Abstract
Pathogenic germline mutations in the RAD51 paralog genes RAD51C and RAD51D, are known to confer susceptibility to ovarian and triple-negative breast cancer. Here, we investigated whether germline loss-of-function variants affecting another RAD51 paralog gene, RAD51B, are also associated with breast and ovarian cancer. Among 3422 consecutively accrued breast and ovarian cancer patients consented to tumor/germline sequencing, the observed carrier frequency of loss-of-function germline RAD51B variants was significantly higher than control cases from the gnomAD population database (0.26% vs 0.09%), with an odds ratio of 2.69 (95% CI: 1.4–5.3). Furthermore, we demonstrate that tumors harboring biallelic RAD51B alteration are deficient in homologous recombination DNA repair deficiency (HRD), as evidenced by analysis of sequencing data and in vitro functional assays. Our findings suggest that RAD51B should be considered as an addition to clinical germline testing panels for breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Approximately 5–10% of breast cancers and 20–25% of ovarian cancers are hereditary in nature1. Pathogenic germline variants in homologous recombination (HR)-related genes, including BRCA1 (MIM: 113705), BRCA2 (MIM: 600185), BRIP1 (MIM: 605882), PALB2 (MIM: 610355), RAD51C (MIM: 602774), and RAD51D (MIM: 602954), confer an increased risk of breast and/or ovarian cancers2,3,4,5,6,7. For female carriers of RAD51C or RAD51D pathogenic germline variants, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommends considering risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy to minimize the risk of ovarian cancer8. The HR deficiency (HRD) characteristic of tumors that arise in individuals harboring germline mutations in HR-related genes can be exploited therapeutically with poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors and platinum compounds9,10.
RAD51B (MIM: 602948) encodes one of five classical RAD51 paralogs (RAD51B, RAD51C, RAD51D, XRCC2 [MIM: 600375], and XRCC3 [MIM: 600675]) known to be required for HR and maintenance of genomic stability11. Structurally related to RAD51, the paralogs are not thought to have a direct role in homology recognition, but act as accessory factors required for proper function of the core RAD51 recombinase12,13. Whilst RAD51C and RAD51D are now established cancer predisposition genes, loss-of-function germline variants in RAD51B have only been reported in individual cases of breast and ovarian cancer14,15,16. Here, we sought to determine whether germline loss-of-function variants in RAD51B confer an increased risk to these cancers, and whether the resulting tumors harbor a therapeutically targetable HRD phenotype.
Results
Germline RAD51B variants and cancer predisposition
To investigate the potential contribution of RAD51B loss-of-function germline variants to cancer predisposition, we analyzed a cohort of 18,087 individuals with cancer whose tumor and blood samples were characterized using MSK-IMPACT. Among the cancers represented in this cohort were 2265 breast and 1157 ovarian cancers. Overall, 13 (0.07%) cases were found to harbor a RAD51B loss-of-function germline variant, a frequency similar to that described in the gnomAD database (0.09%). Notably, 9/10 of the female carriers of a RAD51B loss-of-function germline variant had a diagnosis of breast or ovarian cancer (5/2265 and 4/1157), for an odds ratio for breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility of 2.69 (95% CI: 1.4–5.3, p = 0.004; Table 1). Though segregation data were not available, 8/13 of the RAD51B loss-of-function germline variant carriers had a first or second degree relative with breast or ovarian cancer (Table 1; Supplementary Fig. 3).
