Abstract
Nipah virus (NiV) and Hendra virus (HeV) are zoonotic henipaviruses (HNVs) responsible for outbreaks of encephalitis and respiratory illness with fatality rates of 50–100%. No vaccines or licensed therapeutics currently exist to protect humans against NiV or HeV. HNVs enter host cells by fusing the viral and cellular membranes via the concerted action of the attachment (G) and fusion (F) glycoproteins, the main targets of the humoral immune response. Here, we describe the isolation and humanization of a potent monoclonal antibody cross-neutralizing NiV and HeV. Cryo-electron microscopy, triggering and fusion studies show the antibody binds to a prefusion-specific quaternary epitope, conserved in NiV F and HeV F glycoproteins, and prevents membrane fusion and viral entry. This work supports the importance of the HNV prefusion F conformation for eliciting a robust immune response and paves the way for using this antibody for prophylaxis and post-exposure therapy with NiV- and HeV-infected individuals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Main
Nipah virus (NiV) and Hendra virus (HeV) are related zoonotic paramyxoviruses, belonging to the Henipavirus (HNV) genus. They cause severe encephalitis and respiratory illness, with fatality rates of 50–100%, and are classified as biosafety level 4 (BSL-4) select agents1. Unlike several other paramyxoviruses, HNVs have a broad species tropism (as is the case for canine distemper virus2) and can infect animals from at least six mammalian orders1. Pteropid fruit bats (flying foxes) appear to be the predominant natural reservoir hosts of HNVs3. Since the first outbreaks of HeV in Australia in 1994 and of NiV in Malaysia in 1998, HeV repeatedly infected horses in Australia with resultant human exposures4, while food-borne mediated NiV spillovers have occurred nearly every year in Bangladesh5. Furthermore, NiV outbreaks have occurred in the Philippines and in India6. Besides Asia and Oceania, the detection of anti-HNV antibodies in humans and Pteropus bats in Africa, a continent in which no documented NiV or HeV outbreaks have occurred, further suggests that future HNV zoonotic emergence is likely to happen7. Although more than two billion people live in regions threatened by potential HNV outbreaks, there are no clinically approved vaccines or specific therapeutics against these pathogens.
Paramyxoviruses deliver their genome to the host cytoplasm by fusing their lipid envelope with the cellular membrane to initiate infection. This process requires the concerted action of two surface glycoproteins, attachment (G/H/HN) and fusion (F), which sets the paramyxovirus entry machinery apart from all other class I fusion proteins. G is a type II homotetrameric transmembrane protein with an ectodomain comprising a stalk and a C-terminal β-propeller head, and the latter domain is responsible for binding to ephrinB2 or ephrinB3 (ephrinB2/B3) receptors8,9,10,11,12. F is a homotrimeric type I transmembrane protein that is synthesized as a premature F0 precursor and cleaved by cathepsin L during endocytic recycling to yield the mature, disulfide-linked, F1 and F2 subunits13,14,15. Viral fusion proteins are believed to exist in a kinetically trapped metastable conformation at the virus surface16. Upon binding to ephrinB2/B3, NiV G has been proposed to undergo conformational changes leading to F triggering and insertion of the F hydrophobic fusion peptide into the target membrane8,17,18. Subsequent refolding into the more stable postfusion F conformation drives merger of the viral and host membranes to form a pore for genome delivery to the cell cytoplasm, as shown for other paramyxoviruses and pneumoviruses13,19,20,21,22,23,24.
Paramyxovirus G/H/HN and F glycoproteins are the main targets of the humoral immune response and neutralizing antibodies are the key vaccine-induced protective mechanism against measles virus, for example25. Among the few well-characterized anti-HNV G neutralizing monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), m102.4 was previously isolated from a naïve human phage display library and shown to neutralize all known strains of NiV and HeV26,27,28. Moreover, m102.4 protected ferrets and African green monkeys from HeV/NiV lethal challenges when administered up to several days post infection29,30,31,32. Anti-F mouse polyclonal antibodies and hybridoma-secreted mAbs were shown to protect hamsters from NiV and HeV challenge33,34,35. We further demonstrated that immunization of mice with prefusion NiV F or HeV F led to strong homotypic serum neutralization titers, with lower heterotypic titers, whereas postfusion F failed to elicit a robust neutralizing response17. So far, no information is available about the epitopes recognized by HNV F mAbs and their potential for use as therapeutics in humans or to guide reverse vaccinology initiatives.
We previously isolated a hybridoma secreting a murine mAb that recognizes prefusion NiV F and HeV F glycoproteins, which we designated 5B317. We report here the cloning, sequencing and humanization of 5B3 (h5B3.1) and demonstrate it bound with high affinity to prefusion NiV F and HeV F. Neutralization assays, carried out under BSL-4 containment, showed that 5B3 and h5B3.1 potently inhibited NiV and HeV infection of target cells. We determined a cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the NiV F trimer in complex with 5B3 and found the antibody binds to a prefusion-specific quaternary epitope that is conserved in NiV F and HeV F. Our structural data, combined with F-triggering and membrane fusion assays, demonstrate that 5B3 locks F in the prefusion conformation and prevents membrane fusion via molecular stapling, providing a molecular rationale for its potency. These results define a critical neutralization epitope on the surface of the NiV and HeV F glycoproteins and pave the way for the future use of h5B3.1 for prophylaxis or as therapeutic for NiV- and HeV-infected individuals.
Results
5B3 and h5B3.1 antibodies potently neutralize NiV and HeV
To understand the humoral immune response directed at the HNV F glycoprotein, we cloned and sequenced the 5B3 neutralizing mAb from hybridomas previously obtained upon mice immunization with a prefusion NiV F ectodomain trimer17. The resulting antibody was subsequently humanized (and designated h5B3.1) to enable future therapeutic use in humans. We used biolayer interferometry to characterize the binding kinetics and affinity of the 5B3 and h5B3.1 Fab fragments to prefusion NiV F and HeV F ectodomain trimers immobilized on the surface of biosensors. The 5B3 Fab bound to HeV F/NiV F with equilibrium dissociation constants of 4.6–10 nM, compared to equilibrium dissociation constants of 31–61 nM for interactions with the h5B3.1 Fab (Fig. 1a–d and Supplementary Table 1). Analysis of the determined association and dissociation rate constants indicate that the weaker binding affinity of h5B3.1, compared to 5B3, largely resulted from an enhanced dissociation rate of h5B3.1 (Supplementary Table 1).
a–d, Binding of 5B3 (a,b) or h5B3.1 (c,d) Fab fragments to immobilized NiV F (a,c) or HeV F (b,d) analyzed by biolayer interferometry. The concentrations of injected 5B3 and h5B3.1 are indicated in b and d, respectively. Fitted curves are shown as black dashed lines. The vertical dotted lines correspond to the transition between the association and dissociation phases. The experiments were performed in replicates with two different preparations of NiV F and of HeV F and a representative experiment is shown. e–g, Neutralization of authentic NiV-Malaysia (NiV-M) (e), NiV-Bangladesh (NiV-B) (f) and HeV (g) by the 5B3 (grey) and h5B3.1 (brown) immunoglobulin-Gs (IgGs). D10 (green) is an anti-HIV antibody used as negative control. Data shown are mean and s.d. for n = 3 independent experiments (with independent virus preparations).
Subsequent neutralization assays were carried out using authentic NiV-Malaysia (NiV-M), NiV-Bangladesh (NiV-B) and HeV virions under BSL-4 containment. Plaque reduction assays were performed to analyze the neutralization of viruses pre-incubated with varying amounts of 5B3 or h5B3.1 antibodies. We determined mean half-maximal inhibitory concentrations of 1.2 µg ml−1 (5B3) and 0.9 µg ml−1 (h5B3.1) for NiV-M, 1.3 µg ml−1 (5B3) and 0.6 µg ml−1 (h5B3.1) for NiV-B and 1.4 µg ml−1 (5B3) and 1.3 µg ml−1 (h5B3.1) for HeV (Fig. 1e–g). These results show both 5B3 and h5B3.1 potently inhibited infectious NiV and HeV, the two HNVs responsible for recurrent outbreaks of lethal encephalitis and respiratory diseases in humans.
