Featured
-
-
Article |
 Self-repair protects microtubules from destruction by molecular motors
Self-repair protects microtubules from destruction by molecular motors
Molecular motors destroy a microtubule lattice as they walk on it, but it is now shown that a self-healing process incorporates new dimers in the damaged regions and prevents microtubule disassembly.
- Sarah Triclin
- , Daisuke Inoue
- & Manuel Théry
-
Article |
 Living materials with programmable functionalities grown from engineered microbial co-cultures
Living materials with programmable functionalities grown from engineered microbial co-cultures
A symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast is used to fabricate bacterial cellulose-based living materials that respond to external cues and adapt their structural and functional properties, with implications for sensing and catalytic applications.
- Charlie Gilbert
- , Tzu-Chieh Tang
- & Tom Ellis
-
Editorial |
 A Nobel Prize for genetic scissors
A Nobel Prize for genetic scissors
After years of speculation over who would be recognized for the pioneering work on the gene editing tool CRISPR–Cas9, the Nobel Prize in Chemistry has finally been awarded to Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer Doudna.
-
News & Views |
 Guiding tissue-scale self-organization
Guiding tissue-scale self-organization
A bioprinting approach that utilizes organoid-forming stem cells as a living ink within hydrogels guides tissue-scale self-organization to generate more realistic gastrointestinal and vascular tissue constructs.
- Zev J. Gartner
- & Jennifer L. Hu
-
Article |
 Tumour-associated macrophages drive stromal cell-dependent collagen crosslinking and stiffening to promote breast cancer aggression
Tumour-associated macrophages drive stromal cell-dependent collagen crosslinking and stiffening to promote breast cancer aggression
It is now shown that tumour-associated macrophages recruited early during tumour evolution stimulate stromal fibroblasts to express collagen crosslinking enzymes and that the stromal expression, particularly of lysyl hydroxylase 2, can predict survival in a patient cohort.
- Ori Maller
- , Allison P. Drain
- & Valerie M. Weaver
-
Article |
 Cofactor-free oxidase-mimetic nanomaterials from self-assembled histidine-rich peptides
Cofactor-free oxidase-mimetic nanomaterials from self-assembled histidine-rich peptides
Self-assembling, histidine-rich peptides with similar catalytic functions as those of haem-dependent peroxidases are reported. These findings may have implications for the design of cofactor-free catalytic nanomaterials.
- Qing Liu
- , Kaiwei Wan
- & Baoquan Ding
-
Article |
 Cellular extrusion bioprinting improves kidney organoid reproducibility and conformation
Cellular extrusion bioprinting improves kidney organoid reproducibility and conformation
Extrusion-based bioprinting has been shown to rapidly and reproducibly generate kidney organoids from a cell-only paste, with the number and maturation of functional units within the kidney tissue capable of being further improved by bioprinting tissue sheets.
- Kynan T. Lawlor
- , Jessica M. Vanslambrouck
- & Melissa H. Little
-
News & Views |
 Just dose it
Just dose it
A dose threshold of one trillion nanoparticles in mice has been discovered and is shown to be crucial for overwhelming the nanoparticle uptake kinetics of liver Kupffer cells and for ensuring efficient nanoparticle delivery into solid tumours upon intravenous administration.
- Twan Lammers
-
Review Article |
 Stem-cell-based embryo models for fundamental research and translation
Stem-cell-based embryo models for fundamental research and translation
This Review highlights the recent emergence of stem-cell-derived embryo models for the purpose of advancing our understanding of mammalian embryology as well as their potential uses in regenerative and reproductive medicine.
- Jianping Fu
- , Aryeh Warmflash
- & Matthias P. Lutolf
-
Review Article |
 Rethinking organoid technology through bioengineering
Rethinking organoid technology through bioengineering
This Review provides an overview of bioengineering technologies that can be harnessed to facilitate the culture, self-organization and functionality of human pluripotent stem cell-derived organoids.
- Elena Garreta
- , Roger D. Kamm
- & Nuria Montserrat
-
Article |
 Activating an adaptive immune response from a hydrogel scaffold imparts regenerative wound healing
Activating an adaptive immune response from a hydrogel scaffold imparts regenerative wound healing
Microporous annealed-particle degradable scaffolds have been developed and shown to induce type 2 innate and adaptive immune response that facilitated skin wound healing.
