Featured
-
-
Article |
 Fe–Ni-based alloys as highly active and low-cost oxygen evolution reaction catalyst in alkaline media
Fe–Ni-based alloys as highly active and low-cost oxygen evolution reaction catalyst in alkaline media
NiFe-based oxo-hydroxides are active for the oxygen evolution reaction but suffer from complex synthesis and durability when deposited. Easily processable Fe–Ni alloys with a highly active oxo-hydroxide surface are now shown to pave the way for oxygen-evolving electrodes for alkaline water electrolysers.
- Lucile Magnier
- , Garance Cossard
- & Marian Chatenet
-
Article |
 Highly anisotropic spin transport in ultrathin black phosphorus
Highly anisotropic spin transport in ultrathin black phosphorus
The authors study spin transport anisotropy in a 5.5 nm black phosphorus ribbon encapsulated by boron nitride.
- Luke Cording
- , Jiawei Liu
- & Barbaros Özyilmaz
-
Article |
 Two-dimensional few-atom noble gas clusters in a graphene sandwich
Two-dimensional few-atom noble gas clusters in a graphene sandwich
Direct observation of noble gas structures has been achieved at room temperature using electron microscopy. This was enabled by trapping them between two layers of graphene, where they form two-dimensional clusters.
- Manuel Längle
- , Kenichiro Mizohata
- & Jani Kotakoski
-
Article
| Open Access Shallow defects and variable photoluminescence decay times up to 280 µs in triple-cation perovskites
Shallow defects and variable photoluminescence decay times up to 280 µs in triple-cation perovskites
Quantifying recombination in halide perovskites is crucial, but quantitative analysis remains rare. Here the authors observe a long-lived and continuously changing photoluminescence decay time due to the high density of shallow defects and substantial rates of charge carrier trapping.
- Ye Yuan
- , Genghua Yan
- & Thomas Kirchartz
-
Article
| Open Access Electrochemical and chemical cycle for high-efficiency decoupled water splitting in a near-neutral electrolyte
Electrochemical and chemical cycle for high-efficiency decoupled water splitting in a near-neutral electrolyte
Hydrogen produced by water splitting using renewable electricity is key to achieve net-zero carbon emissions. Decoupling hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions during electrolysis is attractive but efficiency and operational challenges remain. A process producing hydrogen and oxygen in separate cells and supporting continuous operation in a membraneless system is now proposed.
- Ilya Slobodkin
- , Elena Davydova
- & Avner Rothschild
-
Article
| Open Access Parity–time-symmetric photonic topological insulator
Parity–time-symmetric photonic topological insulator
The authors propose a non-Hermitian topological insulator with a real-valued energy spectrum based on a periodically driven Floquet model implemented in a photonic platform where generalized parity–time symmetry is protected against spontaneous symmetry breaking under a spatiotemporal gain and loss distribution.
- Alexander Fritzsche
- , Tobias Biesenthal
- & Alexander Szameit
-
Article |
 Compensating losses in polariton propagation with synthesized complex frequency excitation
Compensating losses in polariton propagation with synthesized complex frequency excitation
Propagation losses have limited the practical use of polaritons in photonic applications. Here the authors demonstrate a substantial enhancement in the propagation distance of phonon polaritons, employing synthetic optical excitation of complex frequency with virtual gain synthesized by combining multiple real frequency measurements.
- Fuxin Guan
- , Xiangdong Guo
- & Shuang Zhang
-
Article |
 Local atomic stacking and symmetry in twisted graphene trilayers
Local atomic stacking and symmetry in twisted graphene trilayers
The local layer alignment in a wide range of trilayer graphene structures has been extracted by interferometric four-dimensional scanning transmission electron microscopy, uncovering the complex picture of lattice reconstruction in twisted trilayers.
- Isaac M. Craig
- , Madeline Van Winkle
- & D. Kwabena Bediako
-
Article |
 All-optical multilevel physical unclonable functions
All-optical multilevel physical unclonable functions
Employing light-transformable polymers, multiple physical unclonable functions are demonstrated within a single device with all-optical reversible reconfigurability. Such devices may enable quantum secure authentication and nonlinear cryptographic key generation applications.
