Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Virtual histological staining of unlabeled autopsy tissue
Virtual histological staining of unlabeled autopsy tissue
Conventional staining of post-mortem samples can be affected by several factors, including tissue autolysis. Here, the authors demonstrate a virtual staining tool using a trained neural network to turn autofluorescence images of label-free autopsy tissue into brightfield equivalent images.
- Yuzhu Li
- , Nir Pillar
- & Aydogan Ozcan
-
Article
| Open Access Large language models streamline automated machine learning for clinical studies
Large language models streamline automated machine learning for clinical studies
A knowledge gap persists between machine learning developers and clinicians. Here, the authors show that the Advanced Data Analysis extension of ChatGPT could bridge this gap and simplify complex data analyses, making them more accessible to clinicians.
- Soroosh Tayebi Arasteh
- , Tianyu Han
- & Sven Nebelung
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic computer-to-brain communication enhancing naturalistic touch sensations via peripheral nerve stimulation
Biomimetic computer-to-brain communication enhancing naturalistic touch sensations via peripheral nerve stimulation
Loss of communication between the brain and the body severely impacts the sensorimotor abilities of disabled individuals. Here, the authors design and test a neuroscience-driven framework for advancing bionic devices that leverages biomimetic stimulation to induce physiologically plausible information flow in animals and enhances patient performance with neuroprostheses.
- Giacomo Valle
- , Natalija Katic Secerovic
- & Stanisa Raspopovic
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular co-assembled strategy tuning protein conformation for cartilage regeneration
Molecular co-assembled strategy tuning protein conformation for cartilage regeneration
The assembly of oligopeptide and polypeptide molecules can reconstruct various ordered advanced structures. Here the authors develop a “molecular velcro”-inspired amphiphilic supramolecular co-assembly strategy, which improves the mechanical strength and cartilaginous regeneration efficiency through conformation transition.
- Chengkun Zhao
- , Xing Li
- & Yong Sun
-
Article
| Open Access A microfluidic platform integrating functional vascularized organoids-on-chip
A microfluidic platform integrating functional vascularized organoids-on-chip
Vascularization remains a significant challenge in organoid technology. Here, the authors develop a microfluidic platform that enhances organoid growth, function and maturation, by establishing functional perfusable vascular networks.
- Clément Quintard
- , Emily Tubbs
- & Xavier Gidrol
-
Article
| Open Access Vascular network-inspired fluidic system (VasFluidics) with spatially functionalizable membranous walls
Vascular network-inspired fluidic system (VasFluidics) with spatially functionalizable membranous walls
Functional features in the spatiotemporal regulation of blood chemistry are not much explored. Here authors show vascular network-inspired fluidics, functionalizable for different region-specific trans-wall transport to regulate fluids over space and time.
- Yafeng Yu
- , Yi Pan
- & Ho Cheung Shum
-
Article
| Open Access Modeling early pathophysiological phenotypes of diabetic retinopathy in a human inner blood-retinal barrier-on-a-chip
Modeling early pathophysiological phenotypes of diabetic retinopathy in a human inner blood-retinal barrier-on-a-chip
Here the authors develop perfusable inner blood-retinal barrier-specific microvascular networks with human primary retinal microvascular cells. They show that chronic diabetic stimulation leads to the generation of early hallmarks of diabetic retinopathy, including pericyte and capillary dropout, ghost vessels, and inflammation.
- Thomas L. Maurissen
- , Alena J. Spielmann
- & Héloïse Ragelle
-
Article
| Open Access A 3D printable tissue adhesive
A 3D printable tissue adhesive
Tissue adhesives have received significant interest for their clinical utility but are typically incompatible with advanced manufacturing methods. Here, the authors introduce a 3D printable tissue adhesive for the fabrication of patches and devices for diverse biomedical applications.
- Sarah J. Wu
- , Jingjing Wu
- & Xuanhe Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Shape-recovery of implanted shape-memory devices remotely triggered via image-guided ultrasound heating
Shape-recovery of implanted shape-memory devices remotely triggered via image-guided ultrasound heating
Focused ultrasound could be used to change the geometry of implanted shape-memory medical devices noninvasively. Here, the authors demonstrate this concept on large animal models, showing device removal and trigger drug release.
