Featured
-
-
Letter |
 Ultrafast pyroelectric photodetection with on-chip spectral filters
Ultrafast pyroelectric photodetection with on-chip spectral filters
The ultrafast response of a pyroelectric sensor with near-infrared responsivity is demonstrated by combining a pyroelectric thermal detector with wavelength-selective nanoparticle absorbers.
- Jon W. Stewart
- , Jarrett H. Vella
- & Maiken H. Mikkelsen
-
Article |
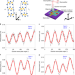 Spatially dispersive circular photogalvanic effect in a Weyl semimetal
Spatially dispersive circular photogalvanic effect in a Weyl semimetal
A spatially dispersive photoresponse is found in a topological semimetal.
- Zhurun Ji
- , Gerui Liu
- & Ritesh Agarwal
-
Review Article |
 Nanophotonic engineering of far-field thermal emitters
Nanophotonic engineering of far-field thermal emitters
This Review covers the basic physics of thermal emission, ways to engineer the thermal field radiated by hot objects in the far field and applications, such as thermophotovoltaics, radiative cooling, camouflage and privacy.
- Denis G. Baranov
- , Yuzhe Xiao
- & Mikhail A. Kats
-
Article |
 Ultrafast generation and control of an electron vortex beam via chiral plasmonic near fields
Ultrafast generation and control of an electron vortex beam via chiral plasmonic near fields
By exciting chiral plasmons within a nanohole by means of circularly polarized light pulses, orbital angular momentum can be imparted onto charged matter waves (here, electrons) and controlled at terahertz speed (femtosecond intervals).
- G. M. Vanacore
- , G. Berruto
- & F. Carbone
-
Letter |
 Ultrafast transition between exciton phases in van der Waals heterostructures
Ultrafast transition between exciton phases in van der Waals heterostructures
Femtosecond pump–probe measurements of Coulomb correlations in WS2/WSe2 heterostructures reveal the interlayer exciton binding energy, determined from the 1s–2p resonance, as well as the dynamics of the conversion of intra- to interlayer excitons.
- P. Merkl
- , F. Mooshammer
- & R. Huber
-
News & Views |
 Lighting up the new order
Lighting up the new order
Irradiating a PbTiO3/SrTiO3 superlattice with ultrafast UV light pulses modifies elastic and electrostatic interactions, resulting in the formation of a stable complex 3D supercrystal.
- J. M. Gregg
-
Article |
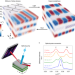 Optical creation of a supercrystal with three-dimensional nanoscale periodicity
Optical creation of a supercrystal with three-dimensional nanoscale periodicity
Upon ultrafast irradiation, a (PbTiO3)/(SrTiO3) superlattice transforms into a complex supercrystal that contains periodicities of up to 30 nm in size and is stable in ambient. Creation and destruction, by heating, of the supercrystal is reversible.
- V. A. Stoica
- , N. Laanait
- & J. W. Freeland
-
Article |
 Colossal mid-infrared bulk photovoltaic effect in a type-I Weyl semimetal
Colossal mid-infrared bulk photovoltaic effect in a type-I Weyl semimetal
A large bulk photovoltaic effect is observed in the type-I Weyl semimetal TaAs, and attributed to the diverging Berry curvature of the Weyl nodes.
- Gavin B. Osterhoudt
- , Laura K. Diebel
- & Kenneth S. Burch
-
News & Views |
 Quantum nonlinearities at the single-particle level
Quantum nonlinearities at the single-particle level
A hybrid state of photons and electronic excitations in semiconductor quantum wells shows nonlinear behaviour at the level of single or few quanta, thus opening the door to the realization of photonic nonlinear quantum devices employing semiconductor technologies.
- Dario Gerace
- , Fabrice Laussy
- & Daniele Sanvitto
-
Letter |
 Towards polariton blockade of confined exciton–polaritons
Towards polariton blockade of confined exciton–polaritons
Confined exciton–polaritons in semiconductor-based quantum wells can give rise to correlations slightly below the level of classical coincidence counts under resonant excitation, such that single or few polariton excitations are sufficient to modify the statistics of the radiation going through the system.
- Aymeric Delteil
- , Thomas Fink
- & Ataç İmamoğlu
-
Letter |
 Emergence of quantum correlations from interacting fibre-cavity polaritons
Emergence of quantum correlations from interacting fibre-cavity polaritons
Two-photon correlation measurements in a resonantly excited fibre-cavity polariton system stay below the classical limit for zero time delay, suggesting quantum correlations between the polaritons.
