News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Letter |
 Magnetic nano-oscillator driven by pure spin current
Magnetic nano-oscillator driven by pure spin current
The dynamical processes associated with the magnetization of a material can be drastically altered by the application of a spin current. This study now demonstrates the feasibility of selectively exciting coherent auto-oscillation modes in magnetic nanostructures.
- Vladislav E. Demidov
- , Sergei Urazhdin
- & Sergej O. Demokritov
-
Article |
 Macroporous nanowire nanoelectronic scaffolds for synthetic tissues
Macroporous nanowire nanoelectronic scaffolds for synthetic tissues
Three-dimensional bioactive scaffolds can support tissue growth for studies in cellular biophysics and regenerative medicine. Such scaffolds have now been integrated with semiconductor nanowires to probe their porous interior, allowing for real-time monitoring of signals such as the response of neural and cardiac tissue models to drugs.
- Bozhi Tian
- , Jia Liu
- & Charles M. Lieber
-
News & Views |
 Still in control
Still in control
The development of synthetic strategies enabling the fabrication of well-defined polymer–biomolecule conjugates, together with advances in top-down nanofabrication, are two highlights from a recent meeting of polymer scientists.
- Jeffrey Pyun
-
-
News & Views |
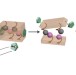 Nanorobots grab cellular control
Nanorobots grab cellular control
Self-assembled barrel-like DNA nanostructures carrying active payloads and pre-programmed with logic operations to reconfigure in response to cell-surface cues can trigger a variety of intracellular functions.
- Johann Elbaz
- & Itamar Willner
-
News & Views |
 Know your molecules
Know your molecules
A new plasmonic sensing platform that not only allows the detection of ultrasmall quantities of biomolecules, but is also sensitive to their identity and conformational state, represents a significant advance in the study of biomolecular interactions.
- Na Liu
- & Annemarie Pucci
-
-
News & Views |
 In a tight corner
In a tight corner
Surfaces are known to act as catalysts for the nucleation of crystals. Using polymer films patterned with nanopores, it is now shown that the shape of the pores can control the kinetics of surface-induced crystal nucleation.
- Richard P. Sear
-
-
Letter |
 Evolution and control of oxygen order in a cuprate superconductor
Evolution and control of oxygen order in a cuprate superconductor
The arrangement of defects in solid-state phases has an enormous influence on material properties. It is here shown that powerful X-rays can be used to change the properties of an oxide superconductor, thus effectively writing superconducting regions within an insulating matrix. The results open the way to the manipulation of superconductors and potentially other phases.
- Nicola Poccia
- , Michela Fratini
- & Antonio Bianconi
-
Commentary |
 The problem of regulating sophisticated materials
The problem of regulating sophisticated materials
As complex new materials such as nanoparticles increasingly make their way into commercial products, regulatory frameworks need to overcome a number of key challenges to remain fit for purpose.
- Andrew Maynard
- , Diana Bowman
- & Graeme Hodge
-
News & Views |
 Swarming towards the target
Swarming towards the target
A system comprising 'signalling' and 'receiving' modules — where the receiving module circulating in the bloodstream is directed to the tumour by a cascade triggered by the signalling module — improves the targeting effect of a nanomedicine.
- Yucai Wang
- , Paige Brown
- & Younan Xia
-
Article |
 Nanoparticles that communicate in vivo to amplify tumour targeting
Nanoparticles that communicate in vivo to amplify tumour targeting
A two-component nanoparticle system that communicates and enhances in vivo drug delivery and diagnostics has been devised. The system comprises ‘signalling’ nanoparticles that target tumours and then broadcast the tumour’s location to ’receiving’ nanoparticles in circulation, which carry therapeutic or diagnostic cargos, hence amplifying tumour targeting.
- Geoffrey von Maltzahn
- , Ji-Ho Park
- & Sangeeta N. Bhatia
-
Letter |
 Creation and control of a two-dimensional electron liquid at the bare SrTiO3 surface
Creation and control of a two-dimensional electron liquid at the bare SrTiO3 surface
Considerable attention has been given in the past few years to two-dimensional electron gases formed at the interface between two bulk insulators. It is now shown that a similar electronic system can be created on the surface of an oxide insulator simply by exposure to UV light.
- W. Meevasana
- , P. D. C. King
- & Z-X. Shen
-
Letter |
 The initialization and manipulation of quantum information stored in silicon by bismuth dopants
The initialization and manipulation of quantum information stored in silicon by bismuth dopants
Single phosphorus dopants in silicon are one of the physical systems that could be used for quantum information technology. It is now shown that bismuth dopants have similar properties to their phosphorus counterparts, and could offer even more possibilities for quantum information applications.
- Gavin W. Morley
- , Marc Warner
- & Gabriel Aeppli
-
News & Views |
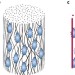 Noodle gels for cells
Noodle gels for cells
Heating and cooling of peptide amphiphile suspensions converts disorganized nanofibres into liquid-crystalline nanofibre bundles that gel on addition of salts. The noodle-shaped strings of gel can entrap and align cells.
- Timothy J. Deming
-
Article |
 Nanopatterning Si(111) surfaces as a selective surface-chemistry route
Nanopatterning Si(111) surfaces as a selective surface-chemistry route
The ability to control the surface chemistry of silicon is important for microelectronic applications. Chemical species can now be stabilized on Si(111) surfaces using a partially alkoxylated surface as a nanopatterning template.
- David J. Michalak
- , Sandrine Rivillon Amy
- & Yves J. Chabal

 Death by magnetism
Death by magnetism