News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 A transparent organic transistor structure for bidirectional stimulation and recording of primary neurons
A transparent organic transistor structure for bidirectional stimulation and recording of primary neurons
A transparent organic field-effect transistor allows the stimulation and recording of the bioelectrical activity of primary neural cells. The cells grow, differentiate and function on the device, which then provides the electrical stimulation, and enables the recording of extracellular current and optical imaging of the modulation of neuronal membrane potential.
- Valentina Benfenati
- , Stefano Toffanin
- & Michele Muccini
-
Article |
 Degradation-mediated cellular traction directs stem cell fate in covalently crosslinked three-dimensional hydrogels
Degradation-mediated cellular traction directs stem cell fate in covalently crosslinked three-dimensional hydrogels
Adhesive interactions between stem cells and the extracellular matrix are known to regulate stem cell differentiation, yet the underlying mechanisms are not well understood. It is now shown that fate decisions of stem cells encapsulated in covalently crosslinked hydrogels are regulated, independently of matrix mechanics and cell morphology, by the cellular tension generated from cell-induced degradation of the hydrogels.
- Sudhir Khetan
- , Murat Guvendiren
- & Jason A. Burdick
-
News & Views |
 Keeping track
Keeping track
Assessing when cell death occurs following in vivo transplantation of stem cells is challenging. Now, pH-sensitive hydrogel capsules containing arginine-based liposomes are shown to act as magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents, allowing cell death to be monitored within the capsules.
- Keren Ziv
- & Sanjiv S. Gambhir
-
Article |
 Polymer multilayer tattooing for enhanced DNA vaccination
Polymer multilayer tattooing for enhanced DNA vaccination
Microneedle arrays coated with a pH-sensitive releasable layer act as an intradermal delivery system for polyelectrolyte films containing bioactive molecules for DNA vaccination. The implanted films co-deliver DNA, transfection agents and adjuvants, promoting local transfection and generating immune responses that can be tuned from days to weeks.
- Peter C. DeMuth
- , Younjin Min
- & Darrell J. Irvine
-
Article |
 Ultrasmall implantable composite microelectrodes with bioactive surfaces for chronic neural interfaces
Ultrasmall implantable composite microelectrodes with bioactive surfaces for chronic neural interfaces
Implantable neural microelectrodes are critical to neuroscience research and emerging clinical applications including brain-controlled prostheses. A composite electrode consisting of a carbon fibre core, an insulating polymer coating and a polythiophene-based recording pad has now been developed that shows reduced chronic reactive tissue response in rats compared with existing architectures, owing to its smaller size and improved mechanical compliance with brain tissue.
- Takashi D. Yoshida Kozai
- , Nicholas B. Langhals
- & Daryl R. Kipke
-
-
News & Views |
 Perfusable vascular networks
Perfusable vascular networks
A rapid vascular casting approach that uses carbohydrate glass as a sacrificial template allows tissues to be built that can be kept alive for longer in the laboratory until needed for transplantation.
- Gabor Forgacs
-
-
-
Article |
 Combination delivery of TGF-β inhibitor and IL-2 by nanoscale liposomal polymeric gels enhances tumour immunotherapy
Combination delivery of TGF-β inhibitor and IL-2 by nanoscale liposomal polymeric gels enhances tumour immunotherapy
The sustained release of both hydrophilic and hydrophobic immunomodulators for metastatic melanoma by nanoscale liposomal polymeric gels administered intratumorally or systemically is demonstrated. It is also shown that such a co-delivery approach delays tumour growth and increases the survival of tumour-bearing mice, and that its efficacy results from the activation of both innate and adaptative immune responses.
- Jason Park
- , Stephen H. Wrzesinski
- & Tarek M. Fahmy
-
Article |
 Tuning the autophagy-inducing activity of lanthanide-based nanocrystals through specific surface-coating peptides
Tuning the autophagy-inducing activity of lanthanide-based nanocrystals through specific surface-coating peptides
Many nanomaterials can induce cell autophagy, which can be either a concern in most in vivo situations or a benefit when exploited in cancer therapeutics. A family of short synthetic peptides that have a varied affinity to lanthanide oxide and lanthanide-based upconversion nanocrystals are now used to tune the degree of interaction between cells and nanocrystals, and thus the nanocrystals’ autophagy-inducing activity.
