Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access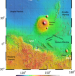 Geology of the InSight landing site on Mars
Geology of the InSight landing site on Mars
The InSight spacecraft landed on Mars on November 2018. Here, the authors characterize the surficial geology of the landing site and compare with observations and models derived from remote sensing data prior to landing and from ongoing in situ geophysical investigations of the subsurface.
- M. Golombek
- , N. H. Warner
- & W. B. Banerdt
-
Article
| Open Access Dust tides and rapid meridional motions in the Martian atmosphere during major dust storms
Dust tides and rapid meridional motions in the Martian atmosphere during major dust storms
The authors here present the diurnal tides of dust within the southern Martian atmosphere. The dust tides imply a fast meridional exchange of heat and materials on Mars and allow water content near the summer pole to be rapidly transported to the middle latitudes in the nighttime which is then lifted by daytime deep convection.
- Zhaopeng Wu
- , Tao Li
- & Jun Cui
-
Article
| Open Access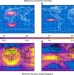 Low cost satellite constellations for nearly continuous global coverage
Low cost satellite constellations for nearly continuous global coverage
Telecommunication, navigation and remote sensing services are highly dependent on how well satellites provide global coverage. Here the authors show a pair of four-satellite low-cost longer-life constellations that provide nearly continuous global coverage to support Earth observation.
- Lake A. Singh
- , William R. Whittecar
- & Patrick M. Reed
-
Article
| Open Access Evolving parsec-scale radio structure in the most distant blazar known
Evolving parsec-scale radio structure in the most distant blazar known
High redshift blazars are efficient probes of supermassive black holes and their environment in the early Universe. Here the authors show measurements of polarised emission and proper motion in the blazar J0906+6930 (redshift of 5.47) characterised by a nascent jet embedded in and interacting with a dense medium.
- Tao An
- , Prashanth Mohan
- & Zhenya Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access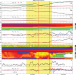 Electron Bernstein waves driven by electron crescents near the electron diffusion region
Electron Bernstein waves driven by electron crescents near the electron diffusion region
Various types of plasma waves are generated around electron diffusion regions (EDRs). Here the authors show electron Bernstein waves (EBWs), at the electron-scale boundary of the Hall current reversal near EDR, are sufficiently strong to diffuse electrons and modify electron pressure tensor.
- W. Y. Li
- , D. B. Graham
- & J. L. Burch
-
Comment
| Open Access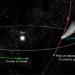 The European Space Agency’s Comet Interceptor lies in wait
The European Space Agency’s Comet Interceptor lies in wait
The European Space Agency (ESA) recently selected Comet Interceptor as its first ‘fast’ (F-class) mission. It will be developed rapidly to share a launch with another mission and is unique, as it will wait in space for a yet-to-be-discovered comet.
- Colin Snodgrass
- & Geraint H Jones
-
Article
| Open Access Minimal biomass deposition in banded iron formations inferred from organic matter and clay relationships
Minimal biomass deposition in banded iron formations inferred from organic matter and clay relationships
Banded iron formations could have formed in the early oceans due to microbial metabolism. Here Dodd and colleagues find little organic carbon in these formations, indicating microbial iron cycling was minimal and could have limited the recycling of important nutrients to overlying waters.
- Matthew S. Dodd
- , Dominic Papineau
- & Juha A. Karhu
-
Article
| Open Access Longitudinal ridges imparted by high-speed granular flow mechanisms in martian landslides
Longitudinal ridges imparted by high-speed granular flow mechanisms in martian landslides
The occurrence of longitudinal ridges on large landslide masses on planetary bodies is enabled by long runout distances, which have so far been attributed to the presence of ice. The authors here present a challenging model based on mechanical instabilities within the flow, suggesting that ice is not needed.
- Giulia Magnarini
- , Thomas M. Mitchell
- & Harrison H. Schmitt
-
Article
| Open Access Origin of two-band chorus in the radiation belt of Earth
Origin of two-band chorus in the radiation belt of Earth
Chorus waves are crucial on radiation belt dynamics in the space of magnetized planets. Here, the authors show that initially excited single-band chorus waves can quickly accelerate medium energy electrons, and divide the anisotropic electrons into low and high energy components, which subsequently excite two-band chorus waves.
