Abstract
In this study, a novel nanocatalyst was successfully prepared by heteropolyacid immobilization of magnetic chitosan-cyanoguanidine composite and fully characterized by different analysis methods, including FTIR, XRD, TGA, SEM, and EDS. The catalytic activity of fabricated composite was examined in a one-pot three-component reaction, involving the diverse active methylene compounds, various aryl aldehydes, and malononitrile in water. The results revealed the efficient catalytic performance of composite, while all reactions proceeded smoothly and led to the formation of the corresponding pyranochromene derivatives in high to excellent yields.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
In recent years, the heteropolyacids (HPAs) have attracted great attention, due to their high catalytic activity, strong Brønsted acidity, low toxicity, and tunable redox properties1,2, which render them a numerous applications in all fields of chemistry, both academically and industrially3. The critical weakness of HPAs attributed to their high solubility in polar solvents and low surface area, which highly limited their catalytic performance and made some difficulty in their separation from the reaction mixture at the end of the reaction4. The dispersion of HPAs on the high surface area solid supports is an efficient strategy to circumvent these problems which led to increasing their active surface area and facilitating their separation from the reaction media to be re-used in another successive run5,6.
Despite achievements in promoting the catalytic potency of a wide variety of catalysts from different points of view, finding an easy and efficient separability of heterogeneous catalysts is still a challenge7,8,9,10. In this regard, the immobilization of HPAs catalyst on the magnetic supports is an efficient approach, in which the heterogeneous catalyst can be easily separated from the reaction mixture by an external magnet without encountering the inherent leaching problems11.
Chitosan is one of the most abundant and intriguing biopolymers in nature, which is widely used in environmental remediation, food, agricultural, and pharmaceutical industries12,13. It possesses intrinsic physicochemical features, such as biodegradability, biocompatibility, high chemical stability, high reactivity, and outstanding chelation behavior14. Considerable efforts have been devoted to preparing magnetic chitosan-based materials in recent years15,16,17 and extensively employed as catalyst supports in a wide range of organic reactions18,19,20. Despite this wide range of applications, there are a few reports on the exploiting of magnetic chitosan, as HPAs’ supports in the catalytic reactions21,22.
The chromene scaffold generates the nucleus of a class of naturally occurring compounds. It is also a part of pharmacophores of a wide variety of biologically active compounds23, including anticancer agents24. Several hetero- and carbo-annulated chromene compounds were found antifungal25, antiplatelet26, and also anticancer molecules27. Figure 1 shows the structures of some pharmacologically important chromene derivatives.
In our previous studies, the extraordinary performance of different kinds of HPAs catalysts in several organic reactions was studied28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36. Also, the application of nanoparticles37,38,39,40,41 and particularly magnetic Fe3O442,43,44,45,46,47, as efficient and easily separable catalysts, was demonstrated in various organic reactions. In this work, a novel magnetically recoverable catalyst containing immobilized phosphotungstic acid (H3PW12O40, HPW), as a Keggin type HPA, cyanoguanidine modified magnetic chitosan was designed. The Al2O3/Fe3O4 core–shell nanoparticles were used as the magnetic core of composite, which improved its chemical stability and led to formation a super-paramagnetic catalyst that can be easily separated from the medium by an external magnet48,49. The phosphotungstic heteropolyacid embedded magnetic chitosan-cyanoguanidine (HPW@Fe3O4–Al2O3–CS–CG) catalyst was characterized using different methods and successfully applied in a one-pot three-component synthesis of pyaranochromene derivatives.
Experimental
Chemicals and instruments
The used chitosan in this work was purchased from Acros Organics, and the other chemicals, including phosphotungstic acid hydrate [H3(PW12O40) xH2O], iron (II, III) oxide Nano powder, aluminium isopropoxide (≥ 98%), glutaraldehyde solution (25%), cyanoguanidine, 3,4-methylene-dioxy-phenol, dimedone, 4-Hydroxy coumarine, 3-methyl-1-phenyl-pyrazole-5-one, malononitrile, and the used solvents, such as toluene, CH3CN, HOAC, and EtOH were all supplied from Sigma-Aldrich Co. and used without further purification.
The prepared HPW@Fe3O4–Al2O3–CS–CG catalyst was characterized by analyzing the obtained data. Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectra were recorded by VERTEX-70 infrared spectrometer (by ATR method). The XRD measurement was carried out using a PANalytical Empyrean powder diffractometer using Cu Ka radiation in 2θ-range of 15–100° (step size = 0.0001°) under ambient temperature and pressure. To investigate the catalyst size and surface morphology Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images were taken using the ultra-high resolution Tescan MIRA 3 scanning electron microscope. Melting points were measured by an electrothermal 9200 apparatus via the capillary tube method and the TMS, as an internal standard (DMSO solution), was employed to record the 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra on a Bruker AQS 500-AVANCE spectrometer at 500 and 125 MHz respectively. The reactions were monitored by TLC and all products were recognized by comparison of their physical and spectroscopic data with those of authentic samples in identical.
