Featured
-
-
Article |
 Uncovering the predictive pathways of lithium and sodium interchange in layered oxides
Uncovering the predictive pathways of lithium and sodium interchange in layered oxides
Ion exchange is a powerful method to access metastable materials for energy storage, but identifying lithium and sodium interchange in layered oxides remains challenging. Using such model materials, vacancy level and corresponding lithium preference are shown to be crucial for ion exchange pathway accessibility.
- Yu Han
- , Weihang Xie
- & Chong Liu
-
Article |
 Nanofeather ruthenium nitride electrodes for electrochemical capacitors
Nanofeather ruthenium nitride electrodes for electrochemical capacitors
Fast charging is driving extensive research on enhanced electrodes for high-performance electrochemical capacitors and micro-supercapacitors. Thick ruthenium nitride pseudocapacitive films are shown to exhibit enhanced capacitance with a time constant of less than 6 s.
- Huy Dinh Khac
- , Grace Whang
- & Christophe Lethien
-
Article
| Open Access Chemo-mechanical failure mechanisms of the silicon anode in solid-state batteries
Chemo-mechanical failure mechanisms of the silicon anode in solid-state batteries
Although silicon anodes are promising for solid-state batteries, they still suffer from poor electrochemical performance. Chemo-mechanical failure mechanisms of composite Si|Li6PS5Cl and solid-electrolyte-free silicon anodes are now revealed and should help in designing improved electrodes.
- Hanyu Huo
- , Ming Jiang
- & Jürgen Janek
-
Article |
 Fe–Ni-based alloys as highly active and low-cost oxygen evolution reaction catalyst in alkaline media
Fe–Ni-based alloys as highly active and low-cost oxygen evolution reaction catalyst in alkaline media
NiFe-based oxo-hydroxides are active for the oxygen evolution reaction but suffer from complex synthesis and durability when deposited. Easily processable Fe–Ni alloys with a highly active oxo-hydroxide surface are now shown to pave the way for oxygen-evolving electrodes for alkaline water electrolysers.
- Lucile Magnier
- , Garance Cossard
- & Marian Chatenet
-
Article
| Open Access Electrochemical and chemical cycle for high-efficiency decoupled water splitting in a near-neutral electrolyte
Electrochemical and chemical cycle for high-efficiency decoupled water splitting in a near-neutral electrolyte
Hydrogen produced by water splitting using renewable electricity is key to achieve net-zero carbon emissions. Decoupling hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions during electrolysis is attractive but efficiency and operational challenges remain. A process producing hydrogen and oxygen in separate cells and supporting continuous operation in a membraneless system is now proposed.
- Ilya Slobodkin
- , Elena Davydova
- & Avner Rothschild
-
Article |
 Fast cycling of lithium metal in solid-state batteries by constriction-susceptible anode materials
Fast cycling of lithium metal in solid-state batteries by constriction-susceptible anode materials
Interfacial reactions between lithium and anodes are not well understood in an all-solid environment. For the silicon anode we now demonstrate that, rather than strong Li–Si alloying at the conventional solid–liquid interface, the lithiation reaction of micrometre-sized Si can be greatly constricted at the solid–solid interface.
- Luhan Ye
- , Yang Lu
- & Xin Li
-
News & Views |
 Beyond lithium for sustainable ammonia synthesis
Beyond lithium for sustainable ammonia synthesis
Using an electrochemical continuous flow cell, nitrogen reduction to ammonia is rigorously demonstrated through a calcium-mediated approach.
- Michael A. Yusov
- & Karthish Manthiram
-
Article |
 Localized high-concentration electrolytes get more localized through micelle-like structures
Localized high-concentration electrolytes get more localized through micelle-like structures
Liquid electrolytes in batteries are considered to be macroscopically homogeneous ionic transport media despite having a complex chemical composition and atomistic solvation structures. A micelle-like structure in a localized high-concentration electrolyte for which the solvent acts as a surfactant is reported.