- Jinxing Li
- , Jacob Bortnik
- & Daniel N. Baker
-
Article
| Open Access Nucleobase synthesis in interstellar ices
Nucleobase synthesis in interstellar ices
The formation of nucleobases can take place in extraterrestrial environments. Here the authors show the simultaneous synthesis of three purine nucleobases and three pyrimidine from interstellar ice analogues that suggest the evolution from molecular clouds to stars and planets provide suitable environment for nucleobase synthesis in space.
- Yasuhiro Oba
- , Yoshinori Takano
- & Akira Kouchi
-
Article
| Open Access Gigantic jet discharges evolve stepwise through the middle atmosphere
Gigantic jet discharges evolve stepwise through the middle atmosphere
Gigantic jets, lightning discharges originating from tropical thunderstorms that can reach the base of the ionosphere at 90 km altitude, have not been captured using high-speed video cameras before. Here, the first such images are reported, showing a step-wise evolution of gigantic jets during their rising phase.
- Oscar A. van der Velde
- , Joan Montanyà
- & Steven A. Cummer
-
Article
| Open Access Descent trajectory reconstruction and landing site positioning of Chang’E-4 on the lunar farside
Descent trajectory reconstruction and landing site positioning of Chang’E-4 on the lunar farside
The Chang’E-4 mission in January 2019 had the major challenge to land on the lunar far side without traditional radiometric techniques due to the missing line-of-sight. The authors here describe landing trajectory reconstruction and positioning techniques based upon the Moon’s digital terrain model that allowed reproducing the entire process of a successful landing.
- Jianjun Liu
- , Xin Ren
- & Weibin Wen
-
Article
| Open Access The impact origin and evolution of Chryse Planitia on Mars revealed by buried craters
The impact origin and evolution of Chryse Planitia on Mars revealed by buried craters
Due to active geological resurfacing, the record of large impact basins (e.g. in Chryse Planitia) on Mars seems to be widely absent. Based on high-quality global datasets, the authors here propose a buried impact basin, covered by up to 1 km of sediments or lava flows after its formation more than 4 billion years ago.
- Lu Pan
- , Cathy Quantin-Nataf
- & Chloé Michaut
-
Article
| Open Access Measuring the ionisation fraction in a jet from a massive protostar
Measuring the ionisation fraction in a jet from a massive protostar
The ionisation fraction of protostellar jets is key to establish their true energetics. Here, the authors determine it in a jet from a high-mass young stellar object, using multi-wavelengths observations, confirming that the ionising mechanism giving rise to the radio emission originates from shocks.
- R. Fedriani
- , A. Caratti o Garatti
- & M. Hoare
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of ubiquitous Alfvén pulses transporting energy from the photosphere to the upper chromosphere
Evidence of ubiquitous Alfvén pulses transporting energy from the photosphere to the upper chromosphere
Heating of the upper solar atmospheric layers is an open question. Here, the authors show observational evidence that ubiquitous Alfven pulses are excited by prevalent photospheric swirls, which are found to propagate upwards and carry enough energy flux needed to balance the local upper chromospheric energy loss.
- Jiajia Liu
- , Chris J. Nelson
- & Robert Erdélyi
-
Article
| Open Access Determining the rotation direction in pulsars
Determining the rotation direction in pulsars
Interstellar magnetic fields determined from pulsar polarimetry in the GHz-band may be biased by mechanical-optical rotation in pulsars’ magnetospheres. Here the authors show how observations at sub-GHz frequencies can be used to resolve such a bias and determine pulsar rotation directions.
