News & Views |
Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Large-scale dielectric metasurfaces
Large-scale dielectric metasurfaces
Researchers develop a simple and low-cost fabrication method for the production of large-scale all-dielectric metasurfaces, which exhibit near-perfect reflectivity in the telecommunications spectral window.
- Nicolas Bonod
-
Article |
 Backward phase-matching for nonlinear optical generation in negative-index materials
Backward phase-matching for nonlinear optical generation in negative-index materials
Phase matching in the backward direction—the so-called nonlinear mirror effect—is demonstrated experimentally between the fundamental and second harmonic, using two distinct modes in a metal–dielectric–metal waveguide.
- Shoufeng Lan
- , Lei Kang
- & Wenshan Cai
-
-
News & Views |
 Perovskite cells charge forward
Perovskite cells charge forward
Now that certified energy conversion efficiencies for perovskite solar cells are above 20%, researchers are exploring other critical areas, such as understanding device hysteresis and film growth, as well as the replacement of lead and the development of tandem cell stacks. Cell stability remains a crucial issue.
- Martin A. Green
- & Thomas Bein
-
Letter |
 Spectroscopic evidence for negative electronic compressibility in a quasi-three-dimensional spin–orbit correlated metal
Spectroscopic evidence for negative electronic compressibility in a quasi-three-dimensional spin–orbit correlated metal
Electron filling causes a reduction of the chemical potential in (Sr1−x Lax)3Ir2O7, which suggests negative electronic compressibility. Studying the concomitant change of the bandgap provides insight into the physical mechanism behind this effect.
- Junfeng He
- , T. Hogan
- & Rui-Hua He
-
-
Article |
 Continuous control of the nonlinearity phase for harmonic generations
Continuous control of the nonlinearity phase for harmonic generations
A concept for the phase control of the nonlinear susceptibility using the left- and right-circular polarization basis for fundamental and harmonic generated light is introduced and tested using metasurfaces containing plasmonic antennas.
- Guixin Li
- , Shumei Chen
- & Shuang Zhang
-
-
News & Views |
 Mid-infrared nanophotonics
Mid-infrared nanophotonics
The confinement and scattering lifetimes of graphene plasmons are improved when graphene is sandwiched between layers of thin hexagonal boron nitride. This finding should pave the way for nanophotonic applications in the low-loss regime.
- Joshua D. Caldwell
- & Kostya S. Novoselov
-
News & Views |
 Energy transfer is speeded up in 2D
Energy transfer is speeded up in 2D
When efficient energy transfer under high carrier densities is required, two-dimensional nanoplatelets are the material of choice, combining an exceptional suppression of nonlinear fluorescence quenching with ultrafast transfer capabilities.
- Iwan Moreels
-
News & Views |
 Lasing from 2D atomic crystals
Lasing from 2D atomic crystals
The coupling of monolayer tungsten diselenide and a photonic-crystal cavity leads to ultralow-threshold lasing.
- Vinod Menon
-
Letter |
 Picosecond energy transfer and multiexciton transfer outpaces Auger recombination in binary CdSe nanoplatelet solids
Picosecond energy transfer and multiexciton transfer outpaces Auger recombination in binary CdSe nanoplatelet solids
Fast fluorescence resonance energy transfer between CdSe nanoplatelets on a picosecond timescale is measured. This process is faster than Auger recombination and leads to the observation of multiexcitonic energy transfer in these materials.
- Clare E. Rowland
- , Igor Fedin
- & Richard D. Schaller
-
Article |
 A photoreversible protein-patterning approach for guiding stem cell fate in three-dimensional gels
A photoreversible protein-patterning approach for guiding stem cell fate in three-dimensional gels
An approach that exploits two bioorthogonal photochemistries to achieve reversible immobilization of full-length proteins in synthetic hydrogels allows for the reversible differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells to osteoblasts.