Cryo-electron microscopy structure of 5B3 in complex with the NiV F glycoprotein
To elucidate the mechanism of 5B3-mediated neutralization of NiV and HeV, we determined a cryo-EM structure of a stabilized NiV F ectodomain trimer in complex with the 5B3 antibody Fab fragment at 3.5 Å resolution (Fig. 2a,b, Table 1 and Extended Data 1). To assist model building, we also crystallized the isolated 5B3 Fab fragment and determined its structure at 1.5 Å resolution using X-ray crystallography (Table 2). In agreement with the features observed in the cryo-EM map, the local resolution is highest for most of the NiV F and the 5B3 variable domains, including the interface between NiV F and 5B3, whereas the Fab constant domains are poorly resolved, due to elbow flexibility between constant and variable domains, and were not modeled. The final model includes NiV F residues 27–480 with a chain break between residues 105 and 112. 5B3 binds to a quaternary epitope on domain III of the NiV F globular head, with a stoichiometry of three Fabs bound to an F trimer (Fig. 2a,b, Table 1 and Extended Data 1 and 2).
a,b, Two orthogonal views of the cryo-EM map at 3.5 Å resolution from the side (a) and from the top (b), facing toward the viral membrane. NiV F ectodomain trimer, teal; NiV F glycans, gold; 5B3 Fab heavy chain, purple; 5B3 Fab light chain, pink. The glycans are rendered using the unsharpened reconstruction.
The cryo-EM map resolves the four N-linked oligosaccharides present on each NiV F protomer (at positions Asn67, Asn99, Asn414 and Asn464) and reveals 5B3 recognizes a glycan-free epitope on the F surface. We could not detect an oligosaccharide at position Asn64 in the cryo-EM reconstruction (Fig. 2a,b), in agreement with previous biochemical studies36,37,38. All six complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) (and the light chain framework region 2) contribute to the paratope and bury 980 Å2 at the interface with the NiV F epitope, which mostly resides within one protomer (Fig. 3a,b). CDRL1 contacts the NiV F heptad-repeat A (HRA) β-hairpin via electrostatic interactions between Gln275B3 and Lys160F, Gln162F and Thr168F (Fig. 3a–c, Extended Data 2). CDRL1, CDRL3 and CDRH3 bind to the core β-sheet in domain III via contacts with both F2 (residues 53–55) and F1 (residues 282–285) subunits (Fig. 3a–c). CDRH2 protrudes at the interface between two NiV F protomers and interacts with a segment C-terminal to the central helix and with the upstream helix of a neighboring protomer (Fig. 3a–c and Extended Data 2). Comparison with the unliganded NiV F structure reveals that 5B3 binding induces a local reorganization (or stabilizes a different conformation) of the HRA β-hairpin (residues 160–170) and of residues 248–252 (Extended Data 3).
a, Ribbon diagram of the NiV F trimer in complex with the 5B3 Fab fragment. One F protomer is rendered in teal and the other two protomers in grey. Only one Fab fragment is shown for clarity. b, Molecular surface representation of the NiV F trimer with the 5B3 CDR loops shown as ribbons, highlighting the quaternary nature of the epitope. c, Enlarged view of the interface between NiV F and 5B3 with selected residues rendered as sticks. NiV F residues are colored teal with oxygen and nitrogen atoms colored red and blue, respectively. In a–c, the 5B3 variable heavy (VH5B3) and light (VL5B3) chains are colored purple and pink, respectively. d, Molecular surface representation of the NiV F trimer showing the 5B3 footprint colored by residue conservation among NiV F and HeV F glycoproteins. Conservative sub.: conservative substitution; semi-conserv. sub.: semi-conservative substitution.
5B3 relies on an atypical binding mode to NiV F with nearly equal contributions of the heavy (48%) and light (52%) chains to the antibody buried surface area. This, in part, results from the fact that CDRL1 is making a greater contribution to the paratope than the nine residue-long CDRH3 (268 Å2 versus 190 Å2 of buried surface area, respectively), in contrast with the canonical CDRH3-dominated antibody/antigen interfaces. To confirm these findings, we probed the NiV F binding ability of single-chain (scFv) chimeric constructs in which either the variable heavy (VH) or variable light (VL) h5B3 chains were replaced with an unrelated chain from a human scFv library. Although h5B3 scFv immunoprecipitated full-length NiV F, none of the scFv chimeras did, in agreement with the equivalent contributions to binding of the heavy and light chains observed in our structure (Fig. 3a,b and Extended Data 4a). The structural data were further validated using site-directed mutagenesis of selected residues participating in the NiV F epitope followed by 5B3-mediated immunoprecipitation to assess residual binding (Extended Data 4b). We also used the prefusion F specific 12B2 antibody as well as a cell–cell fusion assay to probe the conformational integrity of the F mutants analyzed (Extended Data 4b,c). The NiV F K55A substitution inhibited 5B3 recognition, which is probably explained by the loss of interactions with CDRL1 Trp325B3 and CDRL3 Tyr925B3 residues, as visualized in our structure. Furthermore, abrogation of 5B3 binding to NiV F L53D or L53S probably resulted from reduction of favorable interactions with CDRL1 Trp325B3, CDRL3 Phe915B3 and CRH3 Tyr1025B3. Given that the tested mutants bound to the12B2 antibody and retained 40–100% of the wild-type F fusion activity (Extended Data 4b,c), we conclude that the observed loss of binding largely resulted from specific disruption of interactions with 5B3, without major effects on the overall F structure.
Analysis of the structure rationalizes the observed cross-neutralization of NiV and HeV because 35 out of the 39 NiV F residues buried upon 5B3 binding are strictly conserved. Variable positions are Thr81NiV, Asn84NiV, Thr88NiV and Arg336NiV, which are conservatively or semi-conservatively substituted to Ser81HeV, Thr84HeV, Ser88HeV and Lys336HeV, respectively (Fig. 3d).
Isolation of a NiV neutralization-escape mutant
As for other RNA viruses, the high mutation rate of HNVs could yield variants able to overcome 5B3 inhibition. For example, we showed that passaging NiV or HeV with anti-HNV G antibodies led to the isolation of viral mutants escaping neutralization by the respective antibody28,39. To assess the possibility of generating 5B3 neutralization-escape virus mutants, such as the aforementioned binding-deficient F mutants identified by site-directed mutagenesis, we passaged authentic NiV for three rounds in the presence of 5B3 in BSL-4 containment. Plaque purified resistant viruses were isolated, and viral RNA from five NiV isolates was reverse-transcribed into cDNA for sequencing of the F gene. All five NiV escape mutants harbored the same F K55E substitution. This finding supports our aforementioned mutagenesis data because the NiV F K55A was completely defective in 5B3 binding. We recombinantly produced the K55E F mutant and observed it could not bind 5B3 while maintaining its ability to interact with 12B2 and to promote wild-type cell–cell fusion activity (Extended Data 4b,c). These experiments are in full agreement with our structural and biochemical data and show that NiV could escape 5B3 neutralization without affecting F-mediated fusion, although the impact of the identified substitution on viral growth is not known.
The 5B3 antibody inhibits F-mediated fusion
Our structural data suggest 5B3 prevents fusogenic conformational changes leading to membrane fusion by locking NiV F in the prefusion state. The antibody recognizes a discontinuous epitope, spanning two neighboring protomers, present only in prefusion F, based on the conformational changes observed in the related parainfluenza virus 3 postfusion F and respiratory syncytial virus postfusion F structures20,23,24 (Figs. 3a–c and 4a,b). Furthermore, CDRL1 interactions with the HRA β-hairpin hinders refolding of the latter motif to contribute to the formation of an elongated central helix, observed in the postfusion F state. This antibody-mediated molecular stapling strategy, involving simultaneous interactions with protein segments that are close to each other in prefusion F but far apart in postfusion F (Fig. 4a,b), is conceptually equivalent to the disulfide stapling approach implemented for stabilizing the prefusion conformation of measles virus F40, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) F41, HeV F42 and PIV F43 glycoproteins. Finally, we predict unfavorable steric clashes would occur with a 5B3 antibody bound to a neighboring protomer upon F refolding.
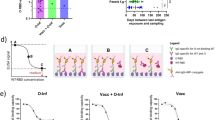
a, Molecular surface representation of the NiV F prefusion trimer showing the 5B3 footprint colored violet. b, Molecular surface representation of a homology model of the NiV F postfusion trimer showing the 5B3 footprint colored violet. Upon refolding, the 5B3 epitope is reorganized. The latter model was obtained by threading the NiV F sequence onto the human parainfluenza virus 3 postfusion F structure20 (PDB 1ZTM). c, 5B3 concentration-dependent inhibition of streptavidin-mediated pulldown of a biotinylated HRB/NiV F conformational intermediate complex in a triggering assay. The non-neutralizing control antibody (13G5), which is specific for postfusion F, had no effect. d, NiV F triggering assay carried out in the presence of 5B3 or h5B3.1 IgGs showing both mAbs prevented F fusogenic conformational changes. Subsequent protein G immunoprecipitation of F/5B3 and F/h5B3.1 complexes that were not pulled down by the biotinylated HRB peptide indicated the antibodies remain bound to F. e, Capture of an F fusogenic conformational intermediate could be partially rescued by raising the temperature to ≥60 °C, as detected by comparing streptavidin-mediated pulldown and protein G immunoprecipitation of F/5B3 and F/h5B3.1 complexes. In a and b, a single 5B3 epitope is colored for clarity. In all panels, precipitated samples were analyzed by western blotting using a rabbit anti-F antibody. f,g, NiV F (f) or HeV F (g) mediated cell-cell fusion could be inhibited by 5B3 or h5B3.1 in a concentration-dependent manner. D54 is an HIV envelope antibody used as negative control. Data shown are mean and s.d. for n = 2 technical replicates. Uncropped images for d and e are available in the source data online.
