Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Nano-oxides boost aluminium heat resistance
Nano-oxides boost aluminium heat resistance
Adding homogeneously dispersed oxide nanoparticles to aluminium pushes its high-temperature strength up to 500 °C.
- Alexis Deschamps
-
Research Briefing |
 Synergistic work hardening by rapid multiplication of dislocations in a multi-principal-element alloy
Synergistic work hardening by rapid multiplication of dislocations in a multi-principal-element alloy
In a multi-principal-element VCoNi alloy, premature necking during Lüders banding has been harnessed to produce rapid dislocation multiplication, leading to both forest hardening and hardening induced by regions of local chemical order. The result is ductility of 20% and a yield strength of 2 GPa, during room-temperature and cryogenic deformation.
-
Article
| Open Access Harnessing instability for work hardening in multi-principal element alloys
Harnessing instability for work hardening in multi-principal element alloys
Harnessing premature necking produces a rapid multiplication of dislocations to interact with local chemical orders for work hardening in VCoNi alloy, achieving ductility of 20% and yield strength of 2 GPa during room-temperature and cryogenic deformation.
- Bowen Xu
- , Huichao Duan
- & Xiaolei Wu
-
Article |
 Nanoconfined polymerization limits crack propagation in hysteresis-free gels
Nanoconfined polymerization limits crack propagation in hysteresis-free gels
Simultaneously highly elastic and deformable gels that maintain their mechanical properties have remained elusive. Here, using in situ polymerization confined within nanochannels, the authors prepare hysteresis-free gels insensitive to crack propagation.
- Weizheng Li
- , Xiaoliang Wang
- & Feng Yan
-
News & Views |
 Toughening through faint crystallization
Toughening through faint crystallization
Oxide glasses can be intrinsically toughened by forming crystal-like, medium-range order clusters, which transform inversely to the amorphous state under stress, exciting multiple shear bands for plastic deformation.
- Hewei Zhao
- & Lin Guo
-
Research Briefing |
 Fractured diamond can heal itself at room temperature
Fractured diamond can heal itself at room temperature
Self-healing behaviour in a nanotwinned diamond composite, at room temperature, has been quantitatively evaluated through tensile testing. The phenomenon is shown to arise from a transition of atomic interactions from repulsion to attraction and the formation of nanoscale diamond ‘osteoblasts’, in analogy to the process of bone healing in living organisms.
-
Article |
 Self-healing of fractured diamond
Self-healing of fractured diamond
The room-temperature self-healing behaviour of a nanotwinned diamond composite is quantitatively evaluated and found to stem from both the formation of nanoscale diamond osteoblasts and the atomic interaction transition from repulsion to attraction.
- Keliang Qiu
- , Jingpeng Hou
- & Lin Guo
-
News & Views |
 Amorphization-mediated plasticity
Amorphization-mediated plasticity
Amorphization can be an additional mechanism to assist plastic deformation in crystalline materials, providing a strategy to improve the load-bearing ability of brittle materials.
- Shiteng Zhao
- & Xiaolei Wu
-
Article |
 Achieving ultrahigh fatigue resistance in AlSi10Mg alloy by additive manufacturing
Achieving ultrahigh fatigue resistance in AlSi10Mg alloy by additive manufacturing
An ultrahigh fatigue-resistant AlSi10Mg alloy is achieved by additive manufacturing, with its three-dimensional dual-phase cellular nanostructure acting as a strong volumetric nanocage to inhibit fatigue damage accumulation.
- Chengyi Dan
- , Yuchi Cui
- & Jian Lu
-
Article |
 Multislip-enabled morphing of all-inorganic perovskites
Multislip-enabled morphing of all-inorganic perovskites
In situ tests show that all-inorganic lead halide perovskite micropillars can morph into distinct shapes without affecting their optoelectronic properties and bandgap, which provides insights into the plastic deformation of semiconductors and also shows their potential for manufacturing relevant devices.
