Featured
-
-
Article |
 Data-driven discovery of a universal indicator for metallic glass forming ability
Data-driven discovery of a universal indicator for metallic glass forming ability
The glass forming ability of alloys is found to be strongly correlated with the full-width at half-maximum of the first diffraction peak in the X-ray diffraction pattern, which facilitates the discovery of bulk metallic glass compositions.
- Ming-Xing Li
- , Yi-Tao Sun
- & Yan-Hui Liu
-
News & Views |
 Built from connected nested tubes
Built from connected nested tubes
Nanoarchitected carbon composed of intricate tube-in-tube beams connected with nanostruts has been fabricated, achieving both ultralightweight and ultrahigh modulus.
- Yujia Wang
- & Xiaoyan Li
-
News & Views |
 Nano goes the distance
Nano goes the distance
Centimetre-scale crack-free metal nanolattices are realized, enabling outstanding high tensile strength in low-density materials.
- Andreas Stein
- & Nathan A. Mara
-
Article |
 Ultra-low-density digitally architected carbon with a strutted tube-in-tube structure
Ultra-low-density digitally architected carbon with a strutted tube-in-tube structure
A nanoscale tube-in-tube sandwich structure is generated by a two-step templating-pyrolysis process, which strengthens the log-pile carbon architecture and slows down the decrease of stiffness with decreasing density.
- Jianchao Ye
- , Ling Liu
- & Juergen Biener
-
Article |
 Three-dimensional atomic packing in amorphous solids with liquid-like structure
Three-dimensional atomic packing in amorphous solids with liquid-like structure
Atomic electron tomography is used to determine the three-dimensional atomic structure of monatomic amorphous solids with liquid-like structure, which is characterized by the existence of pentagonal bipyramid networks with medium-range order.
- Yakun Yuan
- , Dennis S. Kim
- & Jianwei Miao
-
News & Views |
 Visualized atom by atom
Visualized atom by atom
The processes of metallic asperities moving across each other, which are decisive in most machinery, have been visualized at the atomic scale, revealing unexpected behaviour especially when under tensile stress.
- Udo D. Schwarz
-
Article |
 UItra-low friction and edge-pinning effect in large-lattice-mismatch van der Waals heterostructures
UItra-low friction and edge-pinning effect in large-lattice-mismatch van der Waals heterostructures
MoS2/graphite and MoS2/h-BN interfaces are shown to have ultra-low friction coefficients, whereas edges and interface steps mainly contribute to the friction force.
- Mengzhou Liao
- , Paolo Nicolini
- & Guangyu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical heterogeneity enhances hydrogen resistance in high-strength steels
Chemical heterogeneity enhances hydrogen resistance in high-strength steels
Typically undesired chemically heterogeneous microstructures are shown to enhance the resistance of high-strength steel against hydrogen embrittlement, with no loss in strength or ductility.
- Binhan Sun
- , Wenjun Lu
- & Dierk Raabe
-
Article |
 Achieving adjustable elasticity with non-affine to affine transition
Achieving adjustable elasticity with non-affine to affine transition
A non-affine to affine transition in elasticity occurs with the change of system topology in a packing-derived network, which enables the tuning of elastic moduli and Poisson’s ratio.
- Xiangying Shen
- , Chenchao Fang
- & Lei Xu
-
Article |
 Centimetre-scale crack-free self-assembly for ultra-high tensile strength metallic nanolattices
Centimetre-scale crack-free self-assembly for ultra-high tensile strength metallic nanolattices
Metal nanolattices are fabricated at an unprecedented scale by using a crack-free self-assembly method. The dense nanostructures enable tensile strengths that approach the theoretical limit.
- Zhimin Jiang
- & James H. Pikul
-
Article |
 Tension–compression asymmetry in amorphous silicon
Tension–compression asymmetry in amorphous silicon
Submicrometre-sized amorphous silicon samples show an unusually large tensile strength relative to the compressive strength, which is due to the reduced shear modulus and the activation energy barrier for shear transformations under compression.
- Yuecun Wang
- , Jun Ding
- & Zhiwei Shan
-
Letter |
 A medium-range structure motif linking amorphous and crystalline states
A medium-range structure motif linking amorphous and crystalline states
An intermediate cube phase with a medium-range order structure is identified in Pd-Ni-P metallic glass, which links the amorphous and crystalline phases.
- Si Lan
- , Li Zhu
- & Xun-Li Wang
-
News & Views |
 Interacting with current
Interacting with current
Very low-density pulsed current is shown to sharply change the dislocation evolution pattern of Ti–Al alloy with 7 at.% Al, enhancing its strength and ductility.