- Corey M. Efaw
- , Qisheng Wu
- & Bin Li
-
Article |
 Calcium-mediated nitrogen reduction for electrochemical ammonia synthesis
Calcium-mediated nitrogen reduction for electrochemical ammonia synthesis
The production of ammonia via the Haber–Bosch process is carbon-intensive and centralized, but electrochemical methods such as lithium-mediated processes in organic electrolytes could enable decentralized production using renewable energy. Calcium is now shown to mediate nitrogen reduction for ammonia synthesis.
- Xianbiao Fu
- , Valerie A. Niemann
- & Ib Chorkendorff
-
Article |
 Sequencing polymers to enable solid-state lithium batteries
Sequencing polymers to enable solid-state lithium batteries
Solid polymer electrolytes are crucial for the development of lithium batteries, but their lower ionic conductivity compared with liquid/ceramics at room temperature limits their practical use. Precise positioning of designed repeating units in alternating polymer sequences now allows the Li+ conductivity to be tuned by up to three orders of magnitude.
- Shantao Han
- , Peng Wen
- & Mao Chen
-
Article |
 Decoupling the roles of Ni and Co in anionic redox activity of Li-rich NMC cathodes
Decoupling the roles of Ni and Co in anionic redox activity of Li-rich NMC cathodes
Lithium-rich nickel manganese cobalt oxide cathodes are widely explored due to their high capacities related to their anionic redox chemistry. A compositional optimization pathway for these materials investigating the variation of using cobalt and nickel now provides valuable guidelines for future high-capacity cathode design.
- Biao Li
- , Zengqing Zhuo
- & Jean-Marie Tarascon
-
Article |
 Improving lithium-ion cells by replacing polyethylene terephthalate jellyroll tape
Improving lithium-ion cells by replacing polyethylene terephthalate jellyroll tape
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) tape is widely used for lithium-ion batteries but its chemical stability has been largely overlooked. Reversible self-discharge is now shown to be virtually eliminated in LiFePO4–graphite cells by replacing PET with polypropylene jellyroll tape.
- Anu Adamson
- , Kenneth Tuul
- & Michael Metzger
-
News & Views |
 The hole truth
The hole truth
By tracking the electrochromic doping front, a hole-limited electrochemical doping mechanism is discovered in organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors.
- Ruiheng Wu
- , Dilara Meli
- & Jonathan Rivnay
-
Article |
 Extreme lithium-metal cycling enabled by a mixed ion- and electron-conducting garnet three-dimensional architecture
Extreme lithium-metal cycling enabled by a mixed ion- and electron-conducting garnet three-dimensional architecture
The development of solid-state Li-metal batteries has been limited by Li plating and stripping rates and the formation of dendrites at relevant current densities. Single-phase mixed ion- and electron-conducting garnet with comparable Li-ion and electronic conductivities is now proposed to tackle these issues.
- George V. Alexander
- , Changmin Shi
- & Eric D. Wachsman
-
Article
| Open Access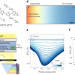 Hole-limited electrochemical doping in conjugated polymers
Hole-limited electrochemical doping in conjugated polymers
Electrochemical doping is assumed to be limited by ion motion due to large mass in mixed ionic-electronic conductors. Here, the authors reveal in a typical polythiophene that electrochemical doping speeds are limited by poor hole transport at low doping levels, leading to much slower switching speeds than expected.
- Scott T. Keene
- , Joonatan E. M. Laulainen
- & George G. Malliaras
-
Article |
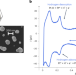 Imaging the strain evolution of a platinum nanoparticle under electrochemical control
Imaging the strain evolution of a platinum nanoparticle under electrochemical control
Surface strain can be used in gas phase catalysis and electrocatalysis to control the binding energies of adsorbates on active sites, but in situ or operando strain measurements can be challenging. Coherent diffraction now allows strain inside individual Pt nanoparticles to be mapped and quantified under electrochemical control.
- Clément Atlan
- , Corentin Chatelier
- & Marie-Ingrid Richard
-
Article |
 Optical method for quantifying the potential of zero charge at the platinum–water electrochemical interface
Optical method for quantifying the potential of zero charge at the platinum–water electrochemical interface
The electric field created at an electrode–electrolyte interface can polarize the electrode’s surface and nearby molecules. Although its effect can be countered by an applied potential, quantifying the value of this potential is difficult. An optical method for determining the potential of zero charge at an electrochemical interface is now presented.
