Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Editorial |
 Life-saving vaccines awarded
Life-saving vaccines awarded
The fundamental discoveries that enabled the development of effective mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 were awarded with this year’s Nobel Prize in Medicine.
-
Review Article |
 Hydrogels for RNA delivery
Hydrogels for RNA delivery
RNA-based therapeutics hold promise for the treatment of several diseases. This Review provides an overview of hydrogels for RNA delivery, discussing how the chemical nature and physical properties of hydrogels can be explored for tailored RNA loading and release, and highlighting the use of these materials in biomedical applications.
- Ruibo Zhong
- , Sepehr Talebian
- & Jinjun Shi
-
News & Views |
 Inhalable mRNA nanoparticles
Inhalable mRNA nanoparticles
A large-scale screening identifies an inhalable polymer nanoparticle formulation that safely and effectively delivers therapeutic mRNA molecules to the lungs of several animal species.
- Ronnie H. Fang
- & Liangfang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access P-selectin-targeted nanocarriers induce active crossing of the blood–brain barrier via caveolin-1-dependent transcytosis
P-selectin-targeted nanocarriers induce active crossing of the blood–brain barrier via caveolin-1-dependent transcytosis
Targeting of tumour vasculature endothelial P-selectin promotes caveolin-1-mediated transcytosis for enhanced blood–brain barrier crossing of therapeutic nanoparticles against medulloblastoma.
- Daniel E. Tylawsky
- , Hiroto Kiguchi
- & Daniel A. Heller
-
Article
| Open Access A TLR7-nanoparticle adjuvant promotes a broad immune response against heterologous strains of influenza and SARS-CoV-2
A TLR7-nanoparticle adjuvant promotes a broad immune response against heterologous strains of influenza and SARS-CoV-2
A nanoparticle-based adjuvant incorporating a Toll-like receptor 7 agonist elicits cross-reactive antibodies for both dominant and subdominant epitopes and enhances immune responses against multiple variants of influenza and SARS-CoV-2.
- Qian Yin
- , Wei Luo
- & Mark M. Davis
-
Article |
 Species-agnostic polymeric formulations for inhalable messenger RNA delivery to the lung
Species-agnostic polymeric formulations for inhalable messenger RNA delivery to the lung
Screening of hundreds of nanoparticle polymers identifies an effective and low-toxicity formulation for the functional delivery of RNA to the lungs of distinct animal species.
- Laura Rotolo
- , Daryll Vanover
- & Philip J. Santangelo
-
Article |
 Nanoparticle-modified microrobots for in vivo antibiotic delivery to treat acute bacterial pneumonia
Nanoparticle-modified microrobots for in vivo antibiotic delivery to treat acute bacterial pneumonia
Biohybrid microrobots consisting of nanoparticle-modified microalgae are constructed for active drug delivery in the lungs. In an acute bacterial pneumonia model, the microrobots effectively reduce bacterial burden and lessen animal mortality.
- Fangyu Zhang
- , Jia Zhuang
- & Joseph Wang
-
Comment |
 Ascendancy of semi-synthetic biomaterials from design towards democratization
Ascendancy of semi-synthetic biomaterials from design towards democratization
Semi-synthetic goldilocks material design integrates the tunable characteristics of synthetic materials and the refined complexity of natural components, enabling for the progress of biomaterials across length scales. Accelerated translational success may thus be possible for more personalized and accessible products.
- Alessondra T. Speidel
- , Christopher L. Grigsby
- & Molly M. Stevens
-
News & Views |
 Lipid nanodiscs give cancer a STING
Lipid nanodiscs give cancer a STING
Lipid nanodiscs carrying a potent STING agonist penetrate deep into solid tumours compared with gold-standard liposomes and enable long-term antitumour immunotherapy.
- Ningqiang Gong
- & Michael J. Mitchell
-
News & Views |
 Getting a grip with kirigami
Getting a grip with kirigami
An implantable stent inspired by kirigami has been developed and integrated with a fluidically driven soft actuator to deliver drugs to tubular organs in the body such as the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts.
- Alexandra Teleki
- & Per Artursson
-
Article |
 Membrane-destabilizing ionizable phospholipids for organ-selective mRNA delivery and CRISPR–Cas gene editing
Membrane-destabilizing ionizable phospholipids for organ-selective mRNA delivery and CRISPR–Cas gene editing
Ionizable phospholipid nanoparticles have been designed to efficiently destabilize endosomal membranes and mediate organ-selective mRNA delivery and CRISPR–Cas9 gene editing.
