Abstract
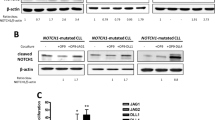
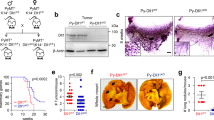
Even if NOTCH1 is commonly mutated in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), its functional impact in the disease remains unclear. Using CRISPR/Cas9-generated Mec-1 cell line models, we show that NOTCH1 regulates growth and homing of CLL cells by dictating expression levels of the tumor suppressor gene DUSP22. Specifically, NOTCH1 affects the methylation of DUSP22 promoter by modulating a nuclear complex, which tunes the activity of DNA methyltransferase 3A (DNMT3A). These effects are enhanced by PEST-domain mutations, which stabilize the molecule and prolong signaling. CLL patients with a NOTCH1-mutated clone showed low levels of DUSP22 and active chemotaxis to CCL19. Lastly, in xenograft models, NOTCH1-mutated cells displayed a unique homing behavior, localizing preferentially to the spleen and brain. These findings connect NOTCH1, DUSP22, and CCL19-driven chemotaxis within a single functional network, suggesting that modulation of the homing process may provide a relevant contribution to the unfavorable prognosis associated with NOTCH1 mutations in CLL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Villamor N, Conde L, Martinez-Trillos A, Cazorla M, Navarro A, Bea S et al. NOTCH1 mutations identify a genetic subgroup of chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients with high risk of transformation and poor outcome. Leukemia 2013; 27: 1100–1106.
Puente XS, Pinyol M, Quesada V, Conde L, Ordonez GR, Villamor N et al. Whole-genome sequencing identifies recurrent mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nature 2011; 475: 101–105.
Fabbri G, Khiabanian H, Holmes AB, Wang J, Messina M, Mullighan CG et al. Genetic lesions associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia transformation to Richter syndrome. J Exp Med 2013; 210: 2273–2288.
Landau DA, Tausch E, Taylor-Weiner AN, Stewart C, Reiter JG, Bahlo J et al. Mutations driving CLL and their evolution in progression and relapse. Nature 2015; 526: 525–530.
Rossi D, Rasi S, Spina V, Bruscaggin A, Monti S, Ciardullo C et al. Integrated mutational and cytogenetic analysis identifies new prognostic subgroups in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2013; 121: 1403–1412.
Fabbri G, Rasi S, Rossi D, Trifonov V, Khiabanian H, Ma J et al. Analysis of the chronic lymphocytic leukemia coding genome: role of NOTCH1 mutational activation. J Exp Med 2011; 208: 1389–1401.
Del Giudice I, Rossi D, Chiaretti S, Marinelli M, Tavolaro S, Gabrielli S et al. NOTCH1 mutations in +12 chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) confer an unfavorable prognosis, induce a distinctive transcriptional profiling and refine the intermediate prognosis of +12 CLL. Haematologica 2012; 97: 437–441.
Weissmann S, Roller A, Jeromin S, Hernandez M, Abaigar M, Hernandez-Rivas JM et al. Prognostic impact and landscape of NOTCH1 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): a study on 852 patients. Leukemia 2013; 27: 2393–2396.
Baliakas P, Hadzidimitriou A, Sutton LA, Rossi D, Minga E, Villamor N et al. Recurrent mutations refine prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2015; 29: 329–336.
Rossi D, Gaidano G . Richter syndrome: pathogenesis and management. Semin Oncol 2016; 43: 311–319.
Sutton LA, Rosenquist R . Deciphering the molecular landscape in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: time frame of disease evolution. Haematologica 2015; 100: 7–16.
Morabito F, Mosca L, Cutrona G, Agnelli L, Tuana G, Ferracin M et al. Clinical monoclonal B lymphocytosis versus Rai 0 chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a comparison of cellular, cytogenetic, molecular, and clinical features. Clinical Cancer Res 2013; 19: 5890–5900.
Ojha J, Secreto C, Rabe K, Ayres-Silva J, Tschumper R, Dyke DV et al. Monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis is characterized by mutations in CLL putative driver genes and clonal heterogeneity many years before disease progression. Leukemia 2014; 28: 2395–2398.
