Abstract
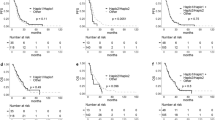
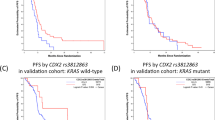
In the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathway, polymorphisms in EGFR and its ligand EGF have been studied as biomarkers for anti-EGFR treatment. However, the potential pharmacogenetic role of other EGFR ligands such as amphiregulin (AREG) and epiregulin (EREG) has not been elucidated. We studied 74 KRAS and BRAF wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with anti-EGFR plus irinotecan. Twenty-two genetic variants in EGFR, EGF, AREG and EREG genes were selected using HapMap database and literature resources. Three tagging single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the AREG gene region (rs11942466 C>A, rs13104811 A>G, and rs9996584 C>T) predicted disease control in the multivariate analyses. AREG rs11942466 C>A and rs9996584 C>T were also associated with overall survival (OS). The functional polymorphism, EGFR rs712829 G>T, was associated with progression-free and OS. Our findings support that intergenic polymorphisms in the AREG gene region might help to identify colorectal cancer patients that will benefit from irinotecan plus anti-EGFR therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, Khayat D, Bleiberg H, Santoro A et al. Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 337–345.
Saltz LB, Meropol NJ, Loehrer PJS, Needle MN, Kopit J, Mayer RJ . Phase II trial of cetuximab in patients with refractory colorectal cancer that expresses the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 1201–1208.
Van Cutsem E, Kohne CH, Hitre E, Zaluski J, Chang Chien CR, Makhson A et al. Cetuximab and chemotherapy as initial treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2009; 360: 1408–1417.
Douillard JY, Siena S, Cassidy J, Tabernero J, Burkes R, Barugel M et al. Randomized phase III trial of panitumumab with infusional fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX4) versus FOLFOX4 alone as first-line treatment in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer: the PRIME study. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 4697–4705.
Lenz HJ . Anti-EGFR mechanism of action: antitumor effect and underlying cause of adverse events. Oncology (Williston Park) 2006; 20: 5–13.
Brand TM, Iida M, Li C, Wheeler DL . The nuclear epidermal growth factor receptor signaling network and its role in cancer. Discov Med 2011; 12: 419–432.
Amado RG, Wolf M, Peeters M, Van Cutsem E, Siena S, Freeman DJ et al. Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2007; 26: 1626–1634.
De Roock W, Claes B, Bernasconi D, De Schutter J, Biesmans B, Fountzilas G et al. Effects of KRAS, BRAF, NRAS, and PIK3CA mutations on the efficacy of cetuximab plus chemotherapy in chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer: a retrospective consortium analysis. Lancet Oncol 2010; 11: 753–762.
Liu W, Innocenti F, Wu MH, Desai AA, Dolan ME, Cook EH Jr et al. A functional common polymorphism in a Sp1 recognition site of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene promoter. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 46–53.
Moriai T, Kobrin MS, Hope C, Speck L, Korc M . A variant epidermal growth factor receptor exhibits altered type alpha transforming growth factor binding and transmembrane signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 10217–10221.
Hsieh YY, Tzeng CH, Chen MH, Chen PM, Wang WS . Epidermal growth factor receptor R521K polymorphism shows favorable outcomes in KRAS wild-type colorectal cancer patients treated with cetuximab-based chemotherapy. Cancer Sci 2012; 103: 791–796.
Gebhardt F, Zanker KS, Brandt B . Modulation of epidermal growth factor receptor gene transcription by a polymorphic dinucleotide repeat in intron 1. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 13176–13180.
Shahbazi M, Pravica V, Nasreen N, Fakhoury H, Fryer AA, Strange RC et al. Association between functional polymorphism in EGF gene and malignant melanoma. Lancet 2002; 359: 397–401.
Graziano F, Ruzzo A, Loupakis F, Canestrari E, Santini D, Catalano V et al. Pharmacogenetic profiling for cetuximab plus irinotecan therapy in patients with refractory advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 1427–1434.