- Shuai Liu
- , Qiang Cheng
- & Daniel J. Siegwart
-
News & Views |
 Long-acting antiretroviral therapy
Long-acting antiretroviral therapy
Nanoformulations of cabotegravir prodrugs have been developed to prolong the pharmacokinetics of the antiretroviral agent. They can be present in the plasma of mice and non-human primates for a year following a single injection.
- Vicente Soriano
- , Pablo Barreiro
- & Carmen de Mendoza
-
Article |
 A year-long extended release nanoformulated cabotegravir prodrug
A year-long extended release nanoformulated cabotegravir prodrug
Nanoformulated long-acting cabotegravir prodrugs are shown to be capable of extending the native drug’s antiretroviral activity, biodistribution and pharmacokinetics for up to 12 months in mice and rhesus macaques.
- Tanmay A. Kulkarni
- , Aditya N. Bade
- & Howard E. Gendelman
-
Editorial |
 Challenging paradigms in tumour drug delivery
Challenging paradigms in tumour drug delivery
A collective effort from materials scientists, life scientists and clinicians is required to systematically address fundamental questions in the mechanisms of nanoparticle delivery in order to overcome the hurdles in translating nanomedicines for tumour therapy.
-
Comment |
 Active transcytosis and new opportunities for cancer nanomedicine
Active transcytosis and new opportunities for cancer nanomedicine
New evidence suggests that the mechanism of nanoparticle entry into solid tumours may be driven by an active process. This insight paves the way for approaches to enhance the efficiency of nanomedicine delivery by harnessing active transport mechanisms, and encourage researchers to rethink how tumours are treated.
- Subehndu Pandit
- , Debapriya Dutta
- & Shuming Nie
-
News & Views |
 A nanoparticle’s pathway into tumours
A nanoparticle’s pathway into tumours
New evidence now suggests that the dominant mechanism of extravasation of nanoparticles into solid tumours may be through an active process of endothelial transcytosis.
- Irene de Lázaro
- & David J. Mooney
-
News & Views |
 Limiting biomaterial fibrosis
Limiting biomaterial fibrosis
Crystallized anti-inflammatory drugs have been shown to inhibit fibrosis on the surface of a number of devices over a long-term period following implantation in rodents and non-human primates.
- Ruud A. Bank
-
Article |
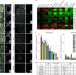 Long-term implant fibrosis prevention in rodents and non-human primates using crystallized drug formulations
Long-term implant fibrosis prevention in rodents and non-human primates using crystallized drug formulations
Foreign body response can result in failure of biomaterials in vivo. Solvent-free crystals containing anti-fibrotic drugs now show the potential for long-term inhibition of fibrosis on a number of implantable devices in rodents and non-human primates.
- Shady Farah
- , Joshua C. Doloff
- & Daniel G. Anderson
-
Perspective |
 Exploiting machine learning for end-to-end drug discovery and development
Exploiting machine learning for end-to-end drug discovery and development
This Perspective describes the application of machine learning models in the design, synthesis and characterisation of molecules at different stages in the drug discovery and development process.
- Sean Ekins
- , Ana C. Puhl
- & Alex M. Clark
-
News & Views |
 Luminal coating of the intestine
Luminal coating of the intestine
An orally administered bifunctional gastrointestinal coating has been developed and shown to limit nutrient absorption through the bowel mucosa ultimately lowering blood glucose and also acting as a platform for delivery of drugs to the gastrointestinal tract.
- Gregor Fuhrmann
-
News & Views |
 Biomaterials driving repair after stroke
Biomaterials driving repair after stroke
An injectable biomaterial with angiogenic and immune-modulatory properties was developed and shown to support brain tissue repair and functional recovery in a mouse model of stroke.
- Anup Tuladhar
- & Molly S. Shoichet
-
Article |
 Quantitative self-assembly prediction yields targeted nanomedicines
Quantitative self-assembly prediction yields targeted nanomedicines
Molecular simulations reveal the self-assembly of small molecules into nanoparticle drug carriers. Targeting of colon and liver cancer cells by the nanoparticles via kinase inhibitors is employed in anti-tumour therapy in vivo.