- Yang Zhu
- , Kaicheng Deng
- & William R. Wagner
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanically resilient hybrid aerogels containing fibers of dual-scale sizes and knotty networks for tissue regeneration
Mechanically resilient hybrid aerogels containing fibers of dual-scale sizes and knotty networks for tissue regeneration
Aerogels are suitable for soft tissue engineering, but often come with brittleness. Here the authors develop a hybrid aerogel with micro- and nanofiber networks that optimizes tensile moduli and fracture energies and show that these materials are super-elastic, fostering rapid tissue ingrowth and allowing minimally invasive procedures.
- S. M. Shatil Shahriar
- , Alec D. McCarthy
- & Jingwei Xie
-
Article
| Open Access An actor-model framework for visual sensory encoding
An actor-model framework for visual sensory encoding
Encoding and downsampling images is key for visual prostheses. Here, the authors show that an actor-model framework using the inherent computation of the retinal network yields better performance in downsampling images compared to learning-free methods.
- Franklin Leong
- , Babak Rahmani
- & Diego Ghezzi
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired handheld time-share driven robot with expandable DoFs
Bioinspired handheld time-share driven robot with expandable DoFs
Handheld robots are limited in controllable degrees of freedom, which can result in lower dexterity for clinical applications. Here, Wang et al. report a handheld time-share driven robot with one motor that powers multiple motion modules for high-dextrous operation.
- Yunjiang Wang
- , Xinben Hu
- & Haoran Jin
-
Article
| Open Access A drug-free cardiovascular stent functionalized with tailored collagen supports in-situ healing of vascular tissues
A drug-free cardiovascular stent functionalized with tailored collagen supports in-situ healing of vascular tissues
The efficacy of drug-eluting stents remains limited due to delayed reendothelialization, impaired intimal remodeling, and potentially increased late restenosis. Here the authors propose a one-produces-multi stent coating, a drug-free strategy that supports in situ healing of vascular tissues, as demonstrated in rabbit and porcine models.
- Haoshuang Wu
- , Li Yang
- & Yunbing Wang
-
Article
| Open Access LNP-RNA-engineered adipose stem cells for accelerated diabetic wound healing
LNP-RNA-engineered adipose stem cells for accelerated diabetic wound healing
Adipose stem cells are promising therapeutic agents in tissue regeneration. Here the authors develop a lipid nanoparticle/RNA engineering platform to enhance the protein production of these cells, which demonstrate superior healing efficacy in a mouse model of diabetic cutaneous wounds.
- Yonger Xue
- , Yuebao Zhang
- & Yizhou Dong
-
Article
| Open Access Shape-changing electrode array for minimally invasive large-scale intracranial brain activity mapping
Shape-changing electrode array for minimally invasive large-scale intracranial brain activity mapping
The invasiveness of extensive craniotomy hinders large-scale cortex mapping. Here, the authors developed a flexible, shape-changing electrode array which enables minimally invasive implantation and achieves high spatiotemporal resolution brain mapping.
- Shiyuan Wei
- , Anqi Jiang
- & Xiaojie Duan
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning-based high-frequency neuronal spike reconstruction from low-frequency and low-sampling-rate recordings
Machine learning-based high-frequency neuronal spike reconstruction from low-frequency and low-sampling-rate recordings
Multichannel neural recording enhances understanding of brain function, but handling large data is challenging. Here, the authors develop machine learning-based high frequency spike reconstruction from subsampled low-frequency neuronal signals.
- Nari Hong
- , Boil Kim
- & Hongki Kang
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering tumor-colonizing E. coli Nissle 1917 for detection and treatment of colorectal neoplasia
Engineering tumor-colonizing E. coli Nissle 1917 for detection and treatment of colorectal neoplasia
There is an unmet medical need for the detection and treatment of early adenomas to prevent their progression to malignant disease. Here the authors show that orally administered E. coli Nissle 1917 can selectively colonize adenomas in mouse models and in patients as a detection tool, as well as deliver immunotherapeutics for colorectal neoplasia treatment.
