Abstract
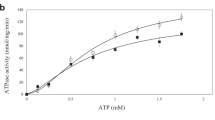
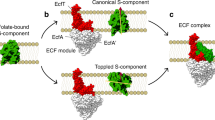
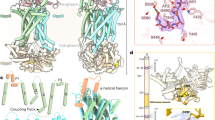
ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters, composed of importers and exporters, form one of the biggest protein superfamilies that transport a variety of substrates across the membrane, powered by ATP hydrolysis. Most ABC transporters are composed of two transmembrane domains and two cytoplasmic nucleotide-binding domains. Also, importers from prokaryotes usually have extra solute-binding proteins in the periplasm that are responsible for the binding of substrates1,2. Structures of importers have been reported that suggested a two-state model for the transport mechanism3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11. Energy-coupling factor (ECF) transporters belong to a new class of ATP-binding cassette importers. Each ECF transporter comprises an energy-coupling module consisting of a transmembrane T protein (EcfT), two nucleotide-binding proteins (EcfA and EcfA′), and another transmembrane substrate-specific binding S protein12,13,14 (EcfS). Despite the similarities with ABC transporters, ECF transporters have different organizational and functional properties. The lack of solute-binding proteins in ECF transporters differentiates them clearly from the canonical ABC importers15. Previously reported structures of the EcfS proteins RibU and ThiT clearly demonstrated the binding site of substrate riboflavin and thiamine, respectively16,17. However, the organization of the four different components and the transport mechanism of ECF transporters remain unknown. Here we present the structure of an intact folate ECF transporter from Lactobacillus brevis at a resolution of 3 Å. This structure was captured in an inward-facing, nucleotide-free conformation with no bound substrate. The folate-binding protein FolT is nearly parallel to the membrane and is bound almost entirely by EcfT, which adopts an L shape and connects to EcfA and EcfA′ through two coupling helices. Two conserved XRX motifs from the coupling helices of EcfT have a vital role in energy coupling by docking into EcfA–EcfA′. We propose a transport model that involves a substantial conformational change of FolT.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Higgins, C. F. ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 8, 67–113 (1992)
Rees, D. C. & Johnson, E. &. Lewinson, O. ABC transporters: the power to change. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 218–227 (2009)
Locher, K. P., Lee, A. T. & Rees, D. C. The E. coli BtuCD structure: a framework for ABC transporter architecture and mechanism. Science 296, 1091–1098 (2002)
Hvorup, R. N. et al. Asymmetry in the structure of the ABC transporter-binding protein complex BtuCD-BtuF. Science 317, 1387–1390 (2007)
Hollenstein, K., Frei, D. C. & Locher, K. P. Structure of an ABC transporter in complex with its binding protein. Nature 446, 213–216 (2007)
Oldham, M. L., Khare, D., Quiocho, F. A., Davidson, A. L. & Chen, J. Crystal structure of a catalytic intermediate of the maltose transporter. Nature 450, 515–521 (2007)
Oldham, M. L. &. Chen, J. Crystal structure of the maltose transporter in a pretranslocation intermediate state. Science 332, 1202–1205 (2011)
Khare, D. Oldham, M. L., Orelle, C., Davidson, A. L. & Chen, J. Alternating access in maltose transporter mediated by rigid-body rotations. Mol. Cell 33, 528–536 (2009)
Oldham, M. L. Davidson, A. L. & Chen, J. Structural insights into ABC transporter mechanism. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 18, 726–733 (2008)
Kadaba, N. S., Kaiser, J. T., Johnson, E., Lee, A. & Rees, D. C. The high-affinity E. coli methionine ABC transporter: structure and allosteric regulation. Science 321, 250–253 (2008)
Gerber, S., Comellas-Bigler, M., Goetz, B. A. & Locher, K. P. Structural basis of trans-inhibition in a molybdate/tungstate ABC transporter. Science 321, 246–250 (2008)
Rodionov, D. A. et al. A novel class of modular transporters for vitamins in prokaryotes. J. Bacteriol. 191, 42–51 (2009)
ter Beek, J., Duurkens, R. H., Erkens, G. B. & Slotboom, D. J. Quaternary structure and functional unit of energy coupling factor (ECF)-type transporters. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 5471–5475 (2011)
Erkens, G. B., Majsnerowska, M., Ter Beek, J. & Slotboom, D. J. Energy coupling factor-type ABC transporters for vitamin uptake in prokaryotes. Biochemistry 51, 4390–4396 (2012)
Eitinger, T., Rodionov, D. A., Grote, M. & Schneider, E. Canonical and ECF-type ATP-binding cassette importers in prokaryotes: diversity in modular organization and cellular functions. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 35, 3–67 (2011)
Zhang, P., Wang, J. & Shi, Y. Structure and mechanism of the S component of a bacterial ECF transporter. Nature 468, 717–720 (2010)
Erkens, G. B. et al. The structural basis of modularity in ECF-type ABC transporters. Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 18, 755–760 (2011)
Neubauer, O. et al. Two essential arginine residues in the T components of energy-coupling factor transporters. J. Bacteriol. 191, 6482–6488 (2009)
Hebbeln, P., Rodionov, D. A., Alfandega, A. & Eitinger, T. Biotin uptake in prokaryotes by solute transporters with an optional ATP-binding cassette-containing module. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 2909–2914 (2007)
Duurkens, R. H., Tol, M. B., Geertsma, E. R., Permentier, H. P. & Slotboom, D. J. Flavin binding to the high affinity riboflavin transporter RibU. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 10380–10386 (2007)
Berntsson, R. P. et al. Structural divergence of paralogous S components from ECF-type ABC transporters. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 109, 13990–13995 (2012)
Eudes, A. et al. Identification of genes encoding the folate- and thiamine-binding membrane proteins in Firmicutes. J. Bacteriol. 190, 7591–7594 (2008)
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol. A 276, 307–326 (1997)
Sheldrick, G. M. Experimental phasing with SHELXC/D/E: combining chain tracing with density modification. Acta Crystallogr. D 66, 479–485 (2010)
Adams, P. D. et al. PHENIX: building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D 58, 1948–1954 (2002)
Emsley, P. & Cowtan, K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D 60, 2126–2132 (2004)
Geertsma, E. R. Nik Mahmood, N. A., Schuurman-Wolters, G. K. & Poolman, B. Membrane reconstitution of ABC transporters and assays of translocator function. Nature Protocols 3, 256–266 (2008)
Acknowledgements
We thank X. Chen and G. Zhao for reading the manuscript and the staff members of Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility for technical assistance in data collection. This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2013CB127000), the Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (2012OHTP, 2009CSP001, 2011KIP101, KSCX2-EW-J-12) and the Shanghai ‘Pujiang Talent’ programme (11PJ1411300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P.Z. initiated the project and designed the experiments; K.X., M.Z., Q.Z., F.Y., H.G. and P.Z. performed the bulk of the experiments; C.W. and F.H. contributed to some experiments and discussions; K.X., M.Z., Q.Z., F.Y. and J.D. contributed to data analysis and manuscript preparation; P.Z. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Table 1 and Supplementary Figures 1-11. (PDF 1428 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, K., Zhang, M., Zhao, Q. et al. Crystal structure of a folate energy-coupling factor transporter from Lactobacillus brevis . Nature 497, 268–271 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12046
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12046
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.