Genomic landscape of RAD51B-deficient tumors
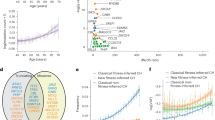
Given the observed association of RAD51B germline truncating variants with breast and ovarian cancer, we then sought to determine the phenotype and repertoire of somatic genetic alterations in cancers arising in RAD51B carriers. Among breast cancers, 4/5 were ER and PR positive and HER2 negative, while the remaining case was ER and PR negative and HER2 positive (Table 2). The average age of breast cancer diagnosis in RAD51B carriers was 49 (range 30–61), and ovarian cancer diagnosis was 67.3 (range 58–79). Six additional cases were identified in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), of which three had biallelic alterations of RAD51B (Supplementary Table 1). The six cases with biallelic RAD51B loss-of-function germline variants (germline variant plus loss-of-heterozygosity (LOH) of the wild-type (WT) allele) consistently displayed genomic features of HRD. All 5 cases with biallelic RAD51B mutation (germline plus LOH) for whom WES was performed harbored dominant signature 3 (Fig. 1A) and high large-scale state transition (LST) scores (Fig. 1B), indicative of defective HR in the tumor17. Tumors harboring biallelic inactivation of RAD51B displayed a small numerical increase in the number of deletions, deletion lengths, and microhomology scores, although this did not reach statistical significance (Fig. 2). Five of six cases with biallelic RAD51B inactivation also harbored biallelic somatic variants in TP53, which are known to be strongly selected for in BRCA-associated HRD cancers18. As LOH events themselves are copy number alterations (CNAs) that could contribute to LST signal, we compared biallelic RAD51B loss-of-function cases with WT RAD51B cases harboring LOH, and found those harboring a loss-of-function RAD51B allele to have significantly higher LST scores on average (p = 0.02), providing further supportive evidence that RAD51B loss leads to genomic scarring characteristic of defective HR, albeit at intermediate levels compared to BRCA1 or BRCA2 loss (Supplementary Fig. 1). Loss of heterozygosity of the WT allele was also observed at a significantly higher rate among tumors harboring a RAD51B loss-of-function germline variant (6/18 cases) vs. those with a variant of unknown significance (VUS; 6/59 cases, p = 0.02), suggesting selection for biallelic loss of RAD51B in tumors.
A Recurrent (present in ≥2 samples) nonsynonymous somatic mutations identified in 18 tumors from patients with germline RAD51B mutations using targeted massively parallel sequencing (MSK-IMPACT; n = 8) or whole-exome sequencing (WES; n = 8). Phenobar provides information on RAD51B germline mutations, dominant mutational signatures and cancer type. Loss of heterozygosity (LOH) of the RAD51B wild-type allele is displayed by a white diagonal line. B Large-scale transition (LST) scores in biallelic RAD51B-associated cancers, monoallelic RAD51B-associated cancers, biallelic BRCA1-associated cancers and biallelic BRCA2-associated cancers from TCGA.
A Number of deletions in biallelic RAD51B-associated cancers, monoallelic RAD51B-associated cancers, biallelic BRCA1-associated cancers and biallelic BRCA2-associated cancers. Note one mon-allelic RAD51B was removed from the plot due to a large number of indels (142) driven by microsatellite instability. B Median deletion length in biallelic RAD51B-associated cancers, monoallelic RAD51B-associated cancers, biallelic BRCA1-associated cancers and biallelic BRCA2-associated cancers. C Deletion microhomology scores in biallelic RAD51B-associated cancers, monoallelic RAD51B-associated cancers, biallelic BRCA1-associated cancers and biallelic BRCA2-associated cancers. A deletion was classified as having microhomology when deletion length was ≥4 bases with homology ≥3 bases. Microhomology scores are calculated by dividing the total number of deletions with microhomology by the total number of deletions.
Functional impact of RAD51B deficiency
To assess the impact of RAD51B-deficiency on HR efficiency, we quantified the effect of RAD51B silencing on the fidelity of HR, as defined by the accumulation of RAD51 nuclear foci following DNA damage, in two breast epithelial cell lines, MCF-10A and MCF-12A. The accumulation of RAD51 nuclear foci in response to DNA damage reflects the fidelity of upstream components of the HR pathway and has been shown to effectively predict clinical responses to HRD-targeting therapies, including PARP inhibition19,20. In comparison to a negative control (shRenilla), expression of two different shRNAs against RAD51B expression resulted in significantly impaired RAD51 nuclear foci formation (Fig. 3). Silencing of RAD51B also resulted in increased sensitivity to olaparib and mitomycin-C, agents that are both known to target HRD cancers (Fig. 4). RAD51B-deficient cells were slightly less sensitive to both agents than BRCA1-deficient cells, concordant with the intermediate LST and signature 3 phenotypes observed for such tumors (Fig. 1B).
A, B RAD51 focus formation assay in MCF-12A and MCF-10A mammary epithelial cells expressing one of two independent RAD51B shRNAs, Renilla shRNA (nontarget control), or BRCA1 shRNA (positive control). Cells were plated onto eight-well chamber slides (EMD Millipore) and exposed to 10 Gy of ionizing radiation or mock irradiated (0 Gy). Nuclear RAD51 foci were visualized and quantified in two independent experiments (Supplemental Methods). Error bars represent standard error of mean (SEM).
