Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Tear-resistant stretchy gels
Tear-resistant stretchy gels
Incorporating additives that contain hydrogen-bonding nanochannels creates nanoconfined polymer gels that are highly stretchable, elastic and insensitive to notch propagation.
- Meixiang Wang
- & Michael D. Dickey
-
News & Views |
 Through the MOF looking glass
Through the MOF looking glass
Processible centimetre-scale porous glasses using zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF) materials are developed, while fine-tuning of the processing conditions allows control of pore size and molecular sieving properties.
- Georgia R. F. Orton
- & Neil R. Champness
-
Article
| Open Access Precise control over gas-transporting channels in zeolitic imidazolate framework glasses
Precise control over gas-transporting channels in zeolitic imidazolate framework glasses
Porosity of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks can be preserved beyond glass transition and melt processing. Here centimetre-scale porous glasses are demonstrated, whereas liquid processing enables fine-tuning of the size of the gas-transporting channels for molecular sieving.
- Oksana Smirnova
- , Seungtaik Hwang
- & Alexander Knebel
-
News & Views |
 Beyond lithium for sustainable ammonia synthesis
Beyond lithium for sustainable ammonia synthesis
Using an electrochemical continuous flow cell, nitrogen reduction to ammonia is rigorously demonstrated through a calcium-mediated approach.
- Michael A. Yusov
- & Karthish Manthiram
-
Article
| Open Access Unit-cell-thick zeolitic imidazolate framework films for membrane application
Unit-cell-thick zeolitic imidazolate framework films for membrane application
Unit-cell-thick films of metal–organic frameworks with ordered porosity would be attractive for membrane applications as these thin systems combine large molecular flux with high selectivity. Here crystalline ZIF films are grown on a crystalline substrate with high H2/N2 gas separation performance.
- Qi Liu
- , Yurun Miao
- & Kumar Varoon Agrawal
-
Article |
 Precise molecular sieving of ethylene from ethane using triptycene-derived submicroporous carbon membranes
Precise molecular sieving of ethylene from ethane using triptycene-derived submicroporous carbon membranes
Ethylene separation from ethane is the most energy-intensive separation in the chemical process industry, but so far membranes have not exceeded an ethylene/ethane selectivity of >20 in mixed gases. Here a carbon molecular sieve with an ethylene selectivity of ~100 and long-term stability under high-pressure gas is reported.
- Khalid Hazazi
- , Yingge Wang
- & Ingo Pinnau
-
News & Views |
 Unlocked sieving potential
Unlocked sieving potential
A strategy of using a high ligand/metal ion concentration ratio eliminates lattice defects in polycrystalline zirconium metal–organic framework membranes, enhancing their molecular sieving performance.
- Jun Lu
- & Huanting Wang
-
Article |
 ZIF-62 glass foam self-supported membranes to address CH4/N2 separations
ZIF-62 glass foam self-supported membranes to address CH4/N2 separations
Membranes formed from porous adsorbents can improve the economics of industrially difficult separations but require support materials that reduce gas permeance. Here an amorphous glassy foam membrane without a support is formed from ZIF-62 that shows high selectivity and permeance for CH4/N2 separations.
- Zibo Yang
- , Youssef Belmabkhout
- & Chongli Zhong
-
Article |
 Eliminating lattice defects in metal–organic framework molecular-sieving membranes
Eliminating lattice defects in metal–organic framework molecular-sieving membranes
MOF membranes can present exceptional molecular-sieving properties, but lattice defects arising from incomplete cluster coordination can hinder this. Here a strategy for the elimination of lattice defects by increasing the ligand to secondary building unit ratio is proposed and demonstrated.
- Guozhen Liu
- , Yanan Guo
- & Nanping Xu
-
-
News & Views |
 Bimodal free volumes uplift gas separation
Bimodal free volumes uplift gas separation
Carbonization of crosslinked polyimides with kinked structures leads to carbon molecular sieves with bimodal free volumes, enabling both a high molecular-sieving ability and gas permeability.
