Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Age-related and disease locus-specific mechanisms contribute to early remodelling of chromatin structure in Huntington’s disease mice
Age-related and disease locus-specific mechanisms contribute to early remodelling of chromatin structure in Huntington’s disease mice
The dynamics of chromatin and transcriptional changes underlying Huntington’s disease remain poorly understood. Here the authors use a Huntington’s mouse model to profile the striatal chromatin landscape, finding that the Huntington’s mutation accelerates age-dependent epigenetic and transcriptional changes, and locally affects 3D chromatin organization.
- Rafael Alcalá-Vida
- , Jonathan Seguin
- & Karine Merienne
-
Perspective
| Open Access A bioengineering perspective on modelling the intestinal epithelial physiology in vitro
A bioengineering perspective on modelling the intestinal epithelial physiology in vitro
Maria Antfolk and Kim Jensen discuss how to model intestinal epithelial cell function in the dish and how various physiologically important environmental conditions, for example, extracellular matrix, pressure and flow, can be modelled and how this is applicable to clinical work.
- Maria Antfolk
- & Kim B. Jensen
-
Article
| Open Access Injury triggers fascia fibroblast collective cell migration to drive scar formation through N-cadherin
Injury triggers fascia fibroblast collective cell migration to drive scar formation through N-cadherin
Extensive scars develop in deep wounds as opposed to superficial wounds but it is unclear why. Here, the authors use live imaging of physiologic wounds and scars formed ex vivo to show that fascia fibroblasts upregulate N-cadherin allowing coordinated cell migration that drives extensive scar formation of deep wounds.
- Dongsheng Jiang
- , Simon Christ
- & Yuval Rinkevich
-
Article
| Open Access Modeling early stage atherosclerosis in a primary human vascular microphysiological system
Modeling early stage atherosclerosis in a primary human vascular microphysiological system
Human microphysiological systems (MPS) have some advantages over animal models to study the mechanisms of disease. Here the authors use a tissue-engineered blood vessel MPS to create a model of early stage atherosclerosis and assess the effect of several drugs.
- Xu Zhang
- , Muath Bishawi
- & George A. Truskey
-
Comment
| Open Access Three questions to ask before using model outputs for decision support
Three questions to ask before using model outputs for decision support
Decision makers must have sufficient confidence in models if they are to influence their decisions. We propose three screening questions to critically evaluate models with respect to their purpose, organization, and evidence. They enable a more transparent, robust, and secure use of model outputs.
- Volker Grimm
- , Alice S. A. Johnston
- & P. Thorbek
-
Comment
| Open AccessEmerging preclinical evidence does not support broad use of hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19 patients
There is an urgent need for drugs, therapies and vaccines to be available to protect the human population against COVID-19. One of the first approaches taken in the COVID-19 global response was to consider repurposing licensed drugs. This commentary highlights an extraordinary international collaborative effort of independent researchers who have recently all come to the same conclusion—that chloroquine or hydroxchloroquine are unlikely to provide clinical benefit against COVID-19.
- S. G. P. Funnell
- , W. E. Dowling
- & C. M. Coleman
-
Article
| Open Access Single cell transcriptomics of human epidermis identifies basal stem cell transition states
Single cell transcriptomics of human epidermis identifies basal stem cell transition states
The mechanisms regulating stem cells to give rise to human interfollicular epidermis are unclear. Here, the authors use single cell RNA sequencing to identify heterogeneity within the human neonatal interfollicular epidermis and distinct spatial positioning of at least four basal stem cell populations.
- Shuxiong Wang
- , Michael L. Drummond
- & Scott X. Atwood
-
Article
| Open Access BRCA1-associated structural variations are a consequence of polymerase theta-mediated end-joining
BRCA1-associated structural variations are a consequence of polymerase theta-mediated end-joining
Cancer mutational signatures have been associated with defects in genome maintenance pathways. Here the authors, by using a worm germline mutagenesis model defective of human orthologue BRCA-1, identify polymerase theta-mediated end-joining (TMEJ) as causing the BRCAness mutational signature.
- J. A. Kamp
- , R. van Schendel
- & M. Tijsterman
-
Article
| Open Access Long-term culture of human pancreatic slices as a model to study real-time islet regeneration
Long-term culture of human pancreatic slices as a model to study real-time islet regeneration
The ability to culture live pancreatic tissue slices for long periods of time would enable longitudinal studies ex vivo. Here the authors culture human and mouse pancreatic slices in a perfluorocarbon-based culture system and show stable endocrine and exocrine function for up to ten days in culture.
