mapped by topochemical single-crystal transformation and operando investigation
Effect of pre-intercalation on Li-ion diffusion mapped by topochemical single-crystal transformation and operando investigation
Pre-intercalation with alkali-metal ions is attractive for accessing higher reversible capacity and improved rate performance in Li-ion batteries. Topochemical single-crystal transformations in a tunnel-structured positive electrode are used to clarify the effect of pre-intercalation in modifying the host lattice and altering diffusion pathways.
- Yuting Luo
- , Joseph V. Handy
- & Sarbajit Banerjee
-
Article
| Open Access Trapped O2 and the origin of voltage fade in layered Li-rich cathodes
Trapped O2 and the origin of voltage fade in layered Li-rich cathodes
Oxygen redox cathodes deliver higher energy densities than those based on transition metal redox but commonly exhibit voltage fade on extended cycling. The loss of O-redox capacity and voltage fade is shown to arise from a reduction in O2−/O2 redox process reversibility and O2 loss.
- John-Joseph Marie
- , Robert A. House
- & Peter G. Bruce
-
Article |
 Nanofeather ruthenium nitride electrodes for electrochemical capacitors
Nanofeather ruthenium nitride electrodes for electrochemical capacitors
Fast charging is driving extensive research on enhanced electrodes for high-performance electrochemical capacitors and micro-supercapacitors. Thick ruthenium nitride pseudocapacitive films are shown to exhibit enhanced capacitance with a time constant of less than 6 s.
- Huy Dinh Khac
- , Grace Whang
- & Christophe Lethien
-
Article |
 Nanosecond solvation dynamics in a polymer electrolyte for lithium batteries
Nanosecond solvation dynamics in a polymer electrolyte for lithium batteries
Solvation dynamics at picosecond timescales critically affect charge transport in aqueous systems, but conflicting values have been reported for organic electrolytes. Lifetimes on the order of 1 ns for mixtures of organic polymer and lithium salt exhibiting ultraslow dynamics of solvation shell break-up are now reported.
- Neel J. Shah
- , Chao Fang
- & Nitash P. Balsara
-
Article
| Open Access Unlocking Li superionic conductivity in face-centred cubic oxides via face-sharing configurations
Unlocking Li superionic conductivity in face-centred cubic oxides via face-sharing configurations
Oxides with a face-centred cubic anion sublattice are generally not considered as solid-state electrolytes. Li superionic conductivity in face-centred cubic oxides with face-sharing Li configurations have now been created through cation over-stoichiometry in rocksalt-type lattices via excess Li.
- Yu Chen
- , Zhengyan Lun
- & Gerbrand Ceder
-
Article
| Open Access Chemo-mechanical failure mechanisms of the silicon anode in solid-state batteries
Chemo-mechanical failure mechanisms of the silicon anode in solid-state batteries
Although silicon anodes are promising for solid-state batteries, they still suffer from poor electrochemical performance. Chemo-mechanical failure mechanisms of composite Si|Li6PS5Cl and solid-electrolyte-free silicon anodes are now revealed and should help in designing improved electrodes.
- Hanyu Huo
- , Ming Jiang
- & Jürgen Janek
-
Article |
 Fast cycling of lithium metal in solid-state batteries by constriction-susceptible anode materials
Fast cycling of lithium metal in solid-state batteries by constriction-susceptible anode materials
Interfacial reactions between lithium and anodes are not well understood in an all-solid environment. For the silicon anode we now demonstrate that, rather than strong Li–Si alloying at the conventional solid–liquid interface, the lithiation reaction of micrometre-sized Si can be greatly constricted at the solid–solid interface.
- Luhan Ye
- , Yang Lu
- & Xin Li
-
Article |
 Localized high-concentration electrolytes get more localized through micelle-like structures
Localized high-concentration electrolytes get more localized through micelle-like structures
Liquid electrolytes in batteries are considered to be macroscopically homogeneous ionic transport media despite having a complex chemical composition and atomistic solvation structures. A micelle-like structure in a localized high-concentration electrolyte for which the solvent acts as a surfactant is reported.
