Featured
-
-
Article |
 High quantum efficiency of hydrogen production from methanol aqueous solution with PtCu–TiO2 photocatalysts
High quantum efficiency of hydrogen production from methanol aqueous solution with PtCu–TiO2 photocatalysts
Liquid water reforming of methanol is a promising method for on-demand hydrogen production. An atomic-level catalyst design strategy, using synergy between single atoms and nanodots, is now shown to demonstrate a high quantum efficiency for hydrogen production.
- Hui Wang
- , Haifeng Qi
- & Junwang Tang
-
Article |
 Direct photo-oxidation of methane to methanol over a mono-iron hydroxyl site
Direct photo-oxidation of methane to methanol over a mono-iron hydroxyl site
The partial oxidation of CH4 to CH3OH is challenging to perform in artificial systems due to ready over-oxidation to CO and CO2. Here by confining mono-iron hydroxyl sites in a metal–organic framework, photo-oxidation of CH4 to CH3OH is achieved with high selectivity and time yield.
- Bing An
- , Zhe Li
- & Martin Schröder
-
Letter |
 Long-term solar water and CO2 splitting with photoelectrochemical BiOI–BiVO4 tandems
Long-term solar water and CO2 splitting with photoelectrochemical BiOI–BiVO4 tandems
Photoelectrochemical devices are used for direct solar fuel production, but the stability of light absorbers can hamper their commercial prospects. Integrating a BiOI light absorber into a robust oxide-based architecture with a graphite paste conductive encapsulant results in photocathodes with long-term H2 evolution activity.
- Virgil Andrei
- , Robert A. Jagt
- & Erwin Reisner
-
Article |
 Inter-facet junction effects on particulate photoelectrodes
Inter-facet junction effects on particulate photoelectrodes
In anisotropically shaped photocatalyst particles different constituent facets may form inter-facet junctions at their adjoining edges. Using multimodal functional imaging, inter-facet junction effects on anisotropically shaped bismuth vanadate particles are revealed.
- Xianwen Mao
- & Peng Chen
-
Article |
 Development of a photoelectrochemically self-improving Si/GaN photocathode for efficient and durable H2 production
Development of a photoelectrochemically self-improving Si/GaN photocathode for efficient and durable H2 production
Development of efficient yet durable photoelectrodes is of paramount importance for deployment of solar-fuel production. The photoelectrochemically self-improving behaviour of a silicon/gallium nitride photocathode highly efficient for hydrogen production is now reported.
- Guosong Zeng
- , Tuan Anh Pham
- & Francesca M. Toma
-
Why it Matters |
Overcoming hurdles facing researchers in Africa
Tebello Nyokong, Bokolombe Ngoy and Edith Amuhaya share their experiences in conducting research in Africa.
- Tebello Nyokong
- , Bokolombe P. Ngoy
- & Edith K. Amuhaya
-
Article |
 Linking in situ charge accumulation to electronic structure in doped SrTiO3 reveals design principles for hydrogen-evolving photocatalysts
Linking in situ charge accumulation to electronic structure in doped SrTiO3 reveals design principles for hydrogen-evolving photocatalysts
Understanding the origin of unprecedented solar-to-hydrogen efficiencies in doped SrTiO3 has proved challenging. Linking in situ charge accumulation to electronic structure in this system now reveals design principles for hydrogen-evolving photocatalysts.
- Benjamin Moss
- , Qian Wang
- & James R. Durrant
-
Article |
 Endothermic reaction at room temperature enabled by deep-ultraviolet plasmons
Endothermic reaction at room temperature enabled by deep-ultraviolet plasmons
Metallic nanoparticles used to harvest energy from a light source typically result in reduced chemical reaction temperature. Endothermic reactions requiring higher activation energy can now be initiated at room temperature using localized surface plasmons in the deep-UV range.
- Canhui Wang
- , Wei-Chang D. Yang
- & Renu Sharma
-
Article |
 Nanoscale semiconductor/catalyst interfaces in photoelectrochemistry
Nanoscale semiconductor/catalyst interfaces in photoelectrochemistry
Although nanocatalysts forming selective contacts are crucial in photoelectrochemistry, the underlying nanoscale interfaces are poorly understood. Using a n-Si/Ni photoanode and potential-sensing AFM, interfacial electron-transfer processes and photovoltage are measured.
