News & Views |
Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Through the MOF looking glass
Through the MOF looking glass
Processible centimetre-scale porous glasses using zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF) materials are developed, while fine-tuning of the processing conditions allows control of pore size and molecular sieving properties.
- Georgia R. F. Orton
- & Neil R. Champness
-
Article
| Open Access Precise control over gas-transporting channels in zeolitic imidazolate framework glasses
Precise control over gas-transporting channels in zeolitic imidazolate framework glasses
Porosity of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks can be preserved beyond glass transition and melt processing. Here centimetre-scale porous glasses are demonstrated, whereas liquid processing enables fine-tuning of the size of the gas-transporting channels for molecular sieving.
- Oksana Smirnova
- , Seungtaik Hwang
- & Alexander Knebel
-
Article |
 Quasi-open Cu(i) sites for efficient CO separation with high O2/H2O tolerance
Quasi-open Cu(i) sites for efficient CO separation with high O2/H2O tolerance
Chemical adsorption of CO on open metal sites enables separation from other gases but leads to selectivity and stability issues. Quasi-open metal sites in metal–organic frameworks are proposed here, which are accessible only by CO-induced structural transformation, enabling CO separation to 9N purity.
- Xue-Wen Zhang
- , Chao Wang
- & Jie-Peng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Unit-cell-thick zeolitic imidazolate framework films for membrane application
Unit-cell-thick zeolitic imidazolate framework films for membrane application
Unit-cell-thick films of metal–organic frameworks with ordered porosity would be attractive for membrane applications as these thin systems combine large molecular flux with high selectivity. Here crystalline ZIF films are grown on a crystalline substrate with high H2/N2 gas separation performance.
- Qi Liu
- , Yurun Miao
- & Kumar Varoon Agrawal
-
News & Views |
 Smoke in the MOF liquid
Smoke in the MOF liquid
An ultra-microporous metal–organic framework glass foam shows outstanding gas sieving properties for challenging gas mixtures.
- Chinmoy Das
- & Sebastian Henke
-
News & Views |
 Unlocked sieving potential
Unlocked sieving potential
A strategy of using a high ligand/metal ion concentration ratio eliminates lattice defects in polycrystalline zirconium metal–organic framework membranes, enhancing their molecular sieving performance.
- Jun Lu
- & Huanting Wang
-
-
Meeting Report |
Materials for a changing planet
About 700 scientists from 45 countries gathered in Dresden for the first time since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic to share their latest findings on metal–organic frameworks and open frameworks compounds.
- Veronique Van Speybroeck
- & Guillaume Maurin
-
News & Views |
 Machine learning heat capacities
Machine learning heat capacities
As metal–organic frameworks move towards practical application, data for an expanded range of physical properties are needed. Molecular-level modelling and data science can play an important role.
- Randall Q. Snurr
-
News & Views |
 Framing fusion and fission
Framing fusion and fission
Engineering inter-triplet exchange coupling allows spin mixing between singlet and quintet manifolds in triplet–triplet pair states in metal–organic frameworks, demonstrating increased room-temperature triplet-fusion rates under relatively small applied magnetic fields.
- Naitik A. Panjwani
- & Jan Behrends
-
Article |
 A data-science approach to predict the heat capacity of nanoporous materials
A data-science approach to predict the heat capacity of nanoporous materials
Heat capacity of nanoporous materials is important for processes such as carbon capture, as this can affect process design energy requirements. Here, a machine learning approach for heat capacity prediction, trained on density functional theory simulations, is presented and experimentally verified.
- Seyed Mohamad Moosavi
- , Balázs Álmos Novotny
- & Berend Smit
-
Comment |
 The development of molecule-based porous material families and their future prospects
The development of molecule-based porous material families and their future prospects
Metal–organic frameworks, porous coordination network materials constructed with metal ions and organic molecules, have grown over the past 20 years into an innovative chemistry that has contributed to solutions for the problems faced by humanity in the environment, resources, energy and health.