- Pengtao Xu
- , Alexander D. von Rueden
- & Jin Suntivich
-
Article |
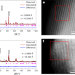 Inhibiting collective cation migration in Li-rich cathode materials as a strategy to mitigate voltage hysteresis
Inhibiting collective cation migration in Li-rich cathode materials as a strategy to mitigate voltage hysteresis
The high energy densities of Li-rich cathodes are promising for Li-ion batteries, but voltage hysteresis limits their practical implementation. Voltage hysteresis is shown to be related to collective migration of metal ions, and isolating migration leads to high-capacity reversible cathodes.
- Jianping Huang
- , Bin Ouyang
- & Gerbrand Ceder
-
Article |
 Resolving complex intralayer transition motifs in high-Ni-content layered cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries
Resolving complex intralayer transition motifs in high-Ni-content layered cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries
High-Ni-content layered cathodes are promising for lithium-ion batteries, but investigating their delithiation-induced phase boundaries is challenging. Intralayer transition motifs at complex phase boundaries in these high-Ni electrodes are now resolved using deep-learning-aided super-resolution electron microscopy.
- Chunyang Wang
- , Xuelong Wang
- & Huolin L. Xin
-
-
Article |
 A near dimensionally invariable high-capacity positive electrode material
A near dimensionally invariable high-capacity positive electrode material
Delivering inherently stable lithium-ion batteries with electrodes that can reversibly insert and extract large quantities of Li+ with inherent stability during cycling are key. Lithium-excess vanadium oxides with a disordered rocksalt structure are now investigated as high-capacity and long-life cathodes.
- Itsuki Konuma
- , Damian Goonetilleke
- & Naoaki Yabuuchi
-
Article |
 Non-iridium-based electrocatalyst for durable acidic oxygen evolution reaction in proton exchange membrane water electrolysis
Non-iridium-based electrocatalyst for durable acidic oxygen evolution reaction in proton exchange membrane water electrolysis
Iridium-based electrocatalysts are traditional anode catalysts for proton exchange membrane water electrolysis but suffer from high cost and low reserves. An alternative, nickel-stabilized ruthenium dioxide catalyst with high activity and durability in acidic oxygen evolution reaction for water electrolysis is reported.
- Zhen-Yu Wu
- , Feng-Yang Chen
- & Haotian Wang
-
Article |
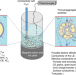 Dense inorganic electrolyte particles as a lever to promote composite electrolyte conductivity
Dense inorganic electrolyte particles as a lever to promote composite electrolyte conductivity
Solid-state electrolytes are key to the development of safer and higher-energy-density batteries. Using liquid electrolyte chemistries as models for polymer electrolytes, the effect of adding a variety of porous and dense ceramic electrolytes on the conductivity is now investigated.
- James A. Isaac
- , Didier Devaux
- & Renaud Bouchet
-
Article |
 Polymorphism of garnet solid electrolytes and its implications for grain-level chemo-mechanics
Polymorphism of garnet solid electrolytes and its implications for grain-level chemo-mechanics
Understanding and mitigating filament formation, short-circuit and solid electrolyte fracture is necessary for advanced all-solid-state batteries. The effect of polymorphism on the grain-level chemo-mechanical behaviour of dense and polycrystalline garnet solid electrolytes is now investigated.
- Marm B. Dixit
- , Bairav S. Vishugopi
- & Kelsey B. Hatzell
-
Article |
 Operando monitoring of single-particle kinetic state-of-charge heterogeneities and cracking in high-rate Li-ion anodes
Operando monitoring of single-particle kinetic state-of-charge heterogeneities and cracking in high-rate Li-ion anodes
Understanding the ion intercalation and degradation mechanisms occurring during realistic battery operation is crucial to developing high-rate battery electrodes. Operando optical scattering microscopy is now used to study single-particle kinetic state-of-charge heterogeneities and cracking in high-rate Li-ion anode materials.