- Donald R. Griffin
- , Maani M. Archang
- & Philip O. Scumpia
-
Comment |
 Towards data-driven next-generation transmission electron microscopy
Towards data-driven next-generation transmission electron microscopy
Electron microscopy touches on nearly every aspect of modern life, underpinning materials development for quantum computing, energy and medicine. We discuss the open, highly integrated and data-driven microscopy architecture needed to realize transformative discoveries in the coming decade.
- Steven R. Spurgeon
- , Colin Ophus
- & Mitra L. Taheri
-
News & Views |
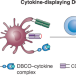 Dendritic cell tracking and modulation
Dendritic cell tracking and modulation
In situ metabolic labelling and targeted modulation of dendritic cells has been achieved using a hydrogel system in combination with covalent capture of antigens and adjuvants, facilitating improved tumour-specific immune response.
- Joshua M. Gammon
- & Christopher M. Jewell
-
Article |
 Stress fibres are embedded in a contractile cortical network
Stress fibres are embedded in a contractile cortical network
The mechanism of stress fibre assembly by the coalescence of actin filaments in the cell cortex has now been found to account for the transmission of mechanical forces throughout the entire cell along stress fibres.
- Timothée Vignaud
- , Calina Copos
- & Laetitia Kurzawa
-
Letter |
 Recapitulating macro-scale tissue self-organization through organoid bioprinting
Recapitulating macro-scale tissue self-organization through organoid bioprinting
A 3D bioprinting approach has been developed to facilitate tissue morphogenesis by directly depositing organoid-forming stem cells in an extracellular matrix, with the ability to generate intestinal epithelia and branched vascular tissue constructs.
- Jonathan A. Brassard
- , Mike Nikolaev
- & Matthias P. Lutolf
-
Article |
 Wnt-modified materials mediate asymmetric stem cell division to direct human osteogenic tissue formation for bone repair
Wnt-modified materials mediate asymmetric stem cell division to direct human osteogenic tissue formation for bone repair
Wnt3a protein has been immobilized on a biocompatible bandage and is now shown to induce oriented asymmetric cell division of human skeletal stem cells and can also promote bone tissue repair in vivo.
- Yoshihisa Okuchi
- , Joshua Reeves
- & Shukry J. Habib
-
Article |
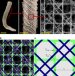 Mechanically robust lattices inspired by deep-sea glass sponges
Mechanically robust lattices inspired by deep-sea glass sponges
Computational analysis and mechanical testing demonstrate that the skeletal system of a marine sponge has, through the course of evolution, achieved a near-optimal resistance to buckling.
- Matheus C. Fernandes
- , Joanna Aizenberg
- & Katia Bertoldi
-
Article |
 ILC1 drive intestinal epithelial and matrix remodelling
ILC1 drive intestinal epithelial and matrix remodelling
Type-1 innate lymphoid cells have been shown to drive intestinal epithelial proliferation and extracellular matrix remodelling through TGF-β1 secretion, which could exacerbate inflammatory bowel disease comorbidities such as cancer and fibrosis.
- Geraldine M. Jowett
- , Michael D. A. Norman
- & Eileen Gentleman
-
Article |
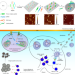 A DNA nanodevice-based vaccine for cancer immunotherapy
A DNA nanodevice-based vaccine for cancer immunotherapy
A DNA nanodevice vaccine has been developed and utilized to stimulate a tumour-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte response in vivo, leading to the inhibition of tumour growth as well as prevention of metastasis.
- Shaoli Liu
- , Qiao Jiang
- & Baoquan Ding
-
News & Views |
 Apical poles without neighbouring cells
Apical poles without neighbouring cells
Functional single-cell liver hemi-canaliculi have been generated in a synthetic microenvironment using a reductionist approach. It is shown that the interaction between the extracellular matrix and static cadherin is sufficient to develop an apicobasal polarity independently of the contact with neighbouring cells.