- Guillermo Muñoz-Matutano
- , Andrew Wood
- & Thomas Volz
-
Article |
 Asymmetrically strained quantum dots with non-fluctuating single-dot emission spectra and subthermal room-temperature linewidths
Asymmetrically strained quantum dots with non-fluctuating single-dot emission spectra and subthermal room-temperature linewidths
Asymmetric strain intrinsic to core/shell nanocrystals based on lattice-mismatched wurtzite semiconductors leads to suppression of spectral fluctuation, narrowing of photoluminescence linewidth and reduced blinking in colloidal nanocrystals.
- Young-Shin Park
- , Jaehoon Lim
- & Victor I. Klimov
-
Article |
 Efficient electrical detection of mid-infrared graphene plasmons at room temperature
Efficient electrical detection of mid-infrared graphene plasmons at room temperature
A system of patterned graphene nanoresonators/nanoribbons can be used as an efficient mid-infrared detector, based on plasmonic resonant absorption and subsequent carrier thermalization.
- Qiushi Guo
- , Renwen Yu
- & Fengnian Xia
-
Letter |
 Two-dimensional itinerant ferromagnetism in atomically thin Fe3GeTe2
Two-dimensional itinerant ferromagnetism in atomically thin Fe3GeTe2
Metallic ferromagnetism is reported in an exfoliated monolayer of the van der Waals material Fe3GeTe2.
- Zaiyao Fei
- , Bevin Huang
- & Xiaodong Xu
-
Letter |
 Terahertz-light quantum tuning of a metastable emergent phase hidden by superconductivity
Terahertz-light quantum tuning of a metastable emergent phase hidden by superconductivity
THz pump–probe experiments of superconducting Nb3Sn reveal that a metastable phase is induced for excitation fields around 250 kV cm−1.
- X. Yang
- , C. Vaswani
- & J. Wang
-
Feature |
 Ferroelectric large polarons
Ferroelectric large polarons
Kiyoshi Miyata and X.-Y. Zhu analyse the ferroelectric-like dielectric response of lead halide perovskites in the terahertz region and discuss the potential role of polar nanodomains in accounting for the defect tolerance and low recombination rates of these materials.
- Kiyoshi Miyata
- & X.-Y. Zhu
-
Feature |
 The influence of the Rashba effect
The influence of the Rashba effect
Heavy atoms and crystal or inversion symmetry breaking may promote Rashba effects in halide perovskites. Sam Stranks and Paulina Plochocka propose experiments to assess the existence of these effects and their implications on the photophysics of perovskites.
- Samuel D. Stranks
- & Paulina Plochocka
-
Letter |
 Solid-state electron spin lifetime limited by phononic vacuum modes
Solid-state electron spin lifetime limited by phononic vacuum modes
A systematic investigation of the spin relaxation in nitrogen vacancy centres in diamonds, induced by phononic vacuum modes at low temperature, reveals an upper limit of eight hours.
- T. Astner
- , J. Gugler
- & J. Majer
-
Letter |
 Ultralow-loss polaritons in isotopically pure boron nitride
Ultralow-loss polaritons in isotopically pure boron nitride
Isotopic enrichment in hexagonal boron nitride is shown to enhance the propagation properties of phonon polaritons, achieving a threefold enhancement in their lifetime.
- Alexander J. Giles
- , Siyuan Dai
- & Joshua D. Caldwell
-
Article |
 Topological order and thermal equilibrium in polariton condensates
Topological order and thermal equilibrium in polariton condensates
The Berezinskii–Kosterlitz–Thouless transition is observed in a 2D gas of exciton-polaritons, through measurements of the first-order coherence both in space and time.
- Davide Caputo
- , Dario Ballarini
- & Daniele Sanvitto
-
Letter |
 Exciton Hall effect in monolayer MoS2
Exciton Hall effect in monolayer MoS2
Polarization-dependent photoluminescent mapping reveals that excitons — composite particles made of electron–hole pairs bound by the Coulomb force — exhibit the Hall effect, which originates from the large exciton Berry curvature.
- Masaru Onga
- , Yijin Zhang
- & Yoshihiro Iwasa
-
Article |
 Realizing the classical XY Hamiltonian in polariton simulators
Realizing the classical XY Hamiltonian in polariton simulators
Lattices of exciton-polariton condensates provide the base for a simulator that can be used to find the global minimum of the classical XY Hamiltonian.
- Natalia G. Berloff
- , Matteo Silva
- & Pavlos G. Lagoudakis
-
Article |
 The processing and heterostructuring of silk with light
The processing and heterostructuring of silk with light
Femtosecond laser pulses can induce local bulging or plasma ablation of silk with limited structural damage, thus offering a technique for cutting, patterning, bending and welding of silk with various other materials.