- Alice J. Merryweather
- , Quentin Jacquet
- & Clare P. Grey
-
News & Views |
 Enabling low-cost and sustainable fuel cells
Enabling low-cost and sustainable fuel cells
A hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cell consisting of a nickel-based anode and a cobalt–manganese–oxide cathode is shown to achieve a power density of 488 mW cm–2 at 95 °C.
- Frédéric Jaouen
-
Article |
 Capturing dynamic ligand-to-metal charge transfer with a long-lived cationic intermediate for anionic redox
Capturing dynamic ligand-to-metal charge transfer with a long-lived cationic intermediate for anionic redox
Understanding reversible anionic redox reactions is key to designing high-energy-density cathodes for lithium-ion batteries. Anionic redox activation in cation-disordered rock-salt Li1.17Ti0.58Ni0.25O2 is shown to involve intermediate Ni3+/4+ species that can evolve to Ni2+ during relaxation.
- Biao Li
- , Khagesh Kumar
- & Jean-Marie Tarascon
-
Article |
 Direct correlation between void formation and lithium dendrite growth in solid-state electrolytes with interlayers
Direct correlation between void formation and lithium dendrite growth in solid-state electrolytes with interlayers
The growth of lithium dendrites across electrolyte layers limits the practical viability of solid-state Li-ion batteries. A direct correlation between void formation and lithium dendrite growth in solid-state electrolytes with metallic interlayers is now observed.
- Vikalp Raj
- , Victor Venturi
- & Naga Phani B. Aetukuri
-
Article |
 An efficient nickel hydrogen oxidation catalyst for hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells
An efficient nickel hydrogen oxidation catalyst for hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells
Hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells are promising as an energy conversion technology, but require platinum group metal electrocatalysts for their application. A Ni-based hydrogen oxidation reaction catalyst is now shown to exhibit unprecedented electrochemical performance.
- Weiyan Ni
- , Teng Wang
- & Xile Hu
-
Article |
 Coupling structural evolution and oxygen-redox electrochemistry in layered transition metal oxides
Coupling structural evolution and oxygen-redox electrochemistry in layered transition metal oxides
Transition metal oxide electrodes are promising for rechargeable batteries but are subject to suffer from structural transformations and electrochemical degradation. The evolution of oxygen-redox activity and reversibility in layered electrodes are shown to arise from cation-migration mechanisms during de/intercalation.
- Donggun Eum
- , Byunghoon Kim
- & Kisuk Kang
-
Article |
 3D-printed hierarchical pillar array electrodes for high-performance semi-artificial photosynthesis
3D-printed hierarchical pillar array electrodes for high-performance semi-artificial photosynthesis
Wiring photosynthetic biomachineries to electrodes is promising for sustainable bio-electricity and fuel generation, but designing such interfaces is challenging. Aerosol jet printing is now used to generate hierarchical pillar array electrodes using indium tin oxide nanoparticles for high-performance semi-artificial photosynthesis.
- Xiaolong Chen
- , Joshua M. Lawrence
- & Jenny Z. Zhang
-
Article |
 Tunable metal hydroxide–organic frameworks for catalysing oxygen evolution
Tunable metal hydroxide–organic frameworks for catalysing oxygen evolution
The oxygen evolution reaction is central to making chemicals and energy carriers using electrons. Metal hydroxide–organic frameworks are shown to act as a tunable catalytic platform for oxygen evolution, with π–π interactions dictating stability and transition metals modulating activity.
- Shuai Yuan
- , Jiayu Peng
- & Yang Shao-Horn
-
Article |
 Stable non-corrosive sulfonimide salt for 4-V-class lithium metal batteries
Stable non-corrosive sulfonimide salt for 4-V-class lithium metal batteries
Lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide is used as a conducting salt for rechargeable lithium metal batteries because of its stability, but corrosion with aluminium current collectors is an issue. A non-corrosive sulfonimide salt is shown to suppress anodic dissolution of an Al current collector at high potentials while improving cycling.