- Cole A. DeForest
- & David A. Tirrell
-
-
Article |
 Highly confined low-loss plasmons in graphene–boron nitride heterostructures
Highly confined low-loss plasmons in graphene–boron nitride heterostructures
Direct imaging and characterization of propagating plasmons in high-quality graphene, encapsulated between two films of hexagonal boron nitride, has now been achieved together with the observation of very low plasmon damping.
- Achim Woessner
- , Mark B. Lundeberg
- & Frank H. L. Koppens
-
News & Views |
 Switchable photovoltaics
Switchable photovoltaics
The migration of ions under the effect of an external electric field locally modifies the doping of organometal halide perovskite films. This is used to reversibly switch the photocurrent direction in very simple photovoltaic architectures.
- Nam-Gyu Park
-
-
-
Article |
 Multimodal plasmonics in fused colloidal networks
Multimodal plasmonics in fused colloidal networks
Harnessing the optical properties of noble metals down to the nanoscale is crucial for fast information processing. Lateral confinement and delocalization of surface plasmons is now observed in self-assembled network chains of fused gold nanoparticles.
- Alexandre Teulle
- , Michel Bosman
- & Erik Dujardin
-
-
News & Views |
 Bringing dark states to light
Bringing dark states to light
Semiconducting quantum dots have been used to harvest triplet excitons produced through singlet fission in organic semiconductors. These hybrid organic–inorganic materials may boost the efficiency of solar cells.
- Christopher J. Bardeen
-
Article |
 Energy harvesting of non-emissive triplet excitons in tetracene by emissive PbS nanocrystals
Energy harvesting of non-emissive triplet excitons in tetracene by emissive PbS nanocrystals
Lead sulphide colloidal nanocrystals are now used to harvest non-emissive triplet excitons generated in a tetracene layer. Depending on the length of the ligands capping the nanocrystals, exciton transfer efficiency as high as 90% can be achieved.
- Nicholas J. Thompson
- , Mark W. B. Wilson
- & Marc A. Baldo
-
-
Article |
 Digital metamaterials
Digital metamaterials
Inspired by Boolean binary algebra, an approach to design electromagnetic metamaterials with desired permittivity by using just two elemental building blocks is demonstrated analytically and numerically.
- Cristian Della Giovampaola
- & Nader Engheta
-
News & Views |
 Continuing to soar
Continuing to soar
The dream of printing highly efficient solar cells is closer than ever to being realized. Solvent engineering has enabled the deposition of uniform perovskite semiconductor films that yield greater than 15% power-conversion efficiency.
- Michael D. McGehee
-
Commentary |
 The light and shade of perovskite solar cells
The light and shade of perovskite solar cells
The rise of metal halide perovskites as light harvesters has stunned the photovoltaic community. As the efficiency race continues, questions on the control of the performance of perovskite solar cells and on its characterization are being addressed.
- Michael Grätzel
-
Letter |
 Redox shuttle mechanism enhances photocatalytic H2 generation on Ni-decorated CdS nanorods
Redox shuttle mechanism enhances photocatalytic H2 generation on Ni-decorated CdS nanorods
Photocatalytic efficiency can be limited by slow transfer of photoexcited holes and high charge recombination rates. Using a hydroxyl anion–radical redox couple leads to enhanced photocatalytic H2 generation on Ni-decorated CdS nanorods.
- Thomas Simon
- , Nicolas Bouchonville
- & Jochen Feldmann
-
Letter |
 Realization of dynamic thermal emission control
Realization of dynamic thermal emission control
The dynamic control of thermal emission via the control of emissivity through intersubband absorption in n-type quantum wells, at a speed four orders of magnitude faster than is currently possible, is now demonstrated.
- Takuya Inoue
- , Menaka De Zoysa
- & Susumu Noda
-
Letter |
 Reconfigurable 3D plasmonic metamolecules
Reconfigurable 3D plasmonic metamolecules
Until now, it has not been possible to switch chirality in plasmonic nanostructures at will and repeatedly. Now, thanks to DNA-regulated conformational changes, reconfigurable 3D plasmonic metamolecules with switchable chirality have been created.