- Stefan Zaefferer
-
Article |
 High-strength scalable graphene sheets by freezing stretch-induced alignment
High-strength scalable graphene sheets by freezing stretch-induced alignment
Stretch-induced alignment of graphene sheets is frozen by sequential covalent and π–π bridging, leading to high in-plane isotropic strength of 1.55 GPa. The graphene sheets are fabricated at near room temperature and are scalable.
- Sijie Wan
- , Ying Chen
- & Qunfeng Cheng
-
Letter |
 A percolation theory for designing corrosion-resistant alloys
A percolation theory for designing corrosion-resistant alloys
A percolation theory of alloy passivation is developed accounting for selective dissolution and the quantity of metal dissolved during the primary passivation process, which provides a quantitative way for designing corrosion-resistant alloy compositions.
- Yusi Xie
- , Dorota M. Artymowicz
- & Karl Sieradzki
-
Article |
 Defect reconfiguration in a Ti–Al alloy via electroplasticity
Defect reconfiguration in a Ti–Al alloy via electroplasticity
Transmission electron microscopy reveals the electroplastic effects in a Ti–Al alloy, which can be uncoupled from Joule heating effects. Electropulsing during deformation enhances wavy slip of dislocations, reconfiguring the dislocation pattern, and hence increases the ductility.
- Shiteng Zhao
- , Ruopeng Zhang
- & Andrew M. Minor
-
Article |
 Atomistic insights into metal hardening
Atomistic insights into metal hardening
In contrast with conventional views, ultra-large-scale atomistic simulations show that the staged character of strain hardening of metals originates from crystal rotation, whereas the dislocation behaviours remain the same across all the stages.
- Luis A. Zepeda-Ruiz
- , Alexander Stukowski
- & Vasily V. Bulatov
-
Letter |
 Natural-mixing guided design of refractory high-entropy alloys with as-cast tensile ductility
Natural-mixing guided design of refractory high-entropy alloys with as-cast tensile ductility
A refractory high-entropy alloy was designed with the composition chosen based on the natural-mixing characteristics among refractory elements; this alloy demonstrates good tensile ductility in the as-cast state and physicochemical stability at high temperatures.
- Shaolou Wei
- , Sang Jun Kim
- & Cemal Cem Tasan
-
Article |
 A natural impact-resistant bicontinuous composite nanoparticle coating
A natural impact-resistant bicontinuous composite nanoparticle coating
A coating made from densely packed hydroxyapatite particles in an organic matrix endows the dactyl club of mantis shrimps with high stiffness and energy damping.
- Wei Huang
- , Mehdi Shishehbor
- & David Kisailus
-
Article |
 Glassy Li metal anode for high-performance rechargeable Li batteries
Glassy Li metal anode for high-performance rechargeable Li batteries
Lithium metal is considered an ideal anode for high-energy rechargeable lithium batteries, but understanding its nucleation and growth at the nanoscale remains challenging. Using cryogenic transmission electron microscopy and simulations, a structural and morphological evolution scenario for Li deposits is proposed.
- Xuefeng Wang
- , Gorakh Pawar
- & Boryann Liaw
-
Comment |
 Post-fire restoration of historic buildings and implications for Notre-Dame de Paris
Post-fire restoration of historic buildings and implications for Notre-Dame de Paris
The restoration of fire-damaged historical monuments entails a wide range of scientific questions. Taking as a starting point the case of Notre-Dame de Paris, this Comment defines the materials science challenges of post-fire restoration, and also briefly outlines the issues of structural integrity, fire safety and preservation ethics.
- Ylenia Praticò
- , John Ochsendorf
- & Robert J. Flatt
-
Article |
 Radiation-induced segregation in a ceramic
Radiation-induced segregation in a ceramic
Radiation-induced segregation is widely observed in metals. Here it is discovered that radiation-induced segregation also occurs in a ceramic, with carbon atoms in silicon carbide segregating to the grain boundaries under irradiation.
- Xing Wang
- , Hongliang Zhang
- & Izabela Szlufarska
-
Article |
 Mechanism of collective interstitial ordering in Fe–C alloys
Mechanism of collective interstitial ordering in Fe–C alloys
The interstitial ordering in Fe–C alloys is shown to be stabilized by local anharmonicity in strain fields, which substantially reduces the critical C concentration for ordering. C segregation into extended defects predominates over ordering at low C concentrations but sharply decreases at high concentrations.
- Xie Zhang
- , Hongcai Wang
- & Jörg Neugebauer
-
News & Views |
 Achieving a better heat conductor
Achieving a better heat conductor
Finding a competitor for diamond as a good heat conductor remains challenging. Measurements on crystals of cubic boron nitride demonstrate a thermal conductivity of 1,600 W m−1 K−1 at room temperature, rivalling diamond.