- Mehra S. Sidhu
- , Bhupesh Kumar
- & Kamal P. Singh
-
News & Views |
 Here comes the spaser
Here comes the spaser
Plasmonic nanolasers embedded in living cells and animal tissues are shown to emit strongly, making them promising potential biocompatible probes.
- Catherine Alix-Panabières
- & Klaus Pantel
-
News & Views |
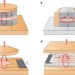 Wiry matter–light coupling
Wiry matter–light coupling
Electrical injection into polaritons, built from admixing excitons in carbon nanotubes with light in a surrounding microcavity, has been achieved.
- Jeremy J. Baumberg
-
Article |
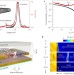 Electrical pumping and tuning of exciton-polaritons in carbon nanotube microcavities
Electrical pumping and tuning of exciton-polaritons in carbon nanotube microcavities
The exciton-polaritons formed using carbon nanotube field-effect transistors strongly coupled to an optical microcavity can sustain electrical pumping under high current densities.
- Arko Graf
- , Martin Held
- & Jana Zaumseil
-
Article |
 Excitation-wavelength-dependent small polaron trapping of photoexcited carriers in α-Fe2O3
Excitation-wavelength-dependent small polaron trapping of photoexcited carriers in α-Fe2O3
The effect of polaron formation on photoconversion efficiency for oxide photocatalysts is not well known. Femtosecond extreme-ultraviolet measurements suggest that polaron localization is responsible for ultrafast trapping of photoexcited carriers in haematite.
- Lucas M. Carneiro
- , Scott K. Cushing
- & Stephen R. Leone
-
News & Views |
 Reaching the third dimension
Reaching the third dimension
X-ray imaging in three dimensions is now possible from a set of 2D coherent Bragg diffraction patterns. This approach overcomes the necessity of having to rotate the sample for a 3D reconstruction.
- Ian Robinson
- & Xiaojing Huang
-
Letter |
 A charge density wave-like instability in a doped spin–orbit-assisted weak Mott insulator
A charge density wave-like instability in a doped spin–orbit-assisted weak Mott insulator
TSr3Ir2O7 is shown to realize a weak Mott state with no cuprate analogue and to exhibit, when electron doped, a charge density wave-like Fermi surface instability with unconventional and possibly short-ranged nature.
- H. Chu
- , L. Zhao
- & D. Hsieh
-
Article |
 Topologically protected bound states in photonic parity–time-symmetric crystals
Topologically protected bound states in photonic parity–time-symmetric crystals
Topologically protected bound states in parity–time-symmetric non-Hermitian photonic lattices are theoretically predicted and experimentally demonstrated.
- S. Weimann
- , M. Kremer
- & A. Szameit
-
Review Article |
 Polaritons in layered two-dimensional materials
Polaritons in layered two-dimensional materials
This Review discusses the properties of polariton modes (plasmon, phonon and exciton) in graphene, hexagonal boron nitride and transition metal dichalcogenides for applications across the terahertz to visible spectrum.
- Tony Low
- , Andrey Chaves
- & Frank Koppens
-
Editorial |
 Shiny condensates
Shiny condensates
Commercialization of exciton–polariton research as well as investigation of exciting physical phenomena in exciton–polariton condensates relies on improving material properties.
-
Commentary |
 Physics and applications of exciton–polariton lasers
Physics and applications of exciton–polariton lasers
Although exciton–polariton lasers have been experimentally demonstrated in a variety of material systems, robust practical implementations are still challenging. Similarities with atomic Bose–Einstein condensates make the system suitable for chip-based quantum simulators for non-trivial many-body physics.
- Michael D. Fraser
- , Sven Höfling
- & Yoshihisa Yamamoto
-
Letter |
 Thermoelectric detection and imaging of propagating graphene plasmons
Thermoelectric detection and imaging of propagating graphene plasmons
A device is presented that can detect mid-infrared plasmons in graphene encapsulated by hexagonal boron nitride via the thermoelectric effect; the natural decay product of the plasmons (electronic heat) is converted into a measurable voltage signal.
- Mark B. Lundeberg
- , Yuanda Gao
- & Frank H. L. Koppens
-
News & Views |
 Electrical spin switching
Electrical spin switching
Ultra-low-power electronic switching of stable exciton–polariton spin states has now been achieved in a semiconductor microcavity. This opens a new route to the integration of spin-based photonics and electronics.
- T. C. H. Liew
-
Review Article |
 The road towards polaritonic devices
The road towards polaritonic devices
This review discusses exciton–polaritons in microcavities and their emerging technological applications, with emphasis on the materials challenges for operation at room temperature.