- Leiqing Hu
- & Haiqing Lin
-
Article |
 Advanced carbon molecular sieve membranes derived from molecularly engineered cross-linkable copolyimide for gas separations
Advanced carbon molecular sieve membranes derived from molecularly engineered cross-linkable copolyimide for gas separations
Carbon molecular sieves (CMS) are formed from pyrolysis of polymeric precursors, forming complex morphologies that enable gas separations. Here, by combining kinked and cross-linkable structures in the precursor, CMS membranes are reported that enable a broad spectrum of challenging gas separations.
- Zhongyun Liu
- , Wulin Qiu
- & William J. Koros
-
News & Views |
 Machine learning heat capacities
Machine learning heat capacities
As metal–organic frameworks move towards practical application, data for an expanded range of physical properties are needed. Molecular-level modelling and data science can play an important role.
- Randall Q. Snurr
-
Article |
 A data-science approach to predict the heat capacity of nanoporous materials
A data-science approach to predict the heat capacity of nanoporous materials
Heat capacity of nanoporous materials is important for processes such as carbon capture, as this can affect process design energy requirements. Here, a machine learning approach for heat capacity prediction, trained on density functional theory simulations, is presented and experimentally verified.
- Seyed Mohamad Moosavi
- , Balázs Álmos Novotny
- & Berend Smit
-
Article |
 Fast water transport and molecular sieving through ultrathin ordered conjugated-polymer-framework membranes
Fast water transport and molecular sieving through ultrathin ordered conjugated-polymer-framework membranes
Carbon nanomaterials such as graphene show intriguing molecular transport properties, but to achieve regular channels over a large area requires perfect sheet alignment. Here, a large-area two-dimensional conjugated-polymer-framework is grown with regular pore distribution, enabling 99.5% salt rejection by forward osmosis.
- Jie Shen
- , Yichen Cai
- & Yu Han
-
Article |
 Ultra-stable all-solid-state sodium metal batteries enabled by perfluoropolyether-based electrolytes
Ultra-stable all-solid-state sodium metal batteries enabled by perfluoropolyether-based electrolytes
Rechargeable batteries with sodium metal anodes are promising as energy-storage systems despite safety concerns related to reactivity and dendrite formation. Solvent-free perfluoropolyether-based electrolytes are now reported for safe and stable all-solid-state sodium metal batteries.
- Xiaoen Wang
- , Cheng Zhang
- & Maria Forsyth
-
News & Views |
 Reassembled nanoprecipitates resisting radiation
Reassembled nanoprecipitates resisting radiation
Outstanding resistance to destructive radiation damage in structural alloys is realized by ultra-high-density reversible nanoprecipitate inclusions, and the improvement is attributed to the reordering process of low-misfit superlattices in highly supersaturated matrices.
- Yanwen Zhang
-
News & Views |
 Stretching out transistors
Stretching out transistors
Bioelectronics demand stretchable devices with steady performance under deformation. By combining an amphiphilic organic semiconducting polymer with tailored film processing, highly stretchable organic electrochemical transistors are demonstrated.
- Fabio Cicoira
-
Article |
 Computational prediction of the molecular configuration of three-dimensional network polymers
Computational prediction of the molecular configuration of three-dimensional network polymers
A computational platform describing the spatial and temporal interactions of monomers during the formation of network polymers provides structure–property relationships that are used to synthesize 3D network polymers with tailored functionalities.
- Lies De Keer
- , Karsu I. Kilic
- & Dagmar R. D’hooge
-
Article |
 Elastohydrodynamic friction of robotic and human fingers on soft micropatterned substrates
Elastohydrodynamic friction of robotic and human fingers on soft micropatterned substrates
A framework for the elastohydrodynamic lubrication between soft patterned surfaces identifies the contributions of substrate elasticity and pattern geometry for friction, which have implications for the engineering of haptic soft materials.
- Yunhu Peng
- , Christopher M. Serfass
- & Lilian C. Hsiao
-
Article |
 Spatiotemporal control of liquid crystal structure and dynamics through activity patterning
Spatiotemporal control of liquid crystal structure and dynamics through activity patterning
Light-responsive myosin motors enable spatial and temporal control over the dynamics and transport of active nematic liquid crystals composed of actin filaments and myosin at an oil–water interface.