- Xiaocui Li
- , You Meng
- & Yang Lu
-
Article |
 Toughening oxide glasses through paracrystallization
Toughening oxide glasses through paracrystallization
Through the approach of paracrystallization under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions, exceptional toughening has been achieved in oxide glasses by enhancing their crystal-like medium-range order structure. This discovery offers possibilities for the design of more resilient glass materials.
- Hu Tang
- , Yong Cheng
- & Tomoo Katsura
-
Article |
 Amorphous shear bands in crystalline materials as drivers of plasticity
Amorphous shear bands in crystalline materials as drivers of plasticity
Amorphous shear bands in crystalline materials are found to increase the toughness of brittle materials, in contrast to their traditional role as precursors to fracture. Criteria for this toughening have been identified.
- Xuanxin Hu
- , Nuohao Liu
- & Izabela Szlufarska
-
News & Views |
 One dislocation at a time
One dislocation at a time
The direct observation of enhanced dislocation mobility in iron by in situ electron microscopy offers key insights and adds to the ongoing debate on the mechanisms of hydrogen embrittlement.
- Vasily Bulatov
- & Wei Cai
-
Article |
 Quantitative tests revealing hydrogen-enhanced dislocation motion in α-iron
Quantitative tests revealing hydrogen-enhanced dislocation motion in α-iron
Screw dislocations in α-iron move more easily in the presence of hydrogen, as evidenced by real-time imaging using quantitative transmission electron microscopy.
- Longchao Huang
- , Dengke Chen
- & Zhiwei Shan
-
Article |
 Tailoring planar slip to achieve pure metal-like ductility in body-centred-cubic multi-principal element alloys
Tailoring planar slip to achieve pure metal-like ductility in body-centred-cubic multi-principal element alloys
This work shows that by designing appropriate alloying elements in a body-centred-cubic high-entropy alloy, local chemical order and lattice distortion can be tuned, which influences the evolution of planar-slip bands, realizing pure-metal-like tensile ductility at gigapascal yield strength.
- Liang Wang
- , Jun Ding
- & En Ma
-
-
News & Views |
 Heat-resistant aluminium alloys
Heat-resistant aluminium alloys
Scandium added to Al–Cu–Mg–Ag alloys leads to an in situ phase transformation of coherent Cu-rich nanoprecipitates at elevated temperature, with Sc atoms diffusing and occupying their interstitial sites. The transformed nanoprecipitates have enhanced thermal stability while maintaining a large volume fraction and these two microstructural features enable high tensile strength of the Al alloy with creep resistance up to 400 °C.
- Amit Shyam
- & Sumit Bahl
-
Article |
 Highly stable coherent nanoprecipitates via diffusion-dominated solute uptake and interstitial ordering
Highly stable coherent nanoprecipitates via diffusion-dominated solute uptake and interstitial ordering
High-density, highly stable coherent nanoprecipitates are created in Al alloys that enable high strength and creep resistance at 400 °C. This is realized via a growth-ledge-triggered in situ phase transformation assembling slow-diffusing solutes with high-solubility solutes into nanoprecipitates.
- Hang Xue
- , Chong Yang
- & Jun Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrastrong conductive in situ composite composed of nanodiamond incoherently embedded in disordered multilayer graphene
Ultrastrong conductive in situ composite composed of nanodiamond incoherently embedded in disordered multilayer graphene
In situ composites consisting of nanodiamond homogeneously dispersed in disordered multilayer graphene with incoherent interfaces and complex bonding are synthesized that exhibit an ultrahigh hardness and compressive strength, and excellent electrical conductivity.
- Zihe Li
- , Yujia Wang
- & Xiaoyan Li
-
Article |
 Ultrastrong nanotwinned titanium alloys through additive manufacturing
Ultrastrong nanotwinned titanium alloys through additive manufacturing
Laser additive manufacturing can be exploited to generate unique internally twinned nanoprecipitates in commercial titanium alloys, paving the way to fabricate ultrastrong metallic materials with intricate shapes for broad applications.
