Research Briefing |
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Anisotropic exchange interaction of two hole-spin qubits
Anisotropic exchange interaction of two hole-spin qubits
A successful silicon spin qubit design should be rapidly scalable by benefiting from industrial transistor technology. This investigation of exchange interactions between two FinFET qubits provides a guide to implementing two-qubit gates for hole spins.
- Simon Geyer
- , Bence Hetényi
- & Andreas V. Kuhlmann
-
Article |
 Strong tunable coupling between two distant superconducting spin qubits
Strong tunable coupling between two distant superconducting spin qubits
The hybrid architecture of Andreev spin qubits made using semiconductor–superconductor nanowires means that supercurrents can be used to inductively couple qubits over long distances.
- Marta Pita-Vidal
- , Jaap J. Wesdorp
- & Christian Kraglund Andersen
-
Research Briefing |
 Mass difference measurements help to determine the neutrino mass
Mass difference measurements help to determine the neutrino mass
The Q-value of electron capture in 163Ho has been determined with an uncertainty of 0.6 eV c–2 through a combination of high-precision Penning-trap mass spectrometry and precise atomic physics calculations. This high-precision measurement provides insight into systematic errors in neutrino mass measurements.
-
Research Briefing |
 Enhanced generation of magnonic frequency combs
Enhanced generation of magnonic frequency combs
As counterparts to optical frequency combs, magnonic frequency combs could have broad applications if their initiation thresholds were low and the ‘teeth’ of the comb plentiful. Progress has now been made through exploiting so-called exceptional points to enhance the nonlinear coupling between magnons and produce wider magnonic frequency combs.
-
Research Briefing |
 A compact neutral-atom fault-tolerant quantum computer based on new quantum codes
A compact neutral-atom fault-tolerant quantum computer based on new quantum codes
A practical and hardware-efficient blueprint for fault-tolerant quantum computing has been developed, using quantum low-density-parity-check codes and reconfigurable neutral-atom arrays. The scheme requires ten times fewer qubits and paves the way towards large-scale quantum computing using existing experimental technologies.
-
Article |
 Constant-overhead fault-tolerant quantum computation with reconfigurable atom arrays
Constant-overhead fault-tolerant quantum computation with reconfigurable atom arrays
Quantum low-density parity-check codes are highly efficient in principle but challenging to implement in practice. This proposal shows that these codes could be implemented in the near term using recently demonstrated neutral-atom arrays.
- Qian Xu
- , J. Pablo Bonilla Ataides
- & Hengyun Zhou
-
Article |
 Enhancement of magnonic frequency combs by exceptional points
Enhancement of magnonic frequency combs by exceptional points
Frequency combs, which are important for applications in precision spectroscopy, depend on material nonlinearities for their function, which can be hard to engineer. Now an approach combining magnons and exceptional points is shown to be effective.
- Congyi Wang
- , Jinwei Rao
- & Wei Lu
-
Article |
 Estimates of the reproduction ratio from epidemic surveillance may be biased in spatially structured populations
Estimates of the reproduction ratio from epidemic surveillance may be biased in spatially structured populations
Spatial dynamics can obscure epidemic trends from surveillance data, biasing reproduction ratio estimates over long periods. A spectral correction reweights incidence data to remove this bias, thus improving monitoring to inform response strategies.
- Piero Birello
- , Michele Re Fiorentin
- & Eugenio Valdano
-
Article
| Open Access Irreversible entropy transport enhanced by fermionic superfluidity
Irreversible entropy transport enhanced by fermionic superfluidity
Connecting two superfluid reservoirs leads to both particle and entropy flow between the systems. Now, a direct measurement of the entropy current and production in ultracold quantum gases reveals how superfluidity enhances entropy transport.
- Philipp Fabritius
- , Jeffrey Mohan
- & Tilman Esslinger
-
Article |
 Spin Berry curvature-enhanced orbital Zeeman effect in a kagome metal
Spin Berry curvature-enhanced orbital Zeeman effect in a kagome metal
Controlling orbital magnetic moments for applications can be difficult. Now local probes of a kagome material, TbV6Sn6, demonstrate how the spin Berry curvature can produce a large orbital Zeeman effect that can be tuned with a magnetic field.
- Hong Li
- , Siyu Cheng
- & Ilija Zeljkovic
-
Article |
 Room-temperature flexible manipulation of the quantum-metric structure in a topological chiral antiferromagnet
Room-temperature flexible manipulation of the quantum-metric structure in a topological chiral antiferromagnet
Manipulation of the quantum-metric structure to produce topological phenomena has rarely been studied. Now, flexible control of the quantum-metric structure is demonstrated in a topological chiral antiferromagnet at room temperature.
