Featured
-
-
Letter |
 An evolutionarily conserved ribosome-rescue pathway maintains epidermal homeostasis
An evolutionarily conserved ribosome-rescue pathway maintains epidermal homeostasis
Loss of the ribosome-rescue factor Pelo in a subset of mouse epidermal stem cells results in hyperproliferation and altered differentiation of these cells.
- Kifayathullah Liakath-Ali
- , Eric W. Mills
- & Fiona M. Watt
-
Letter |
 Vms1 and ANKZF1 peptidyl-tRNA hydrolases release nascent chains from stalled ribosomes
Vms1 and ANKZF1 peptidyl-tRNA hydrolases release nascent chains from stalled ribosomes
The Cdc48 adaptor Vms1 is a peptidyl-tRNA hydrolase that cooperates with the ribosome quality control complex to catalyse the removal of nascent polypeptides from stalled ribosomes.
- Rati Verma
- , Kurt M. Reichermeier
- & Raymond J. Deshaies
-
Letter |
 Mitochondrial translation requires folate-dependent tRNA methylation
Mitochondrial translation requires folate-dependent tRNA methylation
Mammalian mitochondria use folate-bound one-carbon units generated by the enzyme SHMT2 to methylate tRNA, and this modification is required for mitochondrial translation and thus oxidative phosphorylation.
- Raphael J. Morscher
- , Gregory S. Ducker
- & Joshua D. Rabinowitz
-
Letter |
 AMD1 mRNA employs ribosome stalling as a mechanism for molecular memory formation
AMD1 mRNA employs ribosome stalling as a mechanism for molecular memory formation
A regulatory mechanism that limits the number of complete protein molecules that can be synthesized from a single mRNA molecule of the human AMD1 gene encoding adenosylmethionine decarboxylase 1.
- Martina M. Yordanova
- , Gary Loughran
- & Pavel V. Baranov
-
Article |
 Visualization of chemical modifications in the human 80S ribosome structure
Visualization of chemical modifications in the human 80S ribosome structure
A high-resolution structure of the human ribosome determined by cryo-electron microscopy visualizes numerous RNA modifications that are concentrated at functional sites with an extended shell, and suggests the possibility of designing more specific ribosome-targeting drugs.
- S. Kundhavai Natchiar
- , Alexander G. Myasnikov
- & Bruno P. Klaholz
-
Review Article |
 Expanding and reprogramming the genetic code
Expanding and reprogramming the genetic code
A review of the recent developments in reprogramming the genetic code of cells and organisms to include non-canonical amino acids in precisely engineered proteins.
- Jason W. Chin
-
Analysis |
 Ribosomes are optimized for autocatalytic production
Ribosomes are optimized for autocatalytic production
The large number of small, similarly sized proteins and the small number of heavy RNA molecules that make up a ribosome reduce the time required for reproduction.
- Shlomi Reuveni
- , Måns Ehrenberg
- & Johan Paulsson
-
Letter |
 Trans-kingdom mimicry underlies ribosome customization by a poxvirus kinase
Trans-kingdom mimicry underlies ribosome customization by a poxvirus kinase
The poxvirus vaccinia virus phosphorylates serine/threonine residues in the human small ribosomal subunit RACK1, converting it to a plant-like state to favour translation of poxvirus mRNAs
- Sujata Jha
- , Madeline G. Rollins
- & Derek Walsh
-
Article |
 Ensemble cryo-EM elucidates the mechanism of translation fidelity
Ensemble cryo-EM elucidates the mechanism of translation fidelity
Structural ensembles of the 70S ribosome bound to cognate or near-cognate charged tRNAs in complex with EF-Tu illustrate the crucial role of the nucleotide G530 in decoding of mRNA, and demonstrate that translational fidelity results from direct control of GTPase by the decoding centre.
- Anna B. Loveland
- , Gabriel Demo
- & Andrei A. Korostelev
-
Letter |
 Structural basis of co-translational quality control by ArfA and RF2 bound to ribosome
Structural basis of co-translational quality control by ArfA and RF2 bound to ribosome
The structure of the bacterial ribosome in complex with the ArfA and the release factor RF2 shows how ArfA recruits RF2 to terminate translation of messenger RNAs that lack a stop codon in the ribosome.
- Fuxing Zeng
- , Yanbo Chen
- & Hong Jin
-
Letter |
 Mechanistic insights into the alternative translation termination by ArfA and RF2
Mechanistic insights into the alternative translation termination by ArfA and RF2
The structure of the bacterial 70S ribosome in complex with ArfA, the release factor RF2, a short non-stop mRNA and a cognate P-site tRNA is presented, revealing how ArfA and RF2 facilitate alternative translation termination of the non-stop ribosomal complex using a stop-codon surrogate mechanism.