- Satoshi Horike
- & Susumu Kitagawa
-
Article |
 Direct observation of geometric and sliding ferroelectricity in an amphidynamic crystal
Direct observation of geometric and sliding ferroelectricity in an amphidynamic crystal
Two-dimensional materials can present ferroelectricity by layer sliding, but electrical confirmation is lacking due to narrow bandgaps. Here, a single-crystal coordination polymer with large bandgap enabling direct electrical measurement of P–E hysteresis is shown to present sliding ferroelectricity.
- Le-Ping Miao
- , Ning Ding
- & Yi Zhang
-
Comment |
 Stimuli-responsive metal–organic frameworks enabled by intrinsic molecular motion
Stimuli-responsive metal–organic frameworks enabled by intrinsic molecular motion
Synthetic stimuli-responsive systems have become increasingly sophisticated and elegant at the nanoscale. This Comment discusses how rationally designed molecular systems capable of dynamic motions can be deployed in macroscopically porous metal–organic frameworks and respond to various stimuli.
- Jinqiao Dong
- , Vanessa Wee
- & Dan Zhao
-
Article |
 Direct photo-oxidation of methane to methanol over a mono-iron hydroxyl site
Direct photo-oxidation of methane to methanol over a mono-iron hydroxyl site
The partial oxidation of CH4 to CH3OH is challenging to perform in artificial systems due to ready over-oxidation to CO and CO2. Here by confining mono-iron hydroxyl sites in a metal–organic framework, photo-oxidation of CH4 to CH3OH is achieved with high selectivity and time yield.
- Bing An
- , Zhe Li
- & Martin Schröder
-
Article
| Open Access Trace removal of benzene vapour using double-walled metal–dipyrazolate frameworks
Trace removal of benzene vapour using double-walled metal–dipyrazolate frameworks
Volatile organic compounds such as benzene are toxic pollutants that cause health issues even at trace concentrations. Here, a double-walled metal–organic framework is presented that demonstrates high uptake at very low pressures (<10 Pa), allowing the removal of benzene to below acceptable indoor limits.
- Tao He
- , Xiang-Jing Kong
- & Jian-Rong Li
-
Article |
 Tunable metal hydroxide–organic frameworks for catalysing oxygen evolution
Tunable metal hydroxide–organic frameworks for catalysing oxygen evolution
The oxygen evolution reaction is central to making chemicals and energy carriers using electrons. Metal hydroxide–organic frameworks are shown to act as a tunable catalytic platform for oxygen evolution, with π–π interactions dictating stability and transition metals modulating activity.
- Shuai Yuan
- , Jiayu Peng
- & Yang Shao-Horn
-
Perspective |
 The changing state of porous materials
The changing state of porous materials
Highly ordered crystalline porous solids are useful for many applications. This Perspective explores the evolution of these systems from the ordered state to the glassy and liquid states, discusses the different types of porous liquid and considers possible applications of these disordered systems.
- Thomas D. Bennett
- , François-Xavier Coudert
- & Andrew I. Cooper
-
News & Views |
 Making large single crystals of 2D MOFs
Making large single crystals of 2D MOFs
Linking π-conjugated, electron-deficient ligands into atomically precise large single crystals of conducting 2D metal–organic frameworks can allow the determination of intrinsic electrical conductivity and charge transport mechanism.
- Renhao Dong
- & Xinliang Feng
-
Article |
 Highly luminescent and catalytically active suprastructures of magic-sized semiconductor nanoclusters
Highly luminescent and catalytically active suprastructures of magic-sized semiconductor nanoclusters
Assembly of magic-sized nanoclusters into suprastructures leads to enhanced luminescence and catalytic activity for CO2 conversion while substantially extending their ambient stability.