- Rui Zhang
- , Steven A. Redford
- & Juan J. de Pablo
-
News & Views |
 Unfavourable interactions enable stability
Unfavourable interactions enable stability
Use of polymer and small-molecule semiconductors with relatively poor miscibility helps the long-term stability of the morphology and photovoltaic performance of bulk heterojunction films used in organic solar cells.
- Andrew T. Kleinschmidt
- & Darren J. Lipomi
-
Article |
 Gas-sieving zeolitic membranes fabricated by condensation of precursor nanosheets
Gas-sieving zeolitic membranes fabricated by condensation of precursor nanosheets
Zeolite membranes can be used for gas molecular sieving, but synthesis requires complex hydrothermal treatment. Here, single layers of zeolite precursor RUB-15 are exfoliated followed by a condensation reaction, forming zeolite membranes with H2/CO2 selectivity of 20 to 100 in a facile process.
- Mostapha Dakhchoune
- , Luis Francisco Villalobos
- & Kumar Varoon Agrawal
-
Article |
 Solution processable metal–organic frameworks for mixed matrix membranes using porous liquids
Solution processable metal–organic frameworks for mixed matrix membranes using porous liquids
Solution processability is required for many industrial processes, but metal–organic frameworks are in general not dispersible, hindering their application. Here, a surface modification is reported that allows porous liquid formation and so synthesis of highly loaded and mechanically robust mixed matrix membranes.
- Alexander Knebel
- , Anastasiya Bavykina
- & Jorge Gascon
-
News & Views |
 From computer design to gas separation
From computer design to gas separation
The presence of one-dimensional MEL intergrowths in two-dimensional MDI zeolite nanosheets, inferred from experimental and theoretical analysis, allows for world-beating xylene separation performance.
- Jürgen Caro
- & Jörg Kärger
-
Article |
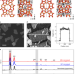 One-dimensional intergrowths in two-dimensional zeolite nanosheets and their effect on ultra-selective transport
One-dimensional intergrowths in two-dimensional zeolite nanosheets and their effect on ultra-selective transport
Two-dimensional zeolite MFI nanosheets show ultra-selective separation of xylene isomers, but it was not known why this occurs. Here, using electron microscopy and atomistic simulation, it is shown that one-dimensional intergrowths of zeolite MEL enable selectivity by formation of more rigid pores.
- Prashant Kumar
- , Dae Woo Kim
- & K. Andre Mkhoyan
-
News & Views |
 Proteins tailor pore geometry
Proteins tailor pore geometry
Using organic solvent shortens formation time of membrane nanosheets comprising proteins and copolymers, while tuning protein structure tailors the pore geometry, resulting in superior water permeation.
- Andrew G. Livingston
- & Zhiwei Jiang
-
Article |
 Rapid fabrication of precise high-throughput filters from membrane protein nanosheets
Rapid fabrication of precise high-throughput filters from membrane protein nanosheets
Protein channels are highly selective, but application in membranes is limited due to low protein content. Here, protein channels are embedded into block copolymers to form nanosheets using rapid solvent casting, with better water permeability and similar molecular exclusions relative to other membrane systems.
- Yu-Ming Tu
- , Woochul Song
- & Manish Kumar
-
News & Views |
 Some stirring required
Some stirring required
Polymer precipitation under turbulent flow is used for the high-throughput synthesis of soft microparticles with fractal coronas that display significant adhesive properties.
- Theodore Hueckel
- & Stefano Sacanna
-
Article |
 Ionomer distribution control in porous carbon-supported catalyst layers for high-power and low Pt-loaded proton exchange membrane fuel cells
Ionomer distribution control in porous carbon-supported catalyst layers for high-power and low Pt-loaded proton exchange membrane fuel cells
Reducing Pt content in cathodes for proton exchange membrane fuel cells is crucial to lower costs but results in high voltage losses. A Pt catalyst/support design that substantially reduces local oxygen-related mass transport resistance is reported.