Preparation of catalyst
Synthesis of magnetic Fe 3 O 4–Al 2 O 3–CS
Above all, the iron oxide nanoparticles/Al2O3 core–shell nanospheres were prepared according to the reported method by Tanhaei et al.16. To prepare Fe3O4–Al2O3–CS, 2 g of chitosan was dissolved in 100 mL of acetic acid and stirred for 2 h to be dissolved and homogenized. Then, the as-prepared magnetic Fe3O4/Al2O3 particles were dispersed in the chitosan solution in an ultrasonic bath. Next, the glutaraldehyde solution (25 wt%) was added until a brown gel product was formed. It was washed several times with acetic acid solution (2%) and deionized water. The obtained Fe3O4–Al2O3–CS solid was finally separated using an external magnet and dried at 60 °C overnight50.
Synthesis of Fe 3 O 4–Al 2 O 3 –CS–CG
Initially, 2 g of Fe3O4–Al2O3–CS was grounded and dispersed in 100 mL of hydrochloric acid solution 1% (v/v), followed by addition of 1.06 g cyanoguanidine under magnetic agitation. The mixture was stirred for 4 h at 90 °C, washed three times with water, and then cooled at room temperature to obtain the cyanoguanidine modified Fe3O4–Al2O3–CS.
Immobilization of H 3 PW 12 O 40 onto Fe 3 O 4–Al 2 O 3–CS–CG
For the synthesis of HPW embedded Fe3O4–Al2O3–CS–CG composite, 1 g of as-prepared Fe3O4–Al2O3–CS–CG was suspended in a solution of distilled water and ethanol (1:2) and stirred for 10 min. Afterward, a solution of H3PW12O40 (5 wt%) was added dropwise to the suspension. The resultant mixture was then stirred at 60 °C for 2 h. Finally, the precipitate was separated by a magnet, washed several times with water, and dried in the oven at 70 °C. The possible preparation mechanism is illustrated in Fig. 2.
Catalytic reactions
General procedure for the synthesis of 6-amino-8-aryl-7-cyano-8H-[1,3]dioxolo-[4,5-g]-chromenes
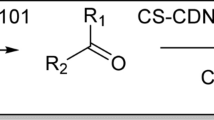
0.04 g of HPW@Fe3O4–Al2O3–CS–CG was added to a solution containing an appropriate aromatic aldehyde (1 mmol), malononitrile (1 mmol), and 3,4-methylene-dioxy-phenol (1 mmol) in H2O (5 mL), and stirred under reflux for a specific time (10–30 min). The reaction was monitored by TLC (Petroleum ether:ethyl acetate = 8:2). After the completion of the reaction, the mixture was cooled to room temperature and the catalyst was easily separated by an external magnet. The catalyst was reused several times without any special treatment and with no loss of appreciable activity at least in four successive runs. The precipitated solid was filtered off and washed with water to obtain the pure products, where any other purification process was not required (Fig. 3).
Synthesis of 4H-benzo [b]pyrans
0.04 g of HPW@Fe3O4–Al2O3–CS–CG was added to a solution of an aromatic aldehyde, malononitrile, and dimedone/4-Hydroxy coumarine/3-methyl-1-phenyl-pyrazole-5-one (1 mmol of each compound) in H2O (5 mL) and stirred for a specific time under heating conditions. After completion of the reaction, which was monitored by TLC, the mixture was cooled to room temperature and the catalyst was separated subsequently. The solid product was collected by filtration, washed with the solution of water and ethanol, and purified by recrystallization from ethanol (Fig. 4).
Results and discussion
Characterization of synthesized nanocatalyst
The designed HPW@Fe3O4–Al2O3–CS–CG catalyst was identified by Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) methods and the obtained spectrum is shown in Fig. 5. As can be seen, the peak at 518 cm−1 and wide peak at 674 cm−1 are related to Fe–O, Al–O, and Fe–Al–O showing the cross-linking of chitosan and iron oxide/Al2O3 core–shell spheres16,51. The peak of C=N at 1630 cm−1 was attributed to the presence of cyanoguanidine and glutaraldehyde as cross-linkers52. The broad band at 3150–3700 cm−1 and the peaks at 1651, 1557 cm−1, and 1387 cm−1 are attributed to hydroxyl (O–H) stretching overlapped with N–H stretch, amide I, II, and CH3 symmetrical angular deformation respectively53. The HPW structure consists of tungsten atoms, linked by oxygen atoms, while the phosphorus atoms are at the center of the tetrahedron. The three characteristic absorption bands of HPW are appeared at 1060 cm−1 (P–O in the central PO4 tetrahedron), 1012 cm−1 (W=O in the exterior), and 879 cm−1 (W–Ob–W bridges between corner sharing octahedron)54.