- Woonhyuk Baek
- , Megalamane S. Bootharaju
- & Taeghwan Hyeon
-
Article |
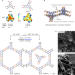 Atomically precise single-crystal structures of electrically conducting 2D metal–organic frameworks
Atomically precise single-crystal structures of electrically conducting 2D metal–organic frameworks
Two-dimensional MOFs can possess porosity and electrical conductivity but are difficult to grow as single crystals. Here, by balancing in-plane and out-of-plane interactions, single crystals of sizes up to 200 µm are grown, allowing in-plane transport measurements and atomic-resolution analysis.
- Jin-Hu Dou
- , Maxx Q. Arguilla
- & Mircea Dincă
-
Article |
 Direct X-ray and electron-beam lithography of halogenated zeolitic imidazolate frameworks
Direct X-ray and electron-beam lithography of halogenated zeolitic imidazolate frameworks
The low dielectric constants and high porosity of MOFs are of interest for applications in electronics and sensors, but patterning techniques for these materials are in their infancy. Here, direct X-ray and electron-beam lithography at sub-50-nm resolution are reported that leave porosity and crystallinity intact.
- Min Tu
- , Benzheng Xia
- & Rob Ameloot
-
Article |
 Efficient metal ion sieving in rectifying subnanochannels enabled by metal–organic frameworks
Efficient metal ion sieving in rectifying subnanochannels enabled by metal–organic frameworks
Here, using an interfacial growth strategy, UiO-66 MOF nanocrystals are asymmetrically embedded into conical pores in a polymer membrane. These pores have a mono/divalent cation selectivity of 103, which can be tuned by pH, and act as ionic rectifiers.
- Jun Lu
- , Huacheng Zhang
- & Huanting Wang
-
Letter |
 Selective nitrogen adsorption via backbonding in a metal–organic framework with exposed vanadium sites
Selective nitrogen adsorption via backbonding in a metal–organic framework with exposed vanadium sites
Nitrogenases use transition metals to selectively capture weak π acids such as N2 by employing backbonding interactions. Here, a metal–organic framework with exposed vanadium sites is presented that uses this approach for selective capture of N2 from CH4, with impressive selectivity and capacity.
- David E. Jaramillo
- , Douglas A. Reed
- & Jeffrey R. Long
-
Article |
 Reversible coordinative binding and separation of sulfur dioxide in a robust metal–organic framework with open copper sites
Reversible coordinative binding and separation of sulfur dioxide in a robust metal–organic framework with open copper sites
Metal–organic framework capture materials could reduce the environmental impact of SO2 emissions but can have limited stability and poor reversibility. Here, a metal–organic framework with open Cu(ii) sites with fully reversible SO2 uptake of 17.5 mmol g−1 under ambient conditions is reported.
- Gemma L. Smith
- , Jennifer E. Eyley
- & Martin Schröder
-
News & Views |
 Separating out the middle
Separating out the middle
A chemically and thermally stable metal–organic framework achieves exceptional separation of styrene from a complex mixture containing larger (ethylbenzene) and smaller (toluene and benzene) molecules.
- Simon M. Vornholt
- & Russell E. Morris
-
Article |
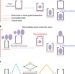 Intermediate-sized molecular sieving of styrene from larger and smaller analogues
Intermediate-sized molecular sieving of styrene from larger and smaller analogues
Molecular sieving separates larger from smaller molecules, but all molecules smaller than the pore adsorb, hindering selectivity. Here, a MOF is reported with both molecular sieving and gate-opening, separating intermediate-sized molecules from larger and smaller analogues.
- Dong-Dong Zhou
- , Pin Chen
- & Jie-Peng Zhang
-
Article |
 Pressure promoted low-temperature melting of metal–organic frameworks
Pressure promoted low-temperature melting of metal–organic frameworks
The simultaneous high-pressure and high-temperature phase diagram of two MOFs, ZIF-4 and ZIF-62, is mapped. Crystalline, pressure- and temperature-amorphous, and liquid states are found, while melting temperature is found to decrease with pressure.