- Renaud Gueroult
- , Yuan Shi
- & Nathaniel J. Fisch
-
Article
| Open Access Strong and selective isotope effect in the vacuum ultraviolet photodissociation branching ratios of carbon monoxide
Strong and selective isotope effect in the vacuum ultraviolet photodissociation branching ratios of carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide is the main C and O reservoir in interstellar media, where it undergoes photochemistry. The authors show that isotopic substitution affects not only its absorption. spectrum and photodissociation rates but also the branching ratio, key to understand isotopic. fractionation in the solar system
- Pan Jiang
- , Xiaoping Chi
- & Hong Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Detection of anti-correlation of hot and cold baryons in galaxy clusters
Detection of anti-correlation of hot and cold baryons in galaxy clusters
Galaxy clusters contain vast amount of dark matter and baryonic matter. Here the authors show the observational detection of the anti-correlation of gas mass and stellar mass observables in the most massive galaxy clusters, indicating such clusters retain close to the cosmic mix of baryons and dark matter.
- Arya Farahi
- , Sarah L. Mulroy
- & Nobuhiro Okabe
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for low density holes in Jupiter’s ionosphere
Evidence for low density holes in Jupiter’s ionosphere
Intense electromagnetic impulses induced by Jupiter’s lightning can produce both low-frequency dispersed whistler emissions and non-dispersed radio pulses. Here, the authors show Jupiter dispersed pulses associated with Jovian lightning that are evidence of low density holes in Jupiter’s ionosphere.
- Masafumi Imai
- , Ivana Kolmašová
- & Steven M. Levin
-
Article
| Open Access Loss-cone instability modulation due to a magnetohydrodynamic sausage mode oscillation in the solar corona
Loss-cone instability modulation due to a magnetohydrodynamic sausage mode oscillation in the solar corona
Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) waves and plasma instabilities can be studied during solar flares. Here the authors show evidence for an MHD sausage mode oscillation periodically triggering electron acceleration at a magnetic null point in the solar corona, indicating MHD oscillations in plasma can indirectly lead to loss-cone instability modulation.
- Eoin P. Carley
- , Laura A. Hayes
- & Peter T. Gallagher
-
Article
| Open Access Sublimation of terrestrial permafrost and the implications for ice-loss processes on Mars
Sublimation of terrestrial permafrost and the implications for ice-loss processes on Mars
Sublimation of ice is believed to have generated a variety of landforms on Mars and other planetary bodies. Here the authors show the first long-term in situ effective diffusion coefficient of terrestrial ice-free loess (Mars analog soil), scaled to Mars average pressure, temperature and CO2 atmosphere.
- Thomas A. Douglas
- & Michael T. Mellon
-
Article
| Open Access Fast negative breakdown in thunderstorms
Fast negative breakdown in thunderstorms
Recent studies have shown that lightning is initiated by a newly-recognized discharge process called fast positive breakdown. Here, the authors present observational evidence of fast breakdown but of negative polarity, seemingly contrary to current understanding of discharge physics.
- Julia N. Tilles
- , Ningyu Liu
- & Jennifer Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access The photospheric origin of the Yonetoku relation in gamma-ray bursts
The photospheric origin of the Yonetoku relation in gamma-ray bursts
Yonetoku relation provides a diagnostic for the radiation mechanism in the prompt phase of gamma-ray burst (GRB) emission. Here, Ito et al. show the reproduction of this relation in 3D hydrodynamical simulations followed by radiative transfer calculations, which suggest the photospheric emission is the dominant component in the prompt phase of GRBs.
- Hirotaka Ito
- , Jin Matsumoto
- & Daisuke Yonetoku
-
Article
| Open Access The operational environment and rotational acceleration of asteroid (101955) Bennu from OSIRIS-REx observations
The operational environment and rotational acceleration of asteroid (101955) Bennu from OSIRIS-REx observations
Vicinity of small bodies might be dangerous to the spacecrafts and to their instrumentation. Here the authors show the operational environment of asteroid Bennu, validate its photometric phase function and demonstrate the accelerating rotational rate due to YORP effect using the data acquired during the approach phase of OSIRIS-REx mission.
- C. W. Hergenrother
- , C. K. Maleszewski
- & B. Marty
-
Article
| Open Access Hydroxyl super rotors from vacuum ultraviolet photodissociation of water
Hydroxyl super rotors from vacuum ultraviolet photodissociation of water
Free electron lasers provide a state-of-the-art tool to investigate the photochemistry of water. Here, the authors show that highly rotationally excited hydroxyl radicals, so-called “super rotors” existing above the bond dissociation energy, are observed from the photodissociation of water, which may have implications for understanding the interstellar medium.