As noted in our Methods, loss-of-function RAD51B alleles were defined as those harboring a single nucleotide variant (SNV) or insertion or deletion (indel) predicted to result in a frameshifted or truncated reading frame. Nevertheless, several truncating alleles in our study, including the c.139 C > T(p.Arg47*) variant carried by 7/13 patients in our cohort, have not been formally classified as pathogenic or likely pathogenic by American College of the Medical Genetics (ACMG) criteria. To provide supporting evidence that the truncating alleles present in our cohort are deleterious to RAD51B function, we used the standard DR-GFP reporter assay established in U2OS cells, as previously described21, to test the HR phenotype of the c.139 C > T(p.Arg47*) variant. As shown in Supplementary Fig. 2, this variant was unable to complement HR proficiency beyond that observed with expression of an empty vector, in contrast to complementation with WT RAD51B, which resulted in an approximately twofold increase in recombination repair.
Discussion
Pathogenic germline mutations in BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2, RAD51C, and RAD51D, all of which are involved in the HR pathway, are known to confer high or moderate penetrance susceptibility to ovarian and/or triple-negative breast cancer. In contrast to these known cancer predisposition genes, the role of RAD51B in conferring susceptibility to hereditary breast and ovarian cancer has not yet been established. Our findings provide evidence that rare loss-of-function germline variants in RAD51B (found in 9/3422 [0.26%] consecutive breast or ovarian cancer cases who consented for germline analysis) are indeed associated with an increased risk of breast and ovarian cancer among women.
Our definition of loss-of-function RAD51B alleles included all SNVs and indels predicted to result in a frameshifted or truncated reading frame. Despite encoding for truncated and/or frameshifted RAD51B protein, several RAD51B alleles in our cohort could arguably be considered variants of unknown significance by formal ACMG criteria22, including the c.139 C > T(p.Arg47*) variant carried by seven patients in our cohort. Our experimental data using the DR-GFP reporter assay of HR proficiency demonstrate that the c.139 C > T(p.Arg47*) variant cannot complement the HR-deficiency observed in RAD51B-deficient cells, and suggests that this allele results in loss of function. While we were unable to test all novel RAD51B variants present in the MSK and TCGA cohorts, functional data suggest that the Walker A and B motifs of RAD51B are important for its interaction with RAD51C and for its function in HR23. Notably, 11 of the 13 patients in our cohort harbored RAD51B alleles predicted to disrupt one or both Walker motifs. As these motifs are important for the interaction of RAD51B with RAD51C and for its function in HR, alleles that truncate or frameshift these domains appear likely to affect protein function. Further experimental data will nevertheless be required to confirm these observations and to assess the pathogenicity of untested alleles that truncate the C-terminus of RAD51B.
In our cohort of 3422 index breast and ovarian cancer cases, we found RAD51B loss-of-function germline variants (9/3422 cases) to be almost as common as those affecting RAD51C and RAD51D (combined 16/3422 cases). The prevalence of mutations affecting these Rad51 paralogs in our cohort was comparable to a prior study of ovarian cancer patients which identified a similar overall prevalence of loss-of-function germline variants in RAD51B/C/D (combined 22/3112 cases)16. At variance with our data, however, this study identified only 2 patients with alterations in RAD51B, with the remaining 20 patients harboring germline inactivation of a RAD51C or RAD51D allele. This study and others3,24, have also demonstrated that carriers of pathogenic RAD51C/D mutations tend to develop triple-negative breast cancers, in contrast to the predominantly (4 of 5 cases) hormone receptor-positive breast cancers identified among carriers of RAD51B mutations in our cohort. Given the rarity of loss-of-function germline RAD51B variants, our study had limited statistical power to assess an association between RAD51B inactivation and hormone receptor status among breast cancer cases, and additional cases will be required to confirm the association. One plausible hypothesis for the differences in molecular subtype associated with each mutated paralog relates to the cell of origin and mammary stem/progenitor cell maturation. The observation that BRCA1 mutation carriers tend to develop triple-negative breast cancers while BRCA2 mutation carriers show the same range of hormonal receptor subtypes as sporadic breast cancer, has previously been attributed to a role for BRCA1 in the maturation of ER-positive mammary epithelial progenitor cells25,26. It remains to be seen, however, whether RAD51C or RAD51D play a similar role in the maturation of mammary progenitor cells.
In addition to providing evidence that RAD51B serves as a cancer predisposition gene, our findings confirm that tumors harboring biallelic inactivation of RAD51B are deficient in HR and are likely to be sensitive to both PARP inhibitors and interstrand crosslinking agents.