- Yuman Zhu
- , Kun Zhang
- & Aijun Huang
-
Article |
 Low-oxygen rare earth steels
Low-oxygen rare earth steels
The variation in the properties of rare earth (RE) steels is shown to stem from the presence of oxygen-based inclusions, and only under very-low-oxygen conditions can RE elements perform a vital role in purifying, modifying and micro-alloying steels.
- Dianzhong Li
- , Pei Wang
- & Yiyi Li
-
Article |
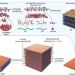 Graphene oxide bulk material reinforced by heterophase platelets with multiscale interface crosslinking
Graphene oxide bulk material reinforced by heterophase platelets with multiscale interface crosslinking
A nacre-inspired, centimetre-sized bulk material is prepared by assembling graphene oxide and microscale amorphous/crystalline heterophase reinforcing platelets adhered together with polymer-based crosslinkers, which shows high flexural strength and fracture toughness.
- Ke Chen
- , Xuke Tang
- & Lin Guo
-
Letter |
 A lightweight strain glass alloy showing nearly temperature-independent low modulus and high strength
A lightweight strain glass alloy showing nearly temperature-independent low modulus and high strength
Temperature-independent (Elinvar) soft elasticity with high strength, which is technologically desired but scientifically challenging, is achieved in a lightweight strain glass Mg alloy.
- Chang Liu
- , Yuanchao Ji
- & Xiaobing Ren
-
Article |
 The toughness of mechanical metamaterials
The toughness of mechanical metamaterials
Microscale architecting enables metamaterials to achieve mechanical properties not accessible to bulk materials. Here the authors show that established design protocols for the fracture of materials need to be revised to predict the failure of these materials.
- Angkur Jyoti Dipanka Shaikeea
- , Huachen Cui
- & Vikram Sudhir Deshpande
-
Article |
 Effect of crystallite geometries on electrochemical performance of porous intercalation electrodes by multiscale operando investigation
Effect of crystallite geometries on electrochemical performance of porous intercalation electrodes by multiscale operando investigation
Designing electrode architectures for Li-ion batteries that can be reversibly accessible for ion storage can be challenging. Using operando techniques the mechanistic origin of lithiation-induced phase transformations in a V2O5 model cathode is now clarified.
- Yuting Luo
- , Yang Bai
- & Sarbajit Banerjee
-
Article |
 Highly compressible glass-like supramolecular polymer networks
Highly compressible glass-like supramolecular polymer networks
Glass-like supramolecular polymer networks with high compressibility and fast self-recovery are fabricated using host–guest crosslinkers with slow dissociation kinetics.
- Zehuan Huang
- , Xiaoyi Chen
- & Oren A. Scherman
-
News & Views |
 Built from connected nested tubes
Built from connected nested tubes
Nanoarchitected carbon composed of intricate tube-in-tube beams connected with nanostruts has been fabricated, achieving both ultralightweight and ultrahigh modulus.
- Yujia Wang
- & Xiaoyan Li
-
Article |
 Ultra-low-density digitally architected carbon with a strutted tube-in-tube structure
Ultra-low-density digitally architected carbon with a strutted tube-in-tube structure
A nanoscale tube-in-tube sandwich structure is generated by a two-step templating-pyrolysis process, which strengthens the log-pile carbon architecture and slows down the decrease of stiffness with decreasing density.
- Jianchao Ye
- , Ling Liu
- & Juergen Biener
-
Article |
 UItra-low friction and edge-pinning effect in large-lattice-mismatch van der Waals heterostructures
UItra-low friction and edge-pinning effect in large-lattice-mismatch van der Waals heterostructures
MoS2/graphite and MoS2/h-BN interfaces are shown to have ultra-low friction coefficients, whereas edges and interface steps mainly contribute to the friction force.
- Mengzhou Liao
- , Paolo Nicolini
- & Guangyu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical heterogeneity enhances hydrogen resistance in high-strength steels
Chemical heterogeneity enhances hydrogen resistance in high-strength steels
Typically undesired chemically heterogeneous microstructures are shown to enhance the resistance of high-strength steel against hydrogen embrittlement, with no loss in strength or ductility.