- Sebastian Ott
- , Alin Orfanidi
- & Peter Strasser
-
Article |
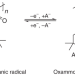 Real-time insight into the doping mechanism of redox-active organic radical polymers
Real-time insight into the doping mechanism of redox-active organic radical polymers
Organic radical polymers are currently being considered as active materials for fast-charging battery electrodes but their transport and charge storage characteristics are not well understood. A quantitative view of in situ ion transport and doping in these systems during the redox process is now provided.
- Shaoyang Wang
- , Fei Li
- & Jodie L. Lutkenhaus
-
News & Views |
 Ordered polymeric membranes using metals
Ordered polymeric membranes using metals
By combining metal ions, organic linkers and polymers, ordered frameworks with controlled crystallite size can form. When fabricated into membranes, they combine superlative CO2/N2 separation properties with good hydrolytic stability.
- Joshua D. Moon
- & Benny D. Freeman
-
Article |
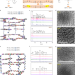 Metal-induced ordered microporous polymers for fabricating large-area gas separation membranes
Metal-induced ordered microporous polymers for fabricating large-area gas separation membranes
Controlling crystallite size can lead to improved applications. Here, this is achieved by a combination of metal ions, organic linkers, and polymers; the resultant membrane displays promising CO2/N2 separation properties and hydrolytic stability.
- Zhihua Qiao
- , Song Zhao
- & Michael D. Guiver
-
Letter |
 Evolutionary selection growth of two-dimensional materials on polycrystalline substrates
Evolutionary selection growth of two-dimensional materials on polycrystalline substrates
Foot-long continuous single-crystal-like monolayer graphene films were fabricated on polycrystalline substrates by evolutionary selection growth, which resembles the Czochralski process in 2D geometry.
- Ivan V. Vlassiouk
- , Yijing Stehle
- & Sergei N. Smirnov
-
News & Views |
 A perfect match
A perfect match
A metal–organic framework with tailored porosity provides a mixed matrix membrane with excellent performance for natural gas purification and butane isomer separation.
- Neil B. McKeown
-
Article |
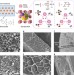 Mixed matrix formulations with MOF molecular sieving for key energy-intensive separations
Mixed matrix formulations with MOF molecular sieving for key energy-intensive separations
Sub-micrometre MOF particles are incorporated into polymers to form mixed matrix membranes. Molecular sieving enables performance far beyond current limits for two applications, butane isomer separation and combined CO2/H2S removal from natural gas.
- Gongping Liu
- , Valeriya Chernikova
- & William J. Koros
-
Article |
 A sol–gel monolithic metal–organic framework with enhanced methane uptake
A sol–gel monolithic metal–organic framework with enhanced methane uptake
Using a sol–gel process, monoliths of metal–organic frameworks were fabricated. With an enhanced methane volumetric uptake of 259 cm3 (STP) cm−3, and robust mechanical properties, this meets technological targets.
- Tian Tian
- , Zhixin Zeng
- & David Fairen-Jimenez
-
Letter |
 Ultrathin graphene-based membrane with precise molecular sieving and ultrafast solvent permeation
Ultrathin graphene-based membrane with precise molecular sieving and ultrafast solvent permeation
Highly laminar graphene oxide flakes (10 to 20 μm in diameter) are fabricated. Reducing flake thickness to 10 nm enables water and organic solvent permeation, enabling the flakes to act as a highly effective organic solvent membrane.
- Q. Yang
- , Y. Su
- & R. R. Nair
-
Article |
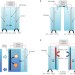 Photoelectrochemical water splitting in separate oxygen and hydrogen cells
Photoelectrochemical water splitting in separate oxygen and hydrogen cells
Solar water splitting is promising for hydrogen production and solar energy storage, but for large-scale utilization cost must be reduced. A membrane-free approach in separate oxygen and hydrogen cells brings water splitting closer to applications.
- Avigail Landman
- , Hen Dotan
- & Avner Rothschild
-
Editorial |
 The state of flux
The state of flux
The development of new membrane materials for chemical separations is progressing rapidly, and their commercial success will require a more concerted effort from academia and industry.