- Yao Chang
- , Yong Yu
- & Xueming Yang
-
Article
| Open Access MMS observations of electron scale magnetic cavity embedded in proton scale magnetic cavity
MMS observations of electron scale magnetic cavity embedded in proton scale magnetic cavity
Magnetic cavities are universal phenomena existing in cosmic plasma environments. Here Liu et al. show electron scale magnetic cavities in proton scale magnetic cavities observed by Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) spacecraft in the Earth’s magnetosheath, and depict the boundary of the electron scale magnetic cavity using particle sounding technique.
- H. Liu
- , Q.-G. Zong
- & R. Rankin
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for electron Landau damping in space plasma turbulence
Evidence for electron Landau damping in space plasma turbulence
Various physical mechanisms are proposed to explain the heating observed in turbulent astrophysical plasmas. Here, Chen et al. find a signature consistent with one of these mechanisms, electron Landau damping, by applying a field-particle correlation technique to in situ spacecraft data of turbulence in the Earth’s magnetosheath.
- C. H. K. Chen
- , K. G. Klein
- & G. G. Howes
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observations of a surface eigenmode of the dayside magnetopause
Direct observations of a surface eigenmode of the dayside magnetopause
Surface waves on the boundary between a magnetosphere and the surrounding plasma might get trapped by the ionosphere forming an eigenmode. Here, Archer et al. show direct observations of this proposed mechanism at Earth’s magnetosphere by analyzing the response to an isolated fast plasma jet detected by the THEMIS satellites.
- M. O. Archer
- , H. Hietala
- & V. Angelopoulos
-
Article
| Open Access Mercury’s anomalous magnetic field caused by a symmetry-breaking self-regulating dynamo
Mercury’s anomalous magnetic field caused by a symmetry-breaking self-regulating dynamo
A new regime of planetary magnetic fields was revealed through the MESSENGER spacecraft mission to Mercury. Here, the authors present a numerical dynamo model that can re-produce both the axisymmetric and anomalously axially offset dipolar magnetic field of Mercury.
- Futoshi Takahashi
- , Hisayoshi Shimizu
- & Hideo Tsunakawa
-
Article
| Open Access A metamaterial-enabled design enhancing decades-old short backfire antenna technology for space applications
A metamaterial-enabled design enhancing decades-old short backfire antenna technology for space applications
There is significant interest in providing real-world applications for metamaterials. Here, the authors design an Advanced Short Backfire Antenna, augmented with anisotropic metamaterial surfaces to achieve high aperture efficiency across two frequency bands, making the antenna ideal for spaceborne applications.
- J. Daniel Binion
- , Erik Lier
- & Douglas H. Werner
-
Article
| Open Access Deoxyribose and deoxysugar derivatives from photoprocessed astrophysical ice analogues and comparison to meteorites
Deoxyribose and deoxysugar derivatives from photoprocessed astrophysical ice analogues and comparison to meteorites
Sugars are known to form from the UV photoprocessing of ices under astrophysical conditions. Here, the authors report the detection of deoxyribose, the sugar of DNA, and other deoxysugars from the UV photoprocessing of H2O:CH3OH ice mixtures, which are compared with materials from carbonaceous meteorites.
- Michel Nuevo
- , George Cooper
- & Scott A. Sandford
-
Article
| Open Access Prediction of the strength and timing of sunspot cycle 25 reveal decadal-scale space environmental conditions
Prediction of the strength and timing of sunspot cycle 25 reveal decadal-scale space environmental conditions
The Sun’s activity cycle impacts space-reliant technologies and the Earth’s climate, but predicting this is challenging. An ensemble forecast based on an innovative combination of two solar magnetic field evolution models indicates a weak, but not insignificant sunspot cycle 25 peaking in 2024.