Arruga F, Gizdic B, Serra S, Vaisitti T, Ciardullo C, Coscia M et al. Functional impact of NOTCH1 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2014; 28: 1060–1070.
Rosati E, Sabatini R, Rampino G, Tabilio A, Di Ianni M, Fettucciari K et al. Constitutively activated Notch signaling is involved in survival and apoptosis resistance of B-CLL cells. Blood 2009; 113: 856–865.
Secchiero P, Melloni E, di Iasio MG, Tiribelli M, Rimondi E, Corallini F et al. Nutlin-3 up-regulates the expression of Notch1 in both myeloid and lymphoid leukemic cells, as part of a negative feedback antiapoptotic mechanism. Blood 2009; 113: 4300–4308.
Ntziachristos P, Lim JS, Sage J, Aifantis I . From fly wings to targeted cancer therapies: a centennial for notch signaling. Cancer Cell 2014; 25: 318–334.
Guruharsha KG, Kankel MW, Artavanis-Tsakonas S . The Notch signalling system: recent insights into the complexity of a conserved pathway. Nat Rev Genet 2012; 13: 654–666.
Pozzo F, Bittolo T, Arruga F, Bulian P, Macor P, Tissino E et al. NOTCH1 mutations associate with low CD20 level in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: evidence for a NOTCH1 mutation-driven epigenetic dysregulation. Leukemia 2016; 30: 182–189.
Vaisitti T, Audrito V, Serra S, Buonincontri R, Sociali G, Mannino E et al. The enzymatic activities of CD38 enhance CLL growth and trafficking: implications for therapeutic targeting. Leukemia 2015; 29: 356–368.
Malet-Engra G, Viaud J, Ysebaert L, Farce M, Lafouresse F, Laurent G et al. CIP4 controls CCL19-driven cell steering and chemotaxis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Res 2013; 73: 3412–3424.
Cuesta-Mateos C, Lopez-Giral S, Alfonso-Perez M, de Soria VG, Loscertales J, Guasch-Vidal S et al. Analysis of migratory and prosurvival pathways induced by the homeostatic chemokines CCL19 and CCL21 in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Exp Hematol 2010; 38: 756–764, 764e1-4.
Forster R, Schubel A, Breitfeld D, Kremmer E, Renner-Muller I, Wolf E et al. CCR7 coordinates the primary immune response by establishing functional microenvironments in secondary lymphoid organs. Cell 1999; 99: 23–33.
Jiang K, Krous LC, Knowlton N, Chen Y, Frank MB, Cadwell C et al. Ablation of Stat3 by siRNA alters gene expression profiles in JEG-3 cells: a systems biology approach. Placenta 2009; 30: 806–815.
Sekine Y, Ikeda O, Hayakawa Y, Tsuji S, Imoto S, Aoki N et al. DUSP22/LMW-DSP2 regulates estrogen receptor-alpha-mediated signaling through dephosphorylation of Ser-118. Oncogene 2007; 26: 6038–6049.
Sekine Y, Tsuji S, Ikeda O, Sato N, Aoki N, Aoyama K et al. Regulation of STAT3-mediated signaling by LMW-DSP2. Oncogene 2006; 25: 5801–5806.
Sanchez-Mut JV, Aso E, Heyn H, Matsuda T, Bock C, Ferrer I et al. Promoter hypermethylation of the phosphatase DUSP22 mediates PKA-dependent TAU phosphorylation and CREB activation in Alzheimer's disease. Hippocampus 2014; 24: 363–368.
Oka M, Meacham AM, Hamazaki T, Rodic N, Chang LJ, Terada N . De novo DNA methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b primarily mediate the cytotoxic effect of 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine. Oncogene 2005; 24: 3091–3099.
Yang L, Rau R, Goodell MA . DNMT3A in haematological malignancies. Nat Rev Cancer 2015; 15: 152–165.