-
Interview |
 Membranes from academia to industry
Membranes from academia to industry
Andrew Livingston (Imperial College London) and Richard Baker (Membrane Technology and Research) talk to Nature Materials about the perks and pitfalls of membrane research and development, and how activities at the new Barrer Centre might lead to next-generation separation technologies.
- Jim Hennessy
-
Commentary |
 From water to organics in membrane separations
From water to organics in membrane separations
Membrane materials provide economical means to achieve various separation processes — and their capabilities for processing organic fluids look set to expand significantly.
- Ryan P. Lively
- & David S. Sholl
-
Letter |
 Selective nitrogen capture by porous hybrid materials containing accessible transition metal ion sites
Selective nitrogen capture by porous hybrid materials containing accessible transition metal ion sites
Mesoporous metal–organic frameworks containing unsaturated Cr(III) sites are able to thermodynamically and selectively capture nitrogen from mixtures with oxygen and methane.
- Ji Woong Yoon
- , Hyunju Chang
- & Jong-San Chang
-
Letter |
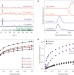 Enhanced ethylene separation and plasticization resistance in polymer membranes incorporating metal–organic framework nanocrystals
Enhanced ethylene separation and plasticization resistance in polymer membranes incorporating metal–organic framework nanocrystals
The dispersion of metal–organic framework nanocrystals within a polyimide yields membranes for selective chemical separations with strong resistance to plasticization.
- Jonathan E. Bachman
- , Zachary P. Smith
- & Jeffrey R. Long
-
Letter |
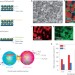 Scalable water splitting on particulate photocatalyst sheets with a solar-to-hydrogen energy conversion efficiency exceeding 1%
Scalable water splitting on particulate photocatalyst sheets with a solar-to-hydrogen energy conversion efficiency exceeding 1%
Photocatalytic water splitting using semiconductors is attractive for converting solar energy into hydrogen. An efficient and scalable system based on particulate photocatalyst sheets is now shown to exhibit energy conversion efficiency exceeding 1%.
- Qian Wang
- , Takashi Hisatomi
- & Kazunari Domen
-
Letter |
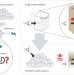 The role of crystal diversity in understanding mass transfer in nanoporous materials
The role of crystal diversity in understanding mass transfer in nanoporous materials
The efficient design of nanoporous materials crucially depends on understanding the mass transfer mechanism. Using micro-imaging techniques we now show that apparently identical crystals can exhibit different uptake rates.
- Julien Cousin Saint Remi
- , Alexander Lauerer
- & Jörg Kärger
-
Letter |
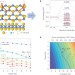 Activating and optimizing MoS2 basal planes for hydrogen evolution through the formation of strained sulphur vacancies
Activating and optimizing MoS2 basal planes for hydrogen evolution through the formation of strained sulphur vacancies
Molybdenum disulphide is a promising non-precious catalyst for hydrogen evolution because it contains active edge sites and an inert basal plane. Introducing sulphur vacancies and strain now leads to activation and optimization of the basal plane.
- Hong Li
- , Charlie Tsai
- & Xiaolin Zheng
-
Letter |
 Tough bonding of hydrogels to diverse non-porous surfaces
Tough bonding of hydrogels to diverse non-porous surfaces
A hydrogel-design strategy achieves transparent and conductive bonding of synthetic hydrogels to a variety of non-porous surfaces, with interfacial toughness values over 1,000 J m−2.
- Hyunwoo Yuk
- , Teng Zhang
- & Xuanhe Zhao
-
Article |
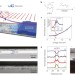 Synthesis of ultrathin polymer insulating layers by initiated chemical vapour deposition for low-power soft electronics
Synthesis of ultrathin polymer insulating layers by initiated chemical vapour deposition for low-power soft electronics
Initiated chemical vapour deposition enables the conformal growth of ultrathin insulating polymer layers. These polymer films can be deposited on a broad range of materials used for organic and flexible electronics, including graphene.
- Hanul Moon
- , Hyejeong Seong
- & Sung Gap Im

 Uncovering the predictive pathways of lithium and sodium interchange in layered oxides
Uncovering the predictive pathways of lithium and sodium interchange in layered oxides Floating artificial leaves
Floating artificial leaves