- Remo N. Widmer
- , Giulio I. Lampronti
- & Thomas D. Bennett
-
News & Views |
 An efficient nanosieve
An efficient nanosieve
A rigid and easily scalable metal–organic framework is shown to be among the most efficient materials for separating ethylene from ethane.
- Anastasiya Bavykina
- & Jorge Gascon
-
Article |
 Molecular sieving of ethylene from ethane using a rigid metal–organic framework
Molecular sieving of ethylene from ethane using a rigid metal–organic framework
Separating ethylene from ethane is highly challenging as they have very similar physical properties. Here, a metal–organic framework is reported that, owing to its pore size and rigidity, adsorbs ethylene but almost completely excludes ethane under ambient conditions.
- Rui-Biao Lin
- , Libo Li
- & Banglin Chen
-
Letter |
 Reversible adsorption of nitrogen dioxide within a robust porous metal–organic framework
Reversible adsorption of nitrogen dioxide within a robust porous metal–organic framework
High and reversible nitrogen dioxide (NO2) uptake, and low-concentration NO2 removal from gas mixtures, is observed in a metal–organic framework. The NO2 is bound within the pores by cooperative supramolecular interactions.
- Xue Han
- , Harry G. W. Godfrey
- & Martin Schröder
-
News & Views |
 Reducing localization
Reducing localization
By inserting potassium into a 3D metal–organic framework band delocalization occurs, enabling mobilities and conductivities similar to organic polymers.
- A. Alec Talin
- & François Léonard
-
Article |
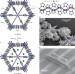 Electron delocalization and charge mobility as a function of reduction in a metal–organic framework
Electron delocalization and charge mobility as a function of reduction in a metal–organic framework
A conducting metal–organic framework with charge delocalization by reductive potassium insertion is demonstrated. Integration into a field-effect transistor shows similar mobilities to semiconductors, with a mobility estimated to be at least 0.84 cm2 V–1 s–1.
- Michael L. Aubrey
- , Brian M. Wiers
- & Jeffrey R. Long
-
Perspective |
 The role of reticular chemistry in the design of CO2 reduction catalysts
The role of reticular chemistry in the design of CO2 reduction catalysts
Catalysts for CO2 photo- or electroreduction must balance activity, selectivity and efficiency. Here, the authors discuss the use of metal–organic frameworks for these processes and the role reticular chemistry may play in designing new catalysts.
- Christian S. Diercks
- , Yuzhong Liu
- & Omar M. Yaghi
-
News & Views |
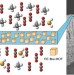 A perfect match
A perfect match
A metal–organic framework with tailored porosity provides a mixed matrix membrane with excellent performance for natural gas purification and butane isomer separation.
- Neil B. McKeown
-
Article |
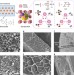 Mixed matrix formulations with MOF molecular sieving for key energy-intensive separations
Mixed matrix formulations with MOF molecular sieving for key energy-intensive separations
Sub-micrometre MOF particles are incorporated into polymers to form mixed matrix membranes. Molecular sieving enables performance far beyond current limits for two applications, butane isomer separation and combined CO2/H2S removal from natural gas.
- Gongping Liu
- , Valeriya Chernikova
- & William J. Koros
-
Article |
 A sol–gel monolithic metal–organic framework with enhanced methane uptake
A sol–gel monolithic metal–organic framework with enhanced methane uptake
Using a sol–gel process, monoliths of metal–organic frameworks were fabricated. With an enhanced methane volumetric uptake of 259 cm3 (STP) cm−3, and robust mechanical properties, this meets technological targets.
- Tian Tian
- , Zhixin Zeng
- & David Fairen-Jimenez
-
News & Views |
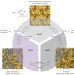 Unveiling liquid MOFs
Unveiling liquid MOFs
Diffraction and simulation studies reveal the presence of significant porosity in both the glass and liquid phases of a metal–organic framework.