The crystallinity, phase components, and molecule structure of the HPW@Fe3O4–Al2O3–CS–CG catalyst were analyzed by XRD, as shown in Fig. 6. It shows the diffraction peaks of Fe3O4 nanoparticles at 30.3°, 35.7°, 43.5°, 53.8°, 57.5°, 63.3°, 67°, and 74.1° with a typical face-centered cubic structure15,16. The characteristic diffraction peaks of cubic face-centered magnetite (Fe3O4) and rhombohedral hematite (Fe2O3), as shown in the Figure, indicate the presence of magnetite nanoparticles in the prepared catalyst. On the other hand, the amorphous hump in the 2θ range of 15 to 25° is corresponded to the amorphous chitosan/HPW phase.
Moreover, the SEM images of the HPW@Fe3O4–Al2O3–CS–CG catalyst are shown in Fig. 7 at different magnifications. Before observation, the catalyst was sputtered with thin gold layers to enhance its electrical conductivity. SEM images show that the final product exhibits the aggregation of particles in the range of 100–500 nm, which can be resulted from the embedding of magnetic iron oxide/Al2O3 particles inside the cross-linked chitosan.
Furthermore, the EDS analysis was also applied to examine the elemental analysis of HPW@Fe3O4–Al2O3–CS–CG catalyst. The spectrum is shown in Fig. 8. The results confirmed the well dispersion of phosphotungstic acid in the catalyst structure.
The TGA curves of the Fe3O4, Al2O3, chitosan, and HPW@Fe3O4–Al2O3–CS–CG are shown in Fig. 9. The thermogravimetric curve of Fe3O4 nanoparticles shows a weight loss of ~ 6.5%. The first weight loss up to the temperature of 150° is attributed to the removal of water from the surface of the nanoparticles, and the rest is related to the removal of water from the structure. The TGA curve of Al2O3 nanoparticles showed two weight loss stages related to the loss of moisture from the surface of the Al2O3 layer (150 °C) and exit of the structured water (200–1000 °C). On the other hand, the water removal occurs in the range of 100 °C in chitosan, followed by the deacetylation process that causes weight loss between 200 and 470 °C. In the case of HPW@Fe3O4–Al2O3–CS–CG, apart from weight loss due to water removal, the second stage of degradation was observed at 260 °C with a mass loss of ~ 40%. The temperature of the second weight loss of catalyst is lower than that of chitosan, showing that the new compound is more thermally stable. Finally, the organic polymer is almost wholly decomposed at 750 °C16.
Effects of the catalyst structure
To establish the possibility of our strategy for the synthesis of 6-amino-8-aryl-7-cyano-8H-[1,3]dioxolo-[4,5-g]-chromene, as well as optimizing the reaction conditions, the condensation of 3,4-methylene-dioxy-phenol, benzaldehde, and malononitrile were studied in the presence of a different solvent, temperature, and also the amount of catalyst. The results are summarized in Table 1. As can be seen, the desired product was produced with a negligible yield in the absence of HPW@Fe3O4-Al2O3-CS-CG catalyst (Table 1, Entry 1). After that, the effect of several solvents and temperature were explored. As listed in Table 1, the results demonstrated that the presence of catalyst and solvent were significantly essential to accomplish the reaction. After optimizing the catalyst loading and temperature, the effect of some solvents was assessed. The optimal reaction condition was obtained using 0.04 g of HPW@Fe3O4-Al2O3-CS-CG catalyst under reflux in water (Table 1, Entry 11).
So, the efficiency of this approach was studied in a wide variety of substituted pyranochromene derivatives synthesis under the obtained optimized conditions. Tables 2 and 3 show the summarized results. They reveal the excellent product yields of all reactions and accommodated a wide range of aromatic aldehydes bearing both electron-withdrawing and electron-donating substituents. The pure product in all cases was isolated by simple filtration and washing with water without any purification process.
Recycling of the catalyst
As one of the most important applicability features of catalyst, the reusability of the HPW@Fe3O4–Al2O3–CS–CG catalyst was also studied. In this regard, the catalyst was separated by an external magnet after completing the model reaction and washed several times with acetone. It was recycled to the reaction catalyst for the second or even more reaction runs, and the yields are presented in Tables 2 and 3. The results show that the catalytic performance of HPW@Fe3O4–Al2O3–CS–CG was almost the same as those of fresh catalyst, after 6 runs of reaction (see Fig. 10).
Uniqueness of our protocol
To demonstrate the exclusivity of HPW@Fe3O4–Al2O3–CS–CG, as a heterogeneous catalyst in the synthesis of [1, 3]dioxolo-[4,5-g]-chromene derivatives, the obtained results in the optimized model reaction conditions were compared with the reported ones in the literature, as displayed in Table 4. Evidently, the HPW@Fe3O4–Al2O3–CS–CG is the most efficient catalyst among them in terms of reaction time and yield. Significantly, the reported synthetic paths have some limitations, such as requiring extreme temperature or long duration, large amounts of the catalyst, and most importantly, using hazardous solvents.