- Corey M. Efaw
- , Qisheng Wu
- & Bin Li
-
Article |
 Sequencing polymers to enable solid-state lithium batteries
Sequencing polymers to enable solid-state lithium batteries
Solid polymer electrolytes are crucial for the development of lithium batteries, but their lower ionic conductivity compared with liquid/ceramics at room temperature limits their practical use. Precise positioning of designed repeating units in alternating polymer sequences now allows the Li+ conductivity to be tuned by up to three orders of magnitude.
- Shantao Han
- , Peng Wen
- & Mao Chen
-
Article |
 Decoupling the roles of Ni and Co in anionic redox activity of Li-rich NMC cathodes
Decoupling the roles of Ni and Co in anionic redox activity of Li-rich NMC cathodes
Lithium-rich nickel manganese cobalt oxide cathodes are widely explored due to their high capacities related to their anionic redox chemistry. A compositional optimization pathway for these materials investigating the variation of using cobalt and nickel now provides valuable guidelines for future high-capacity cathode design.
- Biao Li
- , Zengqing Zhuo
- & Jean-Marie Tarascon
-
Article |
 Improving lithium-ion cells by replacing polyethylene terephthalate jellyroll tape
Improving lithium-ion cells by replacing polyethylene terephthalate jellyroll tape
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) tape is widely used for lithium-ion batteries but its chemical stability has been largely overlooked. Reversible self-discharge is now shown to be virtually eliminated in LiFePO4–graphite cells by replacing PET with polypropylene jellyroll tape.
- Anu Adamson
- , Kenneth Tuul
- & Michael Metzger
-
Article |
 Extreme lithium-metal cycling enabled by a mixed ion- and electron-conducting garnet three-dimensional architecture
Extreme lithium-metal cycling enabled by a mixed ion- and electron-conducting garnet three-dimensional architecture
The development of solid-state Li-metal batteries has been limited by Li plating and stripping rates and the formation of dendrites at relevant current densities. Single-phase mixed ion- and electron-conducting garnet with comparable Li-ion and electronic conductivities is now proposed to tackle these issues.
- George V. Alexander
- , Changmin Shi
- & Eric D. Wachsman
-
Letter
| Open Access Probing lithium mobility at a solid electrolyte surface
Probing lithium mobility at a solid electrolyte surface
Understanding lithium dynamics in solid-state electrolytes used for Li-ion batteries can be challenging. Using nonlinear extreme-ultraviolet spectroscopies, a direct spectral signature of surface lithium ions showing a distinct blueshift relative to the bulk absorption spectra is observed in a prototypical solid-state electrolyte.
- Clarisse Woodahl
- , Sasawat Jamnuch
- & Michael Zuerch
-
Article |
 A soft co-crystalline solid electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries
A soft co-crystalline solid electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries
Alternative solid electrolytes with enhanced thermal and chemical stability are key for advancing lithium batteries. A soft solid electrolyte with improved stability and ionic conductivity, overcoming several limitations of conventional materials, is now reported.
- Prabhat Prakash
- , Birane Fall
- & Michael J. Zdilla
-
Article |
 The role of the electrolyte in non-conjugated radical polymers for metal-free aqueous energy storage electrodes
The role of the electrolyte in non-conjugated radical polymers for metal-free aqueous energy storage electrodes
Redox-active non-conjugated radical polymers are promising candidates for metal-free aqueous batteries but their energy storage mechanism in an aqueous environment remains unclear. The role of the electrolyte in such polymers for designing metal-free aqueous energy storage electrodes is now elucidated.
- Ting Ma
- , Cheng-Han Li
- & Jodie L. Lutkenhaus
-
Article |
 Inhibiting collective cation migration in Li-rich cathode materials as a strategy to mitigate voltage hysteresis
Inhibiting collective cation migration in Li-rich cathode materials as a strategy to mitigate voltage hysteresis
The high energy densities of Li-rich cathodes are promising for Li-ion batteries, but voltage hysteresis limits their practical implementation. Voltage hysteresis is shown to be related to collective migration of metal ions, and isolating migration leads to high-capacity reversible cathodes.