- Binhan Sun
- , Wenjun Lu
- & Dierk Raabe
-
Article |
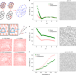 Achieving adjustable elasticity with non-affine to affine transition
Achieving adjustable elasticity with non-affine to affine transition
A non-affine to affine transition in elasticity occurs with the change of system topology in a packing-derived network, which enables the tuning of elastic moduli and Poisson’s ratio.
- Xiangying Shen
- , Chenchao Fang
- & Lei Xu
-
Article |
 Tension–compression asymmetry in amorphous silicon
Tension–compression asymmetry in amorphous silicon
Submicrometre-sized amorphous silicon samples show an unusually large tensile strength relative to the compressive strength, which is due to the reduced shear modulus and the activation energy barrier for shear transformations under compression.
- Yuecun Wang
- , Jun Ding
- & Zhiwei Shan
-
News & Views |
 Actuators powered by water hydrogen bonds
Actuators powered by water hydrogen bonds
Nanoporous tripeptide crystals mechanically deform upon water evaporation due to the strengthening of the water hydrogen bonding inside the pores, which causes the distortion of the surrounding supramolecular network, creating stresses that extend through the crystal lattice and result in actuation.
- Panče Naumov
-
Article |
 High-strength scalable graphene sheets by freezing stretch-induced alignment
High-strength scalable graphene sheets by freezing stretch-induced alignment
Stretch-induced alignment of graphene sheets is frozen by sequential covalent and π–π bridging, leading to high in-plane isotropic strength of 1.55 GPa. The graphene sheets are fabricated at near room temperature and are scalable.
- Sijie Wan
- , Ying Chen
- & Qunfeng Cheng
-
Article |
 Atomistic insights into metal hardening
Atomistic insights into metal hardening
In contrast with conventional views, ultra-large-scale atomistic simulations show that the staged character of strain hardening of metals originates from crystal rotation, whereas the dislocation behaviours remain the same across all the stages.
- Luis A. Zepeda-Ruiz
- , Alexander Stukowski
- & Vasily V. Bulatov
-
Article |
 Defect reconfiguration in a Ti–Al alloy via electroplasticity
Defect reconfiguration in a Ti–Al alloy via electroplasticity
Transmission electron microscopy reveals the electroplastic effects in a Ti–Al alloy, which can be uncoupled from Joule heating effects. Electropulsing during deformation enhances wavy slip of dislocations, reconfiguring the dislocation pattern, and hence increases the ductility.
- Shiteng Zhao
- , Ruopeng Zhang
- & Andrew M. Minor
-
Letter |
 Natural-mixing guided design of refractory high-entropy alloys with as-cast tensile ductility
Natural-mixing guided design of refractory high-entropy alloys with as-cast tensile ductility
A refractory high-entropy alloy was designed with the composition chosen based on the natural-mixing characteristics among refractory elements; this alloy demonstrates good tensile ductility in the as-cast state and physicochemical stability at high temperatures.
- Shaolou Wei
- , Sang Jun Kim
- & Cemal Cem Tasan
-
Comment |
 Post-fire restoration of historic buildings and implications for Notre-Dame de Paris
Post-fire restoration of historic buildings and implications for Notre-Dame de Paris
The restoration of fire-damaged historical monuments entails a wide range of scientific questions. Taking as a starting point the case of Notre-Dame de Paris, this Comment defines the materials science challenges of post-fire restoration, and also briefly outlines the issues of structural integrity, fire safety and preservation ethics.
- Ylenia Praticò
- , John Ochsendorf
- & Robert J. Flatt
-
Article |
 Radiation-induced segregation in a ceramic
Radiation-induced segregation in a ceramic
Radiation-induced segregation is widely observed in metals. Here it is discovered that radiation-induced segregation also occurs in a ceramic, with carbon atoms in silicon carbide segregating to the grain boundaries under irradiation.