- Yosi Shamay
- , Janki Shah
- & Daniel A. Heller
-
Article |
 Designer vaccine nanodiscs for personalized cancer immunotherapy
Designer vaccine nanodiscs for personalized cancer immunotherapy
High-density lipoprotein nanodiscs loaded with immunostimulatory biomolecules can target draining lymph nodes for cancer vaccination.
- Rui Kuai
- , Lukasz J. Ochyl
- & James J. Moon
-
News & Views |
 Leukocyte-like carriers
Leukocyte-like carriers
Drug-loaded liposomes functionalized with proteins from the cell membrane of leukocytes target inflamed tissues without eliciting a substantial immune response.
- Kenneth A. Dawson
- & Yan Yan
-
Article |
 Mechanism of hard-nanomaterial clearance by the liver
Mechanism of hard-nanomaterial clearance by the liver
The blood clearance mechanism, by the liver, of administered hard nanomaterials is reported in relation to blood flow dynamics, organ microarchitecture and cellular phenotype.
- Kim M. Tsoi
- , Sonya A. MacParland
- & Warren C. W. Chan
-
Article |
 Biomimetic proteolipid vesicles for targeting inflamed tissues
Biomimetic proteolipid vesicles for targeting inflamed tissues
Lipid nanoparticles incorporating proteins from the leukocyte plasma membrane retain the properties of liposomal formulations and enable delivery of drugs to inflamed tissues.
- R. Molinaro
- , C. Corbo
- & E. Tasciotti
-
Editorial |
 Graphene steps into biomedicine
Graphene steps into biomedicine
Biomedical applications for graphene are attracting interest from academics and industrial partners aiming to develop next-generation medical devices and therapies.
-
Article |
 A sunblock based on bioadhesive nanoparticles
A sunblock based on bioadhesive nanoparticles
A water-resistant sunblock based on bioadhesive nanoparticles encapsulating a model ultraviolet filter at low concentrations adheres to the stratum corneum without subsequent intra-epidermal or follicular penetration.
- Yang Deng
- , Asiri Ediriwickrema
- & W. Mark Saltzman
-
News & Views |
 Longer and safer gastric residence
Longer and safer gastric residence
A supramolecular polymer that is stable in the acidic environment of the stomach but dissolves in the neutral-pH environment of the intestines prolongs the safe retention of gastric devices.
- Vitaliy V. Khutoryanskiy
-
Letter |
 In vivo delivery of transcription factors with multifunctional oligonucleotides
In vivo delivery of transcription factors with multifunctional oligonucleotides
Clinical translation of transcription factor therapeutics is limited by delivery problems. Now, an oligonucleotide that can bind and deliver transcription factors with high in vivo efficiency and treat acetaminophen-induced liver injury is reported.
- Kunwoo Lee
- , Mohammad Rafi
- & Niren Murthy
-
News & Views |
 Puncturing cells en masse
Puncturing cells en masse
Porous silicon nanoneedles efficiently puncture cell monolayers, delivering biomolecules into cells both in vitro and in vivo.
- Mark R. Prausnitz
-
Article |
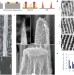 Biodegradable silicon nanoneedles delivering nucleic acids intracellularly induce localized in vivo neovascularization
Biodegradable silicon nanoneedles delivering nucleic acids intracellularly induce localized in vivo neovascularization
Efficient in vivo cytosolic delivery of nucleic acids through cell-membrane puncturing by an array of biodegradable silicon nanoneedles induces sustained local neovascularization in muscle.
- C. Chiappini
- , E. De Rosa
- & E. Tasciotti
-
-
-
Article |
 Etchable plasmonic nanoparticle probes to image and quantify cellular internalization
Etchable plasmonic nanoparticle probes to image and quantify cellular internalization
Nanoparticle-based fluorescence imaging does not usually allow cell membrane-bound particles and intracellular particles to be distinguished from each other. Now, using functionalized silver nanoparticles as plasmonic probes, this distinction can be made following a rapid, non-toxic etching process that selectively removes the extracellular nanoparticles but leaves the intracellular nanoparticles unharmed.
- Gary B. Braun
- , Tomas Friman
- & Erkki Ruoslahti
-
-
-
Commentary |
 Translating materials design to the clinic
Translating materials design to the clinic
Many materials-based therapeutic systems have reached the clinic or are in clinical trials. Here we describe materials design principles and the construction of delivery vehicles, as well as their adaptation and evaluation for human use.