Product characterization data39,56
6-Amino-7-cyano-8-Phenyl-8H-[1,3]dioxolo-[4,5-g] chromene (4a):
M.p. 207–210 °C IR (KBr) υmax = 3441, 3349, 3073, 2910, 2184,1656,1630, 1595, 1479, 1352, 1250, 1089, 1035, 811, 763 cm−1. 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6, 500 MHz) δH = 4.66 (s, 1H, H-8), 5.34 (s, 1H, CH-2), 5.93 (s, 1H, CH-2'), 5.96 (s, 1H, Ar), 6.39(s, 1H, CH), 6.56 (s, 1H, CH), 6.81 (s, 2H, NH2), 6.87–6.88 (d, 2H, J = 8.56), 7.09–7.11 (d, 2H, J = 8.56) ppm.
6-Amino-7-cyano-8-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-8H-[1, 3] dioxolo-[4,5-g] chromene (4b):
M.p. 197–201 °C IR (KBr) υmax = 3440, 3341, 3204, 2972, 2180, 1663, 1606, 1507, 1405, 1247, 1179, 1092, 804, 769 cm−1. 1H-NMR (DMSO d6, 500 MHz) δH = 3.72 (s, 3H, CH3), 4.57 (s, 1H, H-8), 5.94 (s, 1H, CH), 6.0007 (s, 1H, CH), 6.50 (s, 1H, CH), 6.66 (s, 1H, CH), 6.81 (s, 2H, NH2), 6.88–6.87 (d, 2H, J = 8.56), 7.09–7.11 (d, 2H, J = 8.56) ppm. 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6, 125 MHz) δ = 41.011, 55.92, 56.88, 98.52, 102.47, 108.20, 114.88, 116.76, 121.44, 129.20, 138.96, 143.49, 144.85, 147.50, 158.97, 161.08 ppm.
6-Amino-7-cyano-8-(3-Nitrophenyl)-8H-[1, 3] dioxolo-[4,5-g] chromene (4c):
M.p. 212–215 °C IR (KBr) υmax = 3440, 3348, 3203, 2906, 2183, 1657, 1630, 1595, 1402, 1250, 1180, 1088, 806, 763 cm−1. 1H-NMR (DMSO d6, 500 MHz) δH = 4.91 (s, 3H, CH3), 5.96 (s, 1H, H-8), 6.021–6.022 (d, 1H, j = 0.72), 6.61 (s, 1H, CH), 6.72(s, 1H, CH), 7.03 (s, 2H, NH2), 7.63–7.69 (m, 2H), 8.05–8.06(m, 1H, Ar), 8.1–8.12 (m, 1H, Ar)ppm. 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6, 125 MHz) δ = 41.005, 55.694, 98.792, 102.667, 108.135, 115.205, 121.095, 122.576, 122.885, 131.293, 135.046, 143.704, 145.145, 148.018, 148.868, 149.0, 161.501 ppm.
6-Amino-7-cyano-8-(4-Methylphenyl)-8H-[1, 3] dioxolo-[4,5-g] chromene (4d):
M.p. 208–211 °C IR (KBr) υmax = 3451, 3335, 3220, 2887, 2193, 1670, 1602, 1502, 1412, 1243, 1184, 1091, 844, 783 cm−1. 1H-NMR (DMSO d6, 500 MHz) δH = 2.26 (s, 3H, CH3), 4.57 (s, 1H, H-8), 5.94 (s, 1H, CH), 6.004 (s, 1H, CH), 6.51 (s, 1H, CH), 6.66 (s, 1H, CH), 6.83 (s, 2H, NH2), 7.06–7.08 (d, 2H, J = 7.65), 7.11–7.13(d, 2H, J = 7.89) ppm. 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6, 125 MHz) δ = 21.45, 41.20, 56.69, 98.54, 102.48, 108.19, 116.59, 121.41, 128.05, 130.05, 136.77, 143.53, 143.92, 144.85, 147.54, 161.17 ppm.
6-Amino-7-cyano-8-(4-Chlorophenyl)-8H-[1,3]dioxolo-[4,5-g] chromene (4e):
M.p. 205–208 °C IR (KBr) υmax = 3449, 3338, 3256, 2887, 2191, 1668, 1600, 1482, 1411, 1244, 1183, 1093, 838, 791 cm−1. 1H-NMR (DMSO d6, 500 MHz) δH = 4.67 (s, 1H, H-8), 5.95 (s, 1H, CH), 6.01 (s, 1H, CH), 6.54 (s, 1H, CH), 6.68(s, 1H, CH), 6.92 (s, 2H, NH2), 7.21–7.22 (d, 2H, J = 8.41), 7.37–7.39(d, 2H, J = 8.41) ppm. 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6, 125 MHz) δ = 56.17, 98.65, 102.57, 108.126, 115.85, 121.25, 129.51, 130.04, 132.29, 143.6, 144.99, 145.79, 147.77, 161.26 ppm.