- Jiahao Han
- , Tomohiro Uchimura
- & Shunsuke Fukami
-
Article
| Open Access Penning-trap measurement of the Q value of electron capture in 163Ho for the determination of the electron neutrino mass
Penning-trap measurement of the Q value of electron capture in 163Ho for the determination of the electron neutrino mass
Electron capture in 163Ho can be used to determine the electron neutrino mass. The Q value of this process is crucial for the evaluation of the systematic uncertainty in such a measurement, and a 50-fold improvement is now reported.
- Christoph Schweiger
- , Martin Braß
- & Klaus Blaum
-
-
-
Measure for Measure |
 Slightly out of tune
Slightly out of tune
Bart Verberck uses the musical cent as a pretext to touch on some of the intricacies of musical tuning systems.
- Bart Verberck
-
News & Views |
 Electrons bunch up in quantum light
Electrons bunch up in quantum light
When photons impinge on a material, free electrons can be created by the photoelectric effect. The emitted electron current usually fluctuates with Poisson statistics, but if squeezed quantum light is applied, the electrons bunch up.
- Alfred Leitenstorfer
- & Peter Baum
-
Article |
 Distinct elastic properties and their origins in glasses and gels
Distinct elastic properties and their origins in glasses and gels
As amorphous solids, glasses and gels are similar, but the origins of their different elastic properties are unclear. Simulations now suggest differing free-energy-minimizing pathways: structural ordering for glasses and interface reduction for gels.
- Yinqiao Wang
- , Michio Tateno
- & Hajime Tanaka
-
News & Views |
 Search for rule-breaking electrons
Search for rule-breaking electrons
Questioning the validity of axioms can teach us about physics beyond the standard model. A recent search for the violation of charge conservation and the Pauli exclusion principle yields limits on these scenarios.
- Alessio Porcelli
-
Article
| Open Access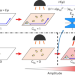 Nonlinearity-induced topological phase transition characterized by the nonlinear Chern number
Nonlinearity-induced topological phase transition characterized by the nonlinear Chern number
Linear topological systems can be characterized using invariants such as the Chern number. This concept can be extended to the nonlinear regime, giving rise to nonlinearity-induced topological phase transitions.
- Kazuki Sone
- , Motohiko Ezawa
- & Takahiro Sagawa
-
Article |
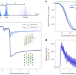 All-optical seeding of a light-induced phase transition with correlated disorder
All-optical seeding of a light-induced phase transition with correlated disorder
Controlling phase transitions in solids is crucial for many applications. Ultrafast laser pulses have now been shown to enable the energy-efficient generation of structural fluctuations in VO2 by harnessing the correlated disorder in the material.
- Allan S. Johnson
- , Ernest Pastor
- & Simon E. Wall
-
Article |
 Search for charge non-conservation and Pauli exclusion principle violation with the Majorana Demonstrator
Search for charge non-conservation and Pauli exclusion principle violation with the Majorana Demonstrator
The Majorana Demonstrator experiment reports searches for the violation of the Pauli exclusion principle and of charge conservation. In the absence of a signal, exclusion limits for these processes are reported.
- I. J. Arnquist
- , F. T. Avignone III
- & B. X. Zhu
-
Comment |
 A call for responsible quantum technology
A call for responsible quantum technology
The time has come to consider appropriate guardrails to ensure quantum technology benefits humanity and the planet. With quantum development still in flux, the science community shares a responsibility in defining principles and practices.
- Urs Gasser
- , Eline De Jong
- & Mauritz Kop
-
Perspective |
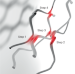 Discrete nonlinear topological photonics
Discrete nonlinear topological photonics
Although topological photonics has been an active field of research for some time, most studies still focus on the linear optical regime. This Perspective summarizes recent investigations into the nonlinear properties of discrete topological photonic systems.
- Alexander Szameit
- & Mikael C. Rechtsman
-
Article |
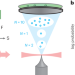 Multiphoton electron emission with non-classical light
Multiphoton electron emission with non-classical light
Photoemission experiments demonstrate that the photon number statistics of the exciting light can be imprinted on the emitted electrons, allowing the controlled generation of classical or non-classical electron number statistics of free electrons.
- Jonas Heimerl
- , Alexander Mikhaylov
- & Peter Hommelhoff
-
Article |
 Observation of the 2D–1D crossover in strongly interacting ultracold bosons
Observation of the 2D–1D crossover in strongly interacting ultracold bosons
Quantum systems exhibit vastly different properties depending on their dimensionality. An experimental study with ultracold bosons now tracks quantum correlation properties during the crossover from two dimensions to one dimension.