- Candice R. Gurbatri
- , Georgette A. Radford
- & Tal Danino
-
Article
| Open Access A magnetic multi-layer soft robot for on-demand targeted adhesion
A magnetic multi-layer soft robot for on-demand targeted adhesion
Magnetic soft robots offer a non-invasive way to deliver bioadhesives to targeted lesion sites to accelerate the healing. Authors present a magnetic multi-layer soft robot that is capable of performing navigated locomotion on biological tissues and on-demand multi-target adhesion at different sites.
- Ziheng Chen
- , Yibin Wang
- & Jiangfan Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Dual electrical stimulation at spinal-muscular interface reconstructs spinal sensorimotor circuits after spinal cord injury
Dual electrical stimulation at spinal-muscular interface reconstructs spinal sensorimotor circuits after spinal cord injury
Electrical signals with characteristic parameters for reconstructing neural circuits remain incompletely understood, limiting the therapeutic potential of electrical neuromodulation techniques. Here, the authors demonstrate that dual electrical stimulation at 10–20 Hz rebuilds the spinal sensorimotor neural circuit after spinal cord injury, indicating the characteristic signals of circuit remodeling.
- Kai Zhou
- , Wei Wei
- & Yaobo Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible, scalable, high channel count stereo-electrode for recording in the human brain
Flexible, scalable, high channel count stereo-electrode for recording in the human brain
Electrodes available for deep brain recording and stimulation have a number of limitations. Here the authors describe a thin-film depth electrode that may offer improved spatial and temporal resolution for recording brain activity.
- Keundong Lee
- , Angelique C. Paulk
- & Shadi. A. Dayeh
-
Perspective
| Open Access Neuromorphic hardware for somatosensory neuroprostheses
Neuromorphic hardware for somatosensory neuroprostheses
Neuroprosthetic devices have recently emerged as promising solutions to restore sensory-motor functions lost due to injury or neurological diseases. In this perspective, Donati and Valle propose to combine neuroprostheses with neuromorphic technologies for designing more natural human-machine interfaces with possible improvements in device performance, acceptability, and embeddability.
- Elisa Donati
- & Giacomo Valle
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancing aortic valve drug delivery with PAR2-targeting magnetic nano-cargoes for calcification alleviation
Enhancing aortic valve drug delivery with PAR2-targeting magnetic nano-cargoes for calcification alleviation
Achieving targeted drug delivery for calcified aortic valve is challenging. Here, the authors find that protease activated receptor 2 (PAR2) is up-regulated on calcified valves and develop a magnetic nanocarrier functionalized with PAR2-targeting peptide for dual-active drug delivery.
- Jinyong Chen
- , Tanchen Ren
- & Xianbao Liu
-
Article
| Open Access A self-powered intracardiac pacemaker in swine model
A self-powered intracardiac pacemaker in swine model
Harvesting biomechanical energy from cardiac motion is an attractive power source for implantable bioelectronic devices. Here, the authors report a battery-free, transcatheter, self-powered intracardiac pacemaker for the treatment of arrhythmia in large animal models.
- Zhuo Liu
- , Yiran Hu
- & Zhong Lin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access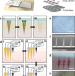 Digital automation of transdermal drug delivery with high spatiotemporal resolution
Digital automation of transdermal drug delivery with high spatiotemporal resolution
Microneedle patches that can actively address individual needles are challenging to realize. Here, the authors introduce a spatiotemporal on-demand patch for precise and personalized drug delivery, utilizing electrically triggered control with drug-loaded microneedles and biocompatible metallic membranes.
- Yihang Wang
- , Zeka Chen
- & Wubin Bai
-
Article
| Open Access Single-sided magnetic resonance-based sensor for point-of-care evaluation of muscle
Single-sided magnetic resonance-based sensor for point-of-care evaluation of muscle
Magnetic resonance imaging is a useful clinical tool, but its widespread use is constrained by size, cost, and time. Here, the authors report the development of a magnetic resonance sensor for the clinical detection of muscle tissue, allowing for new point-of-care quantitative diagnostic measurements
- Sydney E. Sherman
- , Alexa S. Zammit
- & Michael J. Cima
-
Article
| Open Access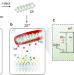 Non-Faradaic optoelectrodes for safe electrical neuromodulation
Non-Faradaic optoelectrodes for safe electrical neuromodulation
Nanoscale optoelectrodes hold the potential to optically stimulate individual neuron. Here, the authors form nanoscale capacitive optoelectrodes by incorporating zinc porphyrin into nanorods, coated by TiO2, a design that allows for far-field optical modulation of neurons with efficiency and negligible side effects.