- Covadonga Díaz-Díaz
- & Fernando Martín-Belmonte
-
Review Article |
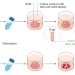 Somatic cell-derived organoids as prototypes of human epithelial tissues and diseases
Somatic cell-derived organoids as prototypes of human epithelial tissues and diseases
This Review highlights approaches used to generate somatic cell-derived organoids for modelling epithelial tissue to understand disease progression and how they are employed in preclinical drug screening.
- Masayuki Fujii
- & Toshiro Sato
-
Article |
 A natural impact-resistant bicontinuous composite nanoparticle coating
A natural impact-resistant bicontinuous composite nanoparticle coating
A coating made from densely packed hydroxyapatite particles in an organic matrix endows the dactyl club of mantis shrimps with high stiffness and energy damping.
- Wei Huang
- , Mehdi Shishehbor
- & David Kisailus
-
Article |
 Monolithic digital patterning of polydimethylsiloxane with successive laser pyrolysis
Monolithic digital patterning of polydimethylsiloxane with successive laser pyrolysis
A laser-based patterning method enables the fast fabrication of high-quality two- and three-dimensional features in polydimethylsiloxane for microfluidics and biomedical applications.
- Jaeho Shin
- , Jihoon Ko
- & Seung Hwan Ko
-
Article |
 The dose threshold for nanoparticle tumour delivery
The dose threshold for nanoparticle tumour delivery
Efficient nanoparticle delivery into tumours has been a challenge in the field. It is now shown that the efficiency can be improved substantially when the dose breaches a specific threshold.
- Ben Ouyang
- , Wilson Poon
- & Warren C. W. Chan
-
Editorial |
 COVID-19 therapies and vaccine landscape
COVID-19 therapies and vaccine landscape
Within a few weeks of the novel coronavirus genome sequence being published, numerous therapies and vaccines have entered clinical trials with a few showing great promise in alleviating symptoms and accelerating recovery.
-
Comment |
 Next-generation vaccine platforms for COVID-19
Next-generation vaccine platforms for COVID-19
Consensus among experts is that only an effective COVID-19 vaccine will end the pandemic. This Comment focuses on how this pandemic has accelerated the development of vaccine platforms distinct from classical vaccines; these novel platforms may also increase the response time when new viruses emerge in the future.
- Debby van Riel
- & Emmie de Wit
-
News & Views |
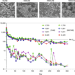 Long-acting antiretroviral therapy
Long-acting antiretroviral therapy
Nanoformulations of cabotegravir prodrugs have been developed to prolong the pharmacokinetics of the antiretroviral agent. They can be present in the plasma of mice and non-human primates for a year following a single injection.
- Vicente Soriano
- , Pablo Barreiro
- & Carmen de Mendoza
-
News & Views |
 Oncogenetic engagement with mechanosensing
Oncogenetic engagement with mechanosensing
Reprogramming normal cells into tumour precursors involves complex reconditioning of the tissue microenvironment. Cumulative integration of genetic drivers with extrinsic mechanical inputs is now shown to engage YAP/TAZ to rewire cell mechanics and initiate tumorigenic reprogramming.
- Sayan Chakraborty
- & Wanjin Hong
-
News & Views |
 Syndecan-4 forces integrins to cooperate
Syndecan-4 forces integrins to cooperate
While integrin-based adhesions are thought to underlie many aspects of cell response to localized tension, another matrix receptor, syndecan-4, has now been shown to act as a mechanosensor, which triggers cell-wide integrin activation and adhesion reinforcement.
- Christophe Guilluy
- & Monika E. Dolega
-
Article |
 Tracking intracellular forces and mechanical property changes in mouse one-cell embryo development
Tracking intracellular forces and mechanical property changes in mouse one-cell embryo development
Mechanical properties and forces sculpt the behaviour of cells in living organisms. Silicon-based nanochips implanted into mouse one-cell embryos have been used to reveal mechanical changes during the early onset of embryonic development.
- Marta Duch
- , Núria Torras
- & Anthony C. F. Perry
-
Article |
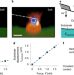 Cortical cell stiffness is independent of substrate mechanics
Cortical cell stiffness is independent of substrate mechanics
Atomic force microscopy indentation measurements of cells cultured on soft substrates may result in an underestimation of cell stiffness. A model has now been developed that takes this soft substrate effect into account, revealing that cortical cell stiffness is largely independent of substrate mechanics.