6-Amino-7-cyano-8-(3-Bromophenyl)-8H-[1, 3]-dioxolo-[4,5-g] chromene (4f.):
M.p. 227–230 °C IR (KBr) υmax = 3449, 3325, 3204, 2894, 2191, 1658, 1595, 1478, 1431, 1249, 1177, 1084, 839, 767 cm−1. 1H-NMR (DMSO d6, 500 MHz) δH = 4.68 (s, 1H, H-8), 5.967–5.969 (d, 1H, CH), 6.021–6.022 (d, 1H, CH), 6.59 (s, 1H, CH), 6.70(s, 1H, CH), 6.96 (s, 2H, NH2), 7.19–7.21 (d, 1H, J = 7.76), 7.28–7.31 (t, 1H, J = 8.41), 7.375–7.379 (d, 1H, J = 1.69), 7.42–7.43 (t, 1H, J = 0.96), 7.44–7.446 (m, 1H) ppm. 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6, 125 MHz) δ = 41.21, 55.97, 98.70, 102.61, 108.09, 115.65, 121.21, 122.78, 127.33, 130.64, 130.73, 131.86, 143.61, 145.04, 147.86, 149.56, 161.39 ppm.
2-Amino-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-3-cyano-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromene-5-one (8b)
IR (KBr) υmax = 3404, 3322,3194, 2202, 1703, 1672, 1531, 1349 cm−1,1HNMR (DMSO-d6,500 MHz): δH = 4.74 (1H, s, H4), 7.44 (1H, d, J = 6.7 Hz), 7.51 (1H, t, J = 7.6 Hz), 7.56 (2H, brs, NH2), 7.64 (1H, t, J = 7.6 Hz), 7.73 (1H, d, J = 7.5, 1.3 Hz), 7.82 (1H, d, J = 6.8 Hz, H2’), 7.92 (1H, dd, J = 6.8), 8.12 (1H, dd, J = 8.4), 8.14 (1H, s, H6’) ppm.
2-Amino-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-3-cyano-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromene-5-one (8c)
IR (KBr):) υmax = 3482,3432, 3371, 3335, 2195, 1718, 1673, 1607, 1506, 1374,1306 cm−1 1HNMR (DMSO-d6,500 MHz): δH = 4.68 (1H, s, H-4), 7.47 (1H,d, J = 8.3 Hz), 7.52 (1H, t, J = 7.7 Hz), 7.57 (2H, bs, NH2), 7.60 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.74 (1H, t, J = 7.8 Hz), 7.91 (1H,d, J = 7.8 Hz), 8.18 (2H, d, J = 8.3 Hz) ppm.
2-Amino-4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-3-cyano-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromene-5-one (8d)
IR (KBr):) υmax = 3463, 3295,3163, 3070, 2198, 1715, 1674, 1590 cm−1; 1HNMR (DMSO-d6,500 MHz): δH = 4.99 (1H, s, H-4), 7.36 (1H, dd,J = 8.3),7.40 (1H, d, J = 8.3 Hz), 7.41 (2H, brs, NH2), 7.46 (1H, d,J = 8.3 Hz), 7.51 (1H, t, J = 7.7 Hz), 7.56 (1H, d, J = 2.1 Hz), 7.73 (1H, t, J = 8.2 Hz), 7.92 (1H, d, J = 8.9 Hz) ppm.
2-Amino-4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-3-cyano-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromene-5-one (8f.)
IR (KBr): ) υmax = 3403, 3294,3179, 2198, 1710, 1672, 1601 cm−1; 1HNMR (DMSO-d6,500 MHz): δH = 5.09 (1H, s, H-4), 7.29–7.35 (2H, m, 7.47–7.55 (5H, m, H7,8,9 &NH2), 7.72–7.75 (1H, m, H6’), 7.92 (1H, dd, J = 7.8) ppm.
Conclusion
In this study, a novel nanocatalyst was successfully prepared by heteropolyacid immobilization of cyanoguanidine modified magnetic chitosan composite and fully characterized by different analysis methods, including FTIR, XRD, TGA, SEM, and EDS. The catalytic activity of fabricated composite was examined in a one-pot three-component reaction, involving the diverse active methylene compounds, various aryl aldehydes, and malononitrile in water. The results revealed the efficient catalytic performance of composite, while all reactions proceeded smoothly and led to the formation of the corresponding pyranochromene derivatives in high to excellent yields.
Data availability
The raw/processed data that supports the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Li, J., Yang, Z., Li, S., Jin, Q. & Zhao, J. Review on oxidative desulfurization of fuel by supported heteropolyacid catalysts. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 82, 1–16 (2020).
Yang, B., Pignatello, J. J., Qu, D. & Xing, B. Reoxidation of photoreduced polyoxotungstate ([PW12O40]4–) by different oxidants in the presence of a model pollutant. Kinetics and reaction mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. A 119, 1055–1065 (2015).
Sadjadi, S., Heravi, M. & M,. Recent advances in applications of POMs and their hybrids in catalysis. Curr. Org. Chem. 20, 1404–1444 (2016).
Heravi, M. M. et al. A novel multi-component synthesis of 4-arylaminoquinazolines. Tetrahedron. Lett. 50, 943–945 (2009).