- Yanliang Guo
- , Hepeng Yao
- & Hanns-Christoph Nägerl
-
News & Views |
 At the breaking point
At the breaking point
The shape and trajectory of a crack plays a crucial role in material fracture. High-precision experiments now directly capture this phenomenon, unveiling the intricate 3D nature of cracks.
- Michael D. Bartlett
-
Article
| Open Access Leggett modes in a Dirac semimetal
Leggett modes in a Dirac semimetal
Leggett modes can occur when superconductivity arises in more than one band in a material and represent oscillation of the relative phases of the two superconducting condensates. Now, this mode is observed in Cd3As2, a Dirac semimetal.
- Joseph J. Cuozzo
- , W. Yu
- & Enrico Rossi
-
Article |
 Emergence of large-scale mechanical spiral waves in bacterial living matter
Emergence of large-scale mechanical spiral waves in bacterial living matter
The occurrence of propagating spiral waves in multicellular organisms is associated with key biological functions. Now this type of wave has also been observed in dense bacterial populations, probably resulting from non-reciprocal cell–cell interactions.
- Shiqi Liu
- , Ye Li
- & Yilin Wu
-
Article |
 Topological Kerr effects in two-dimensional magnets with broken inversion symmetry
Topological Kerr effects in two-dimensional magnets with broken inversion symmetry
The ferromagnet CrVI6 serves as a material platform to demonstrate the topological Kerr effect in two-dimensional magnets. This can be used to identify skyrmions by magneto-optical means.
- Xiaoyin Li
- , Caixing Liu
- & Zhenyu Zhang
-
Article |
 Multistep topological transitions among meron and skyrmion crystals in a centrosymmetric magnet
Multistep topological transitions among meron and skyrmion crystals in a centrosymmetric magnet
Topological magnetic spin structures such as skyrmions and merons have the potential to be used in magnetic information devices. Now multistep transformations between such structures are demonstrated in a centrosymmetric material.
- H. Yoshimochi
- , R. Takagi
- & S. Seki
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetically tunable supercurrent in dilute magnetic topological insulator-based Josephson junctions
Magnetically tunable supercurrent in dilute magnetic topological insulator-based Josephson junctions
Despite their potential device applications, experimental realizations of proximity-induced Fulde–Ferrell–Larkin–Ovchinnikov states are rare. Now Josephson junctions based on a dilute magnetic topological insulator provide evidence of such a state.
- Pankaj Mandal
- , Soumi Mondal
- & Laurens W. Molenkamp
-
News & Views |
 Multiphoton quantum statistics from scattered classical light
Multiphoton quantum statistics from scattered classical light
Even by shining classical light on a single opening, one can perform a double-slit experiment and discover a surprising variety of quantum mechanical multi-photon correlations — thanks to surface plasmon polaritons and photon-number-resolving detectors.
- Martijn Wubs
-
Article |
 Connecting shear flow and vortex array instabilities in annular atomic superfluids
Connecting shear flow and vortex array instabilities in annular atomic superfluids
Two adjacent layers flowing at different velocities in the same fluid are subject to flow instabilities. This phenomenon is now studied in atomic superfluids, revealing that quantized vortices act as both sources and probes of the unstable flow.
- D. Hernández-Rajkov
- , N. Grani
- & G. Roati
-
Article |
 Search for decoherence from quantum gravity with atmospheric neutrinos
Search for decoherence from quantum gravity with atmospheric neutrinos
Interactions of atmospheric neutrinos with quantum-gravity-induced fluctuations of the metric of spacetime would lead to decoherence. The IceCube Collaboration constrains such interactions with atmospheric neutrinos.
- R. Abbasi
- , M. Ackermann
- & M. Zimmerman
-
Article
| Open Access Complexity of crack front geometry enhances toughness of brittle solids
Complexity of crack front geometry enhances toughness of brittle solids
Experiments probing three-dimensional crack propagation show that the critical strain energy needed to drive a crack is directly proportional to its geodesic length. This insight is a step towards a fully three-dimensional theory of crack propagation.
- Xinyue Wei
- , Chenzhuo Li
- & John M. Kolinski
-
News & Views |
 Protons on the line
Protons on the line
Stable regions in four-dimensional phase space have been observed by following the motion of accelerated proton beams subject to nonlinear forces. This provides insights into the physics of dynamical systems and may lead to improved accelerator designs.