Prior in vitro studies using Chinese hamster cells and the chicken DT40 cell line have demonstrated the classical RAD51 paralogs, including RAD51B, to be critical for the integrity of the HR pathway in such model systems13,27. Nevertheless, a recent report using human isogenic cell lines suggested that RAD51B may be distinct from the other paralogs in terms of its essentiality for HR and cellular viability, with RAD51B−/− human cells displaying a weaker, intermediate sensitivity to DNA damage23, despite being known to function in a heterotypic complex with other paralogs (RAD51C, RAD51D, XRCC2)13. Our finding that RAD51B-deficient cells are less sensitive to mitomycin C and olaparib than BRCA1-deficient cells, and yet markedly more sensitive than the corresponding WT controls, are concordant with these reported results. Likewise, our observation that tumors harboring biallelic RAD51B inactivation display an intermediate LST and signature 3 features compared to WT and BRCA1/2-deficient tumors, respectively, is suggestive of a significant but moderately attenuated HR-deficient phenotype among such tumors.
Prior genomic data derived from whole genome-sequenced ovarian tumors have suggested that RAD51B inactivation may be associated with an enrichment of foldback inversions, a structural variant characterized by inverted duplications28. Wang et al. employed hierarchical clustering analysis of 133 whole genome-sequenced ovarian tumors to identify a subgroup characterized by a high prevalence of foldback inversions28. Among 24 tumors in this ‘high’ foldback inversion subgroup, seven (29%) were found to harbor RAD51B somatic inactivation. This subgroup also exhibited an intermediate elevation of genomic features associated with HRD, and was distinct from a separate HR-deficient subgroup that was enriched with BRCA1- and PALB2-deficient tumors. The nature of our sequencing data (whole exome) unfortunately did not allow us to identify such structural variants, but further examination of this link could help to clarify the genomic consequences of RAD51B loss and whether it diverges from other core genes required for HR.
Three male patients in our cohort carrying a RAD51B loss-of-function variant were affected by malignant tumors, but none were of mammary origin (Table 2). To our knowledge, there is no published evidence that RAD51B loss-of-function variants are associated with cancer predisposition among men. Prior reports have found a common single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in intron 7 of RAD51B (rs1314913) to be associated with a low risk of male breast cancer29,30. Orr et al. for example, demonstrated rs1314913 to be significantly associated with male, but not female breast cancer risk, with an odds ratio of ~1.629. As non-coding SNPs often influence their target genes through long-range chromosomal interactions31,32, rather than the closest or most biologically relevant nearby gene30,33, further studies are needed to identify the causative haplotype underlying the association. Given the absence of functional data suggesting a link between the rs1314913 SNP and RAD51B function, as well as the fact that none of the men in our cohort harboring a loss-of-function RAD51B allele presented with breast cancer, there appears to be minimal evidence of a cancer predisposition phenotype for loss-of-function RAD51B variants among men at this juncture.
Our study has important limitations. The frequency of RAD51B loss-of-function variants in our cohort was compared to the entire gnomAD database, hence we cannot exclude the possibility that the proportion of ethnicities do not exactly match the gnomAD database, given that the ethnicities of the individuals in our cohort reflect the diversity of a New York City population. Interestingly, 6/13 of the RAD51B carriers were Hispanic while 2/13 were Turkish. This raises the possibility that RAD51B pathogenic variants may contribute more to breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility in non-Caucasian populations. Further studies are warranted to confirm the role of RAD51B in conferring breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility in additional populations and to define the inclusion of RAD51B in panels for genetic risk prediction multigene assays. An additional 3 breast and ovarian cancer cases were not analyzed in this cohort because in additional to RAD51B germline mutations, they carried another high or moderate penetrance mutation in a cancer susceptibility gene (1 each BRCA2, RAD51D, ATM). However, it is a well-known phenomenon that individuals can have germline mutations in more than one cancer susceptibility gene, including simultaneous BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations34,35,36, and that either one may be an initiating factor in an individual’s cancer or the mutations in the HR pathway may act synergistically in tumor development. Three patients in our MSK cohort harbored germline RAD51B variants that affected canonical dinucleotide splicing sites. While computational algorithms predict that all 3 of these variants effect splicing and the positive predictive value of canonical splice site donor or acceptor disruption has previously been shown to approach >95%37, RNA sequencing data for these cases was unavailable and we could not directly assess for intron retention/deleterious splicing at the transcript level.
Taken together, the data presented here support the notion that RAD51B loss-of-function germline variants result in increased breast and ovarian cancer predisposition and that biallelic loss of RAD51B in tumor cells leads to an HRD phenotype and potential sensitivity to HRD-targeting therapies. If the risk estimates reported here are confirmed, our findings indicate that RAD51B should be included in multigene panel testing for genetic risk prediction.