- Xing Wang
- , Hongliang Zhang
- & Izabela Szlufarska
-
Letter |
 Unprecedented non-hysteretic superelasticity of [001]-oriented NiCoFeGa single crystals
Unprecedented non-hysteretic superelasticity of [001]-oriented NiCoFeGa single crystals
NiCoFeGa single crystals exhibit large non-hysteretic superelasticity over broad temperature and composition ranges. It is attributed to the continuous phase transition with applied stress, which is related to the fluctuation of entangled ordered and disordered crystal structures.
- Haiyang Chen
- , Yan-Dong Wang
- & Yang Ren
-
Article |
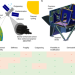 Dimensionally and environmentally ultra-stable polymer composites reinforced with carbon fibres
Dimensionally and environmentally ultra-stable polymer composites reinforced with carbon fibres
Multiple layers of diamond-like carbon films are shown to act as moisture barriers when conformally deposited on carbon fibre reinforced polymers used in space applications.
- J. V. Anguita
- , C. T. G. Smith
- & S. R. P. Silva
-
Article |
 Ideal maximum strengths and defect-induced softening in nanocrystalline-nanotwinned metals
Ideal maximum strengths and defect-induced softening in nanocrystalline-nanotwinned metals
It is believed that the strengthening of metals by formation of nanoscale grains or coherent twin boundaries is limited to a maximum strength. Here, using experiment and theory, it is shown that the fabrication of nanocrystalline-nanotwinned Ag with trace Cu results in a hardness beyond this limit.
- Xing Ke
- , Jianchao Ye
- & Frederic Sansoz
-
Article |
 A hybrid material that reversibly switches between two stable solid states
A hybrid material that reversibly switches between two stable solid states
Mechanically switchable materials made of supercooled fluids embedded in a polymer matrix reversibly shift between soft and hard solid states upon stimulation.
- Fut (Kuo) Yang
- , Aleksander Cholewinski
- & Boxin Zhao
-
News & Views |
 Deformable inorganic semiconductor
Deformable inorganic semiconductor
Unlike conventional inorganic semiconductors, which are typically brittle, α-Ag2S exhibits room-temperature ductility with favourable electrical properties, offering promise for use in high-performance flexible and stretchable devices.
- Dae-Hyeong Kim
- & Gi Doo Cha
-
Article |
 Room-temperature ductile inorganic semiconductor
Room-temperature ductile inorganic semiconductor
Inorganic α-Ag2S semiconductor, which has preferential slip planes in the crystal structure and irregularly distributed bonds of silver atoms preventing cleavage, demonstrates metal-like ductility at room temperature.
- Xun Shi
- , Hongyi Chen
- & Lidong Chen
-
Article |
 Imaging the atomic structure and local chemistry of platelets in natural type Ia diamond
Imaging the atomic structure and local chemistry of platelets in natural type Ia diamond
The accurate structure of the platelet defects in diamond is now resolved by transmission electron microscopy, and, out of all the proposed models, it agrees well with the zigzag atomic model.
- E. J. Olivier
- , J. H. Neethling
- & A. I. Kirkland
-
News & Views |
 Printing steels
Printing steels
Additive manufacturing has been used to fabricate a common stainless steel, which imparts a unique microstructure to this material, making it stronger and more ductile than that produced with conventional methods.
- Iain Todd
-
Article |
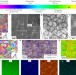 Additively manufactured hierarchical stainless steels with high strength and ductility
Additively manufactured hierarchical stainless steels with high strength and ductility
3D-printed steels with hierarchically heterogeneous microstructures demonstrate high strength and ductility.
- Y. Morris Wang
- , Thomas Voisin
- & Ting Zhu
-
News & Views |
 Making steel strong and cheap
Making steel strong and cheap
Introducing high-density ordered nanoprecipitates into martensitic steel increases strength at modest cost.
- J. W. Morris Jr

 Electrochemomechanical failure in layered oxide cathodes caused by rotational stacking faults
Electrochemomechanical failure in layered oxide cathodes caused by rotational stacking faults Composites from photo-stereochemical patterning
Composites from photo-stereochemical patterning