Abstract
Objective:
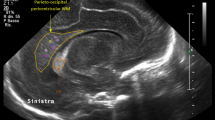
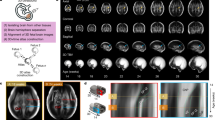
Three-dimensional ultrasound (3D-US) offers new perspectives in cerebral imaging.
Study Design:
This prospective study aimed to determine whether 3D-US is appropriate to assess cortical development of the premature brain, and compare it to previously established reference values assessed by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Preterm infants with a gestational age (GA) of <32 weeks were examined by serial 3D-US scans.
Result:
Data of 30 patients with normal neurological development at the age of 5 years were included in the analysis. Cortical development was graded according to a five-point scoring system, and data were stratified into 6 age groups. Cortical developmental scores were established for various brain regions. In the frontal and frontoparietal regions, 3D-US reference values differed from published MRI reference values, but were consistent with the published data in all other regions.
Conclusion:
3D-US reference values facilitate routine diagnostics and enable the evaluation of cortical development in preterm infants.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leijser LM, de Bruine FT, Steggerda SJ, van der Grond J, Walther FJ, van Wezel-Meijler G . Brain imaging findings in very preterm infants throughout the neonatal period: part I. Incidences and evolution of lesions, comparison between ultrasound and MRI. Early Hum Dev 2009; 85: 101–109.
Shankaran S, Slovis TL, Bedard MP, Poland RL . Sonographic classification of intracranial hemorrhage. a prognostic indicator of mortality, morbidity, and short-term neurological outcome. J Pediatr 1982; 100: 469–475.
McMenamin JB, Shackelford GD, Volpe JJ . Outcome of neonatal intraventricular hemorrhage with periventricular echodense lesion. Ann Neurol 1984; 15: 285–290.
Hintz SR, O'Shea M . Neuroimaging and neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants. Semin Perinatol 2008; 38 (1): 11–19.
Woodward LJ, Anderson PJ, Austin N, Howard K, Inder TE . Neonatal MRI to predict neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants. NEJM 2006; 355: 685–694.
Deipolyi AR, Mukherjee P, Gill K, Henry RG, Partridge SC, Veeraraghavan S et al. Comparing microstructural and macrostructural development of the cerebral cortex in premature newborns; diffusion tensor imaging versus cortical gyration. NeuroImage 2005; 27: 579–586.
Haiden N, Klebermass K, Rücklinger E, Berger A, Prusa AR, Rohrmeister K et al. 3D ultrasonographic imaing of the cerebral ventricular system in very low birth weight infants. Ultrasound in Med & Biol 2005; 31: 7–14.
Riccabona M, Nelson TR, Weitzer C, Resch B, Pretorius DP . Potential of three-dimensional ultrasound in neonatal and paediatric neurosonography. Eur Radiol 2003; 13: 2082–2093.
Ruoss K, Lövblad K, Schroth G, Moessinger AC, Fusch C . Brain development (sulci and gyri) as assessed by early postnatal MR imaging in preterm and term newborn infants. Neuropediatrics 2001; 32: 69–74.
Pistorius LR, Stoutenbeek P, Groenendaal F, De Vries L, Manten G, Mulder E et al. Grade and symmetry of normal fetal cortical development: a longitudinal two- and three-dimensional ultrasound study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2010; 36: 700–708.
Ekblad M, Korkeila J, Parkkola R, Lapinleimu H, Haataja L, Lehtonen L . Maternal smoking during pregnancy and regional brain volumes in preterm infants. J Pediatr 2010; 156 (2): 185–190.
Peterson BS, Vohr B, Staib LH, Cannistraci BA, Dolberg BA, Schneider KC et al. Regional brain volume abnormalities and long-term cognitive outcome in preterm infants. JAMA 2000; 284 (15): 1939–1947.
van der Knaap MS, van Wezel-Meijler G, Barth PG, Barkhof F, Ader HJ, Valk J . Normal gyration and sulcation in preterm and term neonates: appearance on MR images. Radiology 1996; 200 (2): 389–396.
Zubiaurre-Elorza L, Soria-Pastor S, Junque C, Vendrell P, Padilla N, Rametti G et al. Magnetic resonance imaging study of cerebral sulci in low-risk preterm children. Int J Devl Neuroscience 2009; 27 (6): 559–565.
Papile LN, Burnstein J, Burnstein R, Koffler H . Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birthweight less than 1500 g. J Pediatr 1978; 92: 529–534.
de Vries LS, Eken P, Dubowitz LMS . The spectrum of leucomalacia using cranial ultrasound. Behav Brain Res 1992; 49: 1–6.
Melchers P . Manual for Kaufmann assessment battery for children. Swets&Zeitlinger, Frankfurt/Main, 1991.
Beery KE, Buktenica NA, Beery NA . Manual 5th edition for Assessment of visual-motor integration. MHS: Ontario, Canada, 2004.
Dubois J, Benders M, Cachia A, Lazeyras F, Ha-Vinh Leuchter R, Sizonenko SV et al. Mapping the early cortical foldong process in the preterm newborn brain. Cerebral Cortex 2008; 18: 1444–1454.
Soria-Pastor S, Padilla N, Zubiaurre-Elorza L, Ibarretxe-Bilbao N, Botet F, Costas-Moragas C et al. Decreased regional brain volume and cognitive impairment in preterm children at low risk. Pediatrics 2009; 124: e1161–e1170.
Ajayi-Obe M, Saeed N, Cowan FM, Rutherford MA, Edwards AD . Reduced development of cerebral cortex in extremely preterm infants. Lancet 2000; 356 (9236): 1162–1163.
Gimenez M, Dunque C, Vendrell P, Narberhaus A, Bargello N, Botet F et al. Abnormal orbitofrontal development due to prematurity. Neurology 2006; 67: 1818–1822.
Peterson BS, Anderson AW, Ehrenkranz R, Staib LH, Tageldin M, Colson E et al. Regional brain volumes and their later neurodevelopmental correlates in term and preterm infants. Pediatrics 2003; 111 (5 pt 1): 939–948.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from the “Medizinisch-Wissenschaftlichen Fonds des Bürgermeisters der Bundeshauptstadt Wien” (medical-scientific fund of the Major of Vienna) project number 1776.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Journal of Perinatology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klebermass-Schrehof, K., Moerth, S., Vergesslich-Rothschild, K. et al. Regional cortical development in very low birth weight infants with normal neurodevelopmental outcome assessed by 3D-ultrasound. J Perinatol 33, 533–537 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2012.156
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2012.156