- Jian Chen
- , Yanyan Liu
- & Wenbo Bu
-
Article
| Open Access A stapled lipopeptide platform for preventing and treating highly pathogenic viruses of pandemic potential
A stapled lipopeptide platform for preventing and treating highly pathogenic viruses of pandemic potential
The ongoing emergence of highly pathogenic viruses that evade immune-based therapies or lack interventions mandates new approaches, especially for on-demand prophylaxis. Here the authors provide a stapled lipopeptide platform for the rapid development of viral fusion inhibitors to combat outbreaks.
- Gregory H. Bird
- , J. J. Patten
- & Loren D. Walensky
-
Article
| Open Access AI co-pilot bronchoscope robot
AI co-pilot bronchoscope robot
The unequal distribution of medical resources means that bronchoscopic services are often unavailable in underdeveloped areas. Here, the authors present an AI co-pilot bronchoscope robot that features a user-friendly plug-and-play catheter and an AI-human shared control algorithm, to enable novice doctors to conduct lung examinations safely.
- Jingyu Zhang
- , Lilu Liu
- & Haojian Lu
-
Comment
| Open Access From lab to life: how wearable devices can improve health equity
From lab to life: how wearable devices can improve health equity
Wearable devices can provide personalised medicine at the point of need, potentially increasing access to health services and therefore improving health equity. Here the authors discuss their experiences developing wearable devices for vulnerable patient populations, including neonates and pregnant individuals.
- Jessica R. Walter
- , Shuai Xu
- & John A. Rogers
-
Article
| Open Access Injectable hydrogel electrodes as conduction highways to restore native pacing
Injectable hydrogel electrodes as conduction highways to restore native pacing
No preventive treatment addresses the underlying condition that leads to cardiac arrest. Here, researchers developed an injectable hydrogel electrode that achieves pacing that mimics physiological conduction with the potential to eliminate lethal arrhythmias and provide painless defibrillation.
- Gabriel J. Rodriguez-Rivera
- , Allison Post
- & Elizabeth Cosgriff-Hernandez
-
Article
| Open Access High throughput intracellular delivery by viscoelastic mechanoporation
High throughput intracellular delivery by viscoelastic mechanoporation
Scalability of mechanoporation strategies for intracellular delivery remains challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate a microfluidic approach for delivering mRNA and CRISPR-Cas systems to over 250 million cells per minute.
- Derin Sevenler
- & Mehmet Toner
-
Article
| Open Access Design automation of microfluidic single and double emulsion droplets with machine learning
Design automation of microfluidic single and double emulsion droplets with machine learning
Generating microfluidic droplets with application-specific desired characteristics is hard. Here the authors report fluid-agnostic machine learning models capable of accurately predicting device geometries and flow conditions required to generate stable single and double emulsions.
- Ali Lashkaripour
- , David P. McIntyre
- & Polly M. Fordyce
-
Article
| Open Access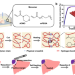 3D printing of self-healing personalized liver models for surgical training and preoperative planning
3D printing of self-healing personalized liver models for surgical training and preoperative planning
High-fidelity personalized anatomical models can offer invaluable support for precision medicine. Here, the authors show the 3D printing of self-healing liver models, which can be resected in a trial and-error manner for surgical training to enhance the safety of hepatic surgery.
- Yahui Lu
- , Xing Chen
- & Yuhua Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access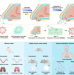 Intranasal mask for protecting the respiratory tract against viral aerosols
Intranasal mask for protecting the respiratory tract against viral aerosols
The spread of many infectious diseases substantially relies on aerosol transmission to the respiratory tract. Here, the authors design an intranasal mask with the ability to intercept viral aerosols, entrap and inactivate virus, thus preventing respiratory tract infection.