Narkhede, N., Singh, S. & Patel, A. Recent progress on supported polyoxometalates for biodiesel synthesis via esterification. Green Chem. 17, 89–107 (2015).
da Silva, M. J., Julio, A. A. & Dorigetto, F. C. S. Solvent-free heteropolyacid-catalyzed glycerol ketalization at room temperature. RSC Adv. 5, 44499–44506 (2015).
Zhang, X. et al. High-performance MoC electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction enabled by surface sulfur substitution. ACS Appl. Mater. Int. 13, 40705–40712 (2021).
Ghobakhloo, F., Azarifar, D., Mohammadi, M., Keypour, H. & Zeynali, H. Copper(II) schiff-base complex modified UiO-66-NH2 (Zr) metal-organic framework catalysts for Knoevenagel condensation-Michael addition–cyclization reactions. Inorg. Chem. 61, 4825–4841 (2022).
Liu, T., Zhang, X., Guo, T., Wu, Z. & Wang, D. Boosted hydrogen evolution from α-MoC1-x-MoP/C heterostructures. Electrochim. Acta 334, 135624 (2020).
Ghorbani-Choghamarani, A., Mohammadi, M., Tamoradi, T. & Ghadermazi, M. Covalent immobilization of Co complex on the surface of SBA-15: Green, novel and efficient catalyst for the oxidation of sulfides and synthesis of polyhydroquinoline derivatives in green condition. Polyhedron 158, 25–35 (2019).
Bhat, P. B., Rajarao, R., Sahajwalla, V. & Bhat, B. R. Immobilized magnetic nano catalyst for oxidation of alcohol. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 409, 42–49 (2015).
Daraie, M. & Heravi, M. M. A biocompatible chitosan-ionic liquid hybrid catalyst for regioselective synthesis of 1, 2, 3-triazols. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 140, 939–948 (2019).
Maleki, G., Woltering, E. J. & Mozafaric, M. R. Applications of chitosan-based carrier as an encapsulating agent in food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 120, 88–99 (2022).
Karimi-Maleh, H. et al. Recent advances in using of chitosan-based adsorbents for removal of pharmaceutical contaminants: A review. J. Clean Prod. 291, 125880 (2021).
Gandha, K. et al. Mesoporous iron oxide nanowires: Synthesis, magnetic and photocatalytic properties. RSC Adv. 6(93), 90537–90546 (2016).
Tanhaei, B., Ayati, A., Lahtinen, M. & Sillanpää, M. Preparation and characterization of a novel chitosan/Al2O3/magnetite nanoparticles composite adsorbent for kinetic, thermodynamic and isotherm studies of Methyl Orange adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 259, 1–10 (2015).
Tanhaei, B., Ayati, A., Iakovleva, E. & Sillanpää, M. Efficient carbon interlayed magnetic chitosan adsorbent for anionic dye removal: Synthesis, characterization and adsorption study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 164, 3621–3631 (2020).
Shaikh, N. & Pamidimukkala, P. Magnetic chitosan stabilized palladium nanostructures: Potential catalysts for aqueous Suzuki coupling reactions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 183, 1560–1573 (2021).
Liandi, A. R., Cahyana, A. H., Yunarti, R. T. & Wendari, T. P. Facile synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4@ Chitosan nanocomposite as environmentally green catalyst in multicomponent Knoevenagel-Michael domino reaction. Ceram. Int. 48, 20266–20274 (2022).
Nasrollahzadeh, M., Motahharifar, N., Sajjadi, M., Naserimanesh, A. & Shokouhimehr, M. Functionalization of chitosan by grafting Cu (II)-5-amino-1H-tetrazole complex as a magnetically recyclable catalyst for CN coupling reaction. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 136, 109135 (2022).
Kong, A. et al. One-pot fabrication of magnetically recoverable acid nanocatalyst, heteropolyacids/chitosan/Fe3O4, and its catalytic performance. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 417–418, 183–189 (2012).
Ayati, A. et al. H3PMo12O40 immobilized chitosan/Fe3O4 as a novel efficient, green and recyclable nanocatalyst in the synthesis of pyrano-pyrazole derivatives. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 13, 2301–2308 (2016).
Rahimzadeh, G., Tajbakhsh, M., Daraie, M., & Mohammadi, M. Dysprosium‐balsalazide complex trapped between the functionalized halloysite and g‐C3N4: A novel heterogeneous catalyst for the synthesis of annulated chromenes in water. Appl. Org. Chem. e6829 (2022).
Sadjadi, S., Heravi, M. M. & Daraie, M. A novel hybrid catalytic system based on immobilization of phosphomolybdic acid on ionic liquid decorated cyclodextrin-nanosponges: Efficient catalyst for the green synthesis of benzochromeno-pyrazole through cascade reaction: Triply green. J. Mol. Liquids 231, 98–105 (2017).
Graham, J. G. et al. Antimycobacterial Naphthopyrones from Senna obliqua. J. Nat. Prod. 67, 225–227 (2004).
Morris, J. et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of antiplatelet 2-aminochromones. J. Med. Chem. 36, 2026–2032 (1993).