- Jianping Huang
- , Bin Ouyang
- & Gerbrand Ceder
-
Article |
 Resolving complex intralayer transition motifs in high-Ni-content layered cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries
Resolving complex intralayer transition motifs in high-Ni-content layered cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries
High-Ni-content layered cathodes are promising for lithium-ion batteries, but investigating their delithiation-induced phase boundaries is challenging. Intralayer transition motifs at complex phase boundaries in these high-Ni electrodes are now resolved using deep-learning-aided super-resolution electron microscopy.
- Chunyang Wang
- , Xuelong Wang
- & Huolin L. Xin
-
Article |
 A near dimensionally invariable high-capacity positive electrode material
A near dimensionally invariable high-capacity positive electrode material
Delivering inherently stable lithium-ion batteries with electrodes that can reversibly insert and extract large quantities of Li+ with inherent stability during cycling are key. Lithium-excess vanadium oxides with a disordered rocksalt structure are now investigated as high-capacity and long-life cathodes.
- Itsuki Konuma
- , Damian Goonetilleke
- & Naoaki Yabuuchi
-
Article |
 Formation and impact of nanoscopic oriented phase domains in electrochemical crystalline electrodes
Formation and impact of nanoscopic oriented phase domains in electrochemical crystalline electrodes
Electrochemical phase transformation in ion-insertion crystalline electrodes is accompanied by compositional and structural changes. The formation of oriented phase domains and the development of strain gradient is now mapped quantitatively during the electrochemical ion-insertion process.
- Wenxiang Chen
- , Xun Zhan
- & Qian Chen
-
Article |
 Dense inorganic electrolyte particles as a lever to promote composite electrolyte conductivity
Dense inorganic electrolyte particles as a lever to promote composite electrolyte conductivity
Solid-state electrolytes are key to the development of safer and higher-energy-density batteries. Using liquid electrolyte chemistries as models for polymer electrolytes, the effect of adding a variety of porous and dense ceramic electrolytes on the conductivity is now investigated.
- James A. Isaac
- , Didier Devaux
- & Renaud Bouchet
-
Article |
 Polymorphism of garnet solid electrolytes and its implications for grain-level chemo-mechanics
Polymorphism of garnet solid electrolytes and its implications for grain-level chemo-mechanics
Understanding and mitigating filament formation, short-circuit and solid electrolyte fracture is necessary for advanced all-solid-state batteries. The effect of polymorphism on the grain-level chemo-mechanical behaviour of dense and polycrystalline garnet solid electrolytes is now investigated.
- Marm B. Dixit
- , Bairav S. Vishugopi
- & Kelsey B. Hatzell
-
Comment |
 Material science as a cornerstone driving battery research
Material science as a cornerstone driving battery research
Materials and surface sciences have been the driving force in the development of modern-day lithium-ion batteries. This Comment explores this journey while contemplating future challenges, such as interface engineering, sustainability and the importance of obtaining high-quality extensive datasets for enhancing data-driven research.
- Jean-Marie Tarascon
-
Comment |
 Materials innovation from quantum to global
Materials innovation from quantum to global
Twentieth-century utopian visions of a space-age future have been eclipsed by dystopian fears of climate change and environmental degradation. Avoiding such grim forecasts depends on materials innovation and our ability to predict and plan not only their behaviour but also their sustainable manufacture, use and recyclability.
- Philip Ball
-
Article |
 Operando monitoring of single-particle kinetic state-of-charge heterogeneities and cracking in high-rate Li-ion anodes
Operando monitoring of single-particle kinetic state-of-charge heterogeneities and cracking in high-rate Li-ion anodes
Understanding the ion intercalation and degradation mechanisms occurring during realistic battery operation is crucial to developing high-rate battery electrodes. Operando optical scattering microscopy is now used to study single-particle kinetic state-of-charge heterogeneities and cracking in high-rate Li-ion anode materials.