- Mirza Muhammad Fahd Qadir
- , Silvia Álvarez-Cubela
- & Juan Domínguez-Bendala
-
Article
| Open Access The tumour microenvironment shapes dendritic cell plasticity in a human organotypic melanoma culture
The tumour microenvironment shapes dendritic cell plasticity in a human organotypic melanoma culture
Conventional co-culture systems often lack physiological complexity of the tumor microenvironment. Here, the authors report an organotypic skin melanoma culture and use this model to investigate the tumor induced suppression on dendritic cells.
- S. Di Blasio
- , G. F. van Wigcheren
- & C. G. Figdor
-
Article
| Open Access Photoactivatable Cre recombinase 3.0 for in vivo mouse applications
Photoactivatable Cre recombinase 3.0 for in vivo mouse applications
Previous versions of photoactivatable Cre recombinase (PA-Cre) suffered from unintentional recombination in dark conditions. Here, the authors develop an improved version of PA-Cre, called PA-Cre 3.0, which shows reduced leakiness and improved efficiency upon activation, and make mouse lines that express PA-Cre 3.0 conditionally.
- Kumi Morikawa
- , Kazuhiro Furuhashi
- & Masayuki Yazawa
-
Article
| Open Access A HaloTag-TEV genetic cassette for mechanical phenotyping of proteins from tissues
A HaloTag-TEV genetic cassette for mechanical phenotyping of proteins from tissues
Testing mechanical forces on native molecules in natural environments remains a challenge. Here the authors engineer titin to carry a HaloTag-TEV insertion to allow analysis of dynamics under force in muscle fibers.
- Jaime Andrés Rivas-Pardo
- , Yong Li
- & Jorge Alegre-Cebollada
-
Article
| Open Access Organoid cultures from normal and cancer-prone human breast tissues preserve complex epithelial lineages
Organoid cultures from normal and cancer-prone human breast tissues preserve complex epithelial lineages
Organoid technology has enabled the generation of several breast cancer organoids. Here, the authors combine propagation of normal human mammary tissues with mass cytometry to evaluate the ability of organoid culture technologies to preserve stem cells and differentiated cell types.
- Jennifer M. Rosenbluth
- , Ron C. J. Schackmann
- & Joan S. Brugge
-
Article
| Open Access Amyloid-β42/40 ratio drives tau pathology in 3D human neural cell culture models of Alzheimer’s disease
Amyloid-β42/40 ratio drives tau pathology in 3D human neural cell culture models of Alzheimer’s disease
The relationship between amyloid-β species and tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease is not fully understood. Here, the authors show that it is the increased ratio of amyloid-β42 and 40 isoforms drives tau pathology in 3D human neural cell culture models of the disease.
- Sang Su Kwak
- , Kevin J. Washicosky
- & Doo Yeon Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Cell-in-the-loop pattern formation with optogenetically emulated cell-to-cell signaling
Cell-in-the-loop pattern formation with optogenetically emulated cell-to-cell signaling
Synthetic biological pattern formation is challenging to engineer due to theoretical complexity and practical limitations. Here, the authors introduce a cell-in-the-loop approach in which cells interact through in silico signaling.
- Melinda Liu Perkins
- , Dirk Benzinger
- & Mustafa Khammash
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of predictors of drug sensitivity using patient-derived models of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Identification of predictors of drug sensitivity using patient-derived models of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Predicting the drug response of patients with cancer is crucial for implementing targeted therapy. Here, Su et al. make patient-derived cell lines and perform targeted sequencing and RNA-seq to identify CDKN2A/2B loss as a predictor of response to CDK4/6 inhibitors in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
- Dan Su
- , Dadong Zhang
- & Weimin Mao
-
Article
| Open Access Lineage tracing of acute myeloid leukemia reveals the impact of hypomethylating agents on chemoresistance selection
Lineage tracing of acute myeloid leukemia reveals the impact of hypomethylating agents on chemoresistance selection
The development of post-chemotherapy resistance is a significant issue in the management of AML. Here, Caiado et al. suggest that the issue might be circumvented via upfront combination with hypomethylating agents that shape the clonal dynamics and transcriptional landscape of relapsing AML
- Francisco Caiado
- , Diogo Maia-Silva
- & Bruno Silva-Santos
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic modeling reveals HOXB genes are critical for the initiation and maintenance of human leukemia
Synthetic modeling reveals HOXB genes are critical for the initiation and maintenance of human leukemia
Studies with patient derived xenografts are hampered by factors such as genetic variability and sample availability. Here, the authors generate a leukemia mouse model by lentiviral transduction of normal human cord blood and show an oncogenic role of HOXB genes.