To validate the hypothesis that 5B3 locks NiV F in the prefusion conformation, we used an in vitro F triggering assay entailing (1) cleavage of the wild-type NiV F0 ectodomain trimer with trypsin, under limited proteolysis conditions, to recapitulate the in vivo cathepsin L-mediated production of F1 and F214,15 and (2) incubation at 50 °C to promote refolding of the trypsin-cleaved prefusion F trimer to the postfusion conformation17,19. We previously showed peptides derived from the heptad-repeat B (HRB) sequence of NiV F or HeV F prevent completion of F refolding and are potent inhibitors of fusion and live virus infection44,45. Furthermore, when the triggering assay was carried out in the presence of a biotinylated HRB peptide, a conformational intermediate of the fusion reaction was captured and could be used as a reporter of F activation. Using this approach, we demonstrate here that addition of 5B3 or h5B3.1 during the triggering assay blocked fusogenic conformational changes in a concentration-dependent manner, whereas a non-neutralizing control antibody (13G5), specific for postfusion F, did not (Fig. 4c,d). Subsequent antibody affinity purification (protein G) of the material not captured by the HRB peptide showed 5B3 (or h5B3.1) remained bound to F (Fig. 4d), supporting the hypothesis that 5B3/h5B3.1 trap NiV F in the prefusion conformation. Finally, capture of an F intermediate could be partially rescued by raising the temperature to ≥60 °C, indicating that binding of 5B3/h5B3.1 stabilizes NiV F by raising the energy barrier for transitioning to the postfusion state (Fig. 4e). In summary, the structural and biochemical data presented here show 5B3/h5B3.1 inhibited fusogenic conformational changes by locking F in the prefusion state and raising the free energy of activation for fusion triggering.
To further study the mechanism of action of 5B3/h5B3.1 in the context of a full-length, membrane-embedded F glycoprotein, we carried out cell–cell fusion assays in the presence of varying concentrations of mAbs. We observed that 5B3 and h5B3.1 prevented NiV F- and HeV F-mediated membrane fusion in a concentration-dependent manner, consistent with the expectation that trapping F in the prefusion conformation actually resulted in inhibition of membrane fusion (Figs. 4f,g and 5).
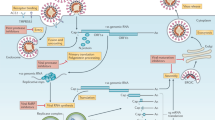
Model of F-mediated membrane fusion. NiV (or HeV) F forms metastable homotrimers at the viral surface. Upon interaction between NiV (or HeV) G and ephrinB2/B3, F undergoes large-scale conformational changes leading to insertion of the fusion peptide in the host cell membrane by forming a hypothetical pre-hairpin extended intermediate conformation16. Subsequent F refolding leads to the postfusion conformation and merger of the viral and host membranes. Addition of 5B3 or h5B3.1 locks F in the prefusion conformation and inhibits membrane fusion.
Discussion
The paramyxovirus and pneumovirus F glycoproteins are key players of viral entry, promoting fusion of the viral and host membranes through large-scale structural rearrangements13,20,21,22,23,24. The F conformation presented to the immune system can be a major determinant of the antibody response elicited by these glycoproteins. Previous work showed that most of the RSV-neutralizing activity in human serum is conferred by antibodies specifically recognizing prefusion F46. Structure-based physical stabilization of the RSV F prefusion state via mutations and fusion to another protein (domain) as well as multivalent display on a computationally designed nanoparticle platform correlated with increased elicitation of neutralizing mAbs22,41,47,48. Prefusion stabilized F also induced greater neutralizing humoral immune responses than postfusion F against parainfluenza viruses in mice and rhesus macaques43. However, antibodies present in the sera of mice immunized with human metapneumovirus prefusion or postfusion F ectodomain trimers bound similarly to either protein conformation and equally neutralized virus infectivity, demonstrating that prefusion and postfusion F share most neutralizing epitopes for this virus49. We previously established that fusing a GCN4 trimeric motif at the C-terminal end of the NiV F and HeV F ectodomains resulted in the production of prefusion stabilized trimers that could elicit a neutralizing antibody response in mice17. No HNV F mAb, however, had been characterized at the molecular level.
Here, we have sequenced and humanized the 5B3 neutralizing mAb and demonstrated its ability to cross-neutralize authentic NiV and HeV. We show 5B3 and h5B3.1 inhibited membrane fusion by locking F in the prefusion conformation upon binding to a conformational (quaternary) epitope, which is reorganized during the fusion reaction. This mechanism of action rationalizes the potent 5B3/h5B3.1-mediated neutralization of NiV and HeV entry into target cells and is reminiscent of D25 inhibition of RSV via binding to and stabilization of prefusion F22. These findings are also in line with the enhanced properties of RSV and parainfluenza virus prefusion-stabilized F glycoproteins as candidate vaccine immunogens compared to the corresponding postfusion F41,43,48. Accordingly, the previously developed disulfide-stabilized prefusion HeV F42, and the corresponding prefusion NiV F construct engineered here, bear the promise of eliciting stronger neutralizing antibody titers than GCN4-only stabilized F glycoprotein ectodomains, by preventing refolding to the postfusion conformation.
So far, m102.4 is the only human mAb that has been used for HNV protection studies in ferrets and African green monkeys29,30,31. Murine antibodies have limited clinical use due to their short serum half-life, inability to trigger human effector functions and the risk of mounting an anti-mouse antibody response. We successfully engineered a humanized version of 5B3 (termed h5B3.1), which retained comparable breadth and potency to the parental mouse mAb and inhibited F-mediated membrane fusion. Therefore, similar to the anti-HNV G m102.4 neutralizing mAb, h5B3.1 could potentially be used for prophylaxis or for post-exposure therapy with individuals exposed to NiV or HeV. Between 2010 and 2017, m102.4 was used on a compassionate basis to treat individuals with significant HeV or NiV exposure risk in Australia, the USA and India (https://www.who.int/blueprint/priority-diseases/key-action/nipah/en/). These individuals showed no evidence of infection or known health complications after administration of the mAb. The fact that m102.4 was used in humans despite the lack of clinical trials or approval by the FDA (or equivalent agencies) emphasizes the urgent need for developing therapeutics and other counter-measures against highly pathogenic HNVs that have fatality rates of 50–100%.
Escape mutants have been isolated upon HNV passaging with m102.439 or with 5B3 (here), but they have never been observed during m102.4 in vivo efficacy tests against NiV or HeV, putatively due to the very high doses of antibodies utilized in those experiments in conjunction with the effective adaptive immune responses of the subjects. We postulate that similar outcomes could be expected with comparably high doses of 5B3/h5B3.1 mAbs. Furthermore, neutralization escape mutations to such an F-specific mAb could have a potentially negative impact on viral growth, replication and virulence, as observed with mutants obtained with anti-G antibodies28. Finally, the use of antibody cocktails has been proposed for Ebola virus50,51,52 or severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV)53 and implemented as a commercially available therapeutic for hepatitis C virus (XTL-6865, XTL Biopharmaceuticals) to prevent and/or limit the emergence of such mutants as well as enhance neutralization breadth. We suggest a similar strategy: combining h5B3.1 and m102.4 or other anti-HNV mAbs, targeting multiple antigenic sites on G and F, could be implemented for treating future NiV and HeV infections.
Methods
Cell lines
HEK293F cells (Life Technologies) were grown in 293FreeStyle expression medium (Life Technologies), cultured at 37 °C with 5% CO2 and 150 r.p.m. HEK293T/17 is a female human embryonic kidney cell line (ATCC). HEK293T/17 cells (kind gift from G. Quinnan) were cultured at 37 °C with 5% CO2 in flasks with DMEM + 10% FBS + penicillin-streptomycin + 10 mM HEPES. VeroE6 cells (ATCC) were grown in serum-free medium (VP-SFM, ThermoFisher) at 37 °C and 5% CO2. HeLa-USU and HeLa-ATCC (ATCC) cells12 were maintained in DMEM (Quality Biologicals), supplemented with 10% Cosmic calf serum (HyClone), and 2 mM l-glutamine. HeLa-USU cells, ephrin-B2 and ephrin-B3 negative, (kind gift from A. Maurelli, Uniformed Services University) and HeLa-CCL2, ephrin-B2 positive (ATCC), have previously undergone cytogenetic analysis. Other cell lines were not authenticated. Cells were not tested for mycoplasma contamination.