- Alice J. Merryweather
- , Quentin Jacquet
- & Clare P. Grey
-
Article |
 Defect-driven anomalous transport in fast-ion conducting solid electrolytes
Defect-driven anomalous transport in fast-ion conducting solid electrolytes
Solid-state ionic conduction is a key enabler of electrochemical energy storage and conversion. A quantitative framework for ionic conduction between atomistic and macroscopic timescales in β- and β″-aluminas is now proposed for ‘atoms-to-device’ multiscale modelling and optimization.
- Andrey D. Poletayev
- , James A. Dawson
- & Aaron M. Lindenberg
-
Article |
 Cationic polymer-in-salt electrolytes for fast metal ion conduction and solid-state battery applications
Cationic polymer-in-salt electrolytes for fast metal ion conduction and solid-state battery applications
Polymer electrolytes provide a safe solution for future solid-state high-energy-density batteries, but combining high ionic conductivity and a high transference number is a challenge. A polymeric ionic liquid used as a polymer solvent is now shown to be promising for both sodium and potassium batteries.
- Fangfang Chen
- , Xiaoen Wang
- & Maria Forsyth
-
Article |
 Ultra-stable all-solid-state sodium metal batteries enabled by perfluoropolyether-based electrolytes
Ultra-stable all-solid-state sodium metal batteries enabled by perfluoropolyether-based electrolytes
Rechargeable batteries with sodium metal anodes are promising as energy-storage systems despite safety concerns related to reactivity and dendrite formation. Solvent-free perfluoropolyether-based electrolytes are now reported for safe and stable all-solid-state sodium metal batteries.
- Xiaoen Wang
- , Cheng Zhang
- & Maria Forsyth
-
Article |
 Capturing dynamic ligand-to-metal charge transfer with a long-lived cationic intermediate for anionic redox
Capturing dynamic ligand-to-metal charge transfer with a long-lived cationic intermediate for anionic redox
Understanding reversible anionic redox reactions is key to designing high-energy-density cathodes for lithium-ion batteries. Anionic redox activation in cation-disordered rock-salt Li1.17Ti0.58Ni0.25O2 is shown to involve intermediate Ni3+/4+ species that can evolve to Ni2+ during relaxation.
- Biao Li
- , Khagesh Kumar
- & Jean-Marie Tarascon
-
Article |
 Direct correlation between void formation and lithium dendrite growth in solid-state electrolytes with interlayers
Direct correlation between void formation and lithium dendrite growth in solid-state electrolytes with interlayers
The growth of lithium dendrites across electrolyte layers limits the practical viability of solid-state Li-ion batteries. A direct correlation between void formation and lithium dendrite growth in solid-state electrolytes with metallic interlayers is now observed.
- Vikalp Raj
- , Victor Venturi
- & Naga Phani B. Aetukuri
-
Article |
 Electrochemically induced amorphous-to-rock-salt phase transformation in niobium oxide electrode for Li-ion batteries
Electrochemically induced amorphous-to-rock-salt phase transformation in niobium oxide electrode for Li-ion batteries
Intercalation-type metal oxides are promising anodes for Li-ion batteries but suffer from low energy and power density together with cycling instability. A nanostructured rock-salt Nb2O5 formed via amorphous-to-crystalline transformation during cycling with Li+ is shown to exhibit enhanced performance.
- Pete Barnes
- , Yunxing Zuo
- & Hui Xiong
-
Article |
 Lithium superionic conductors with corner-sharing frameworks
Lithium superionic conductors with corner-sharing frameworks
Superionic lithium conductivity has only been observed in a few classes of materials, mostly in thiophosphates but rarely in oxides. Corner-sharing connectivity in an oxide crystal structure framework is now shown to promote superionic conductivity.