- Manabu Kusakabe
- , Ann Chong Sun
- & Andrew P. Weng
-
Article
| Open Access Noncoding dsRNA induces retinoic acid synthesis to stimulate hair follicle regeneration via TLR3
Noncoding dsRNA induces retinoic acid synthesis to stimulate hair follicle regeneration via TLR3
During wound induced hair follicle neogenesis (WIHN), stem cells regenerate hair follicles but how this arises is unclear. Here, the authors show that self-noncoding dsRNA activates the antiviral receptor TLR3 to induce intrinsic retinoic acid, which stimulates WIHN in mice, and in isolated human keratinocyte cells.
- Dongwon Kim
- , Ruosi Chen
- & Luis A. Garza
-
Article
| Open Access Brain leptin reduces liver lipids by increasing hepatic triglyceride secretion and lowering lipogenesis
Brain leptin reduces liver lipids by increasing hepatic triglyceride secretion and lowering lipogenesis
Obesity is associated with leptin resistance and rising blood leptin levels while central leptin exposure may be limited. Here, the authors show that brain leptin infusion reduces hepatic lipid content in rats by increasing hepatic VLDL secretion and lowering liver de novo lipogenesis via a vagal mechanism.
- Martina Theresa Hackl
- , Clemens Fürnsinn
- & Thomas Scherer
-
Article
| Open Access Factors other than hTau overexpression that contribute to tauopathy-like phenotype in rTg4510 mice
Factors other than hTau overexpression that contribute to tauopathy-like phenotype in rTg4510 mice
The rTg4510 mosue line has a tauopathy-like phenotype which is attributed to overexpression of human tau in the frontal cortex. Here the authors identify potential confounding genetic factors that could contribute to the phenotype.
- Julia Gamache
- , Kellie Benzow
- & Michael D. Koob
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic electromechanical stimulation to maintain adult myocardial slices in vitro
Biomimetic electromechanical stimulation to maintain adult myocardial slices in vitro
Cultured adult cardiac tissue undergoes rapid dedifferentiation, which hinders chronic in vitro studies. Here the authors investigate biomimetic electromechanical stimulation of adult myocardial slices applying different preload conditions, identifying the optimum sarcomere length for prolonged culturing, and investigating transcriptional profiles associated with functional preservation.
- Samuel A. Watson
- , James Duff
- & Cesare M. Terracciano
-
Article
| Open Access YAP-independent mechanotransduction drives breast cancer progression
YAP-independent mechanotransduction drives breast cancer progression
The transcriptional regulator YAP is regarded as the universal mechanotransducer, largely from 2D culture studies. Here the authors show that in breast cancer patient tissues and cells in 3D culture, mechanical signals are transduced independently of YAP, questioning YAP as a therapeutic target.
- Joanna Y. Lee
- , Jessica K. Chang
- & Ovijit Chaudhuri
-
Article
| Open Access Cortex-wide neural interfacing via transparent polymer skulls
Cortex-wide neural interfacing via transparent polymer skulls
Imaging the mouse brain using glass cranial windows has limitations in terms of flexibility and long-term imaging. Here the authors engineer transparent polymer skulls that can fit various skull morphologies and can be implanted for over 300 days, enabling simultaneous high resolution brain imaging and electrophysiology across large cortical areas.
- Leila Ghanbari
- , Russell E. Carter
- & Suhasa B. Kodandaramaiah
-
Article
| Open Access HIV-1 vaccination by needle-free oral injection induces strong mucosal immunity and protects against SHIV challenge
HIV-1 vaccination by needle-free oral injection induces strong mucosal immunity and protects against SHIV challenge
Oral vaccination is a potential option to elicit systemic and mucosal immunity against HIV. Here, Jones et al. show that oral vaccination with a modified needle-free injector induces protective immunity against SHIV in non-human primates and is superior to topical application of vaccines to oral tissues.