- Prantika Bhowmik
- & Dibyendu Nandy
-
Article
| Open Access H2 roaming chemistry and the formation of H3+ from organic molecules in strong laser fields
H2 roaming chemistry and the formation of H3+ from organic molecules in strong laser fields
H2 roaming is associated with H3+ formation when certain organic molecules are exposed to strong laser fields. Here, the mechanistic details and time-resolved dynamics of H3+ formation from a series of alcohols were obtained and found that the product yield decreases as the carbon chain length increases.
- Nagitha Ekanayake
- , Travis Severt
- & Marcos Dantus
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic reconnection driven by electron dynamics
Magnetic reconnection driven by electron dynamics
Magnetic reconnection is the process of releasing energy by magnetized and space plasma. Here the authors report experimental observation of magnetic reconnection in laser-produced plasma and the role of electron scaling on reconnection.
- Y. Kuramitsu
- , T. Moritaka
- & M. Hoshino
-
Article
| Open Access Formation of electron radiation belts at Saturn by Z-mode wave acceleration
Formation of electron radiation belts at Saturn by Z-mode wave acceleration
Radial diffusion is the only mechanism considered to accelerate trapped electrons to relativistic energies in Saturn’s magnetic field, forming radiation belts. Here the authors show another mechanism, electron acceleration via Doppler shifted cyclotron resonant interaction with Z-mode waves, which can form radiation belts inside the orbit of Enceladus.
- E. E. Woodfield
- , R. B. Horne
- & W. S. Kurth
-
Article
| Open Access Martian magmatism from plume metasomatized mantle
Martian magmatism from plume metasomatized mantle
A unified model for the formation of martian rock types is required to understand Mars’s formation and evolution. Here the authors show that nakhlite and chassignite meteorites originate from melting of metasomatized depleted mantle lithosphere, whereas shergottite melts originate from deep plume sources.
- James M. D. Day
- , Kimberly T. Tait
- & Clive R. Neal
-
Article
| Open Access Unveiling a magnetized jet from a low-mass protostar
Unveiling a magnetized jet from a low-mass protostar
The presence of magnetic fields in protostellar jets has been predicted theoretically, but its experimental confirmation has been elusive so far. Here, the authors report the detection of SiO line polarisation in the HH 211 protostellar jet, indicative of the onset of magnetic fields.
- Chin-Fei Lee
- , Hsiang-Chih Hwang
- & Paul. T. P Ho
-
Article
| Open Access A 34.5 day quasi-periodic oscillation in γ-ray emission from the blazar PKS 2247–131
A 34.5 day quasi-periodic oscillation in γ-ray emission from the blazar PKS 2247–131
PKS 2247–131 is an active galaxy that has been emitting gamma-ray flares since October 2016. Here, the authors used data obtained with the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope to find that PKS 2247–131 presents a relatively short, month-like flux oscillation at gamma-ray energies of 0.1–300 GeV.
- Jianeng Zhou
- , Zhongxiang Wang
- & Jujia Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access A luminous blue kilonova and an off-axis jet from a compact binary merger at z = 0.1341
A luminous blue kilonova and an off-axis jet from a compact binary merger at z = 0.1341
A faint gamma-ray burst (GRB 170817A) has been recently detected in coincidence with the gravitational wave (GW) event GW 170817. Here, the authors report that another faint short GRB at a cosmological distance (GRB150101B) and its late time emission are analogous to the neutron star merger event GRB 170817A.
- E. Troja
- , G. Ryan
- & S. Veilleux
-
Article
| Open Access Electrical conductivity and magnetic dynamos in magma oceans of Super-Earths
Electrical conductivity and magnetic dynamos in magma oceans of Super-Earths
With the discovery of large rocky exoplanets called Super-Earths, questions have arisen regarding the properties of their interiors and their ability to produce a magnetic field. Here, the authors show that under high pressure, molten silicates are semi-metallic and that magma oceans would host a dynamo process.
- François Soubiran
- & Burkhard Militzer
-
Article
| Open Access Strongly lensed repeating fast radio bursts as precision probes of the universe
Strongly lensed repeating fast radio bursts as precision probes of the universe
Fast radio bursts (FRBs) are likely to be gravitationally lensed by intervening galaxies. Here, the authors propose to make accurate measurements of time delays between images of lensed FRBs as a powerful probe for precision cosmology.