Methods
Patient data
Individuals with a RAD51B loss-of-function germline variant were identified from the cohort of patients who consented to undergo somatic and germline analysis under an Institutional Review Board-approved protocol at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) and were profiled using the MSK-IMPACT assay (n = 9287). Three breast and ovarian cancer cases were excluded from the analysis, as in addition to harboring a RAD51B loss-of-function germline variant, they also carried an additional mutation in a cancer susceptibility gene (1 each BRCA2, RAD51D, or ATM [MIM: 607585]). None of the RAD51B-associated cancers included in this analysis harbored germline alterations in known cancer susceptibility genes. All germline RAD51B variants were reviewed by a board-certified molecular pathologist (D.M.); loss-of-function alleles were defined as those harboring an SNV or indel resulting in a frameshifted or truncated reading frame, including start/stop codon changes or canonical dinucleotide splice site disruption. Surgical pathology reports and medical records were reviewed (D.M., Y.K). to establish clinico-pathologic features and family histories. For breast cancer cases, estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and HER2 status were assessed following the American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guidelines38.
Statistical analysis
The carrier frequency of loss-of-function variants in gnomAD was compared to the carrier frequency in the cancer patient cohort using the Fisher exact test (RStudio 1.0.143). All statistical tests were two-sided with p < 0.05 considered statistically significant.
Massively parallel sequencing and bioinformatics analysis
Tumor and matched normal DNA samples were subjected to targeted massively parallel sequencing using the Memorial Sloan Kettering Integrated Mutation Profiling of Actionable Cancer Targets (MSK-IMPACT) assay, which targets all exons and selected introns of 410 (n = 1) or 468 (n = 12) cancer genes, as previously described39,40. Sequencing data was analyzed for SNVs and small insertions and deletions (indels) as previously described41. Loss-of-function alleles were defined as those harboring an SNV or indel resulting in a frameshifted or truncated reading frame, including start/stop codon changes or canonical dinucleotide splice site disruption. FACETS was used to determine CNAs and whether the WT copy of RAD51B was subject to loss of heterozygosity (LOH) in individuals who harbor germline RAD51B truncating variants42. Mutational hotspots were annotated according to Chang et al.43. Data for TCGA cases with RAD51B germline variants were downloaded from the National Cancer Institute (NCI) Genomic Data Commons legacy archive. Signature Multivariate Analysis (SigMA), a tool to detect the HRD mutational signature Sig3 from targeted gene panels44, was employed for samples with ≥5 somatic SNVs. To assess structural/copy number signatures of HRD, LSTs were defined, and a cut-off ≥15 was employed to define LST-high cases, as previously described17. To eliminate the possibility of confounding by treatment-related genomic changes previously treated metastatic samples were excluded from mutational and structural signature analysis. As LOH events themselves are CNAs that could contribute to LST signal, cases harboring RAD51B LOH with a loss-of-function allele were compared to TCGA cases harboring RAD51B LOH with a WT allele. For this analysis, cases harboring a deleterious HR gene mutation or cancer type not present in our cohort were excluded.
Cell culture
The immortalized but non-transformed MCF-12A and MCF-10A breast epithelial cell lines were purchased from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). These cells were short tandem repeat (STR) profiled by the provider and used within the first 20 passages. Cell lines were tested for mycoplasma infection using the Universal Mycoplasma Detection Kit (ATCC) and grown in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM):F12 medium supplemented with 5% horse serum (ThermoFisher), 20 ng/ml epidermal growth factor (PeproTech), 500 ng/ml hydrocortisone (Sigma), 10 µg/ml insulin (Sigma), and 100 ng/ml cholera toxin (EMD Millipore).
