Abstract
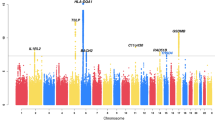
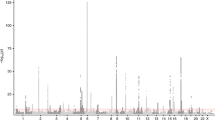
Intermediary quantitative traits are a possible alternative for the identification of disease genes. This may be particularly relevant when diagnostic criteria are not very well defined as described for asthma. We analyzed serum samples from 944 individuals of 218 asthma families for 17 cytokines (eotaxin, GM-CSF, IFNγ, IL1B, IL1RA, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12(p40), IL-13, IL-17, IL-23, IL-33, TSLP and TNF-α) and determined the heritability. Linked chromosomal regions were identified by a genome-wide analysis using 334 autosomal microsatellite marker and association tested by further 550 SNP marker at genes implicated earlier with immune response. Heritability varied with TNF-α and IL-8 levels having the highest and TSLP having the lowest heritability. Linkage was significantly increased only for IL-12(p40) at D17S949. There were multiple significant single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) associations (P<0.05) as found in the transmission disequilibrium test, whereas only a few replicated in parents or children only. These include SNPs in IL1RN that were associated with IL-33 and TSLP levels, and a SNP in NR3C2 that was associated with eotaxin, IL-13 and IFN-γ levels. Circulating level of serum cytokines exhibits genetic associations with asthma traits that are otherwise not detected using clinical diagnosis or when the clinical details are ambiguous.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burrows B, Martinez FD, Halonen M, Barbee RA, Cline MG . Association of asthma with serum IgE levels and skin-test reactivity to allergens. N Engl J Med 1989; 320: 271–277.
Chung KF, Barnes PJ . Cytokines in asthma. Thorax 1999; 54: 825–857.
Verstraelen S, Bloemen K, Nelissen I, Witters H, Schoeters G, Heuvel R . Cell types involved in allergic asthma and their use in in vitro models to assess respiratory sensitization. Toxicol In Vitro 2008; 22: 1419–1431.
Al-Muhsen SZ, Shablovsky G, Olivenstein R, Mazer B, Hamid Q . The expression of stem cell factor and c-kit receptor in human asthmatic airways. Clin Exp Allergy 2004; 34: 911–916.
Silva CA, Reber L, Frossard N . Stem cell factor expression, mast cells and inflammation in asthma. Fund Clin Pharmacol 2006; 20: 21–39.
Soumelis V, Reche PA, Kanzler H, Yuan W, Edward G, Homey B et al. Human epithelial cells trigger dendritic cell-mediated allergic inflammation by producing TSLP. Nat Immunol 2002; 3: 673–680.
Kabesch M, Schedel M, Carr D, Woitsch B, Fritzsch C, Weiland SK et al. IL-4/IL-13 pathway genetics strongly influence serum IgE levels and childhood asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006; 117: 269–274.
Graves PE, Kabesch M, Halonen M, Holberg CJ, Baldini M, Fritzsch C et al. A cluster of seven tightly linked polymorphisms in the IL-13 gene is associated with total serum IgE levels in three populations of white children. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2000; 105: 506–513.
Marsh DG, Neely JD, Breazeale DR, Ghosh B, Freidhoff LR, Ehrlich-Kautzky E et al. Linkage analysis of IL4 and other chromosome 5q31. 1 markers and total serum immunoglobulin E concentrations. Science 1994; 264: 1152–1156.
Flint KC, Leung KB, Hudspith BN, Brostoff J, Pearce FL, Johnson NM . Bronchoalveolar mast cells in extrinsic asthma: a mechanism for the initiation of antigen specific bronchoconstriction. Br Med J) 1985; 291: 923–926.
Kobayashi T, Miura T, Haba T, Sato M, Serizawa I, Nagai H et al. An essential role of mast cells in the development of airway hyperresponsiveness in a murine asthma model. J Immunol 2000; 164: 3855–3861.
Schulte T, Kurrle R, Röllinghoff M, Gessner A . Molecular Characterization and Functional Analysis of Murine Interleukin 4 Receptor Allotypes. J Exp Med 1997; 186: 1419–1429.
Rich SS, Roitman-Johnson B, Greenberg B, Roberts S, Blumenthal MN . Genetic analysis of atopy in three large kindreds: no evidence of linkage to D11S97. Clin Exp Allergy 1992; 22: 1070–1076.