- Anton Kuzyk
- , Robert Schreiber
- & Na Liu
-
Article |
 Solvent engineering for high-performance inorganic–organic hybrid perovskite solar cells
Solvent engineering for high-performance inorganic–organic hybrid perovskite solar cells
The performance of solar cells based on organic–inorganic perovskites strongly depends on the device architecture and processing conditions. It is now shown that solvent engineering enables the deposition of very dense perovskite layers on mesoporous titania, leading to photovoltaic devices with a high light-conversion efficiency and no hysteresis.
- Nam Joong Jeon
- , Jun Hong Noh
- & Sang Il Seok
-
Article |
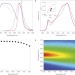 Narrow-band red-emitting Sr[LiAl3N4]:Eu2+ as a next-generation LED-phosphor material
Narrow-band red-emitting Sr[LiAl3N4]:Eu2+ as a next-generation LED-phosphor material
For high-power white-light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to become a technological reality there is a need to find more efficient red-emitting phosphor materials. Eu2+-doped Sr[LiAl3N4], a member of the nitridoaluminates compound class, is now proved to be a high-performance narrow-band red-emitting phosphor material that can be easily coupled with existing GaN-based blue-LED technology for use in white LEDs.
- Philipp Pust
- , Volker Weiler
- & Wolfgang Schnick
-
Letter |
 Stretchable liquid-crystal blue-phase gels
Stretchable liquid-crystal blue-phase gels
Liquid-crystalline elastomers combine rubber-like elasticity with the optical properties of liquid crystals, yet some of their properties depend on the particular liquid-crystal phase. Now, stretchable gels of the liquid-crystalline blue-phase I are reported. The blue-phase gels are electro-optically switchable under a moderate applied voltage, and their optical properties can be manipulated by an applied strain.
- F. Castles
- , S. M. Morris
- & H. J. Coles
-
-
Article |
 Engineering of light confinement in strongly scattering disordered media
Engineering of light confinement in strongly scattering disordered media
Disordered photonic materials have the ability to control the flow of light through random multiple scattering. This has the drawback of randomizing both the direction and phase of the propagating light. Now, confined and interacting light modes are demonstrated for a two-dimensional disordered photonic structure.
- Francesco Riboli
- , Niccolò Caselli
- & Diederik S. Wiersma
-
News & Views |
 Long-distance relationships
Long-distance relationships
By embedding organic dyes in a suitably designed optical microcavity it is possible to strongly mix light and matter excitations, forming states known as microcavity polaritons. These hybrid light–matter states are used to demonstrate energy transfer between organic molecules over long distances.
- Russell J. Holmes
-
Article |
 Polariton-mediated energy transfer between organic dyes in a strongly coupled optical microcavity
Polariton-mediated energy transfer between organic dyes in a strongly coupled optical microcavity
The energy interaction between different exciton species is affected by the optical environment in which they are embedded. It is now shown that mixed exciton–polariton states in strongly coupled microcavities can facilitate energy transfer between organic dyes at length scales greater than the Förster transfer radius.
- David M. Coles
- , Niccolo Somaschi
- & David G. Lidzey
-
Letter |
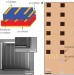 Printing-based assembly of quadruple-junction four-terminal microscale solar cells and their use in high-efficiency modules
Printing-based assembly of quadruple-junction four-terminal microscale solar cells and their use in high-efficiency modules
A strategy to overcome the maximum theoretical efficiency limit of single-junction solar cells is to realize stacked, multi-junction cells that are used under highly concentrated light. Now, a printing-based, scalable approach for the assembly of multi-junction solar cells in concentrator photovoltaic modules that reach a high power conversion efficiency is reported.
