Featured
-
-
Letter |
 Reconfigurable 3D plasmonic metamolecules
Reconfigurable 3D plasmonic metamolecules
Until now, it has not been possible to switch chirality in plasmonic nanostructures at will and repeatedly. Now, thanks to DNA-regulated conformational changes, reconfigurable 3D plasmonic metamolecules with switchable chirality have been created.
- Anton Kuzyk
- , Robert Schreiber
- & Na Liu
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Sliding charges
Sliding charges
In contrast to the ultralow friction that exists between carbon layers in multiwalled carbon nanotubes, multiwalled boron nitride nanotubes are found to exhibit ultrahigh interlayer friction as a result of their ionic character.
- Robert Szoszkiewicz
- & Elisa Riedo
-
Article |
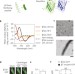 Gradated assembly of multiple proteins into supramolecular nanomaterials
Gradated assembly of multiple proteins into supramolecular nanomaterials
Peptide-based nanofibres with bioactive proteins attached can now be made such that the protein ligands are introduced in a controlled manner. This tailoring of the nanofibre’s composition enables the ratio of multiple different proteins to be highly tuned within the assemblies. By changing the protein content of the nanofibres, it is possible to adjust the antibody responses in mice to the different nanofibres.
- Gregory A. Hudalla
- , Tao Sun
- & Joel H. Collier
-
Letter |
 Ultrahigh interlayer friction in multiwalled boron nitride nanotubes
Ultrahigh interlayer friction in multiwalled boron nitride nanotubes
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and boron nitride nanotubes (BNNTs) have similar surface crystallography and mechanical properties. It is now shown that the interlayer sliding friction in multilayer CNTs and BNNTs is, however, different: whereas the telescopic sliding of semi-metallic multiwalled CNTs is known to be vanishingly small, multiwalled insulating BNNTs exhibit ultrahigh interlayer friction that is proportional to the contact area—a result ascribed to the ionic character of boron nitride.
- A. Niguès
- , A. Siria
- & L. Bocquet
-
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Light management for photovoltaics using high-index nanostructures
Light management for photovoltaics using high-index nanostructures
Strategies to increase light-trapping in solar cells can significantly improve the power-conversion efficiency of these devices. This Review discusses the use of nanostructured high-index layers to manipulate photons in thin-film solar cells, as well as the recent efforts aimed at integrating such layers in large-area devices.
- Mark L. Brongersma
- , Yi Cui
- & Shanhui Fan
-
Article |
 Scalable production of large quantities of defect-free few-layer graphene by shear exfoliation in liquids
Scalable production of large quantities of defect-free few-layer graphene by shear exfoliation in liquids
Methods to achieve large-scale production of defect-free graphene are needed to enable the commercial development of graphene-based devices. It is now shown that high-shear mixing is an effective way to exfoliate graphene and other two-dimensional materials in liquid volumes up to hundreds of litres.
- Keith R. Paton
- , Eswaraiah Varrla
- & Jonathan N. Coleman
-
Letter |
 Hydrogen-bonded structure and mechanical chiral response of a silver nanoparticle superlattice
Hydrogen-bonded structure and mechanical chiral response of a silver nanoparticle superlattice
Self-assembled nanoparticle superlattices, which consist of inorganic cores capped by organic ligands, can show emergent behaviour as a result of the coupling between their nanoscale components. The atom-level structure of a silver nanoparticle superlattice, deduced from X-ray imaging and simulations, is now reported as well as its response to hydrostatic compression, which involves anomalous pressure softening and correlated chiral rotation of the nanoparticles.
- Bokwon Yoon
- , W. D. Luedtke
- & Uzi Landman
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Squeezing out the current
Squeezing out the current
In spite of their promise, practical applications of high-temperature cuprate superconductors have been hard to come by. The development of a method to fabricate round wires of the cuprate system Bi-2212 may begin to change this.
- Joseph V. Minervini
-
Article |
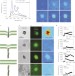 Plant nanobionics approach to augment photosynthesis and biochemical sensing
Plant nanobionics approach to augment photosynthesis and biochemical sensing
Imparting non-native functions to living plants using nanoparticles opens the possibility of creating synthetic materials that can grow and repair themselves using sunlight, water and carbon dioxide. It is now shown that, both in plant extracts and living leaves, carbon nanotubes traverse and localize within the lipid envelope of plant chloroplasts, enhance their photosynthetic activity, and enable near-infrared fluorescence monitoring of nitric oxide.