- Sara Nocentini
- , Ulrich Rührmair
- & Francesco Riboli
-
Article |
 Deciphering the ultra-high plasticity in metal monochalcogenides
Deciphering the ultra-high plasticity in metal monochalcogenides
The metal monochalcogenides are a group of van der Waals layered semiconductors with ultra-high plasticity. It is now revealed that their plasticity is attributed to the ability to transform their stacking order or phases, coupled with the concurrent generation of a micro-crack network.
- Lok Wing Wong
- , Ke Yang
- & Jiong Zhao
-
Article |
 Fast cycling of lithium metal in solid-state batteries by constriction-susceptible anode materials
Fast cycling of lithium metal in solid-state batteries by constriction-susceptible anode materials
Interfacial reactions between lithium and anodes are not well understood in an all-solid environment. For the silicon anode we now demonstrate that, rather than strong Li–Si alloying at the conventional solid–liquid interface, the lithiation reaction of micrometre-sized Si can be greatly constricted at the solid–solid interface.
- Luhan Ye
- , Yang Lu
- & Xin Li
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time single-proton counting with transmissive perovskite nanocrystal scintillators
Real-time single-proton counting with transmissive perovskite nanocrystal scintillators
Current organic proton detectors have poor detection sensitivities due to low light yields and limited radiation toleration. Here the authors report a perovskite nanocrystal-based transmissive thin scintillator that can detect seven protons per second, enabled by radiative emission from biexcitons.
- Zhaohong Mi
- , Hongyu Bian
- & Xiaogang Liu
-
Letter |
 Thermal multiferroics in all-inorganic quasi-two-dimensional halide perovskites
Thermal multiferroics in all-inorganic quasi-two-dimensional halide perovskites
Multiferroics can possess multiple ferroic orders, for example, electric polarization and magnetism, and are of interest for new device applications. Here thermal control is shown to manipulate electric and magnetic orders in a single-phase quasi-two-dimensional halide perovskite.
- Tong Zhu
- , Xue-Zeng Lu
- & Hiroshi Kageyama
-
Article |
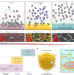 Network of cyano-p-aramid nanofibres creates ultrastiff and water-rich hydrospongels
Network of cyano-p-aramid nanofibres creates ultrastiff and water-rich hydrospongels
Biological tissues are extremely water rich but remain mechanically stiff, behaviour that is difficult to recapitulate in synthetic materials. Here the authors design a hydrogel/sponge hybrid material driven by a self-organized network of cyano-p-aramid nanofibres that combines these properties for biofunctional materials.
- Minkyung Lee
- , Hojung Kwak
- & Dongyeop X. Oh
-
Article |
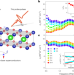 Evidence for d-wave superconductivity of infinite-layer nickelates from low-energy electrodynamics
Evidence for d-wave superconductivity of infinite-layer nickelates from low-energy electrodynamics
The authors utilize both static and ultrafast terahertz conductivity spectroscopy to address the character of the superconducting state of infinite-layer nickelates.
- Bing Cheng
- , Di Cheng
- & Jigang Wang
-
Article |
 Dynamically tunable moiré exciton Rydberg states in a monolayer semiconductor on twisted bilayer graphene
Dynamically tunable moiré exciton Rydberg states in a monolayer semiconductor on twisted bilayer graphene
The authors demonstrate the tunability of moiré potential and emergent moiré exciton Rydberg states in a monolayer transition metal dichalcogenide governed by an adjacent twisted bilayer graphene near the magic angle with gate-tunable local charge density.
- Minhao He
- , Jiaqi Cai
- & Xiaodong Xu
-
Article |
 Remote imprinting of moiré lattices
Remote imprinting of moiré lattices
The authors imprint a moiré potential on a remote monolayer semiconductor through the moiré potential created in a remote MoSe2/WS2 moiré bilayer. The imprinted moiré potential enables gate-controlled generation of flat bands and correlated insulating states in the targeted monolayer.
- Jie Gu
- , Jiacheng Zhu
- & Kin Fai Mak
-
Letter |
 Engineering correlated insulators in bilayer graphene with a remote Coulomb superlattice
Engineering correlated insulators in bilayer graphene with a remote Coulomb superlattice
Employing a remote Coulomb superlattice formed by twisted bilayer WS2, the authors demonstrate the engineering and on/off switching of a Coulomb superlattice of correlated states in bilayer graphene with period and strength determined by the remote superlattice.