- Andrew T. Jones
- , Xiaoying Shen
- & Rama Rao Amara
-
Article
| Open Access Long-term functional and structural preservation of precision-cut human myocardium under continuous electromechanical stimulation in vitro
Long-term functional and structural preservation of precision-cut human myocardium under continuous electromechanical stimulation in vitro
Myocardial tissue undergoes steady functional decline when cultured in vitro. Here, the authors report a protocol for culture of human cardiac slices that allows maintenance of contractility for up to four months, and show that the model is suitable for evaluation of drug safety, as exemplified for drugs interfering with cardiomyocyte repolarization.
- Carola Fischer
- , Hendrik Milting
- & Andreas Dendorfer
-
Article
| Open Access Single cell RNA analysis identifies cellular heterogeneity and adaptive responses of the lung at birth
Single cell RNA analysis identifies cellular heterogeneity and adaptive responses of the lung at birth
The respiratory system is transformed in terms of functional change at birth to adapt to breathing air. Here, the authors examine the molecular changes behind the first breath in the mouse by Drop-seq based RNA sequencing, identifying activation of the unfolded protein response as a perinatal adaptation of the lung.
- Minzhe Guo
- , Yina Du
- & Yan Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Prevention of SIVmac251 reservoir seeding in rhesus monkeys by early antiretroviral therapy
Prevention of SIVmac251 reservoir seeding in rhesus monkeys by early antiretroviral therapy
The latent HIV-1 reservoir is the key obstacle for curing HIV-1 infection, but the timepoint at which the HIV-1 reservoir is established is currently unclear. Here, Whitney et al. show in non-human primates that the SIV reservoir in CD4+ T cells is seeded within the first 2 days after infection.
- James B. Whitney
- , So-Yon Lim
- & Dan H. Barouch
-
Article
| Open Access Tissue engineering of human hair follicles using a biomimetic developmental approach
Tissue engineering of human hair follicles using a biomimetic developmental approach
Human skin constructs hold potential for regenerative medicine, but the incorporation of hair follicles into such constructs is a challenge. Here, the authors use 3D printed molds to pattern hair follicle cell types in a physiological organization, and achieve human hair growth on the back of a mouse.
- Hasan Erbil Abaci
- , Abigail Coffman
- & Angela M. Christiano
-
Article
| Open Access Trisomy silencing by XIST normalizes Down syndrome cell pathogenesis demonstrated for hematopoietic defects in vitro
Trisomy silencing by XIST normalizes Down syndrome cell pathogenesis demonstrated for hematopoietic defects in vitro
Individuals with Down Syndrome have hematopoietic abnormalities including high risk of leukaemia. Here the authors show that transcriptional silencing of one chromosome 21 by XIST effectively corrects cell function and development to prevent excessive production of megakaryocytes and erythroids, shown during hematopoietic differentiation of human iPSCs in culture.
- Jen-Chieh Chiang
- , Jun Jiang
- & Jeanne B. Lawrence
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for persistence of the SHIV reservoir early after MHC haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Evidence for persistence of the SHIV reservoir early after MHC haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT) has led to the cure of HIV in one individual, but the underlying mechanisms are unclear. Here, the authors present a model of allo-HCT in SHIV-infected nonhuman primates and show that the SHIV reservoir persists in multiple tissues early after transplantation.
- Lucrezia Colonna
- , Christopher W. Peterson
- & Leslie S. Kean
-
Article
| Open Access Chemogenetic generation of hydrogen peroxide in the heart induces severe cardiac dysfunction
Chemogenetic generation of hydrogen peroxide in the heart induces severe cardiac dysfunction
Excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is associated with cardiac dysfunction, but the causal role of ROS remains poorly understood. Here the authors use an in vivo chemogenetic approach to develop a heart failure model in which generation of hydrogen peroxide in the heart leads to systolic heart failure without fibrotic remodeling.
- Benjamin Steinhorn
- , Andrea Sorrentino
- & Thomas Michel
-
Article
| Open Access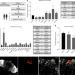 Discovering human diabetes-risk gene function with genetics and physiological assays
Discovering human diabetes-risk gene function with genetics and physiological assays
The function of genes linked to type 2 diabetes is poorly characterized. Here the authors combine Drosophila genetics and physiology with human islet biology to identify new regulators of insulin secretion including BCL11A.