- Lixin Qiao
- , Uxue Oteo
- & Heng Zhang
-
Article |
 Suspension electrolyte with modified Li+ solvation environment for lithium metal batteries
Suspension electrolyte with modified Li+ solvation environment for lithium metal batteries
Stable solid–electrolyte interphases on Li anodes are crucial for reliable Li metal batteries. A suspension electrolyte design that modifies the Li+ solvation environment in liquid electrolytes and creates inorganic-rich interphases on Li is now reported.
- Mun Sek Kim
- , Zewen Zhang
- & Yi Cui
-
Article |
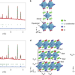 Hydride-ion-conducting K2NiF4-type Ba–Li oxyhydride solid electrolyte
Hydride-ion-conducting K2NiF4-type Ba–Li oxyhydride solid electrolyte
Although using proton (H+) conductors is attractive for energy applications, practical conductivity at intermediate temperatures (200–400 °C) remains a challenge. A K2NiF4-type Ba–Li oxyhydride is shown to exhibit a temperature-independent hydrogen conductivity of more than 0.01 S cm–1 above 315 °C.
- Fumitaka Takeiri
- , Akihiro Watanabe
- & Genki Kobayashi
-
Article |
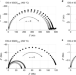 Photo-enhanced ionic conductivity across grain boundaries in polycrystalline ceramics
Photo-enhanced ionic conductivity across grain boundaries in polycrystalline ceramics
Grain boundary conductivity limitations are ubiquitous in material science. Illumination with above-bandgap light is now shown to decrease grain boundary resistance in a model gadolinium-doped ceria solid ionic conductor.
- Thomas Defferriere
- , Dino Klotz
- & Harry L. Tuller
-
Article |
 Inter-facet junction effects on particulate photoelectrodes
Inter-facet junction effects on particulate photoelectrodes
In anisotropically shaped photocatalyst particles different constituent facets may form inter-facet junctions at their adjoining edges. Using multimodal functional imaging, inter-facet junction effects on anisotropically shaped bismuth vanadate particles are revealed.
- Xianwen Mao
- & Peng Chen
-
Article |
 Effect of crystallite geometries on electrochemical performance of porous intercalation electrodes by multiscale operando investigation
Effect of crystallite geometries on electrochemical performance of porous intercalation electrodes by multiscale operando investigation
Designing electrode architectures for Li-ion batteries that can be reversibly accessible for ion storage can be challenging. Using operando techniques the mechanistic origin of lithiation-induced phase transformations in a V2O5 model cathode is now clarified.
- Yuting Luo
- , Yang Bai
- & Sarbajit Banerjee
-
News & Views |
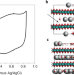 Confined water controls capacitance
Confined water controls capacitance
By using a battery of experimental and theoretical methods, it is shown that ion intercalation into the electrode material birnessite is mediated by structural water.
- Patrice Simon
- & Yury Gogotsi
-
Article |
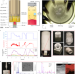 Electrorefining for direct decarburization of molten iron
Electrorefining for direct decarburization of molten iron
Application of electromotive force between molten iron–carbon and slag is shown to decarburize iron. Electrorefining decarburizes by direct interfacial electrochemical reaction, resulting in low solubilized oxygen in iron, even at low carbon concentration.
- William D. Judge
- , Jaesuk Paeng
- & Gisele Azimi
-
Article |
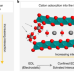 Effects of interlayer confinement and hydration on capacitive charge storage in birnessite
Effects of interlayer confinement and hydration on capacitive charge storage in birnessite
Nanostructured birnessite exhibits high specific capacitance and, while an important electrode material for high-power energy storage devices, its capacitive mechanism remains unclear. Capacitive charge storage in birnessite is now shown to be governed by interlayer cation intercalation.
- Shelby Boyd
- , Karthik Ganeshan
- & Veronica Augustyn
-
Article |
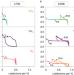 Extending insertion electrochemistry to soluble layered halides with superconcentrated electrolytes
Extending insertion electrochemistry to soluble layered halides with superconcentrated electrolytes
Insertion compounds in layered oxide or sulfide electrodes provide the fundamental basis of current commercialized Li-ion batteries. The feasibility of reversibly intercalating Li+ electrochemically into halide compounds via the use of superconcentrated electrolytes is now demonstrated.