- Xing Sheng
- , Christopher A. Bower
- & John A. Rogers
-
Article |
 Persistent optically induced magnetism in oxygen-deficient strontium titanate
Persistent optically induced magnetism in oxygen-deficient strontium titanate
Strontium titanate is widely studied for the myriad of phenomena that are known to occur in the vicinity of its surface. It is now shown that light can be used to induce magnetism in oxygen-deficient crystals of SrTiO3.
- W. D. Rice
- , P. Ambwani
- & S. A. Crooker
-
News & Views |
 Electric fields line up graphene oxide
Electric fields line up graphene oxide
The macroscopic alignment of dilute dispersions of graphene oxide can be controlled, with extremely large optical sensitivity, through the application of weak electric fields.
- Ju Young Kim
- & Sang Ouk Kim
-
Article |
 Organo-erbium systems for optical amplification at telecommunications wavelengths
Organo-erbium systems for optical amplification at telecommunications wavelengths
Optical amplifiers based on erbium ions typically require high pump power densities to produce gain. Now, an organic optical amplifier material composed of erbium ions and a zinc-based organic chromophore is demonstrated to reach population inversion using low-power visible light.
- H. Q. Ye
- , Z. Li
- & W. P. Gillin
-
News & Views |
 Going soft
Going soft
The experimental observation of polariton condensates at room temperature in soft organic materials makes the study of quantum condensed phases easily accessible and opens inroads to optoelectronic devices based on macroscopic quantum phenomena.
- Pavlos Lagoudakis
-
-
Correspondence |
Reply to 'On the thermodynamics of light trapping in solar cells'
- Harry A. Atwater
- & Albert Polman
-
Review Article |
 Flat optics with designer metasurfaces
Flat optics with designer metasurfaces
Metamaterials are artificially fabricated materials that allow for the control of light and acoustic waves in a manner that is not possible in nature. This Review covers the recent developments in the study of so-called metasurfaces, which offer the possibility of controlling light with ultrathin, planar optical components.
- Nanfang Yu
- & Federico Capasso
-
News & Views |
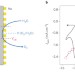 An adaptive junction
An adaptive junction
The energetic and kinetic behaviours of water-oxidation catalysts deposited on semiconductor electrodes are probed in situ, elucidating the junction formed between them, and transforming the design principles of the catalysts.
- Thomas W. Hamann
-
Letter |
 Observing bulk diamond spin coherence in high-purity nanodiamonds
Observing bulk diamond spin coherence in high-purity nanodiamonds
The photoluminescent properties of electron spins at nitrogen–vacancy (NV) centres are promising for use in quantum information and magnetometry. It is now shown that the coherence times of NV centres in nanodiamonds can be engineered to be comparable to those of bulk diamond.
- Helena S. Knowles
- , Dhiren M. Kara
- & Mete Atatüre
-
Article |
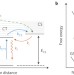 Efficient charge generation by relaxed charge-transfer states at organic interfaces
Efficient charge generation by relaxed charge-transfer states at organic interfaces
The efficiency of organic blends used for photovoltaic applications depends on their ability to convert photoexcited charges into free holes and electrons. It is now demonstrated that the lowermost energetic states formed at the donor/acceptor interface can reach conversion efficiencies close to 100%, and therefore do not behave as traps for charge carriers.
- Koen Vandewal
- , Steve Albrecht
- & Alberto Salleo
-
News & Views |
 A little twist with big consequences
A little twist with big consequences
A study on the subtle interplay between electronic structure and structural defects now explains why the suppression of conduction in the insulating state of bilayer graphene is not as strong as might be expected. It also reveals the possibility of creating graphene-based nanoscale systems with unique electronic properties.
- Philip Hofmann
-
News & Views |
 A source of energetic electrons
A source of energetic electrons
Photoexcited diamond can inject highly energetic electrons in solution and promote the catalysis of a broad range of chemical reactions.
- Christoph E. Nebel

 Trapped in a flat dispersion
Trapped in a flat dispersion Silicon qubits
Silicon qubits