- Heshan Peiris
- , Sangbin Park
- & Seung K. Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Intraamniotic Zika virus inoculation of pregnant rhesus macaques produces fetal neurologic disease
Intraamniotic Zika virus inoculation of pregnant rhesus macaques produces fetal neurologic disease
Zika virus infection of pregnant women can cause congenital brain defects. Here, Coffey et al. establish a pregnant rhesus macaque model, using intravenous and intraamniotic route of infection, that reliably reproduces fetal neurologic defects of congenital Zika syndrome in humans.
- Lark L. Coffey
- , Rebekah I. Keesler
- & Koen K. A. Van Rompay
-
Article
| Open Access Efficacy of a respiratory syncytial virus vaccine candidate in a maternal immunization model
Efficacy of a respiratory syncytial virus vaccine candidate in a maternal immunization model
RSV infection is a major cause of bronchiolitis in infants and maternal vaccination is a potential preventive option. Here, Blanco et al. show efficacy of a Newcastle disease virus-based virus-like particle vaccine candidate in naive and pre-exposed cotton rat dams and their offspring.
- Jorge C. G. Blanco
- , Lioubov M. Pletneva
- & Trudy G. Morrison
-
Article
| Open Access The RNA-binding protein YBX1 regulates epidermal progenitors at a posttranscriptional level
The RNA-binding protein YBX1 regulates epidermal progenitors at a posttranscriptional level
The integrity of the stratified epithelia relies on controlled cell turnover but it is unclear how mRNA binding proteins regulates this. Here, the authors show that the RNA binding protein Y-box binding protein-1 translationally represses cytokines, so preventing senescence and maintaining epidermal homeostasis.
- Eunjeong Kwon
- , Kristina Todorova
- & Anna Mandinova
-
Article
| Open Access Bioluminescence imaging of G protein-coupled receptor activation in living mice
Bioluminescence imaging of G protein-coupled receptor activation in living mice
G protein-coupled receptors are involved in numerous physiological functions, thus, they represent potential pharmaceutical targets. Here Kono et al. describe a new mouse model to image GPCR activation in real-time by exploiting firefly split luciferase fragment complementation that can be detected by bioluminescence imaging.
- Mari Kono
- , Elizabeth G. Conlon
- & Richard L. Proia
-
Article
| Open Access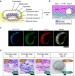 A pluripotent stem cell-based model for post-implantation human amniotic sac development
A pluripotent stem cell-based model for post-implantation human amniotic sac development
Early in human embryonic development, it is unclear how amniotic sac formation is regulated. Here, the authors use a human pluripotent stem cell-based model, termed the post-implantation amniotic sac embryoid, to recapitulate early embryogenic events of human amniotic sac development.
- Yue Shao
- , Kenichiro Taniguchi
- & Jianping Fu
-
Article
| Open Access A novel humanized mouse lacking murine P450 oxidoreductase for studying human drug metabolism
A novel humanized mouse lacking murine P450 oxidoreductase for studying human drug metabolism
Human liver chimeric mice are increasingly used for drug testing in preclinical development, but express residual murine p450 cytochromes. Here the authors generate mice lacking the Por gene in the liver, and show that human cytochrome metabolism is used following repopulation with human hepatocytes.
- Mercedes Barzi
- , Francis P. Pankowicz
- & Karl-Dimiter Bissig
-
Article
| Open Access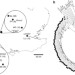 The comparative immunology of wild and laboratory mice, Mus musculus domesticus
The comparative immunology of wild and laboratory mice, Mus musculus domesticus
Laboratory mice are the cornerstone of immunology but how well they represent wild mice is not clear. Here the authors compare and contrast various immune parameters between wild-caught mice and laboratory (C57BL/6) mice and identify a previously unknown myeloid cell population specific to wild mice.
- Stephen Abolins
- , Elizabeth C. King
- & Eleanor M. Riley
-
Article
| Open Access PNPLA1 has a crucial role in skin barrier function by directing acylceramide biosynthesis
PNPLA1 has a crucial role in skin barrier function by directing acylceramide biosynthesis
Loss-of-function mutations inPNPLA1, a gene encoding an enzyme with unknown function, cause dry and scaling skin in humans. Using mouse models with PNPLA1 deficiency, the authors show that PNPLA1 participates in the biosynthesis of acylceramide, a lipid component essential for skin barrier function.
