Abstract
Arising from: M. Sadqi, D. Fushman & V. Muñoz Nature 442, 317–321 (2006)10.1038/nature04859; M. Sadqi et al. reply
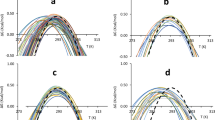
There is controversy as to whether homologues from the peripheral subunit binding domain family of small proteins fold 'downhill' (that is, non-cooperatively, in the absence of free-energy barriers between conformations) and whether they modulate their size for biological function. Sadqi et al.1 claim that Naf-BBL — a naphthylalanine-labelled, truncated version of this domain — folds in this way, on the grounds that they recorded a wide spread of melting temperatures of individual atoms measured by proton nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) during their thermal denaturation. But their data are not of adequate quality to distinguish, within experimental error, between downhill folding and folding with a cooperative transition. Accordingly, their results offer no compelling evidence that Naf-BBL folds downhill, particularly as non-truncated, unmodified peripheral subunit binding domains seem to fold cooperatively2,3.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sadqi, M., Fushman, D. & Muñoz, V. Nature 442, 317–321 (2006).
Ferguson, N., Schartau, P. J., Sharpe, T. D., Sato, S. & Fersht, A. R. J. Mol. Biol. 344, 295–301 (2004).
Ferguson, N. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 353, 427–446 (2005).
Religa, T. L., Markson, J. S., Mayor, U., Freund, S. M. V. & Fersht, A. R. Nature 437, 1053–1056 (2005).
Nicholson, E. M. & Scholtz, J. M. Biochemistry 35, 11369–11378 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferguson, N., Sharpe, T., Johnson, C. et al. Analysis of 'downhill' protein folding. Nature 445, E14–E15 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05643
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05643
This article is cited by
-
The hepatitis B virus preS1 domain hijacks host trafficking proteins by motif mimicry
Nature Chemical Biology (2013)
-
An expanding arsenal of experimental methods yields an explosion of insights into protein folding mechanisms
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2009)
-
Mechanisms of protein folding
European Biophysics Journal (2008)
-
Analysis of 'downhill' protein folding; Analysis of protein-folding cooperativity (Reply)
Nature (2007)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.