- Ashutosh Giri
- & Patrick E. Hopkins
-
Letter |
 Unprecedented non-hysteretic superelasticity of [001]-oriented NiCoFeGa single crystals
Unprecedented non-hysteretic superelasticity of [001]-oriented NiCoFeGa single crystals
NiCoFeGa single crystals exhibit large non-hysteretic superelasticity over broad temperature and composition ranges. It is attributed to the continuous phase transition with applied stress, which is related to the fluctuation of entangled ordered and disordered crystal structures.
- Haiyang Chen
- , Yan-Dong Wang
- & Yang Ren
-
Letter |
 Quantum de-trapping and transport of heavy defects in tungsten
Quantum de-trapping and transport of heavy defects in tungsten
Quantum-assisted de-trapping in tungsten leads to diffusion rates orders of magnitude higher than naive classical estimates suggest. This phenomenon may be generic to any crystalline material.
- Kazuto Arakawa
- , Mihai-Cosmin Marinica
- & Hirotaro Mori
-
Article |
 Dimensionally and environmentally ultra-stable polymer composites reinforced with carbon fibres
Dimensionally and environmentally ultra-stable polymer composites reinforced with carbon fibres
Multiple layers of diamond-like carbon films are shown to act as moisture barriers when conformally deposited on carbon fibre reinforced polymers used in space applications.
- J. V. Anguita
- , C. T. G. Smith
- & S. R. P. Silva
-
Article |
 Three-dimensional printing of multicomponent glasses using phase-separating resins
Three-dimensional printing of multicomponent glasses using phase-separating resins
Photopolymerization-induced phase separation of resins enables the high-resolution 3D printing of glass oxides with intricate shapes and distinct chemical composition.
- David G. Moore
- , Lorenzo Barbera
- & André R. Studart
-
Article |
 Ideal maximum strengths and defect-induced softening in nanocrystalline-nanotwinned metals
Ideal maximum strengths and defect-induced softening in nanocrystalline-nanotwinned metals
It is believed that the strengthening of metals by formation of nanoscale grains or coherent twin boundaries is limited to a maximum strength. Here, using experiment and theory, it is shown that the fabrication of nanocrystalline-nanotwinned Ag with trace Cu results in a hardness beyond this limit.
- Xing Ke
- , Jianchao Ye
- & Frederic Sansoz
-
Article |
 A hybrid material that reversibly switches between two stable solid states
A hybrid material that reversibly switches between two stable solid states
Mechanically switchable materials made of supercooled fluids embedded in a polymer matrix reversibly shift between soft and hard solid states upon stimulation.
- Fut (Kuo) Yang
- , Aleksander Cholewinski
- & Boxin Zhao
-
Article |
 Predictive model of hydrogen trapping and bubbling in nanovoids in bcc metals
Predictive model of hydrogen trapping and bubbling in nanovoids in bcc metals
A model is established to quantitatively predict hydrogen energetics and molecule formation in nanovoids of bcc metals, clarifying the trapping and bubbling mechanisms for understanding hydrogen-induced damage.
- Jie Hou
- , Xiang-Shan Kong
- & C. S. Liu
-
-
Article |
 Three-dimensional printing of piezoelectric materials with designed anisotropy and directional response
Three-dimensional printing of piezoelectric materials with designed anisotropy and directional response
Piezoelectrics convert force into electrical charge, and vice versa, but the coefficients that determine piezoelectric behaviour are constrained by crystal structure. Here, metamaterials are 3D printed that show arbitrary piezoelectric coefficients.
- Huachen Cui
- , Ryan Hensleigh
- & Xiaoyu (Rayne) Zheng
-
News & Views |
 Order in one dimension
Order in one dimension
A crystal structure with one-dimensional order is identified in oxide ceramics, which is distinguished from the well-known categories of solid structures and potentially provides unexpected properties.
- Eric A. Stach
-
Letter |
 Ceramic phases with one-dimensional long-range order
Ceramic phases with one-dimensional long-range order
An ordered structure that has only translational periodicity in one direction— unlike the known solid categories of crystal, quasicrystal and amorphous— is discovered in MgO and Nd2O3 ceramics.
- Deqiang Yin
- , Chunlin Chen
- & Yuichi Ikuhara
-
News & Views |
 Inflating to shape
Inflating to shape
An elastomer sheet with programmed inner channel architecture swiftly shapes into a desired three-dimensional geometry upon the application of pressure.