Hu-Lieskovan S, Vallbohmer D, Zhang W, Yang D, Pohl A, Labonte MJ et al. EGF61 polymorphism predicts complete pathologic response to cetuximab-based chemoradiation independent of KRAS status in locally advanced rectal cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 5161–5169.
Yarden Y, Pines G . The ERBB network: at last, cancer therapy meets systems biology. Nat Rev Cancer 2012; 12: 553–563.
Jacobs B, De Roock W, Piessevaux H, Van Oirbeek R, Biesmans B, De Schutter J et al. Amphiregulin and epiregulin mRNA expression in primary tumors predicts outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 5068–5074.
Ohchi T, Akagi Y, Kinugasa T, Kakuma T, Kawahara A, Sasatomi T et al. Amphiregulin is a prognostic factor in colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res 2012; 32: 2315–2321.
Oliveras-Ferraros C, Massaguer Vall-Llovera A, Vazquez-Martin A, Salip DC, Queralt B et al. Transcriptional upregulation of HER2 expression in the absence of HER2 gene amplification results in cetuximab resistance that is reversed by trastuzumab treatment. Oncol Rep 2012; 27: 1887–1892.
Kohne CH, Cunningham D, Di Costanzo F, Glimelius B, Blijham G, Aranda E et al. Clinical determinants of survival in patients with 5-fluorouracil-based treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: results of a multivariate analysis of 3825 patients. Ann Oncol 2002; 13: 308–317.
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 2009; 45: 228–247.
Akaike H . A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Automat Contr 1974; AC-19: 716–723.
Lurje G, Nagashima F, Zhang W, Yang D, Chang HM, Gordon MA et al. Polymorphisms in cyclooxygenase-2 and epidermal growth factor receptor are associated with progression-free survival independent of K-ras in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with single-agent cetuximab. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 7884–7895.
Garm Spindler KL, Pallisgaard N, Rasmussen AA, Lindebjerg J, Andersen RF, Cruger D et al. The importance of KRAS mutations and EGF61A>G polymorphism to the effect of cetuximab and irinotecan in metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol 2009; 20: 879–884.
Dahan L, Norguet E, Etienne-Grimaldi MC, Formento JL, Gasmi M, Nanni I et al. Pharmacogenetic profiling and cetuximab outcome in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2011; 11: 496.
Khambata-Ford S, Garrett CR, Meropol NJ, Basik M, Harbison CT, Wu S et al. Expression of epiregulin and amphiregulin and K-ras mutation status predict disease control in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with cetuximab. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 3230–3237.
Saridaki Z, Tzardi M, Papadaki C, Sfakianaki M, Pega F, Kalikaki A et al. Impact of KRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA mutations, PTEN, AREG, EREG expression and skin rash in >/=2 line cetuximab-based therapy of colorectal cancer patients. PLoS One 2011; 6: e15980.
The ENCODE project consortium. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 2012; 489: 57–74.
Matys V, Kel-Margoulis OV, Fricke E, Liebich I, Land S, Barre-Dirrie A et al. TRANSFAC® and its module TRANSCompel®: transcriptional gene regulation in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res 2006; 34 (Database issue): D108–D110.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (FIS/1101711, CM11/00102 to Ana Sebio). We thank Carolyn Newey for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the The Pharmacogenomics Journal website
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sebio, A., Páez, D., Salazar, J. et al. Intergenic polymorphisms in the amphiregulin gene region as biomarkers in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with anti-EGFR plus irinotecan. Pharmacogenomics J 14, 256–262 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2013.29
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2013.29
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The role of amphiregulin in ovarian function and disease
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)
-
The Roles of Common Variation and Somatic Mutation in Cancer Pharmacogenomics
Oncology and Therapy (2019)
-
Potential biomarkers for anti-EGFR therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer
Tumor Biology (2016)
-
A novel UGT1 marker associated with better tolerance against irinotecan-induced severe neutropenia in metastatic colorectal cancer patients
The Pharmacogenomics Journal (2015)