- Chengying Ma
- , Daisuke Kurita
- & Ning Gao
-
Letter |
 Structural basis for ArfA–RF2-mediated translation termination on mRNAs lacking stop codons
Structural basis for ArfA–RF2-mediated translation termination on mRNAs lacking stop codons
The structure of the bacterial ribosome stalled on a truncated mRNA in complex with ArfA and the release factor RF2 is presented, revealing how ArfA recruits RF2 to the ribosome and induces conformational changes within RF2 to enable translation termination in the absence of a stop codon.
- Paul Huter
- , Claudia Müller
- & Daniel N. Wilson
-
Article |
 The pathway to GTPase activation of elongation factor SelB on the ribosome
The pathway to GTPase activation of elongation factor SelB on the ribosome
The structures of several states on the pathway of SelB-mediated delivery of selenocysteine-specific tRNA to the ribosome in Escherichia coli reveal the mechanism of UGA stop codon recoding to selenocysteine and show how codon recognition triggers activation of translational GTPases.
- Niels Fischer
- , Piotr Neumann
- & Holger Stark
-
Letter |
 Olfactory receptor pseudo-pseudogenes
Olfactory receptor pseudo-pseudogenes
Drosophila sechellia, a species closely related to the model species Drosophila melanogaster, bypasses a premature stop codon in neuronal cells to express a functional olfactory receptor protein from an assumed pseudogene template.
- Lucia L. Prieto-Godino
- , Raphael Rytz
- & Richard Benton
-
Letter |
 Cotranslational signal-independent SRP preloading during membrane targeting
Cotranslational signal-independent SRP preloading during membrane targeting
The signal recognition particle (SRP) preferentially binds peptides destined for secretion before peptide-targeting signals are translated through recognition of elements in their mRNA, including non-coding sequences.
- Justin W. Chartron
- , Katherine C. L. Hunt
- & Judith Frydman
-
Letter |
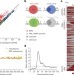 Global profiling of SRP interaction with nascent polypeptides
Global profiling of SRP interaction with nascent polypeptides
Here, the selection of substrates by the protein–RNA complex known as the signal recognition particle (SRP) is investigated in the bacterium Escherichia coli, revealing that the SRP has a strong preference for hydrophobic transmembrane domains of inner membrane proteins.
- Daniela Schibich
- , Felix Gloge
- & Günter Kramer
-
Letter |
 eIF3d is an mRNA cap-binding protein that is required for specialized translation initiation
eIF3d is an mRNA cap-binding protein that is required for specialized translation initiation
The initiation protein eIF3d serves as an alternative cap-recognition factor for a subclass of mRNAs, such as c-Jun; the high-resolution structure of the eIF3d cap-binding domain can be modelled onto the cap structure, defining interactions that are needed for translation of these mRNAs.
- Amy S. Y. Lee
- , Philip J. Kranzusch
- & Jamie H. D. Cate
-
Letter |
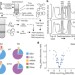 Dynamics of ribosome scanning and recycling revealed by translation complex profiling
Dynamics of ribosome scanning and recycling revealed by translation complex profiling
A translation complex sequencing approach has been developed enabling intermediates of all mRNA-associated processes of translation to be isolated and localized across the transcriptome; the results support longstanding models of initiation and termination and offer new mechanistic insights.
- Stuart K. Archer
- , Nikolay E. Shirokikh
- & Thomas Preiss
-
Letter |
 Rocaglates convert DEAD-box protein eIF4A into a sequence-selective translational repressor
Rocaglates convert DEAD-box protein eIF4A into a sequence-selective translational repressor
The cancer drug rocaglamide A cements the RNA helicase eIF4A on polypurine sequences and thereby prevents scanning of the 43S subunit along the messenger RNA, highlighting how a drug can act by stabilizing sequence-selective RNA–protein interactions.
- Shintaro Iwasaki
- , Stephen N. Floor
- & Nicholas T. Ingolia
-
Letter |
 Translation readthrough mitigation
Translation readthrough mitigation
Translation termination sequences are occasionally bypassed by the ribosome and the resulting proteins can be detrimental to the cell; here it is shown that cells can prevent such proteins from accumulating through peptides that are encoded within the 3' UTR of genes in both humans and C. elegans.
- Joshua A. Arribere
- , Elif S. Cenik
- & Andrew Z. Fire
-
Letter |
 Diverse roles of assembly factors revealed by structures of late nuclear pre-60S ribosomes
Diverse roles of assembly factors revealed by structures of late nuclear pre-60S ribosomes
The cryo-electron microscopy structures of yeast nucleoplasmic pre-60S ribosomal particles give insight into the function of multiple assembly factors in ribosome biogenesis.
- Shan Wu
- , Beril Tutuncuoglu
- & Ning Gao
-
Article |
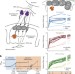 Synchronized mitochondrial and cytosolic translation programs
Synchronized mitochondrial and cytosolic translation programs
The genes encoding the subunits of oxidative phosphorylation complexes are split between the nuclear and mitochondrial genomes, but their translation is synchronized by signalling from the cytosol to the mitochondria.