- Forrest A. L. Laskowski
- , Sebastian Z. Oener
- & Shannon W. Boettcher
-
Letter |
 Oxysulfide photocatalyst for visible-light-driven overall water splitting
Oxysulfide photocatalyst for visible-light-driven overall water splitting
The instability of sulfide ions during water oxidation prevents simultaneous evolution of hydrogen and oxygen. An oxysulfide semiconductor photocatalyst, Y2Ti2O5S2, is shown to evolve H2 and O2 via a water-splitting reaction under visible-light irradiation.
- Qian Wang
- , Mamiko Nakabayashi
- & Kazunari Domen
-
Article |
 Reversible and cooperative photoactivation of single-atom Cu/TiO2 photocatalysts
Reversible and cooperative photoactivation of single-atom Cu/TiO2 photocatalysts
Reversible and cooperative activation processes are important characteristics of biological enzymes and can be used in designing catalysts. Highly active TiO2 photocatalysts incorporated with site-specific single copper atoms are now shown to exhibit such a photoactivation process.
- Byoung-Hoon Lee
- , Sunghak Park
- & Taeghwan Hyeon
-
Article |
 The role of defects and excess surface charges at finite temperature for optimizing oxide photoabsorbers
The role of defects and excess surface charges at finite temperature for optimizing oxide photoabsorbers
Computational screening of materials for solar to fuel conversion technologies has mostly focused on bulk properties. A finite temperature study of WO3 now clarifies the role of defects and excess surface charges for optimizing oxide photoabsorbers.
- Matteo Gerosa
- , Francois Gygi
- & Giulia Galli
-
Article |
 Hybrid photoelectrochemical and photovoltaic cells for simultaneous production of chemical fuels and electrical power
Hybrid photoelectrochemical and photovoltaic cells for simultaneous production of chemical fuels and electrical power
Solar energy is widely used for fuel production and energy storage, but the majority of photoelectrochemical cells cannot operate without an external power source. A device for simultaneous and direct production of renewable fuels and electrical power is now proposed.
- Gideon Segev
- , Jeffrey W. Beeman
- & Ian D. Sharp
-
News & Views |
 Shedding light on black titania
Shedding light on black titania
Multiscale modelling provides atomic-level insights into how oxygen vacancy defect nucleation leads to the formation of the visible light photocatalyst black titania.
- Vassiliki-Alexandra Glezakou
- & Roger Rousseau
-
Article |
 Structural evolution of titanium dioxide during reduction in high-pressure hydrogen
Structural evolution of titanium dioxide during reduction in high-pressure hydrogen
The nature of structural disorder in photocatalytic black TiO2 is not known. Here, using simulations, it is shown that water formation drives surface reduction, with slowly migrating oxygen vacancies at the {001} facets resulting in the nucleation of disorder.
- Sencer Selcuk
- , Xunhua Zhao
- & Annabella Selloni
-
Editorial |
 Hydrogen to the rescue
Hydrogen to the rescue
Large-scale, environmentally friendly hydrogen production will rely on steam methane reforming coupled with carbon capture and electrolysis, but solar fuels could have a disruptive role to play.
-
Article |
 A molecular cross-linking approach for hybrid metal oxides
A molecular cross-linking approach for hybrid metal oxides
TiO2 and other metal oxides were interfaced with molecular boron clusters to form a hybrid material. This modifies the electrochemical and photocatalytic properties, enabling fast electron transfer and dye degradation under red light.
- Dahee Jung
- , Liban M. A. Saleh
- & Alexander M. Spokoyny
-
Article |
 Excitation-wavelength-dependent small polaron trapping of photoexcited carriers in α-Fe2O3
Excitation-wavelength-dependent small polaron trapping of photoexcited carriers in α-Fe2O3
The effect of polaron formation on photoconversion efficiency for oxide photocatalysts is not well known. Femtosecond extreme-ultraviolet measurements suggest that polaron localization is responsible for ultrafast trapping of photoexcited carriers in haematite.
- Lucas M. Carneiro
- , Scott K. Cushing
- & Stephen R. Leone
-
Article |
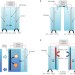 Photoelectrochemical water splitting in separate oxygen and hydrogen cells
Photoelectrochemical water splitting in separate oxygen and hydrogen cells
Solar water splitting is promising for hydrogen production and solar energy storage, but for large-scale utilization cost must be reduced. A membrane-free approach in separate oxygen and hydrogen cells brings water splitting closer to applications.
- Avigail Landman
- , Hen Dotan
- & Avner Rothschild
-
Article |
 Localized dielectric breakdown and antireflection coating in metal–oxide–semiconductor photoelectrodes
Localized dielectric breakdown and antireflection coating in metal–oxide–semiconductor photoelectrodes
Silicon-based photoelectrodes are attractive for solar fuel production, but suffer from vulnerability to corrosion. Using dielectric breakdown, a generic approach to improve the performance of metal-oxide semiconductor photoelectrodes is proposed.