Liu D, Zhou P, Zhang L, Gong W, Huang G, Zheng Y et al. HDAC1/DNMT3A-containing complex is associated with suppression of Oct4 in cervical cancer cells. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2012; 77: 934–940.
Khan DH, He S, Yu J, Winter S, Cao W, Seiser C et al. Protein kinase CK2 regulates the dimerization of histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) and HDAC2 during mitosis. J Biol Chem 2013; 288: 16518–16528.
Jantus Lewintre E, Reinoso Martin C, Montaner D, Marin M, Jose Terol M, Farras R et al. Analysis of chronic lymphotic leukemia transcriptomic profile: differences between molecular subgroups. Leuk Lymphoma 2009; 50: 68–79.
Nadeu F, Delgado J, Royo C, Baumann T, Stankovic T, Pinyol M et al. Clinical impact of clonal and subclonal TP53, SF3B1, BIRC3, NOTCH1, and ATM mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2016; 127: 2122–2130.
Schmitt TM, Zuniga-Pflucker JC . Induction of T cell development from hematopoietic progenitor cells by delta-like-1 in vitro. Immunity 2002; 17: 749–756.
Buonamici S, Trimarchi T, Ruocco MG, Reavie L, Cathelin S, Mar BG et al. CCR7 signalling as an essential regulator of CNS infiltration in T-cell leukaemia. Nature 2009; 459: 1000–1004.
Jung YW, Kim HG, Perry CJ, Kaech SM . CCR7 expression alters memory CD8 T-cell homeostasis by regulating occupancy in IL-7- and IL-15-dependent niches. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2016; 113: 8278–8283.
Li JP, Fu YN, Chen YR, Tan TH . JNK pathway-associated phosphatase dephosphorylates focal adhesion kinase and suppresses cell migration. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 5472–5478.
Yu D, Li Z, Gan M, Zhang H, Yin X, Tang S et al. Decreased expression of dual specificity phosphatase 22 in colorectal cancer and its potential prognostic relevance for stage IV CRC patients. Tumour Biol 2015; 36: 8531–8535.
Strati P, Uhm JH, Kaufmann TJ, Nabhan C, Parikh SA, Hanson CA et al. Prevalence and characteristics of central nervous system involvement by chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2016; 101: 458–465.
Acknowledgements
Supported by the Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro AIRC (IG-17314 to SD, IG-15217 to SO and 5x1000 #100007 to GG), by the Human Genetics Foundation Institutional funds, by the Italian Ministries of Education, University and Research (Futuro in Ricerca 2012 # RBFR12D1CB), the Italian Ministry of Health (Bando Giovani Ricercatori GR-2011-02346826 and Bando Ricerca Finalizzata RF-2011-02349712), the Fondazione Cariplo, grant #2012-0689 and local university funds (ex-60%).
Author contributions
FA: designed the study, performed experiments, analyzed and interpreted data and together with SD wrote the paper; BG, CB, SC, RB, SS, TV, KG, NV, GGar, EM, FD and FN performed experiments; MC, JA, RRF, DR and GGai: provided patient samples and relevant clinical information and contributed to data interpretation; RP and SO: discussed results and contributed to data interpretation; SD: designed the study, interpreted data and together with FA wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arruga, F., Gizdic, B., Bologna, C. et al. Mutations in NOTCH1 PEST domain orchestrate CCL19-driven homing of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells by modulating the tumor suppressor gene DUSP22. Leukemia 31, 1882–1893 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2016.383
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2016.383
This article is cited by
-
Genomic landscape of mature B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas — an appraisal from lymphomagenesis to drug resistance
Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute (2022)
-
PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway alters sensitivity of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia to l-asparaginase
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Hepatocyte phosphatase DUSP22 mitigates NASH-HCC progression by targeting FAK
Nature Communications (2022)
-
High-resolution Melting Analysis for NOTCH1 c.7541-7542delCT Mutation in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Prognostic Significance in Egyptian Patients
Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion (2022)
-
Viral transduction of primary human lymphoma B cells reveals mechanisms of NOTCH-mediated immune escape
Nature Communications (2022)