- Juan Pablo Giraldo
- , Markita P. Landry
- & Michael S. Strano
-
-
Article |
 Platinum–cobalt bimetallic nanoparticles in hollow carbon nanospheres for hydrogenolysis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural
Platinum–cobalt bimetallic nanoparticles in hollow carbon nanospheres for hydrogenolysis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural
Although producing 2,5-dimethylfuran (DMF) from 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) is an attractive way to synthesize renewable fuels, achieving high yields for this reaction has proved difficult. PtCo bimetallic nanoparticle catalysts embedded in hollow carbon nanospheres now show improved catalytic performance for the hydrogenolysis of HMF to DMF (98% yield after 2 hours).
- Guang-Hui Wang
- , Jakob Hilgert
- & Ferdi Schüth
-
News & Views |
 Three rules of design
Three rules of design
By following three empirical rules it is possible to design and fabricate magnetic heterostructures or even devices whose magnetization can be controlled by means of circularly polarized femtosecond laser pulses, instead of applied magnetic fields.
- Alexey V. Kimel
-
Editorial |
 Believing in seeing
Believing in seeing
Materials-based imaging agents are attractive candidates for a diverse range of imaging modalities and combined imaging–therapy applications, but economic implications and practical concerns remain obstacles to their clinical translation.
-
News & Views |
 Lighting up tumours
Lighting up tumours
Detection of a wide range of tumours remains a challenge in cancer diagnostics. By exploiting changes in the tumour microenvironment, a pH-responsive polymeric nanomaterial enables ultrasensitive tumour-specific imaging in many types of cancer.
- Daishun Ling
- , Michael J. Hackett
- & Taeghwan Hyeon
-
News & Views |
 DNA-bonded 'atoms'
DNA-bonded 'atoms'
DNA-capped nanoparticles crystallize into uniform microcrystals of Wulff polyhedra when cooled slowly through the melting temperature of the DNA linkers.
- Shogo Hamada
- , Shawn J. Tan
- & Dan Luo
-
Commentary |
 A targeted approach to cancer imaging and therapy
A targeted approach to cancer imaging and therapy
Nanoparticle-based imaging plays a crucial role in cancer diagnosis and treatment. Here, we discuss the modalities used for molecular imaging of the tumour microenvironment and image-guided interventions including drug delivery, surgery and ablation therapy.
- Chun Li
-
-
-
Letter |
 Giant frictional dissipation peaks and charge-density-wave slips at the NbSe2 surface
Giant frictional dissipation peaks and charge-density-wave slips at the NbSe2 surface
The friction of surfaces in relative motion and separated by a few nanometres is thought to be dominated by electronic effects. It is now found that the friction sensed by an AFM tip oscillating above a NbSe2 surface takes the form of giant dissipation peaks, and that the peaks are related to a hysteresis cycle where the oscillating tip locally pumps 2π slips in the phase of a charge-density wave.
- Markus Langer
- , Marcin Kisiel
- & Ernst Meyer
-
Article |
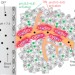 A nanoparticle-based strategy for the imaging of a broad range of tumours by nonlinear amplification of microenvironment signals
A nanoparticle-based strategy for the imaging of a broad range of tumours by nonlinear amplification of microenvironment signals
The imaging of tumours is challenging because of the wide range of different cancers. Now, the rapid detection of tumours, independent of type, is achieved using a nonlinear amplification strategy that employs ultrasensitive pH-responsive fluorescent nanoparticles that illuminate within tumour neovasculature or in response to the tumour’s acidic extracellular environment.
- Yiguang Wang
- , Kejin Zhou
- & Jinming Gao
-
Letter |
 Observing bulk diamond spin coherence in high-purity nanodiamonds
Observing bulk diamond spin coherence in high-purity nanodiamonds
The photoluminescent properties of electron spins at nitrogen–vacancy (NV) centres are promising for use in quantum information and magnetometry. It is now shown that the coherence times of NV centres in nanodiamonds can be engineered to be comparable to those of bulk diamond.