- Yunjiao Zhang
- , Fang Zheng
- & Long-Ping Wen
-
Article |
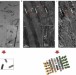 The predominant role of collagen in the nucleation, growth, structure and orientation of bone apatite
The predominant role of collagen in the nucleation, growth, structure and orientation of bone apatite
Calcium-rich non-collagenous proteins in the extracellular matrix of bone are believed to be involved in the different steps of bone mineralization. It is now shown that in the absence of these proteins collagen can initiate and orient growing apatite crystals in vitro, and influence both their structural characteristics on the atomic scale and their larger-scale three-dimensional distribution in bone.
- Yan Wang
- , Thierry Azaïs
- & Nadine Nassif
-
Article |
 Soft fibrin gels promote selection and growth of tumorigenic cells
Soft fibrin gels promote selection and growth of tumorigenic cells
Conventional methods for the selection of tumorigenic cells from cancer cell lines rely on stem-cell markers. It is now shown that soft fibrin gels promote the growth of colonies of tumorigenic cells from single cancer cells from mouse or human cancer cell lines, and that as few as ten fibrin-cultured cells can lead to the formation of tumours in mice more efficiently than marker-selected cells.
- Jing Liu
- , Youhua Tan
- & Bo Huang
-
News & Views |
 Anchoring cell-fate cues
Anchoring cell-fate cues
The spreading and differentiation of stem cells depends on the stiffness of the extracellular matrix. Now, experiments on human epidermal and mesenchymal stem cells cultured on substrates with covalently attached collagen fibres show that the cells sense and respond to the anchoring of the collagen fibres to the substrate.
- Ovijit Chaudhuri
- & David J. Mooney
-
News & Views |
 Inverse sensitivity
Inverse sensitivity
Enzyme-modified plasmonic nanoparticles that generate a signal that is larger when the concentration of the target molecule is lower can detect ultralow levels of the cancer biomarker prostate-specific antigen in whole serum.
- Mikael Käll
-
News & Views |
 Loaded-up microsponges
Loaded-up microsponges
Self-assembled microsponges of hairpin RNA polymers achieve, with one thousand times lower concentration, the same degree of gene silencing in tumour-carrying mice as conventional nanoparticle-based siRNA delivery vehicles.
- Wade W. Grabow
- & Luc Jaeger
-
News & Views |
 Charged for success
Charged for success
DNA-complexated cationic polymers with reduced charge density, high molecular weight and increased hydrophobicity show a lack of detectable cytotoxicity and efficiently deliver the apoptosis-inducing TRAIL gene to transplanted tumours in mice.
- Enrico Mastrobattista
- & Wim E. Hennink
-
News & Views |
 Know your molecules
Know your molecules
A new plasmonic sensing platform that not only allows the detection of ultrasmall quantities of biomolecules, but is also sensitive to their identity and conformational state, represents a significant advance in the study of biomolecular interactions.
- Na Liu
- & Annemarie Pucci
-
Article |
 Biodegradable poly(amine-co-ester) terpolymers for targeted gene delivery
Biodegradable poly(amine-co-ester) terpolymers for targeted gene delivery
Many synthetic polymer nanoparticles used for non-viral gene delivery contain excess cations on their surface, which makes the particles cytotoxic and the delivery of genes inefficient. Terpolymers with a low charge density, high molecular weight and increased hydrophobicity are now shown to have minimal toxicity, and to efficiently deliver the apoptosis-inducing TRAIL gene to transplanted tumours in mice.
- Jiangbing Zhou
- , Jie Liu
- & W. Mark Saltzman
-
News & Views |
 The only way is up
The only way is up
An efficient scheme that realizes broad tunability of photon upconversion in core–shell nanoparticles may lead to applications in biosensing, security labelling and more.
- Nicholas Kotov
-
Article |
 Fano-resonant asymmetric metamaterials for ultrasensitive spectroscopy and identification of molecular monolayers
Fano-resonant asymmetric metamaterials for ultrasensitive spectroscopy and identification of molecular monolayers
Plasmonic nanostructures are known to be an attractive platform for highly sensitive molecular sensors, although they often lack specificity. A plasmonic device with a sharp optical resonance tuned to biomolecules selectively captured on the surface of the device now offers a versatile yet highly specific platform for molecular sensing.