Nawijn MC, Piavaux BJ, Jeurink PV, Gras R, Reinders MA, Stearns T et al. Identification of the Mhc region as an asthma susceptibility locus in recombinant congenic mice. Am J Resp Cell Mol Biol 2011; 45: 295–303.
Wjst M, Fischer G, Immervoll T, Jung M, Saar K, Rueschendorf F et al. A Genome-wide search for linkage to asthma. Genomics 1999; 58: 1–8.
Graves PE, Kabesch M, Halonen M, Holberg CJ, Baldini M, Fritzsch C et al. A cluster of seven tightly linked polymorphisms in the IL-13 gene is associated with total serum IgE levels in three populations of white children. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2000; 105: 506–513.
Ober C, Cox NJ, Abney M, Di Rienzo A, Lander ES, Changyaleket B et al. Genome-wide search for asthma susceptibility loci in a founder population. Hum Mol Genet 1998; 7: 1393–1398.
Raby BA, Silverman EK, Lazarus R, Lange C, Kwiatkowski DJ, Weiss ST . Chromosome 12q harbors multiple genetic loci related to asthma and asthma-related phenotypes. Hum Mol Genet 2003; 12: 1973–1979.
Kimura K, Noguchi E, Shibasaki M, Arinami T, Yokouchi Y, Takeda K et al. Linkage and association of atopic asthma to markers on chromosome 13 in the Japanese population. Hum Mol Genet 1999; 8: 1487–1490.
Rogers AJ, Chu J-H, Darvishi K, Ionita-Laza I, Lehmann H, Mills R et al. Copy number variation prevalence in known asthma genes and their impact on asthma susceptibility. Clin Exp Allergy 2013; 43: 455–462.
Torgerson DG, Capurso D, Mathias RA, Graves PE, Hernandez RD, Beaty TH et al. Resequencing candidate genes implicates rare variants in asthma susceptibility. Am J Hum Genet 2012; 90: 273–281.
Kroegel C, Julius P, Matthys H, Virchow JC, Luttmann W . Endobronchial secretion of interleukin-13 following local allergen challenge in atopic asthma: relationship to interleukin-4 and eosinophil counts. Eur Resp J 1996; 9: 899–904.
Coyle AJ, Le Gros G, Bertrand C, Tsuyuki S, Heusser CH, Kopf M et al. Interleukin-4 is required for the induction of lung Th2 mucosal immunity. Am J Resp Cell Mol Biol 1995; 13: 54–59.
Wills-Karp M, Luyimbazi J, Xu X, Schofield B, Neben TY, Karp CL et al. Interleukin-13: central mediator of allergic asthma. Science 1998; 282: 2258–2261.
Meyts I, Hellings PW, Hens G, Vanaudenaerde BM, Verbinnen B, Heremans H et al. IL-12 contributes to allergen-induced airway inflammation in experimental asthma. J Immunol 2006; 177: 6460–6470.
Kumar RK, Webb DC, Herbert C, Foster PS . Interferon-as a Possible Target in Chronic Asthma. Inflammation Allergy-Drug Targets 2006; 5: 253–256.
Alexander AG, Barkans J, Moqbel R, Barnes NC, Kay AB, Corrigan CJ . Serum interleukin 5 concentrations in atopic and non-atopic patients with glucocorticoid-dependent chronic severe asthma. Thorax 1994; 49: 1231–1233.
Bullens DM, Truyen E, Coteur L, Dilissen E, Hellings PW, Dupont LJ et al. IL-17 mRNA in sputum of asthmatic patients: linking T cell driven inflammation and granulocytic influx. Respir Res 2006; 7: 135–143.
Ying S, O’Connor B, Ratoff J, Meng Q, Mallett K, Cousins D et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin expression is increased in asthmatic airways and correlates with expression of Th2-attracting chemokines and disease severity. J Immunol 2005; 174: 8183–8190.
Préfontaine D, Lajoie-Kadoch S, Foley S, Audusseau S, Olivenstein R, Halayko AJ et al. Increased expression of IL-33 in severe asthma: evidence of expression by airway smooth muscle cells. J Immunol 2009; 183: 5094–5103.
Wakashin H, Hirose K, Maezawa Y, Kagami S-I, Suto A, Watanabe N et al. IL-23 and Th17 cells enhance Th2-cell—mediated eosinophilic airway inflammation in mice. Am J Resp Crit Care Med 2008; 178: 1023–1032.
Wanderer A . Interleukin-1β targeted therapy in severe persistent asthma (SPA) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): proposed similarities between biphasic pathobiology of SPA/COPD and ischemia-reperfusion injury. IMAJ 2008; 10: 837–842.
