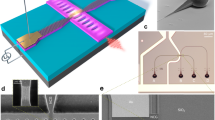
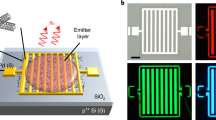
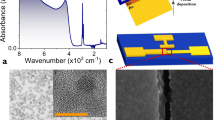
Abstract
Recent studies of the optical properties of semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes1,2,3,4,5,6 suggest that these truly nanometre-scale systems have a promising future in nanophotonics, in addition to their well-known potential in electronics7,8. Semiconducting single-walled nanotubes have a direct, diameter-dependent bandgap8 and can be excited readily by current injection, which makes them attractive as nano-emitters. The electroluminescence is spectrally broad, spatially non-directional, and the radiative yield is low5,9. Here we report the monolithic integration of a single, electrically excited, semiconducting nanotube transistor with a planar λ/2 microcavity10,11,12,13, thus taking an important first step in the development of nanotube-based nanophotonic devices. The spectral full-width at half-maximum of the emission is reduced from ∼300 to ∼40 nm at a cavity resonance of 1.75 µm, and the emission becomes highly directional. The maximum enhancement of the radiative rate is estimated to be 4. We also show that both the optically and electrically excited luminescence of single-walled nanotubes involve the same E11 excitonic transition.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
O'Connell, M. J. et al. Bandgap fluorescence from individual single-walled carbon nanotubes. Science 297, 593–596 (2002).
Bachilo, S. M. et al. Structure-assigned optical spectra of single-walled carbon nanotubes. Science 298, 2361–2366 (2002).
Misewich, J. A. et al. Electrically induced optical emission from a carbon nanotube FET. Science 300, 783–786 (2003).
Freitag, M. et al. Mobile ambipolar domain in carbon-nanotube infrared emitters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 076803 (2004).
Chen, J. et al. Bright infrared emission from electrically induced excitons in carbon nanotubes. Science 310, 1171–1174 (2005).
Freitag, M., Martin, Y., Misewich, J. A., Martel, R. & Avouris, P. Photoconductivity of single carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett. 3, 1067–1071 (2003).
Avouris, P., Chen, Z. & Perebeinos, V. Carbon-based electronics. Nature Nanotech. 2, 605–615 (2007).
Biercuk, M. J., Ilani, S., Marcus, C. M. & McEuen, P. L. in Carbon Nanotubes: Advanced Topics in the Synthesis, Structure, Properties and Applications (eds Jorio, A., Dresselhaus, M. S. & Dresselhaus, G.) (Springer, Berlin, 2008).
Marty, L. et al. Exciton formation and annihilation during 1D impact excitation of carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 136803 (2006).
Brorson, S. D., Yokoyama, H. & Ippen, E. Spontaneous emission rate alteration in optical waveguide structures. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 26, 1492–1499 (1990).
Yamamoto, Y., Machida, S. & Bjork, G. Micro-cavity semiconductor lasers with controlled spontaneous emission. Opt. Quantum Electron. 24, S215–S243 (1992).
Björk, G. On the spontaneous lifetime change in an ideal planar microcavity-transition from a mode continuum to quantized modes. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 30, 2314–2318 (1994).
Abram, I., Robert, I. & Kuszelewicz, R. Spontaneous emission control in semiconductor microcavities with metallic or Bragg mirrors. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 34, 71–76 (1998).
Yuan, Z. et al. Electrically driven single-photon source. Science 295, 102–105 (2002).
Steiner, M., Qian, H., Hartschuh, A. & Meixner, A. J. Controlling non-equilibrium phonon populations in single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett. 8, 2239–2242 (2007).
Vahala, K. J. Optical microcavities. Nature 424, 839–846 (2003).
Steiner, M. et al. Microcavity-controlled single-molecule fluorescence. ChemPhysChem 6, 2190–2196 (2005).
Xia, F., Sekaric, L. & Vlasov, Y. A. Ultra-compact optical buffers on a silicon chip. Nature Photon. 1, 65–71 (2007).
Tans, S. J., Verscheuren, A. R. M. & Dekker, C. Room-temperature transistor based on a single carbon nanotube. Nature 393, 49–52 (1998).
Martel, R., Schmidt, T., Shea, H. R., Hertel, T. & Avouris, P. Single- and multi-wall carbon nanotube field-effect transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 2447–2449 (1998).
Martel, R. et al. Ambipolar electrical transport in semiconducting single-wall carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 256805 (2001).
Heinze, S. et al. Carbon nanotubes as Schottky barrier transistors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 106801 (2002).
Dresselhaus, M. S., Dresselhaus, G., Saito, R. & Jorio, A. Raman spectroscopy of carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rep. 409, 47–99 (2005).
Perebeinos, V. & Avouris, P. Impact excitation by hot carriers in carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B 74, 121410R (2006).
McGuire, D. L. & Pulfrey, D. L. A multi-scale model for mobile and localized electroluminescence in carbon nanotube field-effect transistors. Nanotechnology 17, 5805–5811 (2006).
Weisman, R. B. & Bachilo, S. M. Dependence of optical transition energies on structure for single-walled carbon nanotubes in aqueous suspension: an empirical Kataura plot. Nano Lett. 3, 1235–1238 (2003).
Lefebvre, J., Austing, D. G., Bond, J. & Finnie, P. Photoluminescence imaging of suspended single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett. 6, 1603–1608 (2006).
Song, B. S., Noda, S., Asano, T. & Akahane, Y. Ultra-high-Q photonic double-heterostructure nanocavity. Nature Mater. 4, 207–210 (2005).
Noda, S. Seeking the ultimate nanolaser. Science 314, 260–261 (2006).
Murakami, Y. & Kono, J. Nonlinear photoluminescence excitation spectroscopy of carbon nanotubes: exploring the upper density limit of one-dimensional excitons. Preprint at http://arxiv.org/abs/0804.3190 (2008).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank M. Freitag, Z. Chen, Yu. A. Vlasov, S. Assefa and W. G. Green for helpful discussions, J. Tsang and M. Kinoshita for help with the emission spectra measurements, J. Small for help with the cavity Q measurement, B. Ek for technical support and Central Scientific Services in IBM Thomas J. Watson Research Center for metal deposition and mask fabrications.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, F., Steiner, M., Lin, Ym. et al. A microcavity-controlled, current-driven, on-chip nanotube emitter at infrared wavelengths. Nature Nanotech 3, 609–613 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.241
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.241
This article is cited by
-
Ultralow mode-volume photonic crystal nanobeam cavities for high-efficiency coupling to individual carbon nanotube emitters
Nature Communications (2014)
-
Electrically tunable excitonic light-emitting diodes based on monolayer WSe2 p–n junctions
Nature Nanotechnology (2014)
-
Nanoplasmonic colloidal suspensions for the enhancement of the luminescent emission from single-walled carbon nanotubes
Nano Research (2013)
-
Doping-free carbon nanotube optoelectronic devices
Chinese Science Bulletin (2012)
-
Efficient narrow-band light emission from a single carbon nanotube p–n diode
Nature Nanotechnology (2010)