- Jeffrey A. Hubbell
- & Robert Langer
-
Commentary |
 Strategies for advancing cancer nanomedicine
Strategies for advancing cancer nanomedicine
Cancer nanomedicines approved so far minimize toxicity, but their efficacy is often limited by physiological barriers posed by the tumour microenvironment. Here, we discuss how these barriers can be overcome through innovative nanomedicine design and through creative manipulation of the tumour microenvironment.
- Vikash P. Chauhan
- & Rakesh K. Jain
-
Review Article |
 Delivery materials for siRNA therapeutics
Delivery materials for siRNA therapeutics
Therapeutics based on small interfering RNA (siRNA), which in principle are able to reversibly silence any gene of interest, are under development for the treatment of cancers, viral infections, hereditary disorders and many other diseases. This Review discusses the biological challenges that siRNA delivery materials aim to overcome, as well as the most clinically advanced classes of siRNA delivery systems, including cyclodextrin–polymer nanoparticles, lipid nanoparticles and siRNA conjugates.
- Rosemary Kanasty
- , Joseph Robert Dorkin
- & Daniel Anderson
-
Review Article |
 Engineering synthetic vaccines using cues from natural immunity
Engineering synthetic vaccines using cues from natural immunity
The clinical application of vaccines has expanded from infectious diseases to cancer, enhancing our vision of how the immune system can be used to prevent and treat disease. This Review highlights recent developments, clinical successes and future challenges in the design of prophylactic, therapeutic and tolerance-inducing synthetic vaccines with inspiration from the natural immune system.
- Darrell J. Irvine
- , Melody A. Swartz
- & Gregory L. Szeto
-
Review Article |
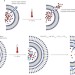 Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery
Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery
Nanoscale materials that deliver drugs in response to specific stimuli offer enhanced control of the drugs' release profile and distribution. This Review provides a comprehensive discussion of progress during the past five years in the design of nanoscale systems that can respond to exogenous stimuli such as temperature or variations in light or magnetic-field intensities, or to endogenous stimuli such as redox gradients or changes in pH or enzyme concentration.
- Simona Mura
- , Julien Nicolas
- & Patrick Couvreur
-
-
-
-
Article |
 Polymer multilayer tattooing for enhanced DNA vaccination
Polymer multilayer tattooing for enhanced DNA vaccination
Microneedle arrays coated with a pH-sensitive releasable layer act as an intradermal delivery system for polyelectrolyte films containing bioactive molecules for DNA vaccination. The implanted films co-deliver DNA, transfection agents and adjuvants, promoting local transfection and generating immune responses that can be tuned from days to weeks.
- Peter C. DeMuth
- , Younjin Min
- & Darrell J. Irvine
-
News & Views |
 Combo combat
Combo combat
Nanoparticle-enabled, sustained delivery of soluble hydrophilic cytokines and hydrophobic inhibitors engages the innate and adaptive immune systems to fight cancer.
- C. Jeffrey Brinker
-
Article |
 Combination delivery of TGF-β inhibitor and IL-2 by nanoscale liposomal polymeric gels enhances tumour immunotherapy
Combination delivery of TGF-β inhibitor and IL-2 by nanoscale liposomal polymeric gels enhances tumour immunotherapy
The sustained release of both hydrophilic and hydrophobic immunomodulators for metastatic melanoma by nanoscale liposomal polymeric gels administered intratumorally or systemically is demonstrated. It is also shown that such a co-delivery approach delays tumour growth and increases the survival of tumour-bearing mice, and that its efficacy results from the activation of both innate and adaptative immune responses.
- Jason Park
- , Stephen H. Wrzesinski
- & Tarek M. Fahmy
-
News & Views |
 Universal glue for cells
Universal glue for cells
A dendritic polymer consisting of inversely oriented lipid head groups on a polyvalent polyglycerol scaffold makes an effective reversible biomembrane adhesive that may find use as a tissue sealant and a drug-delivery vehicle.
- Holger Frey

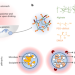 Drinkable in situ-forming tough hydrogels for gastrointestinal therapeutics
Drinkable in situ-forming tough hydrogels for gastrointestinal therapeutics Protein–polymer capsules
Protein–polymer capsules Squeeze to deliver
Squeeze to deliver