Featured
-
-
Article |
 Extreme lithium-metal cycling enabled by a mixed ion- and electron-conducting garnet three-dimensional architecture
Extreme lithium-metal cycling enabled by a mixed ion- and electron-conducting garnet three-dimensional architecture
The development of solid-state Li-metal batteries has been limited by Li plating and stripping rates and the formation of dendrites at relevant current densities. Single-phase mixed ion- and electron-conducting garnet with comparable Li-ion and electronic conductivities is now proposed to tackle these issues.
- George V. Alexander
- , Changmin Shi
- & Eric D. Wachsman
-
Research Briefing |
 Mapping the transmission of single-molecule junctions using photoelectron tunnelling spectroscopy
Mapping the transmission of single-molecule junctions using photoelectron tunnelling spectroscopy
The transmission spectrum of single-molecule junctions provides fingerprint information on the charge-transport properties. A technique called single-molecule photoelectron tunnelling spectroscopy has been developed that enables mapping of the transmission spectrum beyond the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO)–lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) gap at room temperature and can be used to explore the energy-dependent charge transport through single-molecule junctions.
-
Article
| Open Access Li iontronics in single-crystalline T-Nb2O5 thin films with vertical ionic transport channels
Li iontronics in single-crystalline T-Nb2O5 thin films with vertical ionic transport channels
The two-dimensional layered crystal structure of niobium oxide polymorph T-Nb2O5 exhibits fast Li-ion diffusion that is promising for energy storage applications. Epitaxial growth of single-crystalline T-Nb2O5 thin films with ionic transport channels oriented perpendicular to the surface are now demonstrated.
- Hyeon Han
- , Quentin Jacquet
- & Stuart S. P. Parkin
-
Article
| Open Access Hole-limited electrochemical doping in conjugated polymers
Hole-limited electrochemical doping in conjugated polymers
Electrochemical doping is assumed to be limited by ion motion due to large mass in mixed ionic-electronic conductors. Here, the authors reveal in a typical polythiophene that electrochemical doping speeds are limited by poor hole transport at low doping levels, leading to much slower switching speeds than expected.
- Scott T. Keene
- , Joonatan E. M. Laulainen
- & George G. Malliaras
-
Comment |
 Revisiting point defects in ionic solids and semiconductors
Revisiting point defects in ionic solids and semiconductors
The study of point defects in non-metallic crystals has become relevant for an increasing number of materials applications. Progress requires a foundation of consistent definitions and terminology. This Comment clarifies the underlying definitions of point defects, encourages the correct use of relative charge for their description and emphasizes their recognition as quasiparticles.
- Roger De Souza
- & George Harrington
-
News & Views |
 Electrons lighter than ever
Electrons lighter than ever
A two-dimensional conjugated polymer is synthesized that demonstrates low electron effective masses and high mobility. These properties show that this material could act as a viable alternative to silicon-based semiconductors.
- Shu Seki
- & Zhuowei Li
-
Article
| Open Access Exceptionally high charge mobility in phthalocyanine-based poly(benzimidazobenzophenanthroline)-ladder-type two-dimensional conjugated polymers
Exceptionally high charge mobility in phthalocyanine-based poly(benzimidazobenzophenanthroline)-ladder-type two-dimensional conjugated polymers
Linear π-conjugated polymers have attracted great attention as semiconductors for (opto)electronic devices, but charge transfer is only effective along polymer chains. Here poly(benzimidazobenzophenanthroline)-ladder-type two-dimensional conjugated polymers are presented with high charge carrier mobilities.
- Mingchao Wang
- , Shuai Fu
- & Xinliang Feng
-
Article |
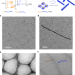 High-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of block copolymer nanofibres with a crystalline core
High-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of block copolymer nanofibres with a crystalline core
Detailed structures of both solvated corona chains and sub-nanometre crystalline core lattice of polymer-based nanofibres in solution are obtained using high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy.
- Jia Tian
- , Song-Hai Xie
- & Ian Manners
-
News & Views |
 Smoke in the MOF liquid
Smoke in the MOF liquid
An ultra-microporous metal–organic framework glass foam shows outstanding gas sieving properties for challenging gas mixtures.
- Chinmoy Das
- & Sebastian Henke
-
News & Views |
 Unlocked sieving potential
Unlocked sieving potential
A strategy of using a high ligand/metal ion concentration ratio eliminates lattice defects in polycrystalline zirconium metal–organic framework membranes, enhancing their molecular sieving performance.