Antibodies and peptides
The rabbit anti-F polyclonal antibody was produced by Spring Valley Laboratories using the NiV F ectodomain trimer fused to GCN417 as an immunogen. The horseradish peroxidase-conjugated rabbit anti-S-peptide antibody was purchased from Bethyl Laboratories. Anti-F murine monoclonal antibodies were produced as previously described17.
The N-terminal biotinylated NiV F HRB peptide (residues 453–488)44 was synthesized by Global Peptide Services.
NiV F and HeV F construct
The NiV F and HeV F ectodomain constructs used for biolayer interferometry and NiV F triggering assay include the codon optimized NiV F (isolate UMMC1; GenBank sequence accession no. AY029767) or HeV F (isolate Horse/Australia/Hendra/1994) ectodomain (residues 1–487) fused to a C-terminal GCN4 followed by a factor Xa sequence and an S-tag (KLKETAAAKFERQHMDS) cloned in a pcDNA Hygro (+)-CMV+ vector for transient expression using FreeStyle 293F cells. For epitope mapping, conversion of specific residues of NiV F to alanine, serine, glutamic acid or aspartic acid was performed via site-directed mutagenesis using the Quick-Change II Site-directed Mutagenesis Kit (Stratagene). The template for the reactions consisted of a C-terminal S-peptide tagged version of the codon optimized full-length NiV F (UMMC1 isolate) cloned in the pcDNA Hygro (+)-CMV+ vector. All mutation-containing constructs were sequence verified.
The NiV F ectodomain construct used for cryo-EM experiments includes a human codon-optimized NiV F ectodomain trimer (amino acid residues 1–494) with a FLAG tag (DYKDDDK) introduced between residues L104-V105 and a C-terminal GCN4 motif (a kind gift from H. Aguilar-Carreno). This construct was engineered by subcloning into a pBS SK(+) vector and introducing the previously described N100C/A119C substitutions42 by site-directed mutagenesis using a QuikChange kit (Agilent) before subsequent subcloning into a pCAGGs vector for transient expression in FreeStyle 293F cells.
Cloning and sequencing of mAb 5B3 cDNA
The 5B3 cDNA was amplified from hybridomas using a SuperScript III Cells Direct cDNA Synthesis Kit (Invitrogen) with random hexamer and IgG2-specific primers54. PCR amplification of VH and VL was performed using the cDNA as a template and degenerate forward primers for the signal sequence or the conserved framework 1 (FR1) of the VH- and VL-encoding sequences and reverse primers for the FR4 or the 3′ end of the constant heavy chain 1 (CH1)- and constant light chain (CL)-encoding sequences54,55. The PCR products were cloned into pCR-Blunt II-TOPO vector (Invitrogen) and transformed into one Shot TOP10 chemically competent Escherichia coli (Invitrogen). Plasmids were extracted from colonies and the cloned PCR products were sequenced using M13 forward and reverse primers.
Humanization of 5B3 to generate h5B3 and h5B3.1
To engineer a humanized version of 5B3, a human scFv library was first generated based on FR1 and FR4 sequence similarity with 5B3. We adapted previously described methods and PCR primers employed for the generation of naive human scFv library constructed from peripheral blood B cells of several healthy donors56 by using only the VH subfamily III and κ VL subfamily I primers. VH and VL were first amplified separately from the IgM cDNA library. For VH, we used forward and reverse primers probing the FR1 and FR4 of VH III with restriction site SfiI added to the 5′ end of the forward primer and (G4S)3 linker sequence added to the 3′ end of the reverse primer. For VL, we used forward and reverse primers probing the FR1 and FR4 of VLκ I with (G4S)3 linker sequence added to the 5′ end of the forward primer and restriction site SfiI added to the 3′ end of the reverse primer. The scFv library was assembled by overlapping PCR combining the VH and VL PCR products as template and using the VH III FR1 SfiI forward and VLκ I FR4 SfiI reverse primers. The amplified scFv was then cloned into a pCom3X vector harboring a C-terminal hexa-histidine tag. Colonies from the scFv library were grown and expressed as previously described57. We selected the 12 best expressing clones for DNA sequencing based on Coomassie blue staining and western blot analysis using an anti-histidine tag antibody. The translated human scFv FR sequences were then aligned against that of 5B3. For humanization of 5B3, conserved human residues from the alignment were identified and replaced into the homologous positions of 5B3 to generate h5B3. To further humanize h5B3, a version named h5B3.1 was generated from h5B3 where one residue on each of the CDR1 and CDR2 and two residues on CDR3 were mutated into conserved human residues based on the sequences from the human scFv library mentioned above.
scFv and IgG1 constructs
The scFv constructs were designed with VH and VL separated by a flexible linker (G4S)3, codon-optimized, synthesized by Genscript and cloned into a promoter-modified pcDNA Hygro (+)-CMV+vector58 with a immunoglobulin κ chain leader sequence and a C-terminal S-peptide tag followed by a hexa-histidine tag.
For IgG constructs, VH and VL were cloned into a pDR12 vector that harbors the κ CL and IgG1 CH fragments as separate open reading frames with independent promoters59. Subsequently, the entire expression cassette of the heavy and light chain of pDR12-h5B3.1 was amplified and sub-cloned into pcDNA Hygro (+)-CMV+ vector for the development of stable cell lines.
Generation of scFv- and IgG1-expressing stable cell lines
HEK 293T cells grown in D-10 were transfected with different scFv or IgG1 constructs using Fugene transfection reagent (Roche Diagnostics). Cells were transfected with 2 µg DNA and 6 µl Fugene per well of a 60% confluent six-well tissue culture plate following the manufacturer’s instructions. At 48 h post transfection, the culture medium was either replaced with selection medium (D-10 supplemented with 150 µg ml−1 of hygromycin B, Invitrogen) for stable cell line development or harvested for S-protein agarose (EMD Biosciences) or Ni-NTA agarose (QIAGEN) precipitation for transient expression evaluation. To generate a cell line for stable expression, hygromycin-resistant cells were then subjected to two rounds of limiting dilution cloning, as previously described58.
Large-scale expression and purification of IgG1
Production and purification of mouse IgGs (5B3, 12B2 and 13G5) from hybridomas was carried out as previously described17.
Transient expression of h5B3.1 IgG1 was carried out by transfecting FreeStyle 293F suspension cells in serum-free FreeStyle 293 expression medium (Invitrogen) in shaker flasks at a density of 1 × 106 cells ml−1 using 293fectin transfection reagent (Invitrogen) following the manufacturer’s protocol. Production of h5B3.1 IgG1 from a stable cell line was carried out by culturing the FreeStyle 293F cells expressing h5B3.1 IgG1 in 70 ml of FreeStyle 293 expression medium in 500 ml shaker flasks at a density of 1 × 106 cells ml−1. The transfected cells or stable cells were allowed to grow for an additional 3–4 days with 50 ml of culture medium added for every subsequent day.
Culture supernatants expressing IgG were collected and centrifuged at 4 °C for 15 min at 5,000g. The supernatant was then filtered through a 0.2 µm low protein binding membrane (Corning) and passed through a HiTrap Protein G HP column (GE Healthcare Biosciences) equilibrated in phosphate-buffered saline (Quality Biologicals). The column was washed with five column volumes of phosphate-buffered saline. The bound mAb was eluted with 0.1 M glycine pH 2 followed by immediate neutralization with 1 M Tris pH 8.0, concentrated, and buffer-exchanged into phosphate-buffered saline using an Amicon Ultra centrifugal concentrator (Millipore).
Generation of Fab fragments from IgG
The 5B3 Fab was obtained by fragmentation of mouse 5B3 IgG using Pierce mouse IgG1 Fab and F(ab′)2 preparation kits according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
The h5B3.1 Fab fragment was obtained by fragmentation of h5B3.1 IgG with Lys-C protease (EMD Millipore) and affinity purification using protein A agarose resin (Genscript). Briefly, 1.0 mg IgG was incubated with 0.5 µg Lys-C for 7 h at 37 °C. The reaction was quenched by addition of PMSF to 1 mM final concentration and the undigested and Fc-containing portion of the sample was removed using a protein A resin. The Fab-containing flow-through from the protein A affinity step was collected.
The Fab-containing fraction was concentrated and further purified using a Superdex 75 10/300 gel filtration column equilibrated in a buffer containing 50 mM Tris pH 8.0 and 150 mM NaCl.
