Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Ionic imbalance induced self-propulsion of liquid metals
Ionic imbalance induced self-propulsion of liquid metals
The control over the motion and deformation of liquid droplets is essential to many microfluidic and actuation systems. Zavabeti et al. demonstrate that applying a pH or ionic gradient across a droplet of liquid metal alloy of gallium results in its motion due to a breaking of the surface charge symmetry.
- Ali Zavabeti
- , Torben Daeneke
- & Kourosh Kalantar-zadeh
-
Article
| Open Access Piezoelectric enhancement under negative pressure
Piezoelectric enhancement under negative pressure
Recently, negative pressure has been observed in perovskite nanowires by annealing the wires from a lower-density phase. Here, the authors show that the negative pressure enhances the piezoelectric coefficient of PbTiO3 and Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 nanowires experimentally and by ab initiocalculations.
- Alexander Kvasov
- , Leo J. McGilly
- & Nava Setter
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering electrocatalytic activity in nanosized perovskite cobaltite through surface spin-state transition
Engineering electrocatalytic activity in nanosized perovskite cobaltite through surface spin-state transition
The activity of electrocatalysts exhibits a strong dependence on their electronic structures. Here, the authors manipulate the eg filling of perovskite cobaltite LaCoO3nanoparticles by changing particle size and show improved oxygen evolution activity with increased numbers of surface high-spin cobalt ions.
- Shiming Zhou
- , Xianbing Miao
- & Jie Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable graphene micro-emitters with fast temporal response and controllable electron emission
Tunable graphene micro-emitters with fast temporal response and controllable electron emission
Controlling the electron emission of microfabricated field emitters can be challenging. Here the authors report controllable and tunable graphene thermionic micro-emitters with well-defined turn-on voltages and switching times in the microsecond range and fabricate uniform micro-emitter arrays.
- Gongtao Wu
- , Xianlong Wei
- & Lianmao Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Designing high-performance layered thermoelectric materials through orbital engineering
Designing high-performance layered thermoelectric materials through orbital engineering
Thermoelectric materials with enhanced performances need to be identified. Here, the authors use the crystal field splitting energy of orbitals as a descriptor to design thermoelectric materials by solid solution maps and strain engineering in layered CaAl2Si2-type Zintl compounds.
- Jiawei Zhang
- , Lirong Song
- & Bo B. Iversen
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible lithium–oxygen battery based on a recoverable cathode
Flexible lithium–oxygen battery based on a recoverable cathode
Flexible energy storage systems usually have limited energy densities. Here the authors report a flexible lithium–oxygen battery with the cathode consisting of titanium dioxide nanowire arrays grown on carbon textiles, which displays high mechanical strength as well as promising electrochemical performance.
- Qing-Chao Liu
- , Ji-Jing Xu
- & Xin-Bo Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance n-type black phosphorus transistors with type control via thickness and contact-metal engineering
High-performance n-type black phosphorus transistors with type control via thickness and contact-metal engineering
Black phosphorus p-type field-effect switching was previously demonstrated, but type control has proven difficult. Here, the authors create n-type black phosphorus Schottky field-effect transistors in which the polarity is controlled via contact-metal engineering and changing the flake thickness.
- David J. Perello
- , Sang Hoon Chae
- & Young Hee Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Band structure engineering via piezoelectric fields in strained anisotropic CdSe/CdS nanocrystals
Band structure engineering via piezoelectric fields in strained anisotropic CdSe/CdS nanocrystals
Quantum dots confine electrons to a nanometre length scale, and this gives rise to numerous quantum effects. Here, the authors directly control the excitonic structure of nanocrystal quantum dots by manipulating intra-particle piezoelectric fields.
- Sotirios Christodoulou
- , Fernando Rajadell
- & Iwan Moreels
-
Article
| Open Access Large Seebeck effect by charge-mobility engineering
Large Seebeck effect by charge-mobility engineering
The Seebeck effect causes an electrical potential across a temperature gradient in a material, and is therefore useful for generating useful current from waste heat. Here, the authors show that the Seebeck effect can arise due to charge-carrier relaxation in addition to the conventional mechanism.
- Peijie Sun
- , Beipei Wei
- & Frank Steglich
-
Article
| Open Access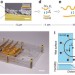 Scaling up nanoscale water-driven energy conversion into evaporation-driven engines and generators
Scaling up nanoscale water-driven energy conversion into evaporation-driven engines and generators
Harvesting energy from evaporation is constrained by the limited transport kinetics of materials and the slowly changing humidity of the environment. Chen et al. follow hierarchical design strategies to overcome these problems and create engines that start and run when placed at air-water interfaces.
- Xi Chen
- , Davis Goodnight
- & Ozgur Sahin
-
Article
| Open Access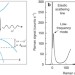 Electronic Raman scattering as an ultra-sensitive probe of strain effects in semiconductors
Electronic Raman scattering as an ultra-sensitive probe of strain effects in semiconductors
Engineering strain in semiconductor structures provides additional control over the optical and electronic properties, which is promising for device applications. Fluegel et al. show that electronic Raman scattering provides a route to sensitively measure the degree of strain in thin semiconductor layers.
- Brian Fluegel
- , Aleksej V. Mialitsin
- & Angelo Mascarenhas
-
Article |
 Long-living terahertz magnons in ultrathin metallic ferromagnets
Long-living terahertz magnons in ultrathin metallic ferromagnets
The technological application of ultrafast terahertz magnons in itinerant ferromagnetic nanostructures is currently limited by magnon relaxation due to Landau damping. Here, Qin et al. demonstrate suppressed Landau damping and enhanced magnon lifetimes in ultrathin films of Fe–Pd alloy.
- H. J. Qin
- , Kh. Zakeri
- & J. Kirschner
-
Article
| Open Access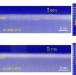 Engineering two-dimensional superconductivity and Rashba spin–orbit coupling in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 quantum wells by selective orbital occupancy
Engineering two-dimensional superconductivity and Rashba spin–orbit coupling in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 quantum wells by selective orbital occupancy
Two-dimensional electron gases at oxide interfaces induce exotic behaviours. By studying samples with different crystal orientation, Herranz et al.show that the extension and anisotropy of the oxide quantum well properties can be controlled through selective sub-band filling via orientational tuning.
- Gervasi Herranz
- , Gyanendra Singh
- & Josep Fontcuberta
-
Article |
 How dead ends undermine power grid stability
How dead ends undermine power grid stability
The cheapest way to add new power stations to a domestic power grid is by tree-like connections to the network. A numerical basin stability analysis of Menck et al.suggests that this undermines a grid’s stability against blackouts but can be fixed with extra transmission lines to these otherwise ‘dead ends’.
- Peter J. Menck
- , Jobst Heitzig
- & Hans Joachim Schellnhuber

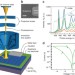 Quantifying redox-induced Schottky barrier variations in memristive devices via in operando spectromicroscopy with graphene electrodes
Quantifying redox-induced Schottky barrier variations in memristive devices via in operando spectromicroscopy with graphene electrodes