Abstract
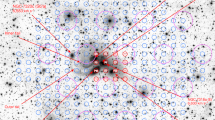
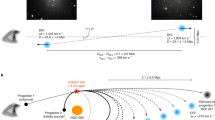
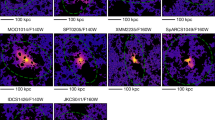
Although the existence of a faint background of starlight in the core of the Coma cluster has been well established1,2, its origin is uncertain. This vast sea of stars could have formed outside the galaxies, using gas left over from the time of the cluster's birth. Alternatively, it might be the accumulated debris generated by interactions between the galaxies over the lifetime of the cluster3. Here we report the discovery of three large, low-surface-brightness features in the Coma cluster, the most spectacular of which is a plume-like structure, 130 kpc long, in the cluster's heart. These structures will disperse over the next one to two billion years, thereby enhancing the general background light. If this epoch is typical, we argue that a significant fraction — perhaps even most — of the intracluster light results from a steady accumulation of tidal debris generated during galaxy–galaxy and galaxy–cluster interactions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zwicky, F. Morphological Astronomy 48 (Springer, Berlin, (1957)).
Biviano, A. in A New Vision of an Old Cluster: Untangling Coma Berenices (eds Mazure, A., Casoli, F., Durret, F. & Gerbal, D.) 1–8 (World Scientific, Singapore, (1998)).
Merritt, D. Relaxation and tidal stripping in rich clusters of galaxies. II — evolution of the luminosity distribution. Astrophys. J. 276, 26–37 (1984).
Trentham, N. & Mobasher, B. The discovery of a giant debris arc in the Coma cluster. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 293, 53–59 (1998).
Welch, G. A. & Sastry, G. N. Photographic detection of “intergalactic” matter in the Coma cluster. Astrophys. J. 169, L3–L5 (1971).
Secker, J. & Harris, W. E. Dwarf galaxies in the Coma cluster I. Detection, measurement and classification techniques. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pacif. 109, 1364–1376 (1997).
Binney, J. & Tremaine, S. Galactic Dynamics (Princeton Univ. Press, (1987)).
Fitchett, M. J. & Webster, R. L. Substructure in the Coma cluster. Astrophys. J. 317, 653–667 (1987).
Mellier, Y., Mathez, G., Mazure, A., Chauvineau, B. & Proust, D. Subclustering and evolution of the Coma cluster. Astron. Astrophys. 199, 67–72 (1988).
White, S. D. M., Briel, U. G. & Henry, J. P. X-ray archaeology in the Coma cluster. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 261, L8–L12 (1993).
Vikhlinin, A., Forman, W. & Jones, C. Another collision for the Coma cluster. Astrophys. J. 474, L7–L10 (1997).
Colless, M. & Dunn, A. M. Structures and dynamics of the Coma cluster. Astrophys. J. 458, 435–454 (1996).
Conselice, C. J. & Gallagher, J. S. Galaxy aggregates in the Coma cluster. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 297, L34–L38 (1998).
Dubinski, J., Mihos, J. C. & Hernquist, L. Using tidal tails to probe dark matter halos. Astrophys. J. 462, 576–593 (1996).
Moore, B., Katz, N., Lake, G., Dressler, A. & Oemler, A. J Galaxy harassment and the evolution of clusters of galaxies. Nature 379, 613–616 (1996).
NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database available at 〈http://nedwww.ipac.caltech.edu〉 ((1998)).
Thompson, L. A. & Gregory, S. A. Dwarf galaxies n the Coma cluster. Astron. J. 106, 2197–2212 (1993).
Lopez-Cruz, O., Yee, H. K. C., Brown, J. P., Jones, C. & Forman, W. Are luminous cD halos formed by the disruption of dwarf galaxies? Astrophys. J. 475, L97–L101 (1997).
Tinsley, B. M. Afirst approximation to the effect of evolution on q0. Astrophys. J. 173, L93–L97 (1972).
Ostriker, J. P. & Tremaine, S. D. Another evolutionary correction to the luminosity of giant galaxies. Astrophys. J. 202, L113–L116 (1975).
Theuns, T. & Warren, S. J. Intergalactic stars in the Fornax cluster. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 284, L11–L15 (1997).
Ferguson, H. C., Tanvir, N. R. & von Hippel, T. Detection of intergalactic red-giant-branch stars in the Virgo cluster. Nature 391, 461–463 (1998).
Ciardullo, R., Jacoby, G. H., Feldmeier, J. J. & Bartlett, R. E. The planetary nebula luminosity function of M87 and the intracluster stars of Virgo. Astrophys. J. 492, 62–73 (1998).
West, M., Cote, P., Jones, C., Forman, W. & Marzke, R. Intracluster globular clusters. Astrophys. J. 453, L77–L80 (1995).
Gregg, M. D. Differential population synthesis of S0 galaxies. I — the data. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 69, 217–232 (1989).
Sandage, A. & Tammann, G. A. A Revised Shapley-Ames Catalog of Bright Galaxies (Carnegie Institute of Washington, Washington DC, (1987)).
Acknowledgements
Part of this work was done at the Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, under the auspices of the US DOE by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. We acknowledge use of the NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database (NED), which is operated by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Caltech, under contract with the NASA. Kitt Peak National Observatory, National Optical Astronomy Observatory, is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc. (AURA), under cooperative agreement with the NSF. Observations were made with the Burrell Schmidt telescope of the Warner and Swasey Observatory, Case Western Reserve University. M.J.W. was supported by the NSERC of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gregg, M., West, M. Galaxy disruption as the origin of intracluster light in the Coma cluster of galaxies. Nature 396, 549–552 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/25078
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/25078
This article is cited by
-
The faint light in groups and clusters of galaxies
Nature Astronomy (2022)
-
The Jay Baum Rich telescope: a Centurion 28 at the Wise Observatory
Astrophysics and Space Science (2015)
-
The fate of dwarf galaxies in clusters and the origin of intracluster stars
Journal of Astrophysics and Astronomy (2009)
-
A class of compact dwarf galaxies from disruptive processes in galaxy clusters
Nature (2003)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.