NiV F and HeV F ectodomain production
Soluble NiV F and HeV F were produced by transient transfection of FreeStyle 293F cells at a density of 1 × 106 cells ml−1 with the corresponding plasmid using 293-Free transfection reagent (Millipore) and Opti-MEM (Thermo-Fisher) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. After five days in a humidified shaking incubator, maintained at 37 °C and 8% CO2, the cell supernatant was harvested and clarified of cell debris by centrifugation. Subsequent affinity purification was carried out using an anti-FLAG resin (Genscript) and elution with 1 mg ml−1 FLAG peptide dissolved in Tris buffer pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl or with S-protein agarose (Millipore Sigma, Novagen) and elution with 0.2 M citric acid pH 2.0 followed by immediate neutralization with 1.0 M Tris pH 9.5. The eluted fraction was buffer-exchanged into 50 mM Tris buffer pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl using a 30 kDa cutoff centrifugal concentrator (Millipore).
Biolayer interferometry
Assays were performed with an Octet Red 96 instrument (ForteBio) at 30 °C while shaking at 1,000 r.p.m. All measurements were corrected by subtracting the background signal obtained from biosensors without immobilized HeV F or NiV F. S-peptide tagged HeV F or NiV F in phosphate buffered saline at pH 7.4 was diluted to 14 µg ml−1 in 10 mM acetate buffer pH 5.0 before immobilization on N-hydroxysuccinimide-(1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride (NHS-EDC). NHS-EDC-activated Amine Reactive 2nd Generation (AR2G, ForteBio) biosensors for 300 s. The sensors were then quenched in 1 M ethanolamine (ForteBio) for 300 s and incubated in kinetics buffer (KB: 1× PBS, 0.01% BSA, 0.02% Tween 20 and 0.005% NaN3 (ForteBio)) for 300 s to establish the baseline signal (nm shift). HeV F- or NiV F-loaded sensors were then immersed in solutions of purified Fab (5B3 or h5B3.1) diluted in KB to the desired concentrations for kinetics analysis (300–1.23 nM for 5B3 Fab and 900–3.7 nM for h5B3.1 Fab). Curve fitting was performed using a 1:1 binding model to determine the binding kinetics with ForteBio data analysis software. Mean kon and koff values were determined with a global fit applied to all data. Experiments were performed twice with independent NiV F and HeV F protein preparations, yielding identical results and kinetic parameters.
Crystallization, data collection and processing of the 5B3 Fab
Crystals were grown in hanging drops set up with a mosquito at 20 °C using 150 nl protein solution and 150 nl mother liquor containing 0.2 M magnesium chloride, 0.1 M Tris-HCl pH 8.5 and 20% PEG 8000. The diffraction dataset was collected at ALS beamline 5.0.1 and processed to 1.5 Å resolution using XDS60 and Aimless61. The structure was solved by molecular replacement using Phaser62 and S230 SARS-CoV Fab63 as search model. The coordinates were subsequently improved and completed using Buccaneer64 and COOT65 and refined with BUSTER-TNT66 and REFMAC567. The quality of the final model was analyzed using MolProbity68 (score 1.13) and Clashscore (3.35). The percentage of poor rotamers was 0.92%; Ramachandran statistics were 98.84% favored and 100% allowed. Other crystallographic data collection and refinement statistics are summarized in Table 2.
Purification of the NiV F–5B3 complex
Purified FLAG-tagged NiV F N100C/A119C ectodomain was combined with an excess molar ratio of 5B3 Fab and incubated on ice for 1 h before injection on a Superose 6 Increase 10/300 column (GE Healthcare) equilibrated in a buffer containing 50 mM Tris pH 8.0 and 150 mM NaCl. The fractions containing the complex were quality-controlled by negative staining EM, pooled, buffer-exchanged and concentrated.
Cryo-electron microscopy specimen preparation and data collection
A 3 µl volume of the purified FLAG-tagged NiV F N100C/A119C 5B3 Fab complex at a concentration of 0.1 mg ml−1 was applied onto glow-discharged C-flat (Cu 200 mesh, CF-1.2/1.3, Protochips) holey carbon grids covered with a thin layer of continuous home-made carbon and incubated for 30 s on grids. Grids were then plunge-frozen in liquid ethane and cooled with liquid nitrogen, using an FEI MK4 Vitrobot with a 3.0 s blot time. The chamber was kept at 20 °C and 100% humidity during the blotting process.
Data acquisition was carried out with the Leginon data collection software69 on an FEI Titan Krios electron microscope operated at 300 kV and equipped with a Gatan BioQuantum energy filter (slit width of 20 eV) and a Gatan K2 Summit camera. The nominal magnification was 105,000× and the pixel size was 1.37 Å. The dose rate was adjusted to 8 counts per pixel per second and each video was acquired in counting mode fractionated in 50 frames of 200 ms each. A total of 2,686 micrographs were collected with a defocus range between 1.5 and 2.5 µm.
Cryo-electron microscopy data processing
Video frame alignment was carried out with MotionCor270. Particles were automatically selected using DoG Picker71 within the Appion interface72. Initial defocus parameters were estimated with GCTF73. A total of 380,459 particles were picked, extracted and processed with a box size of 256 pixel2 and preprocessed using Relion 3.074. Reference-free two-dimensional (2D) classification with cryoSPARC was used to select a subset of particles, which were used to generate an initial model using the Ab-Initio reconstruction function in cryoSPARC75. This 3D map was subsequently used as a reference for running 3D classification with C3 symmetry in Relion on the entire dataset. 262,879 particles were selected from the set of all picked particles for 3D refinement using Relion. CTF refinement in Relion 3.0 was used to refine per-particle defocus values and particle images were subjected to the Bayesian polishing procedure in Relion 3.076 and 3D refinement before performing another round of CTF refinement and 3D refinement. The particles were subsequently subjected to another round of 3D classification in Relion 3.0 without refining angles and shifts. 38,756 particles from the best class (showing a resolved stem) were used for non-uniform refinement in CryoSPARC to obtain the final 3D reconstruction at 3.5 Å resolution. Reported resolutions are based on the gold-standard FSC = 0.143 criterion77,78 and Fourier shell correlation curves were corrected for the effects of soft masking by high-resolution noise substitution79. Local resolution estimation and filtering was carried out using cryoSPARC. Data collection and processing parameters are listed in Table 1.
Model building and analysis
UCSF Chimera80 was used to rigid-body fit the crystal structures of the NiV F ectodomain13 and of the 5B3 Fab crystal structure into the cryo-EM density. The model was subsequently rebuilt manually using Coot81 and refined using Rosetta82,83,84. Glycan refinement relied on a dedicated Rosetta protocol, which uses physically realistic geometries based on prior knowledge of saccharide chemical properties85 and was aided by using both sharpened and unsharpened maps. Models were analyzed using MolProbity68, EMRinger86 and Privateer87. The refinement statistics are listed in Table 1. Figures were generated using UCSF ChimeraX88.
Immunoprecipitation
To evaluate the binding of NiV F mutants with different antibodies, sub-confluent HEK 293T cells were transfected with untagged full-length wild type or one of the mutant NiV F constructs using the Fugene transfection reagent, as described above. Cells were harvested at 48 h post transfection and were lysed in 500 µl buffer containing 0.1 M Tris pH 8.0, 0.1 M NaCl supplemented with complete protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche) and clarified by centrifugation. Clarified lysates were added to 2 µg of IgG followed by 50 µl of 20% slurry protein G sepharose for samples incubated with IgGs or 30 µl of 50% slurry S-protein agarose for those that were not.
To evaluate h5B3 chain binding to F, 300 µl of clarified untagged full-length F-expressing HEK 293T cell lysate was added to the h5B3 scFv-expressing culture supernatants and precipitated with 30 µl of 50% slurry of S-protein agarose.
In all cases, immunoprecipitation/pulldown were performed overnight at 4 °C. The samples were washed three times with a buffer containing 1% Triton X-100, 0.1 M Tris pH 8.0, 0.1 M NaCl and subsequently boiled in reducing SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) sample buffer followed by SDS–PAGE and western blot analyses.
HRB peptide triggering assay
The capture assay was performed as previously described17 with the addition of a competition step in the presence of increasing amounts of IgGs. Briefly, 1 µg of purified S-peptide tagged NiV F ectodomain trimer was cleaved with 10 ng of trypsin (New England Biolabs) in a 10 μl reaction volume of buffer at 4 °C overnight to generate the mature F1 and F2 subunits. The reaction was stopped with 1 μl of 10× complete protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche). Subsequently, 2 µg of biotinylated NiV F HRB peptide was added in the presence or absence of competing IgG. The sample was heated for 15 min at 50 °C, 60 °C, 65 °C or 70 °C and the NiV F/HRB complex was subsequently pulled down using 30 µl of 50% avidin-agarose slurry for 1 h at 4 °C (Thermo Fisher Scientific). When indicated, the unbound fraction was pulled down with protein G sepharose. Samples were washed three times with a buffer containing 1% Triton X-100, 0.1 M Tris pH 8.0, 0.1 M NaCl and boiled in 50 µl of reducing SDS–PAGE sample buffer. To analyze the precipitated product, a 25 µl sample was applied to a 4–12% BT SDS–PAGE (Invitrogen) followed by western blotting and detection using a rabbit anti-NiV F polyclonal antibody.