Rincon M, Irvin CG . Role of IL-6 in asthma and other inflammatory pulmonary diseases. Int Journal Biol Sci 2012; 8: 1281–1290.
Heath H, Qin S, Rao P, Wu L, LaRosa G, Kassam N et al. Chemokine receptor usage by human eosinophils. The importance of CCR3 demonstrated using an antagonistic monoclonal antibody. Jo Clin Invest 1997; 99: 178–184.
Ordoñez CL, Shaughnessy TE, Matthay MA, Fahy JV . Increased neutrophil numbers and IL-8 levels in airway secretions in acute severe asthma: Clinical and biologic significance. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000; 161: 1185–1190.
Gajewska BU, Wiley RE, Jordana M . GM-CSF and dendritic cells in allergic airway inflammation: basic mechanisms and prospects for therapeutic intervention. Curr Drug Targets-Inflammation Allergy 2003; 2: 279–292.
Borish L, Aarons A, Rumbyrt J, Cvietusa P, Negri J, Wenzel S . Interleukin-10 regulation in normal subjects and patients with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1996; 97: 1288–1296.
Mao X-Q, Kawai M, Yamashita T, Enomoto T, Dake Y, Sasaki S et al. Imbalance production between interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra) in bronchial asthma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000; 276: 607–612.
Abecasis GR, Cardon LR, Cookson WOC . A general test of association for quantitative traits in nuclear families. Am J Hum Genet 2000; 66: 279–292.
Fulker DW, Cherny SS, Sham PC, Hewitt JK . Combined linkage and association sib-pair analysis for quantitative traits. Am J Hum Genet 1999; 64: 259–267.
Hull J, Thomson A, Kwiatkowski D . Association of respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis with the interleukin 8 gene region in UK families. Thorax 2000; 55: 1023–1027.
Heinzmann A, Ahlert I, Kurz T, Berner R, Deichmann KA . Association study suggests opposite effects of polymorphisms within IL8 on bronchial asthma and respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2004; 114: 671–676.
Puthothu B, Krueger M, Heinze J, Forster J, Heinzmann A . Impact of IL8 and IL8-receptor alpha polymorphisms on the genetics of bronchial asthma and severe RSV infections. Clin Mol Allergy 2006; 4: 2–8.
Okayama Y, Saito H, Ra C . Targeting human mast cells expressing g-protein-coupled receptors in allergic diseases. Allergol Int 2008; 57: 197–203.
Gohlke H, Illig T, Bahnweg M, Klopp N, André E, Altmüller J et al. Association of the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene with asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2004; 169: 1217–1223.
Pelaia G, Gallelli L, Vatrella A, Grembiale RD, Maselli R, De Sarro GB et al. Potential role of potassium channel openers in the treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Life Sci 2002; 70: 977–990.
Chung KF . p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in asthma and COPD. Chest J 2011; 139: 1470–1479.
Bhavsar P, Khorasani N, Hew M, Johnson M, Chung KF . Effect of p38 MAPK inhibition on corticosteroid suppression of cytokine release in severe asthma. Eur Respir J 2010; 35: 750–756.
Rauly I, Saint-Laurent N, Delesque N, Buscail L, Estéve JP, Vaysse N et al. Induction of a negative autocrine loop by expression of sst2 somatostatin receptor in NIH 3T3 cells. J Clin Invest 1996; 97: 1874–1883.
Van Hagen PM, Krenning EP, Kwekkeboom DJ, Reubi JC, Anker-Lugtenburg PJ, Löwenberg B et al. Somatostatin and the immune and haematopoetic system; a review. Eur J Clin Invest 1994; 24: 91–99.
Petersenn S, Rasch AC, Presch S, Beil FU, Schulte HM . Characterization of the human somatostatin receptor type 4 promoter. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2002; 188: 75–83.
Borie R, Fabre A, Prost F, Marchal-Somme J, Lebtahi R, Marchand-Adam S et al. Activation of somatostatin receptors attenuates pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax 2008; 63: 251–258.
Lopez F, Estève JP, Buscail L, Delesque N, Saint-Laurent N, Vaysse N et al. Molecular mechanisms of antiproliferative effect of somatostatin: involvement of a tyrosine phosphatase. Metabolism 1996; 45: 14–16.