- Zuocheng Zhang
- , Jingxu Xie
- & Feng Wang
-
Article |
 Material assembly from collective action of shape-changing polymers
Material assembly from collective action of shape-changing polymers
Autonomous assembly, reconfiguration and disassembly are observed in living aggregates, but are difficult to replicate in synthetic soft matter. Here mechanically interlocked responsive ribbons form transient viscoelastic solids for the on-demand assembly of functional materials.
- Mustafa K. Abdelrahman
- , Robert J. Wagner
- & Taylor H. Ware
-
Feature |
Lifting the fog in ferroelectric thin-film synthesis
Frustrated by reproducibility in electrical measurements on ferroelectric films, Lane Martin, Jon-Paul Maria and Darrell Schlom discuss tactics to reliably synthesize ‘good’ ferroelectric samples, especially in the search for superior materials and device heterostructures.
- Lane W. Martin
- , Jon-Paul Maria
- & Darrell G. Schlom
-
Feature |
 2D materials for logic device scaling
2D materials for logic device scaling
Peng Wu, Tianyi Zhang, Jiadi Zhu, Tomás Palacios and Jing Kong discuss the reproducibility issues in the synthesis and device fabrication of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides that need to be addressed to enable the lab-to-fab transition.
- Peng Wu
- , Tianyi Zhang
- & Jing Kong
-
Feature |
 Controlling supramolecular gels
Controlling supramolecular gels
Kinetic trapping in supramolecular gels leads to varied morphologies and macroscopic properties. Emily R. Draper and Dave J. Adams discuss subtle experimental effects that can lead to reproducibility issues in these systems.
- Emily R. Draper
- & Dave J. Adams
-
Feature |
 The characterization of superconductivity under high pressure
The characterization of superconductivity under high pressure
M. I. Eremets, V. S. Minkov, A. P. Drozdov and P. P. Kong discuss the substantial progress made in discovering and developing near-room-temperature superconductivity in hydrogen-rich materials. They focus on achieving reproducibility under the challenging experimental conditions of megabar pressures.
- M. I. Eremets
- , V. S. Minkov
- & P. P. Kong
-
Feature |
 Observing deformation in situ
Observing deformation in situ
Marc Legros, Frédéric Mompiou and Daniel Caillard discuss the different aspects that influence the reproducibility and reliability of characterizations performed using in situ mechanical tests in transmission electron microscopes.
- Marc Legros
- , Frédéric Mompiou
- & Daniel Caillard
-
Feature |
 Open computational materials science
Open computational materials science
The materials modelling community is emerging as a champion for reproducible and reusable science. Aron Walsh discusses how FAIR databases, collaborative codes and transparent workflows are advancing this movement.
- Aron Walsh
-
Feature |
 Better standards are needed for membrane materials
Better standards are needed for membrane materials
Tae Hoon Lee and Zachary P. Smith argue that some of the most exciting materials that could be used for gas separations are metastable or crystalline, with properties that are altered by sample preparation and testing, but there are no widely accepted standards.
- Tae Hoon Lee
- & Zachary P. Smith
-
Feature |
 Thermoelectric measurements
Thermoelectric measurements
Joseph Heremans and Joshua Martin discuss the reproducibility of thermoelectric measurements and conclude that the uncertainty on the figure of merit zT is of the order of 15–20%.
- Joseph P. Heremans
- & Joshua Martin
-
Article |
 Imaging moiré excited states with photocurrent tunnelling microscopy
Imaging moiré excited states with photocurrent tunnelling microscopy
The authors combine laser excitation and scanning tunnelling spectroscopy to visualize the electron and hole distributions in photoexcited moiré excitons in twisted bilayer WS2. This photocurrent tunnelling microscopy approach enables the study of photoexcited non-equilibrium moiré phenomena at atomic scales.
- Hongyuan Li
- , Ziyu Xiang
- & Feng Wang
-
Article |
 Solution-processable mixed-anion cluster chalcohalide Rb6Re6S8I8 in a light-emitting diode
Solution-processable mixed-anion cluster chalcohalide Rb6Re6S8I8 in a light-emitting diode
Rhenium chalcohalide cluster compounds are promising photoluminescent materials. Here the authors report a new material in this family, Rb6Re6S8I8, which shows broad photoluminescence (PL) range, high PL quantum yield and long PL lifetime.