Cell–cell fusion assays
Fusion between NiV F and G glycoprotein-expressing effector cells and permissive target cells was measured using a previously described β-galactosidase assay89. Briefly, plasmids encoding S-peptide tagged wild-type NiV F or each mutant of F and NiV G or no DNA (control/mock transfection) were transfected into HeLa-USU effector cells using lipofectamine LTX with Plus reagent (Thermo-Fischer Scientific). The following day, transfected cells were infected with vaccinia virus-encoding T7 RNA polymerase. HeLa-ATCC cells served as receptor-positive target cells and were also infected with the E. coli Lac Z-encoding reporter vaccinia virus. Cells were infected at a multiplicity of infection of 10 and incubated at 37 °C overnight. Cell fusion reactions were conducted by incubating the target and effector cell mixtures at a ratio of 1:1 (2 × 105 total cells per well; 0.2 ml total volume) in 96-well plates at 37 °C. Cytosine arabinoside (40 µg ml−1, Sigma-Aldrich) was added to the fusion reaction mixture to reduce non-specific β-galactosidase production. Nonidet P40 (EMD Millipore Sigma) was added (0.5% final concentration) at 2.5 or 3.0 h, and aliquots of the lysates were assayed for β-galactosidase at ambient temperature with the substrate chlorophenol red–d-galactopyranoside (Roche). Assays were performed in triplicate, and fusion results were calculated and expressed as rates of β-Gal activity (change in optical density at 570 nm min−1 × 1,000) in a VersaMAX microplate reader (Molecular Devices). Equal amounts of leftover F/G-expressing effector cells from each fusion reaction were lysed and clarified by centrifugation. The lysates were then subjected to S-protein agarose precipitation followed by SDS–PAGE and western blotting to evaluate the expression level of each F mutant as compared to wild type. The individual cell fusion reactions mediated by each mutant were converted to percentages of wild-type fusion activity and normalized with the total expression of F and each F mutant as measured by densitometry from the images of western blot bands using ImageQuantTL software (GE Healthcare Biosciences). Normalization of each F mutant percentage of wild-type fusion was calculated with the formula: normalized percentage of wild-type fusion = (100/percentage of wild-type expression) × percentage of wild-type fusion.
NiV and HeV F mAb neutralization assays
The virus infectivity neutralization concentrations of a control antibody D10 IgG2a anti-HIV gp4190, 5B3 IgG anti-F and h5B3.1 IgG1 anti-F were determined for NiV and HeV using a plaque reduction assay. Briefly, antibodies were serially diluted fivefold from 150 μg ml−1 to 1.9 ng ml−1 and incubated with a target of ~100 p.f.u. (plaque-forming units) of NiV-M, NiV-B or HeV for 45 min at 37 °C. Virus and antibody mixtures were then added to individual wells of six-well plates of VeroE6 cells. Plates were stained with neutral red two days after infection and plaques were counted 24 h after staining. Neutralization potency was calculated based on p.f.u. for each virus in the well without antibody. The experiments were performed in triplicate with independent virus preparations and duplicate readings for each replicate. Mean half-maximal inhibitory concentrations were calculated as previously described91.
Escape mutant analysis
Neutralization-resistant NiV mutants were generated by incubating 1 × 105 50% tissue culture infective dose (TCID50) of each virus with a sub-neutralizing concentration of 40 μg of 5B3 IgG, in 100 μl medium for 1 h at 37 °C and then inoculated onto 1 × 106 VeroE6 cells in the presence of IgG at the same concentration. The development of cytopathic effects was monitored over 72 h and progeny viruses were harvested. IgG treatment was repeated two additional times, with cytopathic effects developing slowly with each passage. Viruses from the third passage were plaque purified in the presence of IgG and neutralization resistant viruses were isolated. The experiment was performed in duplicate and the F and G glycoprotein genes of five individual plaques were sequenced. The neutralization titers between wild type and the neutralization-resistant virus were determined using a micro-neutralization assay. Briefly, the 5B3 IgG was serially diluted two fold and incubated with 100 TCID50 of the wild-type and neutralization-resistant NiV for 1 h at 37 °C. Virus and antibodies were then added to a 96-well plate with 2 × 104 VeroE6 cells per well in four wells per antibody dilution. Wells were checked for cytopathic effects three days post infection and the mean half-maximal inhibitory concentrations was determined as the mAb concentration at which at least 50% of wells showed no cytopathic effects.
Reporting Summary
Further information on experimental design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Data availability
The sharpened and unsharpened cryo-EM maps and atomic model have been deposited in the EMDB and wwPDB with accession codes EMD-20584 and 6TYS, respectively. The 5B3 Fab crystal structure has been deposited in the wwPDB with accession code 6U1T. Uncropped images for Fig. 4d,e and Extended Data 4 are available online.
References
Eaton, B. T., Broder, C. C., Middleton, D. & Wang, L. F. Hendra and Nipah viruses: different and dangerous. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 4, 23–35 (2006).
Beineke, A., Baumgartner, W. & Wohlsein, P. Cross-species transmission of canine distemper virus-an update. One Health 1, 49–59 (2015).
Clayton, B. A., Wang, L. F. & Marsh, G. A. Henipaviruses: an updated review focusing on the pteropid reservoir and features of transmission. Zoonoses Public Health 60, 69–83 (2013).
Broder, C. C., Weir, D. L. & Reid, P. A. Hendra virus and Nipah virus animal vaccines. Vaccine 34, 3525–3534 (2016).
Luby, S. P. & Gurley, E. S. Epidemiology of Henipavirus disease in humans. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 359, 25–40 (2012).
Arunkumar, G. et al. Outbreak investigation of Nipah virus disease in Kerala, India, 2018. J. Infect. Dis. 219, 1867–1878 (2018).
Pernet, O. et al. Evidence for henipavirus spillover into human populations in Africa. Nat. Commun. 5, 5342 (2014).
Wong, J. J. W. et al. Monomeric ephrinB2 binding induces allosteric changes in Nipah virus G that precede its full activation. Nat. Commun. 8, 781 (2017).
Xu, K. et al. Host cell recognition by the henipaviruses: crystal structures of the Nipah G attachment glycoprotein and its complex with ephrin-B3. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 9953–9958 (2008).
Negrete, O. A. et al. EphrinB2 is the entry receptor for Nipah virus, an emergent deadly paramyxovirus. Nature 436, 401–405 (2005).
Bowden, T. A. et al. Structural basis of Nipah and Hendra virus attachment to their cell-surface receptor ephrin-B2. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 15, 567–572 (2008).
Bonaparte, M. I. et al. Ephrin-B2 ligand is a functional receptor for Hendra virus and Nipah virus. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 10652–10657 (2005).
Xu, K. et al. Crystal structure of the pre-fusion nipah virus fusion glycoprotein reveals a novel hexamer-of-trimers assembly. PLoS Pathog. 11, e1005322 (2015).
Pager, C. T., Craft, W. W. Jr, Patch, J. & Dutch, R. E. A mature and fusogenic form of the Nipah virus fusion protein requires proteolytic processing by cathepsin L. Virology 346, 251–257 (2006).
Pager, C. T. & Dutch, R. E. Cathepsin L is involved in proteolytic processing of the Hendra virus fusion protein. J. Virol. 79, 12714–12720 (2005).
Harrison, S. C. Viral membrane fusion. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 15, 690–698 (2008).
Chan, Y. P. et al. Biochemical, conformational and immunogenic analysis of soluble trimeric forms of Henipavirus fusion glycoproteins. J. Virol. 86, 11457–11471 (2012).
Liu, Q. et al. Unraveling a three-step spatiotemporal mechanism of triggering of receptor-induced Nipah virus fusion and cell entry. PLoS Pathog. 9, e1003770 (2013).
Connolly, S. A., Leser, G. P., Yin, H. S., Jardetzky, T. S. & Lamb, R. A. Refolding of a paramyxovirus F protein from prefusion to postfusion conformations observed by liposome binding and electron microscopy. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 17903–17908 (2006).
Yin, H. S., Paterson, R. G., Wen, X., Lamb, R. A. & Jardetzky, T. S. Structure of the uncleaved ectodomain of the paramyxovirus (hPIV3) fusion protein. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 9288–9293 (2005).
Yin, H. S., Wen, X., Paterson, R. G., Lamb, R. A. & Jardetzky, T. S. Structure of the parainfluenza virus 5 F protein in its metastable, prefusion conformation. Nature 439, 38–44 (2006).
McLellan, J. S. et al. Structure of RSV fusion glycoprotein trimer bound to a prefusion-specific neutralizing antibody. Science 340, 1113–1117 (2013).