Plasmid construction, lentivirus production, and transduction
Gene knockdowns were achieved using a doxycycline-inducible shRNA strategy. The LT3RENIR lentiviral miR-E-based expression vector backbone was purchased from the MSKCC Gene Editing and Screening Core Facility. For generation of miR-E shRNAs, 97-mer oligonucleotides were purchased (IDT Ultramers) coding for predicted shRNAs using an siRNA prediction tool (Splash RNA, http://splashrna.mskcc.org/). 97-mer oligonucleotides were PCR amplified using the primers miRE-Xho-fw and miRE-Eco-rev. PCR products were purified and both PCR product and LT3RENIR vectors were double digested with EcoRI-HF and XhoHI. PCR product and vector backbone were ligated and transformed in Stbl3 competent cells and grown at 32 °C overnight. Colonies were screened using the miRE-fwd primers. Sequences for 97-mer oligonucleotides and PCR/sequencing primers are listed in the Supplementary Materials. Lentiviral particles expressing shRNA hairpins were generated using Lenti-X 293T cells (Takara). One day prior to transfection, 3.8 million Lenti-X 293T cells were seeded in 10 cm plates. Each 10 cm plate was transfected with a LT3RENIR-based shRNA expression construct along with packaging plasmids psPAX2 and pMD2.G (Cellecta) using polyethylenimine (Sigma). Twenty-four hours after transfection, media containing DNA transfection mixture was replaced with regular DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS. Media containing lentivirus was harvested at 24, 48, and 72 h, prior to being pooled, mixed with Lenti-X concentrator solution, centrifuged, and resuspended in PBS. All shRNAs were assessed at single copy genomic integration by infecting target cell population at <20% of their maximal infection rate, guaranteeing <2% cells with multiple integrations. Transduced cell populations were selected 48 h after infection, using 500–2000 μg/ml G418 (Geneticin, Gibco-Invitrogen).
Immunoblotting
Whole-cell extracts were prepared by lysing cells in radioimmunoprecipitation buffer. Protein (100 g) was loaded into 3–8% Tris acetate gels (Thermo Fisher), subjected to SDS-PAGE, transferred onto nitrocellulose, and blocked with 5% milk–TBST (for 1 h at room temperature. Immunodetection was performed using the following antibodies: anti-RAD51B (sc-53430; Santa Cruz); anti-BRCA1 (OP-92; Calbiochem); anti-Actin (ab14128; Abcam). All immunoblots were derived from same experiment and processed in parallel.
RAD51 foci formation assay
Cells were plated onto eight-well chamber slides (EMD Millipore) and exposed to 10 Gy of ionizing radiation or mock irradiated (0 Gy). After 4 h, cells were fixed, permeabilized, and co-immunostained with primary antibodies targeting RAD51 (polyclonal rabbit antibody, PC-130; EMD Millipore). Nuclei were counterstained with 4′,6-diamidino-2- phenylindole (DAPI). Nuclear RAD51 foci were visualized and quantified in a minimum of 200 cells in three independent experiments with a Zeiss LSM 880 confocal microscope.
Clonogenic survival assays
MCF-12A and MCF-10A cells were seeded in six-well plates and allowed to attach for 4 h before treatment with olaparib (Selleckchem AZD2281) or mitomycin-C (Sigma 10107409001) at the indicated doses. After 10–14 days cells were washed, fixed with methanol, and stained with crystal violet. Colonies containing more than 50 cells were counted. Results were normalized to untreated cells; for each genotype cell viability of untreated cells was defined as 100%.
Direct repeat-green fluorescent reporter (DR-GFP) assay
To assess the influence of the NM_002877.6[RAD51B]: c.139 C > T(p.Arg47*) variant on RAD51B-dependent HR, we used the standard DR-GFP reporter assay established in U2OS cells, as previously described21. In brief, these cells were modified to express an inducible shRNA against the 5′ untranslated region (UTR) of RAD51B. Seventy-two hours after introducing doxycycline to induce expression of RAD51B shRNA, cells were transfected with an expression vector encoding WT RAD51B, the R47Ter variant (NM_002877.6[RAD51B]: c.139 C > T[p.Arg47*]), or an empty reading frame (all expression vectors lacked the 5′UTR of RAD51B). A second transfection was performed 24 h after the first to introduce vectors encoding the I-SceI endonuclease, GFP (positive transfection control) or empty vector (negative control). Forty-eight hours after the second transfection, cells were trypsinized and single cell suspensions were analyzed by flow cytometry
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Data availability
Clinicopathologic data are available in the Supplementary Data. Additional validation for isogenic cell lines are available in the Supplementary Materials. Identifying information for the patients is not available to protect patient privacy. Please note that the materials and reagents used in this study may be subject to an institutional material transfer agreement. All other data generated and analysed during this study are publicly available as described in the following data record: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.1466508645.
References
Nielsen, F. C., van Overeem Hansen, T. & Sorensen, C. S. Hereditary breast and ovarian cancer: new genes in confined pathways. Nat. Rev. Cancer 16, 599–612 (2016).
King, M. C., Marks, J. H. & Mandell, J. B., New York Breast Cancer Study. G. Breast and ovarian cancer risks due to inherited mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2. Science 302, 643–646 (2003).