Ishar, M. P. S., Singh, G., Singh, S., Sreenivasan, K. K. & Singh, G. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of novel 6-chloro-/fluorochromone derivatives as potential topoisomerase inhibitor anticancer agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 16, 1366–1370 (2006).
Daraie, M. et al. Lanthanoid-containing polyoxometalate nanocatalysts in the synthesis of bioactive isatin-based compounds. Sci. Rep. 12, 1–18 (2022).
Daraie, M., Heravi, M. M., Mirzaei, M. & Lotfian, N. Synthesis of Pyrazolo-[4́,3́:5,6] pyrido [2,3-d] pyrimidine-diones catalyzed by a nano-sized surface-grafted neodymium complex of the tungstosilicate via multicomponent reaction. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 33, e5058 (2019).
Lotfian, N., Heravi, M. M., Mirzaei, M. & Daraie, M. Investigation of the uncommon basic properties of [Ln(W5O18)2]9– (Ln= La, Ce, Nd, Gd, Tb) by changing central lanthanoids in the syntheses of pyrazolopyranopyrimidines. J. Mol. Struct. 1199, 126953 (2020).
Esfandyari, M. et al. H3PW12O40: An efficient and green catalyst for the facile and selective oxidation of sulfides to sulfoxides, applied to the last step of the synthesis of omeprazole. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. (IJCCE) 36, 21–29 (2017).
Tajbakhsh, M., Hosseinzadeh, R., Rezaee, P. & Tajbakhsh, M. H3PW12O40 catalyzed synthesis of benzoxazine and quinazoline in aqueous media. Chin. J. Catal. 35, 58–65 (2014).
Habibzadeh, S., Firouzzadeh Pasha, G., Tajbakhsh, M., Amiri Andi, N. & Alaee, E. A novel ternary GO@SiO2-HPW nanocomposite as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for the synthesis of benzazoles in aqueous media. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 66, 934–944 (2019).
Sadjadi, S., Heravi, M. M. & Daraie, M. Heteropolyacid supported on amine-functionalized halloysite nano clay as an efficient catalyst for the synthesis of pyrazolopyranopyrimidines via four-component domino reaction. Res. Chem. Intermed. 43, 2201–2214 (2017).
Sadjadi, S., Heravi, M. M. & Daraie, M. Cyclodextrin nanosponges: A potential catalyst and catalyst support for synthesis of xanthenes. Res. Chem. Intermed. 43, 843–857 (2017).
Germaninezhad, F., Hosseinzadeh, R., Tajbakhsh, M. & Beitollahi, A. Copper ferrite nanoparticles: An effective and recoverable nanomagnetic catalyst for the synthesis of N, N′, N ″-trisubstituted guanidines from the addition reaction of anilines to carbodiimide. Micro Nano Lett. 15, 359–364 (2020).
Daraie, M., Heravi, M. M. & Kazemi, S. S. Pd@ GO/Fe3O4/PAA/DCA: A novel magnetic heterogeneous catalyst for promoting the Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction. J. Coord. Chem. 72, 2279–2293 (2019).
Hossiennejad, T., Daraie, M., Heravi, M. & Tajoddin, N. N. Computational and experimental investigation of immobilization of cui nanoparticles on 3-aminopyridine modified poly (styrene-co-maleic anhydride) and its catalytic application in regioselective synthesis of 1, 2, 3-triazoles. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mat. 27, 861–870 (2017).
Lasemi, Z., Tajbakhsh, M., Alinezhad, H. & Mehrparvar, F. 1, 8-Diazabicyclo [5.4.0] undec-7-ene functionalized cellulose nanofibers as an efficient and reusable nanocatalyst for the synthesis of tetraketones in aqueous medium. Res. Chem. Intermed. 46, 3667–3682 (2020).
Asl, S. M. H., Masomi, M. & Tajbakhsh, M. Hybrid adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems for forecasting benzene, toluene & m-xylene removal from aqueous solutions by HZSM-5 nano-zeolite synthesized from coal fly ash. J. Clean. Prod. 258, 120688 (2020).
Orooji, Y., Pakzad, K., Nasrollahzadeh, M. & Tajbakhsh, M. Novel magnetic lignosulfonate-supported Pd complex as an efficient nanocatalyst for N-arylation of 4-methylbenzenesulfonamide. Int. J. Biolog. Macromol. 182, 564–573 (2021).
Hosseinzadeh, R., Mavvaji, M., Tajbakhsh, M., Lasemi, Z. & Aghili, N. Selective oxidation of hydrocarbons and alcohols using Phen-MCM-41 as an efficient co-catalyst in combination with NHPI-based nano-magnetic catalyst. Org. Prep. Proced. Int. 52, 99–109 (2020).
Tajbakhsh, M. et al. Carbon-heteroatom bond formation via coupling reactions performed on a magnetic nanoparticle bed. Appl. Chem 1, 75–89 (2021).
Daraie, M., Heravi, M. M., Mohammadi, P. & Daraie, A. Silver incorporated into g-C3N4/Alginate as an efficient and heterogeneous catalyst for promoting click and A3 and KA2 coupling reaction. Sci. Rep. 11, 1–13 (2021).