McLellan, J. S., Yang, Y., Graham, B. S. & Kwong, P. D. Structure of respiratory syncytial virus fusion glycoprotein in the postfusion conformation reveals preservation of neutralizing epitopes. J. Virol. 85, 7788–7796 (2011).
Swanson, K. A. et al. Structural basis for immunization with postfusion respiratory syncytial virus fusion F glycoprotein (RSV F) to elicit high neutralizing antibody titers. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, 9619–9624 (2011).
Griffin, D. E. Immune responses during measles virus infection. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 191, 117–134 (1995).
Zhu, Z. et al. Exceptionally potent cross-reactive neutralization of Nipah and Hendra viruses by a human monoclonal antibody. J. Infect. Dis. 197, 846–853 (2008).
Zhu, Z. et al. Potent neutralization of Hendra and Nipah viruses by human monoclonal antibodies. J. Virol. 80, 891–899 (2006).
Borisevich, V. et al. Escape from monoclonal antibody neutralization affects Henipavirus fitness in vitro and in vivo. J. Infect. Dis. 213, 448–455 (2016).
Bossart, K. N. et al. A neutralizing human monoclonal antibody protects against lethal disease in a new ferret model of acute Nipah virus infection. PLoS Pathog. 5, e1000642 (2009).
Bossart, K. N. et al. A neutralizing human monoclonal antibody protects african green monkeys from Hendra virus challenge. Sci. Transl. Med. 3, 105ra103 (2011).
Geisbert, T. W. et al. Therapeutic treatment of Nipah virus infection in nonhuman primates with a neutralizing human monoclonal antibody. Sci. Transl. Med. 6, 242ra82 (2014).
Mire, C. E. et al. Pathogenic differences between Nipah virus Bangladesh and Malaysia strains in primates: implications for antibody therapy. Sci. Rep. 6, 30916 (2016).
Guillaume, V. et al. Antibody prophylaxis and therapy against Nipah virus infection in hamsters. J. Virol. 80, 1972–1978 (2006).
Guillaume, V. et al. Acute Hendra virus infection: analysis of the pathogenesis and passive antibody protection in the hamster model. Virology 387, 459–465 (2009).
Broder, C. C. et al. Immunization strategies against henipaviruses. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 359, 197–223 (2012).
Aguilar, H. C. et al. N-glycans on Nipah virus fusion protein protect against neutralization but reduce membrane fusion and viral entry. J. Virol. 80, 4878–4889 (2006).
Carter, J. R., Pager, C. T., Fowler, S. D. & Dutch, R. E. Role of N-linked glycosylation of the Hendra virus fusion protein. J. Virol. 79, 7922–7925 (2005).
Moll, M., Kaufmann, A. & Maisner, A. Influence of N-glycans on processing and biological activity of the Nipah virus fusion protein. J. Virol. 78, 7274–7278 (2004).
Xu, K. et al. Crystal structure of the Hendra virus attachment G glycoprotein bound to a potent cross-reactive neutralizing human monoclonal antibody. PLoS Pathog. 9, e1003684 (2013).
Lee, J. K., Prussia, A., Snyder, J. P. & Plemper, R. K. Reversible inhibition of the fusion activity of measles virus F protein by an engineered intersubunit disulfide bridge. J. Virol. 81, 8821–8826 (2007).
McLellan, J. S. et al. Structure-based design of a fusion glycoprotein vaccine for respiratory syncytial virus. Science 342, 592–598 (2013).
Wong, J. J., Paterson, R. G., Lamb, R. A. & Jardetzky, T. S. Structure and stabilization of the Hendra virus F glycoprotein in its prefusion form. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 113, 1056–1061 (2016).
Stewart-Jones, G. B. E. et al. Structure-based design of a quadrivalent fusion glycoprotein vaccine for human parainfluenza virus types 1–4. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 115, 12265–12270 (2018).
Bossart, K. N. et al. Inhibition of Henipavirus fusion and infection by heptad-derived peptides of the Nipah virus fusion glycoprotein. Virol. J. 2, 57 (2005).
Bossart, K. N. et al. Membrane fusion tropism and heterotypic functional activities of the Nipah virus and Hendra virus envelope glycoproteins. J. Virol. 76, 11186–11198 (2002).
Sastre, P., Melero, J. A., Garcia-Barreno, B. & Palomo, C. Comparison of affinity chromatography and adsorption to vaccinia virus recombinant infected cells for depletion of antibodies directed against respiratory syncytial virus glycoproteins present in a human immunoglobulin preparation. J. Med. Virol. 76, 248–255 (2005).
Krarup, A. et al. A highly stable prefusion RSV F vaccine derived from structural analysis of the fusion mechanism. Nat. Commun. 6, 8143 (2015).
Marcandalli, J. et al. Induction of potent neutralizing antibody responses by a designed protein nanoparticle vaccine for respiratory syncytial virus. Cell 176, 1420–1431.e17 (2019).
Battles, M. B. et al. Structure and immunogenicity of pre-fusion-stabilized human metapneumovirus F glycoprotein. Nat. Commun. 8, 1528 (2017).
Qiu, X. et al. Reversion of advanced Ebola virus disease in nonhuman primates with ZMapp. Nature 514, 47–53 (2014).
Wec, A. Z. et al. Development of a human antibody cocktail that deploys multiple functions to confer pan-ebolavirus protection. Cell Host Microbe 25, 39–48.e5 (2019).
Bornholdt, Z. A. et al. A two-antibody pan-ebolavirus cocktail confers broad therapeutic protection in ferrets and nonhuman primates. Cell Host Microbe 25, 49–58.e5 (2019).
Rockx, B. et al. Escape from human monoclonal antibody neutralization affects in vitro and in vivo fitness of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Infect. Dis. 201, 946–955 (2010).
Debat, H. et al. Overpassing an aberrant Vκ gene to sequence an anti-idiotypic abzyme with β-lactamase-like activity that could have a linkage with autoimmune diseases. FASEB J. 15, 815–822 (2001).
Wang, Z. et al. Universal PCR amplification of mouse immunoglobulin gene variable regions: the design of degenerate primers and an assessment of the effect of DNA polymerase 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity. J. Immunol. Methods 233, 167–177 (2000).
Zhu, Z. & Dimitrov, D. S. Construction of a large naive human phage-displayed Fab library through one-step cloning. Methods Mol. Biol. 525, 129–142 (2009).
Dimitrova, D., Choudhry, V. & Broder, C. C. Antibody fragment expression and purification. Methods Mol. Biol. 525, 491–498 (2009).
Chan, Y. P., Yan, L., Feng, Y. R. & Broder, C. C. Preparation of recombinant viral glycoproteins for novel and therapeutic antibody discovery. Methods Mol. Biol. 525, 31–58 (2009).
Feng, Y. & Dimitrov, D. S. Scaling-up and production of therapeutic antibodies for preclinical studies. Methods Mol. Biol. 525, 499–508 (2009).
Kabsch, W. XDS. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 66, 125–132 (2010).
Evans, P. R. & Murshudov, G. N. How good are my data and what is the resolution? Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 69, 1204–1214 (2013).
McCoy, A. J. et al. Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 40, 658–674 (2007).
Walls, A. C. et al. Unexpected receptor functional mimicry elucidates activation of coronavirus fusion. Cell 176, 1026–1039.e15 (2019).
Cowtan, K. The Buccaneer software for automated model building. 1. Tracing protein chains. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 62, 1002–1011 (2006).
Emsley, P., Lohkamp, B., Scott, W. G. & Cowtan, K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 66, 486–501 (2010).
Blanc, E. et al. Refinement of severely incomplete structures with maximum likelihood in BUSTER-TNT. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 60, 2210–2221 (2004).
Vagin, A. A. et al. REFMAC5 dictionary: organization of prior chemical knowledge and guidelines for its use. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 60, 2184–2195 (2004).
Chen, V. B. et al. MolProbity: all-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 66, 12–21 (2010).
Suloway, C. et al. Automated molecular microscopy: the new Leginon system. J. Struct. Biol. 151, 41–60 (2005).
Zheng, S. Q. et al. MotionCor2: anisotropic correction of beam-induced motion for improved cryo-electron microscopy. Nat. Methods 14, 331–332 (2017).
Voss, N. R., Yoshioka, C. K., Radermacher, M., Potter, C. S. & Carragher, B. DoG Picker and TiltPicker: software tools to facilitate particle selection in single particle electron microscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 166, 205–213 (2009).
Lander, G. C. et al. Appion: an integrated, database-driven pipeline to facilitate EM image processing. J. Struct. Biol. 166, 95–102 (2009).
Zhang, K. Gctf: real-time CTF determination and correction. J. Struct. Biol. 193, 1–12 (2016).
Zivanov, J. et al. New tools for automated high-resolution cryo-EM structure determination in RELION-3. Elife 7, e42166 (2018).