- Jun Lu
- & Huanting Wang
-
Article |
 ZIF-62 glass foam self-supported membranes to address CH4/N2 separations
ZIF-62 glass foam self-supported membranes to address CH4/N2 separations
Membranes formed from porous adsorbents can improve the economics of industrially difficult separations but require support materials that reduce gas permeance. Here an amorphous glassy foam membrane without a support is formed from ZIF-62 that shows high selectivity and permeance for CH4/N2 separations.
- Zibo Yang
- , Youssef Belmabkhout
- & Chongli Zhong
-
Article |
 Eliminating lattice defects in metal–organic framework molecular-sieving membranes
Eliminating lattice defects in metal–organic framework molecular-sieving membranes
MOF membranes can present exceptional molecular-sieving properties, but lattice defects arising from incomplete cluster coordination can hinder this. Here a strategy for the elimination of lattice defects by increasing the ligand to secondary building unit ratio is proposed and demonstrated.
- Guozhen Liu
- , Yanan Guo
- & Nanping Xu
-
News & Views |
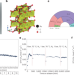 A catalyst for low-temperature CO2 activation
A catalyst for low-temperature CO2 activation
A low-valence carbon-doped ruthenium oxide-based catalytic material achieved a catalytic trinity of superior activity, selectivity and stability during the conversion of carbon dioxide into methane at low temperatures.
- Xin Zhang
- & Abhishek Dutta Chowdhury
-
Article |
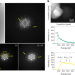 Low-oxidation-state Ru sites stabilized in carbon-doped RuO2 with low-temperature CO2 activation to yield methane
Low-oxidation-state Ru sites stabilized in carbon-doped RuO2 with low-temperature CO2 activation to yield methane
Activating CO2 to form methane is a potential strategy for energy decarbonization, but to activate CO2 typically requires high temperatures. Here a ruthenium oxycarbonate is presented that forms by carbon interstitial doping of RuO2, and this catalyst enables CO2 activation at 50 °C.
- Carmen Tébar-Soler
- , Vlad Martin-Diaconescu
- & Avelino Corma
-
Letter
| Open Access Probing lithium mobility at a solid electrolyte surface
Probing lithium mobility at a solid electrolyte surface
Understanding lithium dynamics in solid-state electrolytes used for Li-ion batteries can be challenging. Using nonlinear extreme-ultraviolet spectroscopies, a direct spectral signature of surface lithium ions showing a distinct blueshift relative to the bulk absorption spectra is observed in a prototypical solid-state electrolyte.
- Clarisse Woodahl
- , Sasawat Jamnuch
- & Michael Zuerch
-
Article |
 Imaging the strain evolution of a platinum nanoparticle under electrochemical control
Imaging the strain evolution of a platinum nanoparticle under electrochemical control
Surface strain can be used in gas phase catalysis and electrocatalysis to control the binding energies of adsorbates on active sites, but in situ or operando strain measurements can be challenging. Coherent diffraction now allows strain inside individual Pt nanoparticles to be mapped and quantified under electrochemical control.
- Clément Atlan
- , Corentin Chatelier
- & Marie-Ingrid Richard
-
Article |
 Operando NMR electrochemical gating studies of ion dynamics in PEDOT:PSS
Operando NMR electrochemical gating studies of ion dynamics in PEDOT:PSS
Understanding charge-compensating interactions and ionic dynamics in organic mixed conductors can be challenging. Operando NMR spectroscopy is now used to quantify cation and water movement during doping/dedoping in mixed conductor films.
- Dongxun Lyu
- , Yanting Jin
- & Clare P. Grey
-
Article |
 High quantum efficiency of hydrogen production from methanol aqueous solution with PtCu–TiO2 photocatalysts
High quantum efficiency of hydrogen production from methanol aqueous solution with PtCu–TiO2 photocatalysts
Liquid water reforming of methanol is a promising method for on-demand hydrogen production. An atomic-level catalyst design strategy, using synergy between single atoms and nanodots, is now shown to demonstrate a high quantum efficiency for hydrogen production.