- Craig C. Laing
- , Daehan Kim
- & Mercouri G. Kanatzidis
-
Article |
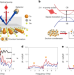 Terahertz parametric amplification as a reporter of exciton condensate dynamics
Terahertz parametric amplification as a reporter of exciton condensate dynamics
Employing nonlinear, time-resolved terahertz spectroscopy to study condensate dynamics on Ta2NiSe5—a narrow-bandgap semiconductor and putative excitonic insulator—the authors reveal enhanced terahertz reflectivity upon photoexcitation and condensation-like temperature dependence below the structural transition critical temperature.
- Sheikh Rubaiat Ul Haque
- , Marios H. Michael
- & Richard D. Averitt
-
Letter |
 Unravelling the jerky glide of dislocations in body-centred cubic crystals
Unravelling the jerky glide of dislocations in body-centred cubic crystals
Plastic deformation requires the propagation of a kinked profile along dislocations. It is shown that each kink acts as a set of travelling thermal spikes, favouring the nucleation of supplementary kinks and long dislocation jumps that are observed experimentally.
- Laurent Proville
- & Anshuman Choudhury
-
Article
| Open Access Space charge governs the kinetics of metal exsolution
Space charge governs the kinetics of metal exsolution
The self-assembly of metallic nanoparticles on oxide supports via metal exsolution relies on dopant transport, but strong electrostatic gradients and space charges typically control the properties of surfaces. The surface–dopant interaction is shown to be the main determining factor for the exsolution kinetics of nickel in a perovskite system.
- Moritz L. Weber
- , Břetislav Šmíd
- & Christian Lenser
-
News & Views |
 Imaging the twist of antiferromagnetic merons in a blood-red iron oxide
Imaging the twist of antiferromagnetic merons in a blood-red iron oxide
The antiferromagnetic material haematite, named for its blood-red colour, hosts swirling spin vortices termed merons. The rotation sense of such antiferromagnetic vortices has now been imaged in real space.
- Leonie Spitz
- & Max Hirschberger
-
Research Briefing |
 Sublattice matching enables texturing of dissimilar materials
Sublattice matching enables texturing of dissimilar materials
Inspired by the observed coherent interface between hexagonal α-Fe2O3 and tetragonal fluorine-doped SnO2, an oxygen sublattice-matching paradigm is proposed to grow textured films on lattice-mismatched substrates. Through assessing the similarity of Voronoi cells for sublattices, this approach offers opportunities to synthesize (semi)coherent heterostructures and textured films.
-
News & Views |
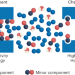 Engineering porous crystals to do different things
Engineering porous crystals to do different things
An important but difficult separation, the removal of carbon monoxide from humid gas mixtures comprising oxygen, nitrogen and hydrocarbons, is addressed by exploiting Cu(I) coordination chemistry and framework flexibility.
- Michael J. Zaworotko
-
News & Views |
 Tear-resistant stretchy gels
Tear-resistant stretchy gels
Incorporating additives that contain hydrogen-bonding nanochannels creates nanoconfined polymer gels that are highly stretchable, elastic and insensitive to notch propagation.
- Meixiang Wang
- & Michael D. Dickey
-
News & Views |
 Molecular motion cools off gold nanoclusters
Molecular motion cools off gold nanoclusters
Engineered ligand shells on gold nanoclusters utilizing molecular motion improve the thermal conductance between the cluster and the solvent, increasing thermal stability and enhancing performance in the photothermal treatment of cancerous tumours.
- Jacob L. Beckham
- & James M. Tour
-
News & Views |
 Through the MOF looking glass
Through the MOF looking glass
Processible centimetre-scale porous glasses using zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF) materials are developed, while fine-tuning of the processing conditions allows control of pore size and molecular sieving properties.
- Georgia R. F. Orton
- & Neil R. Champness
-
News & Views |
 Beyond moiré in twisted two-dimensional magnets
Beyond moiré in twisted two-dimensional magnets
Orthogonally twisted CrSBr ferromagnetic monolayers with in-plane Ising anisotropies are found to exhibit multistep magnetoresistance switching with a magnetic hysteresis opening. This work emphasizes the role of spin dimensionality in two-dimensional magnets, and the potential of orthogonal and large-twist-angle van der Waals magnets.