Scott FL, Eyre HJ, Lioumi M, Ragoussis J, Irving JA, Sutherland GA et al. Human ovalbumin serpin evolution: phylogenic analysis, gene organization, and identification of new PI8-related genes suggest that two interchromosomal and several intrachromosomal duplications generated the gene clusters at 18q21-q23 and 6p25. Genomics 1999; 62: 490–499.
Tzortzaki EG, Dimakou K, Neofytou E, Tsikritsaki K, Samara K, Avgousti M et al. Oxidative DNA damage and somatic mutations: a link to the molecular pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory airway diseases. Chest 2012; 141: 1243–1250.
Zervou MI, Tzortzaki EG, Makris D, Gaga M, Zervas E, Economidou E et al. Differences in microsatellite DNA level between asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Resp J 2006; 28: 472–478.
Hebert ML, Wells RD . Roles of Double-strand Breaks, Nicks, and Gaps in Stimulating Deletions of CTG.CAG Repeats by Intramolecular DNA Repair. J Mol Biol 2005; 353: 961–979.
Callinan PA, Batzer MA . Retrotransposable Elements and Human Disease 2006; 1: 104–115.
Arcot SS, Fontius JJ, Deininger PL, Batzer MA . Identification and analysis of a ‘young polymorphic Alu element. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Struct Express 1995; 1263: 99–102.
Paraskakis E, Sourvinos G, Passam F, Tzanakis N, Tzortzaki EG, Zervou M et al. Microsatellite DNA instability and loss of heterozygosity in bronchial asthma. Eur Respir J 2003; 22: 951–955.
Zhou B, Comeau MR, De Smedt T, Liggitt HD, Dahl ME, Lewis DB et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin as a key initiator of allergic airway inflammation in mice. Nat Immunol 2005; 6: 1047–1053.
Pattaro C, Heinrich J, Werner M, de Marco R, Wjst M . Association between interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene and asthma-related traits in a German adult population. Allergy 2006; 61: 239–244.
Griffithsjohnson G, Collins C, Rossi R, Jose J, Williams W . The chemokine, eotaxin, activates guinea-pig eosinophils in vitro and causes their accumulation into the lung in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1993; 197: 1167–1172.
Gerber BO, Zanni MP, Uguccioni M, Loetscher M, Mackay CR, Pichler WJ et al. Functional expression of the eotaxin receptor CCR3 in T lymphocytes co-localizing with eosinophils. Curr Biol 1997; 7: 836–843.
Yahav Y, Dany S, Katznelson D, Farfel Z . Sodium cromoglycate in asthma: correlation between response and serum concentrations. Archiv Dis Childhood 1988; 63: 592–597.
Kimata H . Increased serum levels of soluble adhesion molecules in young children with atopic dermatitis. Eur J Pediatr 1999; 158: 529–530.
Nie M, Knox AJ, Pang L . β2-Adrenoceptor agonists, like glucocorticoids, repress eotaxin gene transcription by selective inhibition of histone H4 acetylation. J Immunol 2005; 175: 478–486.
Rihoux JP, Michel L, Arnold R, König W . Hypothetical mechanisms of action of an H1-antihistamine in asthma. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 1999; 118: 380–383.
Pukelsheim KAS, Kutschke TA, Ganguly DA, Wjst M . Cytokine profiles in asthma families depend on age and phenotype. PLoS One 2010; 5: e14299.
Wjst M, Altmüller J, Faus-Kessler T, Braig C, Bahnweg M, André E . Asthma families show transmission disequilibrium of gene variants in the vitamin D metabolism and signaling pathway. Respir Res 2006; 7: 60–71.
Altmüller J, Seidel C, Lee Y-A, Loesgen S, Bulle D, Friedrichs F et al. Phenotypic and genetic heterogeneity in a genome-wide linkage study of asthma families. BMC Pulmonary Med 2005; 5: 1–11.
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF . A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 1988; 16: 1215.
Meyers DA, Wjst M, Ober C . Description of three data sets: Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Asthma (CSGA), the German Affected-Sib-Pair Study, and the Hutterites of South Dakota. Genetic Epidemiol 2001; 21: S4.
Acknowledgements
We thank BMBF, Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and National Genome Network. MS and MW are funded by HMGU (Helmholtz Center Munich), and the EU Grant Europrevall. We also thank all the participating families for their help and the members of the clinical centers for their work.
Disclaimer
The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Genes and Immunity website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sargurupremraj, M., Pukelsheim, K., Hofer, T. et al. Intermediary quantitative traits—an alternative in the identification of disease genes in asthma?. Genes Immun 15, 1–7 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2013.53
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2013.53