Punjani, A., Rubinstein, J. L., Fleet, D. J. & Brubaker, M. A. cryoSPARC: algorithms for rapid unsupervised cryo-EM structure determination. Nat. Methods 14, 290–296 (2017).
Zivanov, J., Nakane, T. & Scheres, S. H. W. A Bayesian approach to beam-induced motion correction in cryo-EM single-particle analysis. IUCrJ 6, 5–17 (2019).
Scheres, S. H. & Chen, S. Prevention of overfitting in cryo-EM structure determination. Nat. Methods 9, 853–854 (2012).
Rosenthal, P. B. & Henderson, R. Optimal determination of particle orientation, absolute hand and contrast loss in single-particle electron cryomicroscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 333, 721–745 (2003).
Chen, S. et al. High-resolution noise substitution to measure overfitting and validate resolution in 3D structure determination by single particle electron cryomicroscopy. Ultramicroscopy 135, 24–35 (2013).
Goddard, T. D., Huang, C. C. & Ferrin, T. E. Visualizing density maps with UCSF Chimera. J. Struct. Biol. 157, 281–287 (2007).
Brown, A. et al. Tools for macromolecular model building and refinement into electron cryo-microscopy reconstructions. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 71, 136–153 (2015).
DiMaio, F., Leaver-Fay, A., Bradley, P., Baker, D. & Andre, I. Modeling symmetric macromolecular structures in Rosetta3. PLoS One 6, e20450 (2011).
DiMaio, F. et al. Atomic-accuracy models from 4.5-Å cryo-electron microscopy data with density-guided iterative local refinement. Nat. Methods 12, 361–365 (2015).
Wang, R. Y. et al. Automated structure refinement of macromolecular assemblies from cryo-EM maps using Rosetta. Elife 5, e17219 (2016).
Frenz, B. et al. Automatically fixing errors in glycoprotein structures with Rosetta. Structure 27, 134–139 (2019).
Barad, B. A. et al. EMRinger: side chain-directed model and map validation for 3D cryo-electron microscopy. Nat. Methods 12, 943–946 (2015).
Agirre, J. et al. Privateer: software for the conformational validation of carbohydrate structures. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 22, 833–834 (2015).
Goddard, T. D. et al. UCSF ChimeraX: meeting modern challenges in visualization and analysis. Protein Sci. 27, 14–25 (2018).
Bossart, K. N. & Broder, C. C. Viral glycoprotein-mediated cell fusion assays using vaccinia virus vectors. Methods Mol. Biol. 269, 309–332 (2004).
Broder, C. C. et al. Antigenic implications of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope quaternary structure: oligomer-specific and -sensitive monoclonal antibodies. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 91, 11699–11703 (1994).
Ferrara, F. & Temperton, N. Pseudotype neutralization assays: from laboratory bench to data analysis. Methods Protoc. 1, 8 (2018).
Acknowledgements
We thank M.M. Sauer for his assistance with biolayer interferometry assays and N. Zheng for providing access to his crystallization robot. This study was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (D.V., HHSN272201700059C; C.C.B., AI054715, AI077995 and AI142764), the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (D.V., GM120553), an Investigators in the Pathogenesis of Infectious Disease Award from the Burroughs Wellcome Fund (D.V.), a Pew Biomedical Scholars Award (D.V.), the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (J.S., Rubicon 019.2015.2.310.006), the European Molecular Biology Organisation (J.S., ALTF933-2015), the University of Washington Arnold and Mabel Beckman cryo-EM center and Proteomics Resource (UWPR95794) and Beamline 5.0.1 at the Advanced Light Source at Lawrence Berkley National Laboratory, which is a Department of Energy Office of Science User Facility under contract no. DE-AC02-05CH11231 and is supported by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and NIH grant no. S10OD021832.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.V.D., Y.-P.C., Y.-J.P., J.S., C.E.M., C.C.B. and D.V. designed the experiments. H.V.D. and Y.-P.C. designed and cloned the protein constructs. Y.-P.C. and S.C.D.S. performed the fusion assays. H.V.D., Y.-P.C., L.Y. and Y.-R.F. expressed and purified the proteins used in this study. Y.-P.C. and B.V. humanized 5B3 and generated stable cell lines. H.V.D., Y.-J.P. and D.V. performed cryo-EM sample preparation, data collection, processing, model building and refinement. H.V.D. and Y.-J.P. crystallized 5B3, collected and processed the data, and built and refined the atomic model. H.V.D., Y.-P.C. and B.V. performed all binding assays. T.G. and C.E.M. carried out the neutralization assays. B.R. isolated the neutralization escape mutants. H.V.D., Y.-P.C., Y.-J.P., J.S., C.E.M., C.C.B. and D.V. analyzed the data. H.V.D., Y.-P.C., C.C.B. and D.V. prepared the manuscript, with input from all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Y.P.C. and C.B. are inventors on US patent 2016/0347827 A1 ‘Antibodies against F glycoprotein of Hendra and Nipah viruses’.
Additional information
Peer review information Inês Chen was the primary editor on this article and managed its editorial process and peer review in collaboration with the rest of the editorial team.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Extended data
Extended Data Fig. 1 Cryo-EM characterization of the NiV F glycoprotein in complex with the neutralizing antibody 5B3 Fab fragment.
a, Representative micrograph. Scale bar, 100 nm. b, Reference-free 2D class averages. Scale bar, 100 Å. c, Gold-standard (black) and map/model (red) Fourier shell correlation curves. Dotted lines indicate 0.143 and 0.5 thresholds. d, Two orthogonal views of the cryo-EM reconstruction colored by local resolution computed using cryoSPARC. e, Enlarged view of the model with the cryo-EM reconstruction rendered as a blue mesh.
Extended Data Fig. 2 Architecture of the prefusion NiV F glycoprotein.
a,b, Ribbon diagrams of a NiV F ectodomain protomer from the cryo-EM structure of NiV F in complex with the 5B3 Fab fragment. HRA, heptad-repeat A; HRB, heptad-repeat B.
Extended Data Fig. 3 5B3 binding is associated with a local structural reorganization of the HRA β-hairpin.
a, Ribbon diagrams of the superimposed 5B3-bound and apo NiV F trimers. The 5B3 Fab fragments are omitted for clarity. The cyan square highlights the region of the structure shown in b–e. b,c, Enlarged views showing the HRA conformational change. d,e, Enlarged views rotated 45° relative to b and c. In all panels, 5B3-bound and apo-NiV F trimers are rendered grey and orange, respectively. In c–e, one 5B3 Fab fragment is shown with its heavy and light chains colored purple and pink, respectively, whereas the cyan star indicates clashes that would occur between 5B3 and the HRA β-hairpin conformation observed in the apo-NiV structure13 (PDB 5EVM).
Extended Data Fig. 4 Validation of the binding epitope on NiV F.
a, Analysis of h5B3 scFv binding to full-length NiV F. scFv chimeric constructs in which the variable heavy h5B3 chain (VH5B3), the variable light h5B3 chain (VL5B3) or both chains were replaced with unrelated chains (VHhVLh) from a human scFv library were assessed for binding to secreted wild-type NiV F. VH5B3/VL5B3 scFv was used as a positive control. Western blotting was carried out using an anti-F polyclonal antibody to detect NiV F or anti-S-peptide antibody to detect the scFv. b, Site-directed mutagenesis of the 5B3 epitope. A panel of S-peptide tagged NiV F ectdomain mutants were generated and expressed in HEK 293T cells. The F-expressing cell lysates were divided equally and incubated with 5B3, 12B2 or S-protein agarose before immunoprecipitation/pulldown. Samples in which mAb 5B3 or 12B2 were added were precipitated with protein G Sepharose. Western blotting detection of the precipitated products was carried out using an anti-S-peptide antibody. The Gly247Ala substitution was used as positive control. c, Cell–cell fusion mediated by the NiV F mutants shown in b. Data are the mean percentage of wild-type fusion levels for each mutant normalized relative to total F expression, as measured by densitometry of western blot bands. The bars represent the standard error from three separate experiments.
Supplementary information
Source data
Source Data Fig. 4
Unprocessed Western Blots
Source Data Extended Data Fig. 4
Unprocessed Western Blots
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dang, H.V., Chan, YP., Park, YJ. et al. An antibody against the F glycoprotein inhibits Nipah and Hendra virus infections. Nat Struct Mol Biol 26, 980–987 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-019-0308-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-019-0308-9
This article is cited by
-
The cryo-EM structure of homotetrameric attachment glycoprotein from langya henipavirus
Nature Communications (2024)
-
A general computational design strategy for stabilizing viral class I fusion proteins
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Structure and antigenicity of divergent Henipavirus fusion glycoproteins
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Structural basis for antibody recognition of vulnerable epitopes on Nipah virus F protein
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Learning from prepandemic data to forecast viral escape
Nature (2023)