- Lan Wang
-
News & Views |
 Bridging the gap in mesoscopic length scales
Bridging the gap in mesoscopic length scales
Elastic microphase separation controls the characteristic mesoscopic length scale of bulk bicontinuous materials.
- Jörg G. Werner
-
Article
| Open Access Precise control over gas-transporting channels in zeolitic imidazolate framework glasses
Precise control over gas-transporting channels in zeolitic imidazolate framework glasses
Porosity of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks can be preserved beyond glass transition and melt processing. Here centimetre-scale porous glasses are demonstrated, whereas liquid processing enables fine-tuning of the size of the gas-transporting channels for molecular sieving.
- Oksana Smirnova
- , Seungtaik Hwang
- & Alexander Knebel
-
News & Views |
 All-electric writing of a chiral quantum memory
All-electric writing of a chiral quantum memory
An all-electric switch of the persistent electron swirl in a quantum anomalous Hall state enables researchers to flip the electronic chirality of this quantum state.
- Philip J. W. Moll
-
News & Views |
 Beyond lithium for sustainable ammonia synthesis
Beyond lithium for sustainable ammonia synthesis
Using an electrochemical continuous flow cell, nitrogen reduction to ammonia is rigorously demonstrated through a calcium-mediated approach.
- Michael A. Yusov
- & Karthish Manthiram
-
News & Views |
 Breaking symmetry creates polar auxeticity
Breaking symmetry creates polar auxeticity
By forming a heterostructure interface, and by judicious choice of crystallographic orientation, piezoelectrics are developed that show expansion or contraction along all axes on application of an electric field.
- Eugene A. Eliseev
- & Anna N. Morozovska
-
Research Briefing |
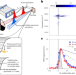 Vibrational optical control via cation motions in perovskite solar cells
Vibrational optical control via cation motions in perovskite solar cells
Hybrid organic–inorganic perovskite materials have promise as the photovoltaic technology of the future. A method for spectroscopic optical control reveals how the structural dynamics and vibrations of a perovskite’s organic cations affect the electronic performance of working photovoltaic devices.
-
Article |
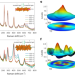 Stacking textured films on lattice-mismatched transparent conducting oxides via matched Voronoi cell of oxygen sublattice
Stacking textured films on lattice-mismatched transparent conducting oxides via matched Voronoi cell of oxygen sublattice
Depositing textured functional materials on transparent conducting oxides remains a challenge. We demonstrate the formation of a coherent interface between a set of functional oxides and fluorine-doped-tin-oxide-based transparent conducting oxide substrate despite the lattice mismatch, owing to dimensional and chemical matching of oxygen sublattices at the interface.
- Huiting Huang
- , Jun Wang
- & Zhigang Zou
-
Research Briefing |
 Nano-oxide networks in metallic glass nanotubes lead to superelastic properties
Nano-oxide networks in metallic glass nanotubes lead to superelastic properties
Oxidation can degrade the properties and functionality of three-dimensional bulk metallic glasses. However, the formation of percolating oxide networks in metallic glass nanotubes or nanosheets can induce interesting properties, such as a recoverable strain of 10–20% and elastic modulus of 20–30 GPa, which are rarely observed in their bulk counterparts.
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing emergent magnetic charge in an antiferromagnet with diamond quantum magnetometry
Revealing emergent magnetic charge in an antiferromagnet with diamond quantum magnetometry
Diamond quantum magnetometry is utilized to directly read the vorticity of antiferromagnetic spin textures through coupled multi-polar emergent magnetic charge distributions.
- Anthony K. C. Tan
- , Hariom Jani
- & Mete Atatüre
-
Letter |
 Oxidation-induced superelasticity in metallic glass nanotubes
Oxidation-induced superelasticity in metallic glass nanotubes
Oxidation normally deteriorates the mechanical properties of metals. But it is now shown that the formation of a percolating oxide network in metallic glass nanotubes can result in an unprecedented superelasticity of 14% at room temperature.
- Fucheng Li
- , Zhibo Zhang
- & Yong Yang

 Field-free switching of perpendicular magnetization by two-dimensional PtTe2/WTe2 van der Waals heterostructures with high spin Hall conductivity
Field-free switching of perpendicular magnetization by two-dimensional PtTe2/WTe2 van der Waals heterostructures with high spin Hall conductivity