- Tetsuya Hirabayashi
- , Tatsuki Anjo
- & Makoto Murakami
-
Article
| Open Access Hyperactivation of Nrf2 in early tubular development induces nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
Hyperactivation of Nrf2 in early tubular development induces nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
Nrf2 regulates oxidative and electrophilic stress responses by modulating the expression of enzymes involved in detoxification pathways. Here Suzukiet al. show that Nrf2 activation in early tubular development promotes nephrogenic diabetes insipidus by regulating aquaporin 2 expression and trafficking and water permeability.
- Takafumi Suzuki
- , Shiori Seki
- & Masayuki Yamamoto
-
Article
| Open Access Wnt and Neuregulin1/ErbB signalling extends 3D culture of hormone responsive mammary organoids
Wnt and Neuregulin1/ErbB signalling extends 3D culture of hormone responsive mammary organoids
Three-dimensional culture systems and organoids for mammary glands are important to understand mammary gland development. Here, the authors identify conditions (including Neuregulin 1 and R-spondin 1) that allow the culture of organoids that are responsive to hormonal stimulation for up to 2.5 months.
- Thierry Jardé
- , Bethan Lloyd-Lewis
- & Trevor C. Dale
-
Article
| Open Access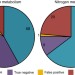 Metabolic modelling reveals the specialization of secondary replicons for niche adaptation in Sinorhizobium meliloti
Metabolic modelling reveals the specialization of secondary replicons for niche adaptation in Sinorhizobium meliloti
The genome of some bacteria consists of two or more chromosomes or replicons. Here, diCenzo et al. integrate genome-scale metabolic modelling and growth data from a collection of mutants of the plant symbiont Sinorhizobium melilotito estimate the fitness contribution of each replicon in three environments.
- George C. diCenzo
- , Alice Checcucci
- & Marco Fondi
-
Article
| Open Access A rhesus macaque model of Asian-lineage Zika virus infection
A rhesus macaque model of Asian-lineage Zika virus infection
Animal models of infection with Zika virus (ZIKV) are urgently needed for a better understanding of pathogenesis and for testing potential therapies. Here, the authors describe infection of rhesus macaques with an Asian-lineage ZIKV strain as a relevant animal model for studying ZIKV pathogenesis.
- Dawn M. Dudley
- , Matthew T. Aliota
- & David H. O’Connor
-
Article
| Open Access Antibody-based PET imaging of amyloid beta in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease
Antibody-based PET imaging of amyloid beta in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease
Imaging tools for evaluating progression of Alzheimer’s disease have been lacking. Here the authors develop a blood brain barrier-permeable Aß probe based on a radiolabelled, anti-Aß antibody, and report age-dependent brain uptake visualized in vivo with PET in mouse models of the disease.
- Dag Sehlin
- , Xiaotian T. Fang
- & Stina Syvänen
-
Article
| Open Access Complex disease and phenotype mapping in the domestic dog
Complex disease and phenotype mapping in the domestic dog
The domestic dog is an important model organism for our understanding of cancer and other diseases. Here the authors conduct a genome-wide association study across multiple breeds and identify novel loci significantly associated with several complex diseases and morphological traits.
- Jessica J. Hayward
- , Marta G. Castelhano
- & Adam R. Boyko
-
Article
| Open Access ENPP1-Fc prevents mortality and vascular calcifications in rodent model of generalized arterial calcification of infancy
ENPP1-Fc prevents mortality and vascular calcifications in rodent model of generalized arterial calcification of infancy
Generalized arterial calcification of infancy (GACI) is a terminal disease caused by the ENPP1 enzyme deficiency. Here, Albrigh et al. show that ENPP1 enzyme replacement therapy prevents the ectopic calcifications and mortality in mice with GACI, suggesting a novel treatment for vascular calcification in humans.
- Ronald A. Albright
- , Paul Stabach
- & Demetrios T. Braddock
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmodium falciparum full life cycle and Plasmodium ovale liver stages in humanized mice
Plasmodium falciparum full life cycle and Plasmodium ovale liver stages in humanized mice
Mice engrafted with human cells are useful models for research on human malaria parasites. Here the authors show that the complete life cycle of Plasmodium falciparum and the liver stages of Plasmodium ovalecan be studied in mice doubly engrafted with human primary hepatocytes and red blood cells.
- Valérie Soulard
- , Henriette Bosson-Vanga
- & Dominique Mazier

 H3K27me3-rich genomic regions can function as silencers to repress gene expression via chromatin interactions
H3K27me3-rich genomic regions can function as silencers to repress gene expression via chromatin interactions