Featured
-
-
Article |
 Long-term stability of aerophilic metallic surfaces underwater
Long-term stability of aerophilic metallic surfaces underwater
Trapped films of air known as plastrons are promising for underwater engineering but typically have short lifetimes. Here, aerophilic titanium alloy surfaces are developed with thermodynamically stabilized plastrons for antifouling applications.
- Alexander B. Tesler
- , Stefan Kolle
- & Wolfgang H. Goldmann
-
News & Views |
 Measuring the potential of zero charge
Measuring the potential of zero charge
A second-harmonic generation approach enables the direct measurement of the potential of zero charge at electrochemical interfaces.
- Jan Rossmeisl
-
Article |
 Optical method for quantifying the potential of zero charge at the platinum–water electrochemical interface
Optical method for quantifying the potential of zero charge at the platinum–water electrochemical interface
The electric field created at an electrode–electrolyte interface can polarize the electrode’s surface and nearby molecules. Although its effect can be countered by an applied potential, quantifying the value of this potential is difficult. An optical method for determining the potential of zero charge at an electrochemical interface is now presented.
- Pengtao Xu
- , Alexander D. von Rueden
- & Jin Suntivich
-
Article |
 In situ imaging of amorphous intermediates during brucite carbonation in supercritical CO2
In situ imaging of amorphous intermediates during brucite carbonation in supercritical CO2
Non-classical crystallization may proceed through formation of intermediate phases, but it is not known whether these are linked to the final crystallization. Here, using an atomic force microscope at 90 bar, brucite carbonation is directly observed, with an amorphous intermediate acting as the seed for crystalline nesquehonite.
- Xin Zhang
- , Alan S. Lea
- & Kevin M. Rosso
-
Article |
 Tuning surface d bands with bimetallic electrodes to facilitate electron transport across molecular junctions
Tuning surface d bands with bimetallic electrodes to facilitate electron transport across molecular junctions
Coating Au electrodes with Ag or Cu monolayers is shown to improve molecule–electrode binding and electrical conductivity of single-molecule junctions as a result of the tuning of the surface d bands of the metal.
- Mong-Wen Gu
- , Hao Howard Peng
- & Chun-hsien Chen
-
Perspective |
 Flow and extraction of energy and charge carriers in hybrid plasmonic nanostructures
Flow and extraction of energy and charge carriers in hybrid plasmonic nanostructures
Recent developments in the emerging field of hybrid plasmonics focusing on fundamental aspects related to nanoscopic flow of energy and excited charge carriers in these multicomponent materials and their potential applications are now discussed.
- Suljo Linic
- , Steven Chavez
- & Rachel Elias
-
Perspective |
 Chiral metal surfaces for enantioselective processes
Chiral metal surfaces for enantioselective processes
Chiral surfaces are fundamental materials for the preparation of enantiomerically pure pharmaceuticals. This Perspective discusses the recent advances in the fabrication of chiral surfaces and the progress towards scalable, high-surface-area, enantiomerically pure surfaces.
- Nisha Shukla
- & Andrew J. Gellman
-
Article |
 Synthesis of mesoscale ordered two-dimensional π-conjugated polymers with semiconducting properties
Synthesis of mesoscale ordered two-dimensional π-conjugated polymers with semiconducting properties
Optimized Ullmann coupling reaction of heterotriangulene precursors allows the synthesis of two-dimensional π-conjugated polymers with ordered domains larger than 100 × 100 nm2 showing both Dirac cones and flat bands in their electronic structure.
- G. Galeotti
- , F. De Marchi
- & G. Contini
-
Article |
 Quantum dynamics of a single molecule magnet on superconducting Pb(111)
Quantum dynamics of a single molecule magnet on superconducting Pb(111)
A superconducting transition is used to switch a single molecule magnet from a blocked magnetization state to a resonant quantum tunnelling regime
- Giulia Serrano
- , Lorenzo Poggini
- & Roberta Sessoli
-
Letter |
 In situ probing electrified interfacial water structures at atomically flat surfaces
In situ probing electrified interfacial water structures at atomically flat surfaces
Interfacial water structures in electric double layers under bias potentials can impact the electrochemical performance of electrodes. Two structural transitions of interfacial water at electrified Au single-crystal electrode surfaces have now been identified.
- Chao-Yu Li
- , Jia-Bo Le
- & Zhong-Qun Tian
-
Letter |
 Electrifying model catalysts for understanding electrocatalytic reactions in liquid electrolytes
Electrifying model catalysts for understanding electrocatalytic reactions in liquid electrolytes
Fundamental understanding of electrocatalysis is key to a transition to renewable energy systems. A strategy to ‘electrify’ complex oxide-based model catalysts is now proposed to explore electrocatalytic reactions in liquid electrolytes.