- Efi Efrati
-
Letter |
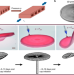 Bio-inspired pneumatic shape-morphing elastomers
Bio-inspired pneumatic shape-morphing elastomers
Elastomer sheets with programmable air channel organization swiftly shape into complex three-dimensional structures upon the application of pressure.
- Emmanuel Siéfert
- , Etienne Reyssat
- & Benoît Roman
-
News & Views |
 Excess solvent in precipitates
Excess solvent in precipitates
Although precipitates’ compositions are theoretically determined by thermodynamics, their formation kinetics can also lead to composition variations that allow further structural evolution, making the precipitation path more complex.
- Emmanuel Clouet
-
Article |
 Decoupling the role of stress and corrosion in the intergranular cracking of noble-metal alloys
Decoupling the role of stress and corrosion in the intergranular cracking of noble-metal alloys
The model alloy of Au–Ag is studied to decouple the role of stress and corrosion in intergranular cracking caused by metal dissolution. Nanoporous corrosion layers can mechanically inject a crack into grain boundaries of the parent phase.
- N. Badwe
- , X. Chen
- & K. Sieradzki
-
Article |
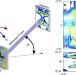 Long-range symmetry breaking in embedded ferroelectrics
Long-range symmetry breaking in embedded ferroelectrics
Ferroelectricity can be modified by domain wall strain fields that extend over nanometres. Here, with X-ray microscopy, strain fields over several micrometres are observed in BaTiO3, suggesting ferroelectricity is globally altered throughout the material.
- Hugh Simons
- , Astri Bjørnetun Haugen
- & Henning Friis Poulsen
-
News & Views |
 Still plenty to explore
Still plenty to explore
Advanced characterization and modelling techniques provide unique insights into oxidant transport processes in growing scales of high-temperature alloys and alloy design for improving their degradation resistance in harsh environments.
- Brian Gleeson
-
Article |
 Interplay of water and reactive elements in oxidation of alumina-forming alloys
Interplay of water and reactive elements in oxidation of alumina-forming alloys
The crucial interaction between reactive elements and water vapour during the oxide scale growth of alumina-forming alloys is revealed, providing insights to improve corrosion resistance of high-temperature alloys.
- N. Mortazavi
- , C. Geers
- & L. G. Johansson
-
Letter |
 Atomic origins of water-vapour-promoted alloy oxidation
Atomic origins of water-vapour-promoted alloy oxidation
In situ transmission electron microscopy observations reveal atomistic mechanism of water-vapour-enhanced oxidation of Ni–Cr alloys. Protons derived from water promote vacancy formation, migration and clustering.
- Langli Luo
- , Mao Su
- & Chongmin Wang
-
Article |
 A molecular cross-linking approach for hybrid metal oxides
A molecular cross-linking approach for hybrid metal oxides
TiO2 and other metal oxides were interfaced with molecular boron clusters to form a hybrid material. This modifies the electrochemical and photocatalytic properties, enabling fast electron transfer and dye degradation under red light.
- Dahee Jung
- , Liban M. A. Saleh
- & Alexander M. Spokoyny
-
Article |
 Imaging the atomic structure and local chemistry of platelets in natural type Ia diamond
Imaging the atomic structure and local chemistry of platelets in natural type Ia diamond
The accurate structure of the platelet defects in diamond is now resolved by transmission electron microscopy, and, out of all the proposed models, it agrees well with the zigzag atomic model.
- E. J. Olivier
- , J. H. Neethling
- & A. I. Kirkland
-
-
News & Views |
 Printing steels
Printing steels
Additive manufacturing has been used to fabricate a common stainless steel, which imparts a unique microstructure to this material, making it stronger and more ductile than that produced with conventional methods.
- Iain Todd
-
News & Views |
 Activity at the surface
Activity at the surface
In situ transmission electron microscopy resolves atomic structures and dislocation dynamics of surface segregation, providing insights that open a pathway to new advances in interface engineering.
- Simon P. Ringer
-
Article |
 Dislocation nucleation facilitated by atomic segregation
Dislocation nucleation facilitated by atomic segregation
In situ transmission electron microscopy combined with theory modelling reveals that surface segregation in CuAu solid solution generates misfit dislocations, providing atomistic mechanisms of dislocation nucleation and dynamics at heterointerfaces.
- Lianfeng Zou
- , Chaoming Yang
- & Guangwen Zhou

 Atomic-scale observation of non-classical nucleation-mediated phase transformation in a titanium alloy
Atomic-scale observation of non-classical nucleation-mediated phase transformation in a titanium alloy Our elemental footprint
Our elemental footprint All that glitters
All that glitters