- Xiaoming Hu
- , Shuang Wang
- & Wei Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning-based phenotyping reclassifies combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma
Deep learning-based phenotyping reclassifies combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma
Combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinomas (cHCC-CCA) are challenging to diagnose, as they exhibit features of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICCA). Here, the authors use deep learning to re-classify cHCC-CCA tumours into HCC or ICCA based on histopathology images.
- Julien Calderaro
- , Narmin Ghaffari Laleh
- & Jakob Nikolas Kather
-
Article
| Open Access A patterned human primitive heart organoid model generated by pluripotent stem cell self-organization
A patterned human primitive heart organoid model generated by pluripotent stem cell self-organization
Pluripotent stem cell-derived organoids can recapitulate significant hallmarks of human organ development and are becoming critical tools for human research. Here, the authors report significant technical steps for generating sophisticated synthetic human primitive heart organoids.
- Brett Volmert
- , Artem Kiselev
- & Aitor Aguirre
-
Article
| Open Access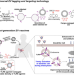 Metabolic tagging of extracellular vesicles and development of enhanced extracellular vesicle based cancer vaccines
Metabolic tagging of extracellular vesicles and development of enhanced extracellular vesicle based cancer vaccines
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) have been actively explored for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Here, the authors report a universal metabolic tagging technology to generate chemically tagged EVs from parent cells, modulate EV-cell interactions, and develop potent EV-based cancer vaccines.
- Rimsha Bhatta
- , Joonsu Han
- & Hua Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Fully implanted battery-free high power platform for chronic spinal and muscular functional electrical stimulation
Fully implanted battery-free high power platform for chronic spinal and muscular functional electrical stimulation
Electrical stimulation of the neuromuscular system holds promise for therapeutic biomedical applications, but is currently restricted by power. Here, the authors introduce fully implantable resonator-based designs achieving ±20 V compliance and >300 mW output, enabling multichannel, biphasic, current-controlled operation to evoke functional gate patterns for 6-weeks in freely behaving rats.
- Alex Burton
- , Zhong Wang
- & Philipp Gutruf
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-durable cell-free bioactive hydrogel with fast shape memory and on-demand drug release for cartilage regeneration
Ultra-durable cell-free bioactive hydrogel with fast shape memory and on-demand drug release for cartilage regeneration
Achieving successful in vivo cartilage regeneration remains challenging. Here they present a cell-free, multiple hydrogen-bond crosslinked hydrogel loaded with tannic acid and Kartogenin with ultra-durable mechanical properties and stage-dependent drug release behavior to promote cartilage regeneration.
- Yuxuan Yang
- , Xiaodan Zhao
- & Xuesi Chen
-
Article
| Open Access A fully integrated, standalone stretchable device platform with in-sensor adaptive machine learning for rehabilitation
A fully integrated, standalone stretchable device platform with in-sensor adaptive machine learning for rehabilitation
Methods for the wireless, continuous monitoring and analysis of activities directly from the throat skin have not been developed. Here, the authors present a stretchable device platform that provides wireless measurements and machine learning-based analysis of vibrations and muscle electrical activities from the throat.
- Hongcheng Xu
- , Weihao Zheng
- & Libo Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Local H2 release remodels senescence microenvironment for improved repair of injured bone
Local H2 release remodels senescence microenvironment for improved repair of injured bone
Senescence microenvironment inhibits tissue repair in elderly individuals. Here, the authors demonstrate that local H2 supply has anti-inflammation and anti-senescence effects, and develop a H2-releasing scaffold to enhance aging bone defect repair.
- Shengqiang Chen
- , Yuanman Yu
- & Qianjun He
-
Article
| Open Access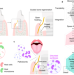 Occlusive membranes for guided regeneration of inflamed tissue defects
Occlusive membranes for guided regeneration of inflamed tissue defects
Symbiosis should be maintained during the oral regeneration period. Herein, authors develop an occlusive membrane that induces symbiosis, thereby improving the performance of guided bone generation therapy.