- Nicolas Dubouis
- , Thomas Marchandier
- & Alexis Grimaud
-
Article |
 Chemical vapour deposition of Fe–N–C oxygen reduction catalysts with full utilization of dense Fe–N4 sites
Chemical vapour deposition of Fe–N–C oxygen reduction catalysts with full utilization of dense Fe–N4 sites
Replacing platinum with metal–nitrogen–carbon catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction in proton exchange membrane fuel cells has been impeded by low activity. These limitations have now been overcome by the trans-metalation of Zn–N4 sites into Fe–N4 sites.
- Li Jiao
- , Jingkun Li
- & Qingying Jia
-
Article |
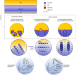 Revealing the role of the cathode–electrolyte interface on solid-state batteries
Revealing the role of the cathode–electrolyte interface on solid-state batteries
Interfaces play crucial, but still poorly understood, roles in the performance of secondary solid-state batteries. Using crystallographically oriented and highly faceted thick cathodes, the impact of cathode crystallography and morphology on long-term performance is investigated.
- Beniamin Zahiri
- , Arghya Patra
- & Paul V. Braun
-
Article |
 Microstructural origin of locally enhanced CO2 electroreduction activity on gold
Microstructural origin of locally enhanced CO2 electroreduction activity on gold
Although bulk defects can influence the performance of electrocatalysts used for energy conversion, their structural origins are still unclear. The effects of bulk defects on CO2 electroreduction and H2 evolution activity on Au electrodes are now elucidated.
- Ruperto G. Mariano
- , Minkyung Kang
- & Matthew W. Kanan
-
Article |
 Fictitious phase separation in Li layered oxides driven by electro-autocatalysis
Fictitious phase separation in Li layered oxides driven by electro-autocatalysis
Although layered oxides electrodes in lithium-ion batteries are designed under conditions avoiding phase transitions, phase separation during delithiation has been observed. This apparent phase separation is shown to be a dynamical artefact occurring in a many-particle system driven by autocatalytic electrochemical reactions.
- Jungjin Park
- , Hongbo Zhao
- & William C. Chueh
-
Article |
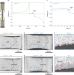 Linking void and interphase evolution to electrochemistry in solid-state batteries using operando X-ray tomography
Linking void and interphase evolution to electrochemistry in solid-state batteries using operando X-ray tomography
Understanding electrochemical behaviour and stability at solid–solid interfaces remains challenging. Operando synchrotron X-ray computed microtomography loss reveals that reconfiguration of interfacial contact is critical to explain cell failure during solid-state battery cycling.
- John A. Lewis
- , Francisco Javier Quintero Cortes
- & Matthew T. McDowell
-
Article |
 Revisiting metal fluorides as lithium-ion battery cathodes
Revisiting metal fluorides as lithium-ion battery cathodes
Metal-fluoride-based lithium-ion battery cathodes are typically classified as conversion materials because reconstructive phase transitions are presumed to occur upon lithiation. Metal fluoride lithiation is now shown to be dominated instead by diffusion-controlled displacement mechanisms.
- Xiao Hua
- , Alexander S. Eggeman
- & Clare P. Grey
-
Article |
 Tuning electrochemically driven surface transformation in atomically flat LaNiO3 thin films for enhanced water electrolysis
Tuning electrochemically driven surface transformation in atomically flat LaNiO3 thin films for enhanced water electrolysis
Structure–activity relationships built on descriptors of surfaces can help to design electrocatalysts, but their identification for electrochemically driven surface transformations is challenging. The composition of LaNiO3 thin film surfaces can now dictate surface transformation and activity of the oxygen evolution reaction.
- Christoph Baeumer
- , Jiang Li
- & William C. Chueh

 Electrochemomechanical failure in layered oxide cathodes caused by rotational stacking faults
Electrochemomechanical failure in layered oxide cathodes caused by rotational stacking faults Floating artificial leaves
Floating artificial leaves