- Hui Wang
- , Haifeng Qi
- & Junwang Tang
-
Article |
 Covalent organic framework atropisomers with multiple gas-triggered structural flexibilities
Covalent organic framework atropisomers with multiple gas-triggered structural flexibilities
Soft porous crystals combine high crystallinity with structural transformability, potentially enabling applications. Here, an atropisomeric covalent organic framework is reported, which demonstrates different structural transformations upon exposure to different gases.
- Chengjun Kang
- , Zhaoqiang Zhang
- & Dan Zhao
-
News & Views |
 Measuring the potential of zero charge
Measuring the potential of zero charge
A second-harmonic generation approach enables the direct measurement of the potential of zero charge at electrochemical interfaces.
- Jan Rossmeisl
-
Article |
 Optical method for quantifying the potential of zero charge at the platinum–water electrochemical interface
Optical method for quantifying the potential of zero charge at the platinum–water electrochemical interface
The electric field created at an electrode–electrolyte interface can polarize the electrode’s surface and nearby molecules. Although its effect can be countered by an applied potential, quantifying the value of this potential is difficult. An optical method for determining the potential of zero charge at an electrochemical interface is now presented.
- Pengtao Xu
- , Alexander D. von Rueden
- & Jin Suntivich
-
Editorial |
 Simple connections take the prize
Simple connections take the prize
Click chemistry and bioorthogonal chemistry have finally been recognized with the Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
-
Article |
 Inhibiting collective cation migration in Li-rich cathode materials as a strategy to mitigate voltage hysteresis
Inhibiting collective cation migration in Li-rich cathode materials as a strategy to mitigate voltage hysteresis
The high energy densities of Li-rich cathodes are promising for Li-ion batteries, but voltage hysteresis limits their practical implementation. Voltage hysteresis is shown to be related to collective migration of metal ions, and isolating migration leads to high-capacity reversible cathodes.
- Jianping Huang
- , Bin Ouyang
- & Gerbrand Ceder
-
Article |
 Resolving complex intralayer transition motifs in high-Ni-content layered cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries
Resolving complex intralayer transition motifs in high-Ni-content layered cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries
High-Ni-content layered cathodes are promising for lithium-ion batteries, but investigating their delithiation-induced phase boundaries is challenging. Intralayer transition motifs at complex phase boundaries in these high-Ni electrodes are now resolved using deep-learning-aided super-resolution electron microscopy.
- Chunyang Wang
- , Xuelong Wang
- & Huolin L. Xin
-
Article |
 From enhanced diffusion to ultrafast ballistic motion of hybrid light–matter excitations
From enhanced diffusion to ultrafast ballistic motion of hybrid light–matter excitations
The authors study ultrafast spatiotemporal dynamics of polaritons formed by mixing surface-bound optical waves with excitons observing a mobility transition from diffusive to ballistic transport flow at two-thirds the speed of light.
- Mukundakumar Balasubrahmaniyam
- , Arie Simkhovich
- & Tal Schwartz
-
Article
| Open Access Ion-tunable antiambipolarity in mixed ion–electron conducting polymers enables biorealistic organic electrochemical neurons
Ion-tunable antiambipolarity in mixed ion–electron conducting polymers enables biorealistic organic electrochemical neurons
Silicon-based complementary metal-oxide semiconductors or negative differential resistance device circuits can emulate neural features, yet are complicated to fabricate and not biocompatible. Here, the authors report an ion-modulated antiambipolarity in mixed ion–electron conducting polymers demonstrating capability of sensing, spiking, emulating the most critical biological neural features, and stimulating biological nerves in vivo.
- Padinhare Cholakkal Harikesh
- , Chi-Yuan Yang
- & Simone Fabiano
-
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Bimodal free volumes uplift gas separation
Bimodal free volumes uplift gas separation
Carbonization of crosslinked polyimides with kinked structures leads to carbon molecular sieves with bimodal free volumes, enabling both a high molecular-sieving ability and gas permeability.
- Leiqing Hu
- & Haiqing Lin
-
Article |
 A near dimensionally invariable high-capacity positive electrode material
A near dimensionally invariable high-capacity positive electrode material
Delivering inherently stable lithium-ion batteries with electrodes that can reversibly insert and extract large quantities of Li+ with inherent stability during cycling are key. Lithium-excess vanadium oxides with a disordered rocksalt structure are now investigated as high-capacity and long-life cathodes.