- Zheng-Xiang Li
- , He Gao
- & Bing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Sounding-rocket microgravity experiments on alumina dust
Sounding-rocket microgravity experiments on alumina dust
Alumina is thought to be the main condensate to form in the gas outflow from oxygen-rich evolved stars. Here, the authors perform a condensation experiment with alumina in a low-gravity environment, and find spectroscopic evidence for a sharp feature at a wavelength of 13.55 μm.
- Shinnosuke Ishizuka
- , Yuki Kimura
- & Yuko Inatomi
-
Article
| Open Access Less absorbed solar energy and more internal heat for Jupiter
Less absorbed solar energy and more internal heat for Jupiter
Radiant energy budgets and internal heat play a key role in the evolution of planets. Here, the authors analyze data from the Cassini mission to show that Jupiter’s radiant energy and internal heat budgets are significantly larger than previous estimates.
- Liming Li
- , X. Jiang
- & R. W. Schmude Jr.
-
Article
| Open Access A hexagon in Saturn’s northern stratosphere surrounding the emerging summertime polar vortex
A hexagon in Saturn’s northern stratosphere surrounding the emerging summertime polar vortex
The Cassini spacecraft has provided an unprecedented characterisation of seasonal changes on Saturn. Here the authors describe the development of a warm polar vortex in Saturn’s northern summer, and show that the hexagon extends hundreds of kilometres from the troposphere into the stratosphere.
- L. N. Fletcher
- , G. S. Orton
- & S. B. Calcutt
-
Article
| Open Access Solar superstorm of AD 774 recorded subannually by Arctic tree rings
Solar superstorm of AD 774 recorded subannually by Arctic tree rings
Tree rings retain information of sudden variations of ancient radiocarbon (14C) content, however the origin and exact timing of these events often remain uncertain. Here, the authors analyze a set of Arctic tree rings and link a rapid increase in 14C to a solar event that occurred during the spring of AD 774.
- J. Uusitalo
- , L. Arppe
- & M. Oinonen
-
Article
| Open Access Strong whistler mode waves observed in the vicinity of Jupiter’s moons
Strong whistler mode waves observed in the vicinity of Jupiter’s moons
Observations of Jupiter’s magnetosphere provide opportunities to understand how magnetic fields interact with particles. Here, the authors report that the chorus wave power is increased in the vicinity of Europa and Ganymede. The generated waves are able to accelerate particles to very high energy.
- Y. Y. Shprits
- , J. D. Menietti
- & D. A. Gurnett
-
Article
| Open Access The Medusae Fossae Formation as the single largest source of dust on Mars
The Medusae Fossae Formation as the single largest source of dust on Mars
Martian dust is globally enriched in S and Cl and has a distinct mean S:Cl ratio. Here the authors identify that the largest potential source region for Martian dust based on analysis of elemental abundance data may be the Medusae Fossae Formation.
- Lujendra Ojha
- , Kevin Lewis
- & Mariek Schmidt
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of nuclear quantum effects and hydrogen bond symmetrisation in high pressure ice
Observation of nuclear quantum effects and hydrogen bond symmetrisation in high pressure ice
Hydrogen atoms in water ices, under pressures at which they might exist in ocean exoplanets and icy moons, exhibit dynamics that are still poorly understood. Here, 1H-NMR experiments approaching the Mbar range shed light on the symmetrisation of hydrogen bonds preceding and accompanying the transformation of ice VII into ice X.
- Thomas Meier
- , Sylvain Petitgirard
- & Leonid Dubrovinsky
-
Correspondence
| Open Access On the origin of molecular oxygen in cometary comae
On the origin of molecular oxygen in cometary comae
- K. L. Heritier
- , K. Altwegg
- & E Vigren

 Iron whiskers on asteroid Itokawa indicate sulfide destruction by space weathering
Iron whiskers on asteroid Itokawa indicate sulfide destruction by space weathering