- Chihhui Wu
- , Alexander B. Khanikaev
- & Gennady Shvets
-
-
News & Views |
 Multipotency retained
Multipotency retained
Stem cells that are cultured in the laboratory differentiate in response to the mechanical properties of the substrate and its topography. It is now shown that mesenchymal stem cell multipotency is prolonged when the cells are cultured on a surface patterned with an ordered arrangement of nanoscale pits.
- Milan Mrksich
-
Letter |
 Maltodextrin-based imaging probes detect bacteria in vivo with high sensitivity and specificity
Maltodextrin-based imaging probes detect bacteria in vivo with high sensitivity and specificity
The in vivo optical detection of bacterial infections requires highly specific imaging probes with small affinity to mammalian tissue. It is now shown that fluorescent dyes that are conjugated to maltohexaose can be internalized rapidly via the bacteria-specific maltodextrin transport pathway, enabling the in vivo imaging of Escherichia coli down to 105 colony-forming units.
- Xinghai Ning
- , Seungjun Lee
- & Niren Murthy
-
Article |
 Nanoscale surfaces for the long-term maintenance of mesenchymal stem cell phenotype and multipotency
Nanoscale surfaces for the long-term maintenance of mesenchymal stem cell phenotype and multipotency
On standard tissue culture platforms, mesenchymal stem cells tend to spontaneously differentiate with the loss of multi-lineage potential. Now, a robust and reproducible nanotopographical platform has been shown to maintain stem cell phenotype and promote stem cell growth over several months whilst implicating mechanisms for the observed stem cell behaviour
- Rebecca J. McMurray
- , Nikolaj Gadegaard
- & Matthew J. Dalby
-
Letter |
 Short-term plasticity and long-term potentiation mimicked in single inorganic synapses
Short-term plasticity and long-term potentiation mimicked in single inorganic synapses
The electronic properties of inorganic devices such as memristors can be used to simulate neurological behaviour. In particular, ionic and electronic effects in a silver sulphide device are now shown to mimic short- and long-term synaptic functions.
- Takeo Ohno
- , Tsuyoshi Hasegawa
- & Masakazu Aono
-
News & Views |
 Moving under peer pressure
Moving under peer pressure
Collective cell motion in a continuous tissue is found to be guided by cooperative intercellular forces.
- Nir Gov
-
Article |
 Collective cell guidance by cooperative intercellular forces
Collective cell guidance by cooperative intercellular forces
The mechanical stresses within and between cells inside an advancing cellular monolayer are mapped experimentally. Cellular migration is found to be oriented in the direction of maximum principal stress indicating that cells collectively migrate to maintain minimal local intercellular shear stress.
- Dhananjay T. Tambe
- , C. Corey Hardin
- & Xavier Trepat
-
News & Views |
 To knot or not to knot?
To knot or not to knot?
A knot-containing protein is found to fold reversibly at biologically relevant timescales despite not having naturally evolved for this ability.
- Eugene Shakhnovich
-
News & Views |
 Gene libraries open up
Gene libraries open up
By combining gene cloning and amplification techniques, a new one-pot, parallel synthesis method for the generation of long, repetitive genes is realized. The method promises to open up the discovery of protein polymer biomaterials.
- Sheng Ding
- , Xiaoxiao Wang
- & Annelise E. Barron
-
Article |
 A highly parallel method for synthesizing DNA repeats enables the discovery of ‘smart’ protein polymers
A highly parallel method for synthesizing DNA repeats enables the discovery of ‘smart’ protein polymers
A one-pot, high-throughput method for the recombinant polymerization of monomer DNA sequences is reported. The method enables the rapid synthesis of diverse libraries of artificial repetitive polypeptides, exemplified by the isolation of protease-responsive polymers and a family of polypeptides with reversible thermally responsive behaviour.
- Miriam Amiram
- , Felipe Garcia Quiroz
- & Ashutosh Chilkoti
-
News & Views |
 Contracting to stiffness
Contracting to stiffness
Atomic force microscopy experiments on individual blood platelets reveal their dynamic contractile response to varied stiffness of the substrate.
- Allen Ehrlicher
- & John H. Hartwig
-
Letter |
 Orally delivered thioketal nanoparticles loaded with TNF-α–siRNA target inflammation and inhibit gene expression in the intestines
Orally delivered thioketal nanoparticles loaded with TNF-α–siRNA target inflammation and inhibit gene expression in the intestines
The oral delivery of small interfering RNA (siRNA) to diseased intestinal tissue is challenging because of the harsh environment created by gastrointestinal fluids and mucosa. Now, such delivery of siRNA to sites of intestinal inflammation is achieved using polythioketal nanoparticles and gene expression is successfully inhibited in the inflamed tissue.