- Woojin Choi
- , Utkarsh Mangal
- & Jinkee Hong
-
Article
| Open Access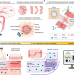 3D bioprinted multilayered cerebrovascular conduits to study cancer extravasation mechanism related with vascular geometry
3D bioprinted multilayered cerebrovascular conduits to study cancer extravasation mechanism related with vascular geometry
Geometrical complexities of blood vessels alter biophysical behaviors of circulating tumor cells, influencing cancer metastasis. Here, the authors develop a 3D bioprinted in vitro brain blood vessel-on-a-chip to investigate continuities between vascular geometry and metastatic cancer development.
- Wonbin Park
- , Jae-Seong Lee
- & Dong-Woo Cho
-
Article
| Open Access A semiconductor 96-microplate platform for electrical-imaging based high-throughput phenotypic screening
A semiconductor 96-microplate platform for electrical-imaging based high-throughput phenotypic screening
Cell-based phenotypic assays link in vitro discovery to disease pathology. Here, the authors report a semiconductor-based microplate platform to perform high-throughput, high-dimensional “electrical imaging” for label-free assessment of live cell morphology and function.
- Shalaka Chitale
- , Wenxuan Wu
- & Jeffrey Abbott
-
Article
| Open Access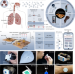 Wireless, battery-free, multifunctional integrated bioelectronics for respiratory pathogens monitoring and severity evaluation
Wireless, battery-free, multifunctional integrated bioelectronics for respiratory pathogens monitoring and severity evaluation
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic highlighted our need for methods that allow rapid viral surveillance. Here, authors report a wireless, battery-free and wearable self-diagnosis platform that can continuously capture viral particles, diagnose infection status and evaluate symptom severity via breath and blow.
- Hu Li
- , Huarui Gong
- & Xinge Yu
-
Article
| Open Access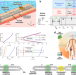 Amphibious epidermal area networks for uninterrupted wireless data and power transfer
Amphibious epidermal area networks for uninterrupted wireless data and power transfer
Body area networks represent a wearable technology suitable for applications like virtual reality and health monitoring. Here, the study presents a wireless battery-free channel that works reliably in harsh environments, including underwater. It utilizes stretchable magneto-inductive metamaterials to enable uninterrupted communication.
- Amirhossein Hajiaghajani
- , Patrick Rwei
- & Peter Tseng
-
Article
| Open Access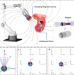 Three-degrees-of-freedom orientation manipulation of small untethered robots with a single anisotropic soft magnet
Three-degrees-of-freedom orientation manipulation of small untethered robots with a single anisotropic soft magnet
Existing magnetic actuation systems using a single permanent magnet can only achieve 2-DoF orientation manipulation. Wang et al. propose a magnetic actuation method that uses a single anisotropic soft magnet instead of a permanent magnet to enable full 3-DoF orientation manipulation of small, untethered robots.
- Heng Wang
- , Junhao Cui
- & Yuxiang Han
-
Article
| Open Access An on-demand bioresorbable neurostimulator
An on-demand bioresorbable neurostimulator
Despite promising advantages, bioresorbable electronics face practical limitations due to unpredictable device lifetimes. Here, the authors introduce an on-demand bioresorbable neurostimulator powered by biosafe ultrasound to treat peripheral nerve injury and neuropathies.
- Dong-Min Lee
- , Minki Kang
- & Sang-Woo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Lung SORT LNPs enable precise homology-directed repair mediated CRISPR/Cas genome correction in cystic fibrosis models
Lung SORT LNPs enable precise homology-directed repair mediated CRISPR/Cas genome correction in cystic fibrosis models
Roughly 10% of Cystic Fibrosis (CF) patients still have no effective medicine to take. Lung Selective Organ Targeting (SORT) Lipid Nanoparticles can efficiently deliver Cas9 mRNA, sgRNA, and donor ssDNA templates for precise homology-directed repair-mediated gene correction in ex vivo and in vivo CF models.
- Tuo Wei
- , Yehui Sun
- & Daniel J. Siegwart

 In situ combinatorial synthesis of degradable branched lipidoids for systemic delivery of mRNA therapeutics and gene editors
In situ combinatorial synthesis of degradable branched lipidoids for systemic delivery of mRNA therapeutics and gene editors