- Daniele Sanvitto
- & Stéphane Kéna-Cohen
-
Letter |
 Cooperative photoinduced metastable phase control in strained manganite films
Cooperative photoinduced metastable phase control in strained manganite films
Strain engineering can ‘hide’ the ordinal ferrometallic state in manganite films, pushing the system to a metastable state, which can then be controlled through photoexcitation.
- Jingdi Zhang
- , Xuelian Tan
- & R. D. Averitt
-
Letter |
 Soliton-dependent plasmon reflection at bilayer graphene domain walls
Soliton-dependent plasmon reflection at bilayer graphene domain walls
2D surface plasmon polaritons are used to probe the domain-wall solitons in bilayer graphene; near-field infrared nanoscopy reveals various domain-wall structures in mechanically exfoliated graphene bilayers.
- Lili Jiang
- , Zhiwen Shi
- & Feng Wang
-
News & Views |
 Exciton-mediated superconductivity
Exciton-mediated superconductivity
Laser-generated exciton–polariton condensates in transition metal dichalcogenide heterostructures may trigger Cooper pairing of electrons and induce high-temperature superconductivity.
- Alexey Kavokin
- & Pavlos Lagoudakis
-
Article |
 Reversible optical switching of highly confined phonon–polaritons with an ultrathin phase-change material
Reversible optical switching of highly confined phonon–polaritons with an ultrathin phase-change material
Optically rewritable surface phonon–polariton resonators are demonstrated in a system combining phase-change materials that can reversibly switch between amorphous and crystalline phases, with polar crystals that support surface phonon–polaritons.
- Peining Li
- , Xiaosheng Yang
- & Thomas Taubner
-
Letter |
 Ultrafast energy- and momentum-resolved dynamics of magnetic correlations in the photo-doped Mott insulator Sr2IrO4
Ultrafast energy- and momentum-resolved dynamics of magnetic correlations in the photo-doped Mott insulator Sr2IrO4
The dynamics of the magnetic correlations after photo-doping Sr2IrO4 are studied through ultrafast time-resolved resonant inelastic X-ray spectroscopy. The timescales are found to depend on the dimensionality of the correlations.
- M. P. M. Dean
- , Y. Cao
- & J. P. Hill
-
News & Views |
 Flexible yet robust
Flexible yet robust
Researchers have experimentally demonstrated a new type of pathway for electromagnetic waves, which allows an easy reconfiguration into various shapes while significantly suppressing backscattering.
- Bo Zhen
- & Marin Soljačić
-
Correspondence |
 Optical activity from racemates
Optical activity from racemates
- Romain Gautier
- , Jordan M. Klingsporn
- & Kenneth R. Poeppelmeier
-
Progress Article |
 Electromagnetic toroidal excitations in matter and free space
Electromagnetic toroidal excitations in matter and free space
A review on toroidal excitations, from static toroidal moments in condensed matter, to dynamic toroidal multipoles demonstrated experimentally with metamaterials.
- N. Papasimakis
- , V. A. Fedotov
- & N. I. Zheludev
-
News & Views |
 Plasmons in moiré superlattices
Plasmons in moiré superlattices
The propagation of plasmons in graphene–hexagonal boron nitride moiré patterns is experimentally studied for the first time via infrared scattering near-field optical spectroscopy.
- Marco Polini
- & Frank H. L. Koppens
-
-
Article |
 Plasmons in graphene moiré superlattices
Plasmons in graphene moiré superlattices
Graphene/hBN moiré superlattices exhibit a new set of Dirac mini-bands, whose interband transitions—together with free electrons in the ordinary Dirac bands—modify the nature of the plasmons, as revealed by infrared near-field microscopy.
- G. X. Ni
- , H. Wang
- & D. N. Basov
-
-
Article |
 Backward phase-matching for nonlinear optical generation in negative-index materials
Backward phase-matching for nonlinear optical generation in negative-index materials
Phase matching in the backward direction—the so-called nonlinear mirror effect—is demonstrated experimentally between the fundamental and second harmonic, using two distinct modes in a metal–dielectric–metal waveguide.
- Shoufeng Lan
- , Lei Kang
- & Wenshan Cai
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Atom optics
- High-harmonic generation
- Magneto-optics
- Micro-optics
- Nanophotonics and plasmonics
- Nonlinear optics
- Polaritons
- Quantum optics
- Single photons and quantum effects
- Slow light
- Solitons
- Sub-wavelength optics
- Supercontinuum generation
- Terahertz optics
- Transformation optics
- Ultrafast photonics
- X-rays

 Realizing spin Hamiltonians in nanoscale active photonic lattices
Realizing spin Hamiltonians in nanoscale active photonic lattices Ultrafast responses
Ultrafast responses Diamonds in waveguides
Diamonds in waveguides