- D. Scott Wilson
- , Guillaume Dalmasso
- & Niren Murthy
-
News & Views |
 Bundles from boundaries
Bundles from boundaries
Using a micropatterning technique, the architecture of actin networks is revealed to be influenced by the spatial organization of actin filament nucleation. Considering the geometric boundaries within live cells, implications in the realm of actin-induced cell functions are vast.
- Denis Wirtz
- & Shyam B. Khatau
-
Letter |
 Nucleation geometry governs ordered actin networks structures
Nucleation geometry governs ordered actin networks structures
Actin filaments are a principal component of the cell cytoskeleton. Using micropatterning methods, physical influences on the growth of highly ordered actin structures are investigated. The spatial organization of actin nucleation sites is discovered to play an important role in establishing the architecture of actin networks.
- Anne-Cécile Reymann
- , Jean-Louis Martiel
- & Manuel Théry
-
Review Article |
 The Fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials
The Fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials
- Boris Luk'yanchuk
- , Nikolay I. Zheludev
- & Chong Tow Chong
-
Article |
 Combinatorial development of biomaterials for clonal growth of human pluripotent stem cells
Combinatorial development of biomaterials for clonal growth of human pluripotent stem cells
Structure–property relationships between material properties and stem cell behaviour are investigated using high-throughput methods. The data identify the optimal substrates within a range of different polymeric surfaces to support the growth and self-renewal of human embryonic stem cells from fully dissociated single cells.
- Ying Mei
- , Krishanu Saha
- & Daniel G. Anderson
-
News & Views |
Quantum leaves in fact and fiction
-
Editorial |
 A matter of choice
A matter of choice
The United Kingdom's tough budget for science may force researchers to pick winners and losers. But can it work?
-
News & Views |
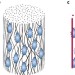 Noodle gels for cells
Noodle gels for cells
Heating and cooling of peptide amphiphile suspensions converts disorganized nanofibres into liquid-crystalline nanofibre bundles that gel on addition of salts. The noodle-shaped strings of gel can entrap and align cells.
- Timothy J. Deming
-
-
Commentary |
 Biomaterials offer cancer research the third dimension
Biomaterials offer cancer research the third dimension
To deepen understanding and hasten the development of treatments, cancer needs to be modelled more accurately in vitro; applying tissue-engineering concepts and approaches in this field could bridge the gap between two-dimensional studies and in vivo animal models.
- Dietmar W. Hutmacher
-
Article |
 Multimeric small interfering ribonucleic acid for highly efficient sequence-specific gene silencing
Multimeric small interfering ribonucleic acid for highly efficient sequence-specific gene silencing
Small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) is used to silence genes and treat conditions such as human immunodeficiency virus. Safe and efficient delivery, however, is proving problematic. A new class of biologically active siRNA polyelectrolyte complexes based on chemically self-crosslinked siRNA is presented, which shows greatly enhanced gene-silencing efficiencies in vitro and in vivo without significantly eliciting an immune response.
- Hyejung Mok
- , Soo Hyeon Lee
- & Tae Gwan Park
-
News & Views |
 Stressed-out stem cells
Stressed-out stem cells
Experiments have shown that the physical characteristics of the matrix surrounding a stem cell can affect its behaviour. This picture gets further complicated by studies of stem cells and their differentiated counterparts that show that the cells' own softness also has a clear role in how they respond to stress.
- Andrew W. Holle
- & Adam J. Engler
Browse narrower subjects
- Biochemistry
- Biological techniques
- Biophysics
- Biotechnology
- Cancer
- Cell biology
- Chemical biology
- Computational biology and bioinformatics
- Developmental biology
- Drug discovery
- Ecology
- Evolution
- Genetics
- Immunology
- Microbiology
- Molecular biology
- Neuroscience
- Physiology
- Plant sciences
- Psychology
- Stem cells
- Structural biology
- Systems biology
- Zoology

 Orbicular origins
Orbicular origins SNAREd bilayers
SNAREd bilayers A flare for cancer
A flare for cancer Replication and reproduction
Replication and reproduction