Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
We hypothesized that the cost of a lactation program can be reduced without significantly affecting the incidence of breastfeeding.
STUDY DESIGN:
We conducted a retrospective analysis of breastfeeding among all 7942 mothers whose neonates were admitted to the well baby nursery at Jacobi Medical Center (JMC) over a 44-month period We used multiway frequency analysis to compare the incidence of breastfeeding in three successive models of counseling: (1) full-time lactation coordinator, (2) obstetric personnel trained in breastfeeding counseling and full-time lactation coordinator, and (3) obstetric personnel and half-time lactation coordinator. Mothers were further classified into three groups according to location of prenatal care and attendance at breastfeeding education sessions.
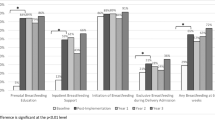
RESULTS:
Breastfeeding increased with the initiation of education and the involvement of obstetric personnel and did not significantly decrease when the lactation coordinator became half-time. The transition to model 3 resulted in decreased costs without significantly affecting the incidence of breastfeeding. Breastfeeding was significantly associated with counseling by obstetric personnel, with prenatal care at JMC, and with breastfeeding education sessions.
CONCLUSION: Involving obstetric personnel in breastfeeding counseling may enhance the effectiveness of a lactation program. In our population, the most cost-conscious model included counseling by trained obstetric personnel and a half-time lactation coordinator.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Preliminary results were presented at the First Annual InternationalMeeting Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine, Rochester, NY, October 11,1996, and were published in abstract form (Pediatr Res 1998;43:329A).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Russell, B., Aviles, M. & Brion, L. Relationship Between Perinatal Counseling and Incidence of Breastfeeding in an Inner-City Population. J Perinatol 19, 501–504 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7200257
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7200257