- Li Ji
- , Hsien-Yi Hsu
- & Edward T. Yu
-
Article |
 A multifunctional biphasic water splitting catalyst tailored for integration with high-performance semiconductor photoanodes
A multifunctional biphasic water splitting catalyst tailored for integration with high-performance semiconductor photoanodes
In photosynthesis the oxidation of water is a requirement for providing sufficient protons and electrons for fuel formation. A biphasic water splitting catalyst tailored for integration with high-performance semiconductor photoanodes is now reported.
- Jinhui Yang
- , Jason K. Cooper
- & Ian D. Sharp
-
Letter |
 Scalable water splitting on particulate photocatalyst sheets with a solar-to-hydrogen energy conversion efficiency exceeding 1%
Scalable water splitting on particulate photocatalyst sheets with a solar-to-hydrogen energy conversion efficiency exceeding 1%
Photocatalytic water splitting using semiconductors is attractive for converting solar energy into hydrogen. An efficient and scalable system based on particulate photocatalyst sheets is now shown to exhibit energy conversion efficiency exceeding 1%.
- Qian Wang
- , Takashi Hisatomi
- & Kazunari Domen
-
Article |
 Water reduction by a p-GaInP2 photoelectrode stabilized by an amorphous TiO2 coating and a molecular cobalt catalyst
Water reduction by a p-GaInP2 photoelectrode stabilized by an amorphous TiO2 coating and a molecular cobalt catalyst
Producing hydrogen via solar water splitting with metal-based molecular catalysts offers scalability. An active p-GaInP2 photocathode stabilized by a TiO2 layer functionalized by a cobaloxime molecular catalyst is now reported for water reduction.
- Jing Gu
- , Yong Yan
- & John A. Turner
-
Article |
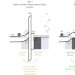 Design principles for maximizing photovoltage in metal-oxide-protected water-splitting photoanodes
Design principles for maximizing photovoltage in metal-oxide-protected water-splitting photoanodes
Although protecting photoanodes using metal oxides is attractive for solar fuel applications, the photoanodes typically suffer from poor photovoltage. Now, insulating oxide layers are shown to promote enhanced photovoltages and general design principles are suggested.
- Andrew G. Scheuermann
- , John P. Lawrence
- & Paul C. McIntyre
-
Review Article |
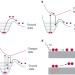 Photochemical transformations on plasmonic metal nanoparticles
Photochemical transformations on plasmonic metal nanoparticles
Optically excited plasmonic nanoparticles can activate chemical reactions on their surfaces. The underlying physical mechanisms responsible for the chemical activity and advances in photocatalysis on plasmonic metallic nanostructures are discussed.
- Suljo Linic
- , Umar Aslam
- & Matthew Morabito
-
Letter |
 Conducting polymer nanostructures for photocatalysis under visible light
Conducting polymer nanostructures for photocatalysis under visible light
Visible-light-responsive photocatalysts can directly harvest energy from solar light. Stable conducting polymer nanostructures show high photocatalytic activity under visible light without using sacrificial reagents or precious metal co-catalysts.
- Srabanti Ghosh
- , Natalie A. Kouamé
- & Hynd Remita
-
-
Letter |
 Redox shuttle mechanism enhances photocatalytic H2 generation on Ni-decorated CdS nanorods
Redox shuttle mechanism enhances photocatalytic H2 generation on Ni-decorated CdS nanorods
Photocatalytic efficiency can be limited by slow transfer of photoexcited holes and high charge recombination rates. Using a hydroxyl anion–radical redox couple leads to enhanced photocatalytic H2 generation on Ni-decorated CdS nanorods.
- Thomas Simon
- , Nicolas Bouchonville
- & Jochen Feldmann
-
Article |
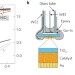 Adaptive semiconductor/electrocatalyst junctions in water-splitting photoanodes
Adaptive semiconductor/electrocatalyst junctions in water-splitting photoanodes
Photoelectrochemical water-splitting devices require integrating electrocatalysts with light-absorbing semiconductors, but understanding charge-transfer processes at interfaces has proved difficult. Ion-permeable electrocatalysts deposited onto TiO2 photoelectrodes now result in adaptive semiconductor/electrocatalyst junctions where both the effective interface barrier height and the photovoltage output change depending on the oxidation state of the electrocatalyst.