- Giulio Stancari
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of fixed lines induced by a nonlinear resonance in the CERN Super Proton Synchrotron
Observation of fixed lines induced by a nonlinear resonance in the CERN Super Proton Synchrotron
Nonlinear resonances can cause particle loss in accelerators. Experiments confirm that a coupled nonlinear resonance traps beam particles on a four-dimensional closed curve. This finding allows the development of mitigation strategies.
- H. Bartosik
- , G. Franchetti
- & F. Schmidt
-
Article |
 Melting of the charge density wave by generation of pairs of topological defects in UTe2
Melting of the charge density wave by generation of pairs of topological defects in UTe2
A mechanism for the phase transition of charge density wave states via the generation and proliferation of topological defects with opposite phase windings is demonstrated in a heavy-fermion superconductor.
- Anuva Aishwarya
- , Julian May-Mann
- & Vidya Madhavan
-
Article |
 Flexoelectricity-driven toroidal polar topology in liquid-matter helielectrics
Flexoelectricity-driven toroidal polar topology in liquid-matter helielectrics
Exploring and exploiting electric dipole arrangements analogously to what is possible with magnetic spin textures is an emerging prospect. Now a spontaneous toroidal polar topology is observed in ferroelectric liquid crystals.
- Jidan Yang
- , Yu Zou
- & Satoshi Aya
-
-
-
Comment |
Computing in physics education
Computing is central to the enterprise of physics but few undergraduate physics courses include it in their curricula. Here we discuss why and how to integrate computing into physics education.
- Marcos D. Caballero
- & Tor Ole B. Odden
-
Comment |
Racial equity in physics education research
Injustices and oppression are pervasive in society, including education. An intersectional, equity-oriented approach can help remove systemic obstacles and improve the experience of marginalized people in physics education through decolonial and critical race lenses.
- Geraldine L. Cochran
- , Simone Hyater-Adams
- & Ramón S. Barthelemy
-
Comment |
 A physics curriculum for the modern world
A physics curriculum for the modern world
Increasingly, physics graduates take jobs outside academia. Active teaching approaches lead to deeper conceptual understanding and a more varied skill set and are therefore more likely to prepare students for successful careers.
- Jenaro Guisasola
- & Kristina Zuza
-
Perspective |
 Epistemic agency as a critical mediator of physics learning
Epistemic agency as a critical mediator of physics learning
Encouraging students to take ownership of their learning can improve their outcomes. This Perspective discusses ways to achieve this in the context of physics education and how digital technology can help Gen Z students in particular.
- Nam-Hwa Kang
-
Review Article |
Towards meaningful diversity, equity and inclusion in physics learning environments
Women and ethnic and racial minority students are underrepresented in physics. This Review summarizes research on equity and inclusion in physics education and makes recommendations for making physics learning environments more equitable.
- Alexandru Maries
- & Chandralekha Singh
-
Article |
 Manipulation of chiral interface states in a moiré quantum anomalous Hall insulator
Manipulation of chiral interface states in a moiré quantum anomalous Hall insulator
The local electronic structure of interface states between topologically distinct domains is imaged and controlled, allowing visualization of the interplay between strong interactions and non-trivial topology.
- Canxun Zhang
- , Tiancong Zhu
- & Michael F. Crommie
-
Article |
 Superconducting stripes induced by ferromagnetic proximity in an oxide heterostructure
Superconducting stripes induced by ferromagnetic proximity in an oxide heterostructure
Copper-based and iron-based compounds exhibit an interplay between magnetism and superconductivity. Now, this idea is extended to two-dimensional oxide heterostructures, where a spatially varying superconducting order is demonstrated at the EuO/KTaO3 interface.
- Xiangyu Hua
- , Zimeng Zeng
- & Xianhui Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Demonstration and imaging of cryogenic magneto-thermoelectric cooling in a van der Waals semimetal
Demonstration and imaging of cryogenic magneto-thermoelectric cooling in a van der Waals semimetal
Cooling efficiency in thermoelectric devices decreases considerably at lower temperatures. Now thermoelectric cooling at cryogenic temperatures is directly imaged in a van der Waals semimetal.
- T. Völkl
- , A. Aharon-Steinberg
- & E. Zeldov

 Rotational symmetry influences the mechanical properties of graphene
Rotational symmetry influences the mechanical properties of graphene Quantum sensing at the megabar frontier
Quantum sensing at the megabar frontier Naturally superconducting
Naturally superconducting Batter quality
Batter quality Fruity blues
Fruity blues