- Johannes Rheinlaender
- , Andrea Dimitracopoulos
- & Kristian Franze
-
Comment |
 Materials science approaches in the development of broad-spectrum antiviral therapies
Materials science approaches in the development of broad-spectrum antiviral therapies
The COVID-19 pandemic has reignited efforts to develop materials science innovations aimed at stopping viral infections. One of the greatest opportunities lies in developing broad-spectrum antiviral technologies that work against many viruses, which could be the key to thwarting outbreaks in the future.
- Nam Joon Cho
- & Jeffrey S. Glenn
-
Article |
 Metabolic labeling and targeted modulation of dendritic cells
Metabolic labeling and targeted modulation of dendritic cells
Dendritic cells concentrated in vivo within a hydrogel have been metabolically tagged with azido groups to enable tracking as well as delivery of antigens, adjuvants and cytokines, thereby facilitating targeted immunomodulation.
- Hua Wang
- , Miguel C. Sobral
- & David J. Mooney
-
Article |
 A year-long extended release nanoformulated cabotegravir prodrug
A year-long extended release nanoformulated cabotegravir prodrug
Nanoformulated long-acting cabotegravir prodrugs are shown to be capable of extending the native drug’s antiretroviral activity, biodistribution and pharmacokinetics for up to 12 months in mice and rhesus macaques.
- Tanmay A. Kulkarni
- , Aditya N. Bade
- & Howard E. Gendelman
-
Article |
 Biomimetic niches reveal the minimal cues to trigger apical lumen formation in single hepatocytes
Biomimetic niches reveal the minimal cues to trigger apical lumen formation in single hepatocytes
The polarity of primary hepatocytes has now been shown to be inducible at the single-cell level by passive artificial micro-niches, indicating that the early development of polarity occurs largely independently of the types and response of the neighbouring cells.
- Yue Zhang
- , Richard De Mets
- & Virgile Viasnoff
-
News & Views |
 A nanoparticle’s pathway into tumours
A nanoparticle’s pathway into tumours
New evidence now suggests that the dominant mechanism of extravasation of nanoparticles into solid tumours may be through an active process of endothelial transcytosis.
- Irene de Lázaro
- & David J. Mooney
-
News & Views |
 Pushing the limit on laminopathies
Pushing the limit on laminopathies
Mutations in lamins in skeletal muscle cells have been shown to reduce nuclear stability, increase nuclear envelope rupture, and induce DNA damage and cell death. New research shows that limiting mechanical loads can rescue myofibre function and viability.
- Joel C. Eissenberg
- & Susana Gonzalo
-
Why it Matters |
 Sipping a bit of science
Sipping a bit of science
Laura Benzonana and Nikos Sgantzis reflect on their experience as organizers for Pint of Science in Greece.
- Laura Benzonana
- & Nikolaos Sgantzis
-
Article |
 Reprogramming normal cells into tumour precursors requires ECM stiffness and oncogene-mediated changes of cell mechanical properties
Reprogramming normal cells into tumour precursors requires ECM stiffness and oncogene-mediated changes of cell mechanical properties
Receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)–Ras oncogenes have now been shown to reprogram normal primary human and mouse cells into tumour precursors by empowering cellular mechanotransduction, in a process requiring permissive extracellular-matrix rigidity and intracellular YAP/TAZ/Rac mechanical signalling sustained by activated oncogenes.
- Tito Panciera
- , Anna Citron
- & Stefano Piccolo
-
News & Views |
 Life and death agendas of actin filaments
Life and death agendas of actin filaments
Cancer cells have now been shown to lack rigidity-sensing due to alteration in cytoskeletal sensor proteins, but can be reversed from a transformed to a rigidity-dependent growth state by the sensor proteins, resulting in restoration of contractility and adhesion.
- Edna C. Hardeman
- & Peter W. Gunning
-
News & Views |
 Proteins tailor pore geometry
Proteins tailor pore geometry
Using organic solvent shortens formation time of membrane nanosheets comprising proteins and copolymers, while tuning protein structure tailors the pore geometry, resulting in superior water permeation.
