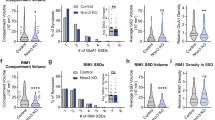
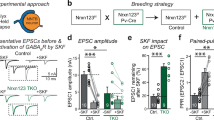
Abstract
Coordinated signalling between presynaptic terminals and their postsynaptic targets is essential for the development and function of central synapses. In addition to diffusible molecules1, this bidirectional flow of information could involve direct interactions through cell-adhesion molecules2,3. Here, we show that one class of cell-adhesion molecule, the integrins, are required for the functional maturation of hippocampal synapses in vitro. At immature synapses, a high probability of glutamate release (Pr) was correlated with the expression of postsynaptic NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) receptors containing the NR2B subunit. The activity-dependent reduction in Pr and a switch in the subunit composition of synaptic NMDA receptors was prevented by chronic blockade with peptides containing the integrin-binding site Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD), or by a functional antibody against the β3 integrin subunit. Active synapses, monitored by the uptake of antibodies against the intraluminal domain of synaptotagmin I, also had β3 subunit immunoreactivity. Our results provide evidence that integrin-mediated signalling is essential for the orchestrated maturation of central excitatory synapses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fitzsimonds, R. M. & Poo, M. M. Retrograde signaling in the development and modification of synapses. Physiol. Rev. 78, 143–170 (1998).
Kohmura, N. et al. Diversity revealed by a novel family of cadherins expressed in neurons at a synaptic complex. Neuron 20, 1137–1151 (1998).
Song, J. Y., Ichtchenko, K., Sudhof, T. C. & Brose, N. Neuroligin 1 is a postsynaptic cell-adhesion molecule of excitatory synapses. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 1100–1105 (1999).
Rosenmund, C., Clements, J. D. & Westbrook, G. L. Nonuniform probability of glutamate release at a hippocampal synapse. Science 262, 754–757 (1993).
Hessler, N. A., Shirke, A. M. & Malinow, R. The probability of transmitter release at a mammalian central synapse. Nature 366, 569–572 (1993).
Murthy, V. N., Sejnowski, T. J. & Stevens, C. F. Heterogeneous release properties of visualized individual hippocampal synapses. Neuron 18, 599–612 (1997).
Bolshakov, V. Y. & Siegelbaum, S. A. Regulation of hippocampal transmitter release during development and long-term potentiation. Science 269, 1730–1734 (1995).
Chavis, P. & Westbrook, G. L. ‘Pure’ NR2B-containing synapses have a high release probability in cultured hippocampal neurons. Soc. Neurosci. Abs. (1998).
Williams, K., Russell, S. L., Shen, Y. M. & Molinoff, P. B. Developmental switch in the expression of NMDA receptors occurs in vivo and in vitro. Neuron 10, 267–278 (1993).
Williams, K. Ifenprodil discriminates subtypes of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor: selectivity and mechanisms at recombinant heteromeric receptors. Mol. Pharm. 44, 851–859 (1993).
Vicini, S. et al. Functional and pharmacological differences between recombinant N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. J. Neurophysiol. 79, 555–566 (1998).
Tovar, K. R. & Westbrook, G. L. The incorporation of NMDA receptors with a distinct subunit composition at nascent hippocampal synapses in vitro. J. Neurosci. 19, 4180–4188 (1999).
Staubli, U., Chun, D. & Lynch, G. Time-dependent reversal of long-term potentiation by an integrin antagonist. J. Neurosci. 18, 3460–3469 (1998).
Grotewiel, M. S., Beck, C. D., Wu, K. H., Zhu, X. R. & Davis, R. L. Integrin-mediated short-term memory in Drosophila. Nature 391, 455–460 (1998).
Aplin, A. E., Howe, A., Alahari, S. K. & Juliano, R. L. Signal transduction and signal modulation by cell adhesion receptors: the role of integrins, cadherins, immunoglobulin-cell adhesion molecules, and selectins. Pharmacol. Rev. 50, 197–263 (1998).
Ruoslahti, E. RGD and other recognition sequences for integrins. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 12, 697–715 (1996).
Tang, L., Hung, C. P. & Schuman, E. M. A role for the cadherin family of cell adhesion molecules in hippocampal long-term potentiation. Neuron 20, 1165–1175 (1998).
Pinkstaff, J. K., Detterich, J., Lynch, G. & Gall, C. Integrin subunit gene expression is regionally differentiated in adult brain. J. Neurosci. 19, 1541–1556 (1999).
Pfaff, M., McLane, M. A., Beviglia, L., Niewiarowski, S. & Timpl, R. Comparison of disintegrins with limited variation in the RGD loop in their binding to purified integrins alpha IIb beta 3, alpha V beta 3 and alpha 5 beta 1 and in cell adhesion inhibition. Cell. Adhes. Commun. 2, 491–501 (1994).
Chavis, P., Mollard, P., Bockaert, J. & Manzoni, O. Visualization of cyclic AMP-regulated presynaptic activity at cerebellar granule cells. Neuron 20, 773–781 (1998).
Schlaepfer, D. D. & Hunter, T. Integrin signalling and tyrosine phosphorylation: just the FAKs? Trends Cell Biol. 8, 151–157 (1998).
Boyer, C., Schikorski, T. & Stevens, C. F. Comparison of hippocampal dendritic spines in culture and in brain. J. Neurosci. 18, 5294–5300 (1998).
Schikorski, T. & Stevens, C. F. Quantitative ultrastructural analysis of hippocampal excitatory synapses. J. Neurosci. 17, 5858–5867 (1997).
Lau, L. F. & Huganir, R. L. Differential tyrosine phosphorylation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 20036–20041 (1995).
Blaess, S., Kammerer, R. A. & Hall, H. Structural analysis of the sixth immunoglobulin-like domain of mouse neural cell adhesion molecule L1 and its interactions with alpha(v)beta3, alpha(IIb)beta3, and alpha5beta1 integrins. J. Neurochem. 71, 2615–2625 (1998).
Luthi, A., Laurent, J. P., Figurov, A., Muller, D. & Schachner, M. Hippocampal long-term potentiation and neural cell adhesion molecules L1 and NCAM. Nature 372, 777–779 (1994).
Scheiffele, P., Fan, J., Choih, J., Fetter, R. & Serafini, T. Neuroligin expressed in nonneuronal cells triggers presynaptic development in contacting axons. Cell 101, 657–669 (2000).
Acknowledgements
We thank G. Alonso, K. Tovar and A. Puel for discussions and O. Manzoni, C. Jahr and J. Bockaert for critical reading of the manuscript. We also thank A. Miller for technical support and M. Passama for the artwork. This work was supported by NIH (G.L.W.), the Human Frontiers Science Program, INSERM, and by FRM (P.C.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chavis, P., Westbrook, G. Integrins mediate functional pre- and postsynaptic maturation at a hippocampal synapse. Nature 411, 317–321 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/35077101
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35077101
This article is cited by
-
A new advanced cellular model of functional cholinergic-like neurons developed by reprogramming the human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line
Cell Death Discovery (2024)
-
Integrin β3 in forebrain Emx1-expressing cells regulates repetitive self-grooming and sociability in mice
BMC Neuroscience (2022)
-
Presynaptic LTP in Blockade of NMDA2B Receptors
Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology (2020)
-
Mechanotransduction in neuronal cell development and functioning
Biophysical Reviews (2019)
-
Osteopontin counters human immunodeficiency virus type 1–induced impairment of neurite growth through mammalian target of rapamycin and beta-integrin signaling pathways
Journal of NeuroVirology (2019)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.