- Satoshi Horike
- & Susumu Kitagawa
-
-
News & Views |
 Uniformity begets selectivity
Uniformity begets selectivity
A Pd4 cluster, supported by a metal–organic framework and formed by post-synthesis methods, shows high catalytic activity and selectivity for carbene-mediated reactions. This crystallographically precise material may lead to a large class of catalysts.
- Dong Yang
- & Bruce C. Gates
-
Article |
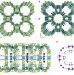 The MOF-driven synthesis of supported palladium clusters with catalytic activity for carbene-mediated chemistry
The MOF-driven synthesis of supported palladium clusters with catalytic activity for carbene-mediated chemistry
Mixed-valence clusters of Pd4 organized within a metal–organic framework exhibit robust catalytic capacities during carbene-mediated chemical reactions.
- Francisco R. Fortea-Pérez
- , Marta Mon
- & Emilio Pardo
-
News & Views |
 Look but don't touch
Look but don't touch
By combining an electron-counting camera with low-energy transmission electron microscopy, it is possible to directly image the surface structure of delicate metal–organic framework crystals and their coherent interfaces.
- Ben Slater
- & Sanliang Ling
-
News & Views |
 Lining up metal–organic frameworks
Lining up metal–organic frameworks
A new report demonstrates an innovative approach to aligning crystallites of metal–organic frameworks such that thin films are created with oriented channels — potentially overcoming one of the major barriers to application of these highly topical materials.
- Neil R. Champness
-
News & Views |
 Wired metal–organic chalcogenides
Wired metal–organic chalcogenides
Self-assembled transition metal–organic chalcogenide nanowires pave the way to a new family of electron conducting materials with tunable properties.
- Fernando Rey
- & José L. Jordá
-
Letter |
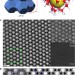 Unravelling surface and interfacial structures of a metal–organic framework by transmission electron microscopy
Unravelling surface and interfacial structures of a metal–organic framework by transmission electron microscopy
The operational conditions used for electron microscopy can limit the insight that can be gained from fragile material samples. It is shown here how high-resolution TEM analysis of delicate MOFs can be achieved.
- Yihan Zhu
- , Jim Ciston
- & Yu Han
-
News & Views |
 Porous materials get energized
Porous materials get energized
By making use of a semiconducting metal–organic graphene analogue, researchers propose a new generation of supercapacitors with potential as tunable molecular materials for energy.
- Alexandru Vlad
- & Andrea Balducci
-
Letter |
 Selective nitrogen capture by porous hybrid materials containing accessible transition metal ion sites
Selective nitrogen capture by porous hybrid materials containing accessible transition metal ion sites
Mesoporous metal–organic frameworks containing unsaturated Cr(III) sites are able to thermodynamically and selectively capture nitrogen from mixtures with oxygen and methane.
- Ji Woong Yoon
- , Hyunju Chang
- & Jong-San Chang
-
Letter |
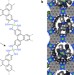 Conductive MOF electrodes for stable supercapacitors with high areal capacitance
Conductive MOF electrodes for stable supercapacitors with high areal capacitance
Using MOFs as active electrodes in electrochemical double layer capacitors has so far proved difficult. An electrically conductive MOF used as an electrode is now shown to exhibit electrochemical performance similar to most carbon-based materials.
- Dennis Sheberla
- , John C. Bachman
- & Mircea Dincă
-
Letter |
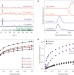 Enhanced ethylene separation and plasticization resistance in polymer membranes incorporating metal–organic framework nanocrystals
Enhanced ethylene separation and plasticization resistance in polymer membranes incorporating metal–organic framework nanocrystals
The dispersion of metal–organic framework nanocrystals within a polyimide yields membranes for selective chemical separations with strong resistance to plasticization.
- Jonathan E. Bachman
- , Zachary P. Smith
- & Jeffrey R. Long

 Engineering porous crystals to do different things
Engineering porous crystals to do different things Water discrimination by differing diffusions
Water discrimination by differing diffusions Flexing with the flow
Flexing with the flow