- Andrew G. Livingston
- & Zhiwei Jiang
-
News & Views |
 Bringing order to the matrix
Bringing order to the matrix
Aligned anisotropic organization of the extracellular matrix by fibroblasts has now been shown to depend on cell reorientation following collision, with the cell collision guidance dependent on the transcription factor, TFAP2C.
- Paolo P. Provenzano
-
Article |
 Rapid fabrication of precise high-throughput filters from membrane protein nanosheets
Rapid fabrication of precise high-throughput filters from membrane protein nanosheets
Protein channels are highly selective, but application in membranes is limited due to low protein content. Here, protein channels are embedded into block copolymers to form nanosheets using rapid solvent casting, with better water permeability and similar molecular exclusions relative to other membrane systems.
- Yu-Ming Tu
- , Woochul Song
- & Manish Kumar
-
Article |
 Protease-activated receptor signalling initiates α5β1-integrin-mediated adhesion in non-haematopoietic cells
Protease-activated receptor signalling initiates α5β1-integrin-mediated adhesion in non-haematopoietic cells
As in haematopoietic cells and platelets, agonist binding to protease-activated receptors PAR1 and PAR2 in non-haematopoietic cells also triggers signalling pathways that lead to α5β1-integrin-mediated cell adhesion.
- Patrizia M. Spoerri
- , Nico Strohmeyer
- & Daniel J. Müller
-
Article |
 The entry of nanoparticles into solid tumours
The entry of nanoparticles into solid tumours
The dominant mechanism of nanoparticle entry into solid tumours has now been shown to be an active trans-endothelial pathway rather than the currently established passive transport via inter-endothelial gaps.
- Shrey Sindhwani
- , Abdullah Muhammad Syed
- & Warren C. W. Chan
-
Article |
 Syndecan-4 tunes cell mechanics by activating the kindlin-integrin-RhoA pathway
Syndecan-4 tunes cell mechanics by activating the kindlin-integrin-RhoA pathway
A mechanism of cell response to localized tension shows that syndecan-4 synergizes with EGFR to elicit a mechanosignalling cascade that leads to adaptive cell stiffening through PI3K/kindlin-2 mediated integrin activation.
- Antonios Chronopoulos
- , Stephen D. Thorpe
- & Armando E. del Río Hernández
-
News & Views |
 To buckle or not to buckle
To buckle or not to buckle
Epithelial layers under compression avoid buckling by active contraction, but only up to a well-defined threshold at 35% strain, beyond which buckling occurs.
- Ulrich S. Schwarz
-
News & Views |
 Materials modulate immunity and gut microbiome
Materials modulate immunity and gut microbiome
In a murine model of acute colitis, hyaluronic acid–bilirubin-based nanomaterials have been shown to modulate immune response and the gut microbiome, as well as restore the epithelial barrier.
- Ankur Singh
-
Article |
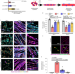 Mutant lamins cause nuclear envelope rupture and DNA damage in skeletal muscle cells
Mutant lamins cause nuclear envelope rupture and DNA damage in skeletal muscle cells
Lamin mutations responsible for muscular dystrophy are shown to reduce nuclear envelope stability, resulting in mechanically induced nuclear envelope rupture, DNA damage and activation of DNA damage response pathways that lead to muscle cell death. Preventing nuclear envelope damage by reducing cytoskeletal forces on the nucleus improves muscle fibre health and function.
- Ashley J. Earle
- , Tyler J. Kirby
- & Jan Lammerding
Browse narrower subjects
- Biochemistry
- Biological techniques
- Biophysics
- Biotechnology
- Cancer
- Cell biology
- Chemical biology
- Computational biology and bioinformatics
- Developmental biology
- Drug discovery
- Ecology
- Evolution
- Genetics
- Immunology
- Microbiology
- Molecular biology
- Neuroscience
- Physiology
- Plant sciences
- Psychology
- Stem cells
- Structural biology
- Systems biology
- Zoology

 Basement membrane stiffness determines metastases formation
Basement membrane stiffness determines metastases formation