Mohammadi, P., Heravi, M. & Daraie, M. Ag nanoparticles immobilized on new magnetic alginate halloysite as a recoverable catalyst for reduction of nitroaromatics in aqueous media. Sci. Rep. 11, 1–10 (2021).
Daraie, M., Tamoradi, T., Heravi, M. M. & Karmakar, B. Ce immobilized 1H-pyrazole-3, 5-dicarboxylic acid (PDA) modified CoFe2O4: A potential magnetic nanocomposite catalyst towards the synthesis of diverse benzo [a] pyrano [2,3-c] phenazine derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. 1245, 131089 (2021).
Tamoradi, T., Daraie, M., Heravi, M. M. & Karmakar, B. Erbium anchored iminodiacetic acid (IDA) functionalized CoFe2O4 nano particles: An efficient magnetically isolable nanocomposite for the facile synthesis of 1, 8-naphthyridines. New J. Chem. 44, 11049–11055 (2020).
Karimi, F. et al. Removal of metal ions using a new magnetic chitosan nano-bio-adsorbent; A powerful approach in water treatment. Environ. Res. 203, 111753 (2022).
Pisanic, T. R., Blackwell, J. D., Shubayev, V. I., Fiñones, R. R. & Jin, S. Nanotoxicity of iron oxide nanoparticle internalization in growing neurons. Biomaterials 28, 2572–2581 (2007).
Giakisikli, G. & Anthemidis, A. N. Magnetic materials as sorbents for metal/metalloid preconcentration and/or separation. A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 789, 1–16 (2013).
Ghorbani-Choghamarani, A., Mohammadi, M., Hudson, R. H. E. & Tamoradi, T. Boehmite@tryptophan-Pd nanoparticles: A new catalyst for C-C bond formation. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 33, e4977 (2019).
Lei, Z., Pang, X., Li, N., Lin, L. & Li, Y. A novel two-step modifying process for preparation of chitosan-coated Fe3O4/SiO2 microspheres. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209, 3218–3225 (2009).
Monier, M., Ayad, D. M., Wei, Y. & Sarhan, A. A. Preparation and characterization of magnetic chelating resin based on chitosan for adsorption of Cu(II), Co(II), and Ni(II) ions. React. Funct. Polym. 70, 257–266 (2010).
Zhang, L. et al. H3PW12O40 immobilized on silylated palygorskite and catalytic activity in esterification reactions. Appl. Clay Sci. 47, 229–234 (2010).
Heravi, M. M. & Daraie, M. Heterogeneous catalytic three-component one-pot synthesis of novel 8H-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]chromenes by basic alumina in water. Monatshefte Chem. Chem. Mon. 145, 1479–1482 (2014).
Heravi, M. M. & Daraie, M. Mn(pbdo)2Cl2/MCM-41 as a green catalyst in multi-component syntheses of some heterocycles. Res. Chem. Intermed. 42, 2979–2988 (2016).
Álvarez-Toledano, C. et al. Three-component synthesis of 2-Amino-3-cyano-4H-chromenes, In Silico analysis of their pharmacological profile, and in vitro anticancer and antifungal testing. Pharmaceuticals 14, 1110 (2021).
Abdolmohammadi, S. R., Rasouli Nasrabadi, M. R., Dabiri, S. M. & Banihashemi, S. M. TiO2 nanoparticles immobilized on carbon nanotubes: An efficient heterogeneous catalyst in cyclocondensation reaction of Isatins with Malononitrile and 4-Hydroxycoumarin or 3,4-Methylenedioxyphenol under Mild Reaction Conditions. Appl. Organometal Chem. 34, e5462 (2020).
Roberto, B. et al. Three-component process for the synthesis of 2-amino-2-chromenes in aqueous media. Tetrahedron 57(1395), 1398 (2001).
Shestopalov, A. M. et al. Polyalkoxy substituted 4H-Chromenes: Synthesis by Domino reaction and anticancer activity. ACS Comb. Sci. 14, 484–490 (2012).
Acknowledgements
G. Rahimzadeh and M. Tajbakhsh are grateful to Iran National Science Foundation (INSF) for the financial support provided by the post-doctoral project (98012096). We also appreciate University of Mazandaran Research Council for their help and supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.R.: Methodology, Funding acquisition, Investigation; M.T.: Conceptualization, Supervision, Main idea, Writing-review and editing, Project administration, Visualization. M.D.: Conceptualization, Supervision, Main idea, Software, Data curation, Writing-original draft preparation. A.A.: Experimental work, Formal analysis, Writing-original draft preparation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Rahimzadeh, G., Tajbakhsh, M., Daraie, M. et al. Heteropolyacid coupled with cyanoguanidine decorated magnetic chitosan as an efficient catalyst for the synthesis of pyranochromene derivatives. Sci Rep 12, 17027 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-21196-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-21196-2
This article is cited by
-
Advanced adsorbents for ibuprofen removal from aquatic environments: a review
Environmental Chemistry Letters (2024)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.