Shimelis, H. et al. Triple-negative breast cancer risk genes identified by multigene hereditary cancer panel testing. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 110, 855–862 (2018).
Li, N. et al. Combined tumor sequencing and case/control analyses of RAD51C in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst, https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djz045 (2019).
Loveday, C. et al. Germline mutations in RAD51D confer susceptibility to ovarian cancer. Nat. Genet 43, 879–882 (2011).
Meindl, A. et al. Germline mutations in breast and ovarian cancer pedigrees establish RAD51C as a human cancer susceptibility gene. Nat. Genet 42, 410–414 (2010).
Rahman, N. et al. PALB2, which encodes a BRCA2-interacting protein, is a breast cancer susceptibility gene. Nat. Genet 39, 165–167 (2007).
Domb, B. G. et al. The effect of liposomal bupivacaine injection during total hip arthroplasty: a controlled cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 15, 310 (2014).
Lord, C. J. & Ashworth, A. BRCAness revisited. Nat. Rev. Cancer 16, 110–120 (2016).
Moore, K. et al. Maintenance olaparib in patients with newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 379, 2495–2505 (2018).
Suwaki, N., Klare, K. & Tarsounas, M. RAD51 paralogs: roles in DNA damage signalling, recombinational repair and tumorigenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 22, 898–905 (2011).
Godin, S. K., Sullivan, M. R. & Bernstein, K. A. Novel insights into RAD51 activity and regulation during homologous recombination and DNA replication. Biochem. Cell Biol. 94, 407–418 (2016).
Chun, J., Buechelmaier, E. S. & Powell, S. N. Rad51 paralog complexes BCDX2 and CX3 act at different stages in the BRCA1-BRCA2-dependent homologous recombination pathway. Mol. Cell Biol. 33, 387–395 (2013).
Golmard, L. et al. Contribution of germline deleterious variants in the RAD51 paralogs to breast and ovarian cancers. Eur. J. Hum. Genet 25, 1345–1353 (2017).
Golmard, L. et al. Germline mutation in the RAD51B gene confers predisposition to breast cancer. BMC Cancer 13, 484 (2013).
Song, H. et al. Contribution of germline mutations in the RAD51B, RAD51C, and RAD51D genes to ovarian cancer in the population. J. Clin. Oncol. 33, 2901–2907 (2015).
Popova, T. et al. Ploidy and large-scale genomic instability consistently identify basal-like breast carcinomas with BRCA1/2 inactivation. Cancer Res. 72, 5454–5462 (2012).
Holstege, H. et al. High incidence of protein-truncating TP53 mutations in BRCA1-related breast cancer. Cancer Res. 69, 3625–3633 (2009).
Mutter, R. W. et al. Bi-allelic alterations in DNA repair genes underpin homologous recombination DNA repair defects in breast cancer. J. Pathol. 242, 165–177 (2017).
Cruz, C. et al. RAD51 foci as a functional biomarker of homologous recombination repair and PARP inhibitor resistance in germline BRCA-mutated breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 29, 1203–1210 (2018).
Xia, B. et al. Control of BRCA2 cellular and clinical functions by a nuclear partner, PALB2. Mol. Cell 22, 719–729 (2006).
Richards, S. et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 17, 405–424 (2015).
Garcin, E. B. et al. Differential requirements for the RAD51 paralogs in genome repair and maintenance in human cells. PLoS Genet 15, e1008355 (2019).
Li, N. et al. Combined tumor sequencing and case-control analyses of RAD51C in breast cancer. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 111, 1332–1338 (2019).
Liu, S. et al. BRCA1 regulates human mammary stem/progenitor cell fate. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 1680–1685 (2008).
Joosse, S. A. BRCA1 and BRCA2: a common pathway of genome protection but different breast cancer subtypes. Nat. Rev. Cancer 12, 372 (2012). author reply 372.
Masson, J. Y. et al. Identification and purification of two distinct complexes containing the five RAD51 paralogs. Genes Dev. 15, 3296–3307 (2001).
Wang, Y. K. et al. Genomic consequences of aberrant DNA repair mechanisms stratify ovarian cancer histotypes. Nat. Genet 49, 856–865 (2017).
Orr, N. et al. Genome-wide association study identifies a common variant in RAD51B associated with male breast cancer risk. Nat. Genet 44, 1182–1184 (2012).