- Itsuki Konuma
- , Damian Goonetilleke
- & Naoaki Yabuuchi
-
News & Views |
 Compound semiconductor devices for the skin
Compound semiconductor devices for the skin
Nanomembranes of GaN grown by remote epitaxy form the basis of surface acoustic wave sensors in wireless electronic skins for health monitoring.
- Jong Uk Kim
- , Seung Gi Seo
- & John A. Rogers
-
-
Meeting Report |
Materials for a changing planet
About 700 scientists from 45 countries gathered in Dresden for the first time since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic to share their latest findings on metal–organic frameworks and open frameworks compounds.
- Veronique Van Speybroeck
- & Guillaume Maurin
-
News & Views |
 Machine learning heat capacities
Machine learning heat capacities
As metal–organic frameworks move towards practical application, data for an expanded range of physical properties are needed. Molecular-level modelling and data science can play an important role.
- Randall Q. Snurr
-
Article |
 Suppressing ion migration in metal halide perovskite via interstitial doping with a trace amount of multivalent cations
Suppressing ion migration in metal halide perovskite via interstitial doping with a trace amount of multivalent cations
Ion migration has a detrimental effect on the performance and stability of halide perovskite optoelectronics. Here, the authors incorporated a small dosage of high-valence neodymium cation to suppress this, with a minimal impact on the lattice microstrain.
- Yepin Zhao
- , Ilhan Yavuz
- & Yang Yang
-
Article |
 Hierarchically engineered nanostructures from compositionally anisotropic molecular building blocks
Hierarchically engineered nanostructures from compositionally anisotropic molecular building blocks
Independently tailored nano- and mesoscale features are obtained in hierarchically assembled mixed graft block copolymers with precisely defined side-chain sequences.
- Ruiqi Liang
- , Yazhen Xue
- & Mingjiang Zhong
-
Article |
 Non-iridium-based electrocatalyst for durable acidic oxygen evolution reaction in proton exchange membrane water electrolysis
Non-iridium-based electrocatalyst for durable acidic oxygen evolution reaction in proton exchange membrane water electrolysis
Iridium-based electrocatalysts are traditional anode catalysts for proton exchange membrane water electrolysis but suffer from high cost and low reserves. An alternative, nickel-stabilized ruthenium dioxide catalyst with high activity and durability in acidic oxygen evolution reaction for water electrolysis is reported.
- Zhen-Yu Wu
- , Feng-Yang Chen
- & Haotian Wang
-
Article |
 A data-science approach to predict the heat capacity of nanoporous materials
A data-science approach to predict the heat capacity of nanoporous materials
Heat capacity of nanoporous materials is important for processes such as carbon capture, as this can affect process design energy requirements. Here, a machine learning approach for heat capacity prediction, trained on density functional theory simulations, is presented and experimentally verified.
- Seyed Mohamad Moosavi
- , Balázs Álmos Novotny
- & Berend Smit
-
Article |
 Dense inorganic electrolyte particles as a lever to promote composite electrolyte conductivity
Dense inorganic electrolyte particles as a lever to promote composite electrolyte conductivity
Solid-state electrolytes are key to the development of safer and higher-energy-density batteries. Using liquid electrolyte chemistries as models for polymer electrolytes, the effect of adding a variety of porous and dense ceramic electrolytes on the conductivity is now investigated.
- James A. Isaac
- , Didier Devaux
- & Renaud Bouchet
-
Comment |
 The development of molecule-based porous material families and their future prospects
The development of molecule-based porous material families and their future prospects
Metal–organic frameworks, porous coordination network materials constructed with metal ions and organic molecules, have grown over the past 20 years into an innovative chemistry that has contributed to solutions for the problems faced by humanity in the environment, resources, energy and health.
- Satoshi Horike
- & Susumu Kitagawa
-
Article |
 Operando monitoring of single-particle kinetic state-of-charge heterogeneities and cracking in high-rate Li-ion anodes
Operando monitoring of single-particle kinetic state-of-charge heterogeneities and cracking in high-rate Li-ion anodes
Understanding the ion intercalation and degradation mechanisms occurring during realistic battery operation is crucial to developing high-rate battery electrodes. Operando optical scattering microscopy is now used to study single-particle kinetic state-of-charge heterogeneities and cracking in high-rate Li-ion anode materials.