- Helena S. Knowles
- , Dhiren M. Kara
- & Mete Atatüre
-
-
News & Views |
 Streaks of conduction
Streaks of conduction
Scanning probe techniques reveal an intricate interplay between the formation of structural domains in strontium titanate and electronic transport effects at oxide interfaces.
- Alexander Brinkman
-
-
-
-
Commentary |
 Strategies for advancing cancer nanomedicine
Strategies for advancing cancer nanomedicine
Cancer nanomedicines approved so far minimize toxicity, but their efficacy is often limited by physiological barriers posed by the tumour microenvironment. Here, we discuss how these barriers can be overcome through innovative nanomedicine design and through creative manipulation of the tumour microenvironment.
- Vikash P. Chauhan
- & Rakesh K. Jain
-
Commentary |
 Translating materials design to the clinic
Translating materials design to the clinic
Many materials-based therapeutic systems have reached the clinic or are in clinical trials. Here we describe materials design principles and the construction of delivery vehicles, as well as their adaptation and evaluation for human use.
- Jeffrey A. Hubbell
- & Robert Langer
-
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Doping for superior dielectrics
Doping for superior dielectrics
The search for materials with colossal permittivity for use in capacitors has been met with limited success. A newly discovered co-doped titanium oxide material has an extremely high permittivity and negligible dielectric losses, and is likely to enable further scaling in electronic and energy-storage devices.
- Christopher C. Homes
- & Thomas Vogt
-
News & Views |
 Bonding them all
Bonding them all
A general approach for decorating nanoparticles with a highly dense shell of DNA linkers expands the range of building blocks that can be used for DNA-mediated nanoparticle self-assembly.
- Ulrich Simon
-
News & Views |
 It's all about imperfections
It's all about imperfections
Experiments and simulations show that coherent twin boundaries, commonly believed to be perfect, are riddled with kinks and other defects.
- Julia R. Greer
-
-
Article |
 Compositional segregation in shaped Pt alloy nanoparticles and their structural behaviour during electrocatalysis
Compositional segregation in shaped Pt alloy nanoparticles and their structural behaviour during electrocatalysis
Although site-dependent metal surface segregation in bimetallic nanoalloys affects catalytic activity and stability, segregation on shaped nanocatalysts and their atomic-scale evolution is largely unexplored. PtxNi1−x alloy nanoparticle electrocatalysts with unique activity for oxygen reduction reactions exhibit an unexpected compositional segregation structure across the {111} facets.
- Chunhua Cui
- , Lin Gan
- & Peter Strasser
-
-
Letter |
 Cinnamate-based DNA photolithography
Cinnamate-based DNA photolithography
A highly selective and efficient approach to covalently bond complementary DNA strands in solution and on surfaces on demand is shown. The approach involves the substitution of a pair of complementary bases by cinnamate-based crosslinks, which can be activated on exposure to ultraviolet light, and allows chemical patterning of flat and curved surfaces down to micrometre and potentially submicrometre resolutions.
- Lang Feng
- , Joy Romulus
- & Paul Chaikin
-
News & Views |
 Down to the nanometre scale
Down to the nanometre scale
The rich dynamics of magnetic materials subject to very short laser pulses is important for both information processing and recording technology. The characterization of these phenomena with nanoscale spatial resolution shines new light on our understanding of them.
- Jean-Yves Bigot
-
-
Article |
 Exploring electrolyte organization in supercapacitor electrodes with solid-state NMR
Exploring electrolyte organization in supercapacitor electrodes with solid-state NMR
Supercapacitors are electrochemical energy-storage devices that take advantage of electrostatic interactions between high-surface-area nanoporous electrodes and electrolyte ions. Molecular mechanisms at work inside supercapacitor carbon electrodes are now clarified with solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance.
- Michaël Deschamps
- , Edouard Gilbert
- & François Béguin

 Imaging of spin waves in atomically designed nanomagnets
Imaging of spin waves in atomically designed nanomagnets Wide angle vision
Wide angle vision Base-pair quality check
Base-pair quality check Flat and functional
Flat and functional Live diffraction
Live diffraction Rough with the smooth
Rough with the smooth Improving pore performance
Improving pore performance Changing domains
Changing domains