Silvestri, V. et al. Novel and known genetic variants for male breast cancer risk at 8q24.21, 9p21.3, 11q13.3 and 14q24.1: results from a multicenter study in Italy. Eur. J. Cancer 51, 2289–2295 (2015).
Zhang, X., Cowper-Sal lari, R., Bailey, S. D., Moore, J. H. & Lupien, M. Integrative functional genomics identifies an enhancer looping to the SOX9 gene disrupted by the 17q24.3 prostate cancer risk locus. Genome Res. 22, 1437–1446 (2012).
Sanyal, A., Lajoie, B. R., Jain, G. & Dekker, J. The long-range interaction landscape of gene promoters. Nature 489, 109–113 (2012).
Pomerantz, M. M. et al. The 8q24 cancer risk variant rs6983267 shows long-range interaction with MYC in colorectal cancer. Nat. Genet 41, 882–884 (2009).
Ramus, S. J. et al. A breast/ovarian cancer patient with germline mutations in both BRCA1 and BRCA2. Nat. Genet 15, 14–15 (1997).
Friedman, E. et al. Double heterozygotes for the Ashkenazi founder mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. Am. J. Hum. Genet 63, 1224–1227 (1998).
Tsongalis, G. J. et al. Double heterozygosity for mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes in a breast cancer patient. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 122, 548–550 (1998).
Lord, J. et al. Pathogenicity and selective constraint on variation near splice sites. Genome Res. 29, 159–170 (2019).
Wolff, A. C. et al. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Testing in Breast Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists Clinical Practice Guideline Focused Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 36, 2105–2122 (2018).
Mandelker, D. et al. Mutation detection in patients with advanced cancer by universal sequencing of cancer-related genes in tumor and normal DNA vs guideline-based germline testing. JAMA 318, 825–835 (2017).
Zehir, A. et al. Mutational landscape of metastatic cancer revealed from prospective clinical sequencing of 10,000 patients. Nat. Med. 23, 703–713 (2017).
Geyer, F. C. et al. Recurrent hotspot mutations in HRAS Q61 and PI3K-AKT pathway genes as drivers of breast adenomyoepitheliomas. Nat. Commun. 9, 1816 (2018).
Shen, R. & Seshan, V. E. FACETS: allele-specific copy number and clonal heterogeneity analysis tool for high-throughput DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, e131 (2016).
Chang, M. T. et al. Accelerating discovery of functional mutant alleles in cancer. Cancer Discov. 8, 174–183 (2018).
Gulhan, D. C., Lee, J. J., Melloni, G. E. M., Cortes-Ciriano, I. & Park, P. J. Detecting the mutational signature of homologous recombination deficiency in clinical samples. Nat. Genet 51, 912–919 (2019).
Setton, J. et al. Metadata record for the article: Germline RAD51B loss-of-function variants confer susceptibility to hereditary breast and ovarian cancers and result in homologous recombination-deficient tumors. figshare https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.14665086 (2021).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Breast Cancer Research Foundation (to J.S.R.-F.); the Sarah Jenkins Fund (to J.S.R.-F.); the National Cancer Institute at the National Institutes of Health Paul Calabresi Career Development Award for Clinical Oncology (to J.S., K12 CA184746); and the National Cancer Institute at the National Institutes of Health Cancer Center Support Grant (P30 CA008747). The funders had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication. We are grateful to the members of the Reis-Filho, Offit, and Powell labs for their advice, discussion, and insight.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.M., J.S. and J.S.R.-F. conceived the study. P.S., I.X.P. and D.B. performed bioinformatics analyses. D.M., J.S., S.M., Y.K, O.C.-B., M.S., K.T., L.Z., K.C., S.P., B.W., M.R., N.R., K.O. and J.S.R.-F. interpreted the data. R.S., I.P. and B.K. performed the functional studies. D.M., J.S., P.S. and J.S.R.-F. wrote the first draft of the manuscript, which was edited and approved by all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
J.S.R.-F. is a consultant with paid honoraria of Goldman Sachs and REPARE Therapeutics, a member of the scientific advisory boards of Volition RX and Paige.AI, and an ad hoc member of the scientific advisory boards of Roche Tissue Diagnostics, Ventana Medical Systems, Novartis, Roche, Genentech and InVicro. He is also a deputy editor for NPJ Breast Cancer. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Setton, J., Selenica, P., Mukherjee, S. et al. Germline RAD51B variants confer susceptibility to breast and ovarian cancers deficient in homologous recombination. npj Breast Cancer 7, 135 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41523-021-00339-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41523-021-00339-0