- Fuding Lin
- & Shannon W. Boettcher
-
-
Letter |
 Band alignment of rutile and anatase TiO2
Band alignment of rutile and anatase TiO2
A convincing explanation of why mixed phases of anatase and rutile TiO2 outperform individual polymorphs is lacking. An energetic band alignment of ~0.4 eV is now shown to exist between the two phases with anatase possessing the higher electron affinity. This observation explains the separation of photoexcited charge carriers between phases and could lead to improved photocatalysts.
- David O. Scanlon
- , Charles W. Dunnill
- & Alexey A. Sokol
-
News & Views |
 A source of energetic electrons
A source of energetic electrons
Photoexcited diamond can inject highly energetic electrons in solution and promote the catalysis of a broad range of chemical reactions.
- Christoph E. Nebel
-
Article |
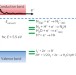 Photo-illuminated diamond as a solid-state source of solvated electrons in water for nitrogen reduction
Photo-illuminated diamond as a solid-state source of solvated electrons in water for nitrogen reduction
Solid-state catalysts do not participate efficiently in the reduction of N2 to NH3 because they tend not to form strong bonds with nitrogen molecules. It is now shown that, under ultraviolet radiation, hydrogen-terminated diamond can eject electrons directly in a liquid solution, thus allowing nitrogen reduction without requiring its preliminary adsorption on a solid surface.
- Di Zhu
- , Linghong Zhang
- & Robert J. Hamers
-
Article |
 Singular characteristics and unique chemical bond activation mechanisms of photocatalytic reactions on plasmonic nanostructures
Singular characteristics and unique chemical bond activation mechanisms of photocatalytic reactions on plasmonic nanostructures
It is now shown that, unlike most semiconductors, plasmonic metal nanostructures constructively couple the energy of photons and thermal energy, with the reaction rate positively responding to both stimuli. These unique characteristics suggest that these photocatalysts could prove useful for heterogeneous catalytic processes that cannot be activated using conventional thermal processes on metals or photocatalytic processes on semiconductors.
- Phillip Christopher
- , Hongliang Xin
- & Suljo Linic
-
Letter |
 A red metallic oxide photocatalyst
A red metallic oxide photocatalyst
Light absorption across the bandgap in semiconductors is exploited in many important applications such as photovoltaics, light-emitting diodes and photocatalytic conversion, but whether coloured metals can be used in such applications is unclear. A red metallic oxide Sr1-xNbO3 is now shown to be effective under visible light to photocatalyse the oxidation of methylene blue, and the oxidation and reduction of water.
- Xiaoxiang Xu
- , Chamnan Randorn
- & John T. S. Irvine
-
Review Article |
 Plasmonic-metal nanostructures for efficient conversion of solar to chemical energy
Plasmonic-metal nanostructures for efficient conversion of solar to chemical energy
Although heterogeneous photocatalysts for converting solar to chemical energy are mostly semiconductors, metallic plasmonic nanostructures have started to attract interest. Recent progress on plasmon-enhanced, water-splitting composite photocatalysts and photocatalytic reactions on the surface of plasmonic nanostructures of noble metals are now reviewed.
- Suljo Linic
- , Phillip Christopher
- & David B. Ingram
-
Article |
 Highly active oxide photocathode for photoelectrochemical water reduction
Highly active oxide photocathode for photoelectrochemical water reduction
Production of chemical fuels by solar energy is an attractive and sustainable solution to our energy problems. A highly active photocathode, consisting of electrodeposited cuprous oxide with platinum nanoparticles is now activated for hydrogen evolution resulting from photelectrochemical water reduction.
- Adriana Paracchino
- , Vincent Laporte
- & Elijah Thimsen
-
Letter |
 An orthophosphate semiconductor with photooxidation properties under visible-light irradiation
An orthophosphate semiconductor with photooxidation properties under visible-light irradiation
The search for active semiconductor photocatalysts that split water directly under visible-light irradiation remains challenging for solar applications. An orthophosphate semiconductor, Ag3PO4, which is capable of harnessing visible light to oxidize water as well as decompose organic contaminants in aqueous solution is now reported.
- Zhiguo Yi
- , Jinhua Ye
- & Ray L. Withers

 Photochemical tuning of dynamic defects for high-performance atomically dispersed catalysts
Photochemical tuning of dynamic defects for high-performance atomically dispersed catalysts Hydrogels evolve hydrogen
Hydrogels evolve hydrogen Aerobic oxidation
Aerobic oxidation