- KyuJung Jun
- , Yingzhi Sun
- & Gerbrand Ceder
-
Article |
 Coupling structural evolution and oxygen-redox electrochemistry in layered transition metal oxides
Coupling structural evolution and oxygen-redox electrochemistry in layered transition metal oxides
Transition metal oxide electrodes are promising for rechargeable batteries but are subject to suffer from structural transformations and electrochemical degradation. The evolution of oxygen-redox activity and reversibility in layered electrodes are shown to arise from cation-migration mechanisms during de/intercalation.
- Donggun Eum
- , Byunghoon Kim
- & Kisuk Kang
-
Article |
 Stable non-corrosive sulfonimide salt for 4-V-class lithium metal batteries
Stable non-corrosive sulfonimide salt for 4-V-class lithium metal batteries
Lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide is used as a conducting salt for rechargeable lithium metal batteries because of its stability, but corrosion with aluminium current collectors is an issue. A non-corrosive sulfonimide salt is shown to suppress anodic dissolution of an Al current collector at high potentials while improving cycling.
- Lixin Qiao
- , Uxue Oteo
- & Heng Zhang
-
Article |
 Suspension electrolyte with modified Li+ solvation environment for lithium metal batteries
Suspension electrolyte with modified Li+ solvation environment for lithium metal batteries
Stable solid–electrolyte interphases on Li anodes are crucial for reliable Li metal batteries. A suspension electrolyte design that modifies the Li+ solvation environment in liquid electrolytes and creates inorganic-rich interphases on Li is now reported.
- Mun Sek Kim
- , Zewen Zhang
- & Yi Cui
-
Article |
 Effect of crystallite geometries on electrochemical performance of porous intercalation electrodes by multiscale operando investigation
Effect of crystallite geometries on electrochemical performance of porous intercalation electrodes by multiscale operando investigation
Designing electrode architectures for Li-ion batteries that can be reversibly accessible for ion storage can be challenging. Using operando techniques the mechanistic origin of lithiation-induced phase transformations in a V2O5 model cathode is now clarified.
- Yuting Luo
- , Yang Bai
- & Sarbajit Banerjee
-
News & Views |
 Confined water controls capacitance
Confined water controls capacitance
By using a battery of experimental and theoretical methods, it is shown that ion intercalation into the electrode material birnessite is mediated by structural water.
- Patrice Simon
- & Yury Gogotsi
-
Article |
 Zwitterionic materials with disorder and plasticity and their application as non-volatile solid or liquid electrolytes
Zwitterionic materials with disorder and plasticity and their application as non-volatile solid or liquid electrolytes
The tunability of covalently bound cationic and anionic moieties of zwitterionic materials makes them attractive for potential applications. A family of zwitterions exhibiting molecular disorder and plasticity allows their use as a solid-state conductive matrix.
- Faezeh Makhlooghiazad
- , Luke A. O’Dell
- & Jennifer M. Pringle
-
Article |
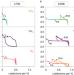 Extending insertion electrochemistry to soluble layered halides with superconcentrated electrolytes
Extending insertion electrochemistry to soluble layered halides with superconcentrated electrolytes
Insertion compounds in layered oxide or sulfide electrodes provide the fundamental basis of current commercialized Li-ion batteries. The feasibility of reversibly intercalating Li+ electrochemically into halide compounds via the use of superconcentrated electrolytes is now demonstrated.
- Nicolas Dubouis
- , Thomas Marchandier
- & Alexis Grimaud
-
Letter |
 Local electronic structure variation resulting in Li ‘filament’ formation within solid electrolytes
Local electronic structure variation resulting in Li ‘filament’ formation within solid electrolytes
Solid electrolytes are promising for enabling the use of Li metal anodes but Li infiltration along grain boundaries can lead to battery failure. Li infiltration in a model solid oxide electrolyte is now found to be strongly associated with local electronic band structure.
- Xiaoming Liu
- , Regina Garcia-Mendez
- & Miaofang Chi
-
Article |
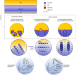 Revealing the role of the cathode–electrolyte interface on solid-state batteries
Revealing the role of the cathode–electrolyte interface on solid-state batteries
Interfaces play crucial, but still poorly understood, roles in the performance of secondary solid-state batteries. Using crystallographically oriented and highly faceted thick cathodes, the impact of cathode crystallography and morphology on long-term performance is investigated.