- Firas Faisal
- , Corinna Stumm
- & Jörg Libuda
-
Article |
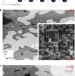 Structure of a model TiO2 photocatalytic interface
Structure of a model TiO2 photocatalytic interface
The interaction of water with TiO2 is crucial for applications such as photocatalytic water splitting. The interfacial structure between water and rutile TiO2 is now shown to consist of an array of hydroxyl molecules with water in the second layer.
- H. Hussain
- , G. Tocci
- & G. Thornton
-
Article |
 Nanoscale structural oscillations in perovskite oxides induced by oxygen evolution
Nanoscale structural oscillations in perovskite oxides induced by oxygen evolution
Understanding interactions between water and oxides is crucial for energy storage and photocatalysis. The combined effect of water and electron irradiation on perovskite catalysts results in structural oscillation triggered by gaseous bubbles.
- Binghong Han
- , Kelsey A. Stoerzinger
- & Yang Shao-Horn
-
Letter |
 Colloidal metal oxide nanocrystal catalysis by sustained chemically driven ligand displacement
Colloidal metal oxide nanocrystal catalysis by sustained chemically driven ligand displacement
Here the authors show that nanocrystals of hafnium oxide can be applied as stable catalytic materials using a dynamic ligand-exchange reaction mechanism.
- Jonathan De Roo
- , Isabel Van Driessche
- & Zeger Hens
-
Review Article |
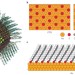 The surface science of nanocrystals
The surface science of nanocrystals
The role of surface ligands in tuning the optoelectronic properties, controlling the stability and determining the performance in applications of colloidal nanocrystals is discussed in this Review.
- Michael A. Boles
- , Daishun Ling
- & Dmitri V. Talapin
-
Article |
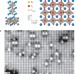 Adsorption of water at the SrO surface of ruthenates
Adsorption of water at the SrO surface of ruthenates
The interaction between perovskite oxides and water can have a significant influence on practical performance. Here the authors study the dynamics of surface water adsorption and hydroxide formation during monolayer formation on a ruthenate.
- Daniel Halwidl
- , Bernhard Stöger
- & Ulrike Diebold
-
Article |
 Single-layer ionic conduction on carboxyl-terminated silane monolayers patterned by constructive lithography
Single-layer ionic conduction on carboxyl-terminated silane monolayers patterned by constructive lithography
Local oxidation of the methyl groups of self-assembled silane monolayers into carboxylic acid functional groups allows the realization of solid ion-conducting channels, on top of which single layers of metal ions can drift when a voltage is applied.
- Jonathan Berson
- , Doron Burshtain
- & Jacob Sagiv
-
News & Views |
 Sharpened interface
Sharpened interface
The finding of a sharp interface between a chemically attacked surface and the pristine bulk in a borosilicate glass is at odds with the widely held diffusion-based mechanisms of glass durability.
- Andrew Putnis
-
Commentary |
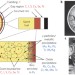 Long-term storage of spent nuclear fuel
Long-term storage of spent nuclear fuel
To design reliable and safe geological repositories it is critical to understand how the characteristics of spent nuclear fuel evolve with time, and how this affects the storage environment.
- Rodney C. Ewing
-
-
-
Letter |
 Carbon monoxide-induced adatom sintering in a Pd–Fe3O4 model catalyst
Carbon monoxide-induced adatom sintering in a Pd–Fe3O4 model catalyst
Although the coarsening of catalytically active metal clusters can be accelerated by the presence of gases, the role played by gas molecules is difficult to ascertain. Carbon monoxide-induced coalescence of Pd adatoms supported on a Fe3O4 surface is now investigated at room temperature, and Pd-carbonyl species are shown to be responsible for their mobility.
- Gareth S. Parkinson
- , Zbynek Novotny
- & Ulrike Diebold
-
Letter |
 Surface chemistry mediates thermal transport in three-dimensional nanocrystal arrays
Surface chemistry mediates thermal transport in three-dimensional nanocrystal arrays
The optical and electronic performance of inorganic nanocrystal assemblies stabilized by organic ligands has been extensively investigated, whereas less attention has been paid to their thermal transport properties. It is now shown that the thermal conductivity of these composite systems is determined by the vibrational states of both inorganic and ligand regions, as well as by their relative volumes.
- Wee-Liat Ong
- , Sara M. Rupich
- & Jonathan A. Malen

 Atomically precise photothermal nanomachines
Atomically precise photothermal nanomachines Snapped in the act
Snapped in the act