Series |
Collections
Filters
-
Collection Type
-
-
Series |
 Global change
Global change
In this article series, Nature Reviews Microbiology explores the relationship between microorganisms and global change, and considers the wider environmental and health challenges.
Image: Johan Swanepoel / Alamy Stock Photo -
Series |
 Antimicrobial resistance
Antimicrobial resistance
In this series of articles, Nature Reviews Microbiology explores the insights that have been gained from a flurry of research into the origin, evolution and spread of multidrug-resistant pathogens, the identification of resistance markers, the mechanistic links between the drug target and the associated resistant mutations, the need to improve quantitative risk assessment and the surveillance of resistance gene distribution, as well as the latest developments in antimicrobial drug discovery to produce the next generation of new, safe and effective antimicrobials.
Image: Philip Patenall -
Series |
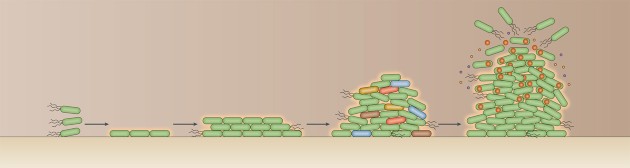 Microbial biofilms
Microbial biofilms
In this series of articles, Nature Reviews Microbiology explores the fascinating insights into biofilm ecology, the molecular mechanisms and regulation of biofilm formation, and the emerging physiological properties of this universal microbial lifestyle.
-
Series |
 Microbiome
Microbiome
In this series of articles, Nature Reviews Microbiology explores the latest developments in the study of environmental and host-associated microbiomes.
-
Series |
Microbiology pioneers
Nature Reviews Microbiologyturned 10 in October 2013. To mark the occasion of our 10th anniversary, we have commissioned a special Essay series entitled Microbiology Pioneers. We asked leading scientists across the different disciplines within microbiology to contribute an Essay on the individual or individuals who they feel have been the pioneers in their field. Each Essay in the series will have a different slant, with some focusing purely on the science and others being more personal, but we hope that each will be a fascinating read, providing an insight into the contributions of some unsung heroes. The image showsEscherichia coliexpressing the DsRed-Express2 fluorescent protein. Image courtesy of Sanna Koskiniemi, University of California, Santa Barbara, USA.
-
Series |
 New technologies: methods and applications
New technologies: methods and applications
In this series of articles, Nature Reviews Microbiology explores some of the most recent technological developments and their applications, highlighting the ways in which this powerful toolkit is changing the face of modern-day microbiology.
-
Series |
Antibiotic alternatives
The twentieth century was without doubt 'the age of the antibiotic'; all the known major antibiotic drug classes were identified, and the widespread use of antibiotics saw a substantial decrease in mortality and morbidity from common bacterial infections. However, that age is now well and truly over; the emergence of resistance to most commonly used antibiotics and the dwindling number of new antibiotics making it through the drug discovery pipeline pose a double threat to our continued protection from bacterial pathogens. In addition to limiting the spread of resistance through more prudent use of our current arsenal, it will become increasingly important to identify new classes of antibiotics and to develop alternative antimicrobial strategies that can replace antibiotics as they become ineffective. In this series of articles, Nature Reviews Microbiologyhighlights a number of alternative antimicrobial approaches that are currently being developed.
-
Series |
 Vector-borne diseases
Vector-borne diseases
In this article series, Nature Reviews Microbiology highlights the distinct features of a range of vector-borne pathogens and the diseases they cause, as well as how the host responds to these infections.
-
Series |
Systems Microbiology
Systems microbiology aims to integrate basic biological information with genomics, transcriptomics, metabolomics, glycomics, proteomics and other data to create an integrated model of how a microbial cell or community functions. Microorganisms are ideal for systems biology studies because they are easy to manipulate and have crucial roles in the biosphere and human health. This series examines some of the latest developments in this fast-moving field.
-
Series |
Food Microbiology
An abundant and safe food supply is the minimum expectation from our agricultural industry. Fulfilling this demand is a complex process involving plant cultivation, soil and water management, animal husbandry, harvesting, processing, storage and transport. The impact of microorganisms permeate every stage of this process — both positively and negatively — and understanding their role will be crucial to sustaining and improving food production, quality and safety. In this series of articles, Nature Reviews Microbiologyexplores the latest developments in the field of food microbiology.
-
Series |
Tropical Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases kill more than 14 million people each year, 90% of whom live in the developing world. In this series of articles we focus on the biology of infectious diseases that disproportionally affect poor and marginalized populations. This series will also examine the strategies being developed to contain and, ultimately, eradicate these diseases. The 'Tropical Infectious Disease' article series has been developed in collaboration with the WHO/TDR.

 COVID-19
COVID-19