- Beniamin Zahiri
- , Arghya Patra
- & Paul V. Braun
-
Matters Arising |
Reply to: On the observation of photo-excitation effects in molecules using muon spin spectroscopy
- M. Jingliang
- , K. Wang
- & A. J. Drew
-
News & Views |
 Towards practical organic batteries
Towards practical organic batteries
Conjugated sulfonamides have been demonstrated as cathodes with high redox potentials and exceptional atmospheric stability, providing a sustainable alternative to traditional inorganic materials used in commercial lithium-ion batteries.
- Jing Xie
- & Yi-Chun Lu
-
Article |
 Visualizing plating-induced cracking in lithium-anode solid-electrolyte cells
Visualizing plating-induced cracking in lithium-anode solid-electrolyte cells
Lithium dendrite propagation through ceramic electrolytes can prevent the realization of high-energy-density all-solid-state lithium-anode batteries. The propagation of cracks and lithium dendrites through a solid electrolyte has now been tracked as a function of charge.
- Ziyang Ning
- , Dominic Spencer Jolly
- & Peter G. Bruce
-
Article |
 Fictitious phase separation in Li layered oxides driven by electro-autocatalysis
Fictitious phase separation in Li layered oxides driven by electro-autocatalysis
Although layered oxides electrodes in lithium-ion batteries are designed under conditions avoiding phase transitions, phase separation during delithiation has been observed. This apparent phase separation is shown to be a dynamical artefact occurring in a many-particle system driven by autocatalytic electrochemical reactions.
- Jungjin Park
- , Hongbo Zhao
- & William C. Chueh
-
Article |
 Electrolyte melt infiltration for scalable manufacturing of inorganic all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries
Electrolyte melt infiltration for scalable manufacturing of inorganic all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries
All-solid-state lithium-ion batteries provide improved safety but typically suffer from high cost and low volumetric energy density. An electrolyte melt-infiltration approach offering reduced manufacturing costs and improved volumetric energy density in all solid cells is proposed.
- Yiran Xiao
- , Kostiantyn Turcheniuk
- & Gleb Yushin
-
Article |
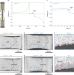 Linking void and interphase evolution to electrochemistry in solid-state batteries using operando X-ray tomography
Linking void and interphase evolution to electrochemistry in solid-state batteries using operando X-ray tomography
Understanding electrochemical behaviour and stability at solid–solid interfaces remains challenging. Operando synchrotron X-ray computed microtomography loss reveals that reconfiguration of interfacial contact is critical to explain cell failure during solid-state battery cycling.
- John A. Lewis
- , Francisco Javier Quintero Cortes
- & Matthew T. McDowell
-
Article |
 Revisiting metal fluorides as lithium-ion battery cathodes
Revisiting metal fluorides as lithium-ion battery cathodes
Metal-fluoride-based lithium-ion battery cathodes are typically classified as conversion materials because reconstructive phase transitions are presumed to occur upon lithiation. Metal fluoride lithiation is now shown to be dominated instead by diffusion-controlled displacement mechanisms.
- Xiao Hua
- , Alexander S. Eggeman
- & Clare P. Grey
-
Article |
 Unlocking anionic redox activity in O3-type sodium 3d layered oxides via Li substitution
Unlocking anionic redox activity in O3-type sodium 3d layered oxides via Li substitution
Sodium ion batteries could be an attractive alternative to Li-ion technology but designing high energy density and moisture stable Na-based cathodes is challenging. Adjusting synthesis conditions and stoichiometry, an O3-type NaLi1/3Mn2/3O2 phase with anionic redox activity is reported.
- Qing Wang
- , Sathiya Mariyappan
- & Jean-Marie Tarascon

 Phase segregation and nanoconfined fluid O2 in a lithium-rich oxide cathode
Phase segregation and nanoconfined fluid O2 in a lithium-rich oxide cathode