- Alice J. Merryweather
- , Quentin Jacquet
- & Clare P. Grey
-
Article |
 Fast water transport and molecular sieving through ultrathin ordered conjugated-polymer-framework membranes
Fast water transport and molecular sieving through ultrathin ordered conjugated-polymer-framework membranes
Carbon nanomaterials such as graphene show intriguing molecular transport properties, but to achieve regular channels over a large area requires perfect sheet alignment. Here, a large-area two-dimensional conjugated-polymer-framework is grown with regular pore distribution, enabling 99.5% salt rejection by forward osmosis.
- Jie Shen
- , Yichen Cai
- & Yu Han
-
News & Views |
 Polarization from sliding molecular rotors
Polarization from sliding molecular rotors
The direct manipulation of a new kind of ferroelectric state, arising from the sliding of van der Waals layers in a coordination polymer, is demonstrated.
- Mark S. Senn
- & Andrew L. Goodwin
-
Article |
 Dielectric control of reverse intersystem crossing in thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitters
Dielectric control of reverse intersystem crossing in thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitters
The role of the dielectric environment in thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) is not yet fully understood. Here the authors reveal the relevance of environment–emitter interactions in gating the reverse intersystem crossing and its particular relevance in dipolar TADF emitters.
- Alexander J. Gillett
- , Anton Pershin
- & David Beljonne
-
Article |
 Direct observation of geometric and sliding ferroelectricity in an amphidynamic crystal
Direct observation of geometric and sliding ferroelectricity in an amphidynamic crystal
Two-dimensional materials can present ferroelectricity by layer sliding, but electrical confirmation is lacking due to narrow bandgaps. Here, a single-crystal coordination polymer with large bandgap enabling direct electrical measurement of P–E hysteresis is shown to present sliding ferroelectricity.
- Le-Ping Miao
- , Ning Ding
- & Yi Zhang
-
Article |
 Cationic polymer-in-salt electrolytes for fast metal ion conduction and solid-state battery applications
Cationic polymer-in-salt electrolytes for fast metal ion conduction and solid-state battery applications
Polymer electrolytes provide a safe solution for future solid-state high-energy-density batteries, but combining high ionic conductivity and a high transference number is a challenge. A polymeric ionic liquid used as a polymer solvent is now shown to be promising for both sodium and potassium batteries.
- Fangfang Chen
- , Xiaoen Wang
- & Maria Forsyth
-
Comment |
 Stimuli-responsive metal–organic frameworks enabled by intrinsic molecular motion
Stimuli-responsive metal–organic frameworks enabled by intrinsic molecular motion
Synthetic stimuli-responsive systems have become increasingly sophisticated and elegant at the nanoscale. This Comment discusses how rationally designed molecular systems capable of dynamic motions can be deployed in macroscopically porous metal–organic frameworks and respond to various stimuli.
- Jinqiao Dong
- , Vanessa Wee
- & Dan Zhao
-
Article |
 Room-temperature logic-in-memory operations in single-metallofullerene devices
Room-temperature logic-in-memory operations in single-metallofullerene devices
Single-molecule electronics provide the potential solution for high-density integration and low-power consumption in massive data-driven applications, but have yet to be explored. Here, the authors report low-power logic-in-memory operations, based on single electric dipole flipping in the two-terminal single-metallofullerene device at room temperature.
- Jing Li
- , Songjun Hou
- & Wenjing Hong
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Analytical chemistry
- Biochemistry
- Biosynthesis
- Catalysis
- Chemical biology
- Chemical education
- Chemical engineering
- Chemical safety
- Cheminformatics
- Chemistry publishing
- Communicating chemistry
- Coordination chemistry
- Electrochemistry
- Energy
- Environmental chemistry
- Green chemistry
- History of chemistry
- Inorganic chemistry
- Materials chemistry
- Medicinal chemistry
- Nuclear chemistry
- Organic chemistry
- Chemical origin of life
- Photochemistry
- Physical chemistry
- Polymer chemistry
- Process chemistry
- Supramolecular chemistry
- Surface chemistry
- Chemical synthesis
- Theoretical chemistry

 Electric-field-induced colour switching in colloidal quantum dot molecules at room temperature
Electric-field-induced colour switching in colloidal quantum dot molecules at room temperature Composites from photo-stereochemical patterning
Composites from photo-stereochemical patterning Water discrimination by differing diffusions
Water discrimination by differing diffusions Floating artificial leaves
Floating artificial leaves Setting stable catalysts
Setting stable catalysts