- Mary T. Couvillion
- , Iliana C. Soto
- & L. Stirling Churchman
-
Letter |
 Ribosome-dependent activation of stringent control
Ribosome-dependent activation of stringent control
The structure of a bacterial ribosome–RelA complex reveals that RelA, a protein recruited to the ribosome in the case of scarce amino acids, binds in a different location to translation factors, and that this binding event suppresses auto-inhibition to activate synthesis of the (p)ppGpp secondary messenger, thus initiating stringent control.
- Alan Brown
- , Israel S. Fernández
- & V. Ramakrishnan
-
Letter |
 Musashi-2 attenuates AHR signalling to expand human haematopoietic stem cells
Musashi-2 attenuates AHR signalling to expand human haematopoietic stem cells
The RNA-binding protein Musashi-2 increases the self-renewing abilities of human haematopoietic stem cells, which have the potential to be used for regenerative therapies.
- Stefan Rentas
- , Nicholas T. Holzapfel
- & Kristin J. Hope
-
Article |
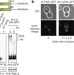 Failure of RQC machinery causes protein aggregation and proteotoxic stress
Failure of RQC machinery causes protein aggregation and proteotoxic stress
Defects in the ribosome quality control (RQC) complex, which clears proteins that stalled during translation, can cause neurodegeneration; here it is shown that in RQC-defective cells a peptide tail added by the RQC subunit 2 to stalled polypeptides promotes their aggregation and the sequestration of chaperones in these aggregates, affecting normal protein quality control processes.
- Young-Jun Choe
- , Sae-Hun Park
- & F. Ulrich Hartl
-
Letter |
 Crystal structure of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B
Crystal structure of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B
The crystal structure of Schizosaccharomyces pombe guanine nucleotide exchange factor eIF2B, providing a structural framework for the eIF2B-mediated mechanism of stress-induced translational control.
- Kazuhiro Kashiwagi
- , Mari Takahashi
- & Shigeyuki Yokoyama
-
Letter |
 Tumour-specific proline vulnerability uncovered by differential ribosome codon reading
Tumour-specific proline vulnerability uncovered by differential ribosome codon reading
Tumours can require certain amino acids for their proliferation, and the diricore method described here helps to identify such restrictive amino acids; using this method in kidney cancer tissue and breast carcinoma cells, the authors observe an association between proline deficiency and upregulation of PYCR1, an enzyme required for proline synthesis.
- Fabricio Loayza-Puch
- , Koos Rooijers
- & Reuven Agami
-
Article |
 Codon influence on protein expression in E. coli correlates with mRNA levels
Codon influence on protein expression in E. coli correlates with mRNA levels
In-depth analyses of protein expression studies are used to derive a new codon-influence metric that correlates with global protein levels, mRNA levels and mRNA lifetimes in vivo, indicating tight coupling between translation efficiency and mRNA stability; genes redesigned based on these analyses consistently yield high protein expression levels both in vivo and in vitro.
- Grégory Boël
- , Reka Letso
- & John F. Hunt
-
Letter |
 Dynamic m6A mRNA methylation directs translational control of heat shock response
Dynamic m6A mRNA methylation directs translational control of heat shock response
Under stress, such as heat shock, the N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification is shown to accumulate primarily in the 5′ untranslated region of induced mRNAs owing to the translocation of an m6A interacting protein, YTHDF2, into the nucleus, resulting in increased cap-independent translation of these mRNAs, indicating one possible mechanism by which stress-responsive genes can be preferentially expressed.
- Jun Zhou
- , Ji Wan
- & Shu-Bing Qian
-
Article |
 Structure of mammalian eIF3 in the context of the 43S preinitiation complex
Structure of mammalian eIF3 in the context of the 43S preinitiation complex
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of the eukaryotic initiation factor 3 (eIF3) within the larger 43S complex is determined; the improved resolution enables visualization of the secondary structures of the subunits, as well as the contacts between eIF3 and both eIF2 and DHX29.
- Amedee des Georges
- , Vidya Dhote
- & Yaser Hashem
-
Letter |
 Structural basis for stop codon recognition in eukaryotes
Structural basis for stop codon recognition in eukaryotes
All eukaryotes utilize a single termination factor, eRF1, to halt translation when the ribosome encounters one of three possible stop codons; here electron cryo-microscopy structures of ribosome–eRF1 complexes in the process of recognizing each stop codon reveal how stop codons are discriminated from sense codons.
- Alan Brown
- , Sichen Shao
- & V. Ramakrishnan
-
Letter |
 Protein synthesis by ribosomes with tethered subunits
Protein synthesis by ribosomes with tethered subunits
A ribosome with tethered subunits, ‘Ribo-T’, is engineered by making a hybrid RNA composed of ribosomal RNA of large and small subunits; Ribo-T can support cell growth in vivo in the absence of wild-type ribosomes, and is used to establish a fully orthogonal ribosome–mRNA system.
- Cédric Orelle
- , Erik D. Carlson
- & Alexander S. Mankin
-
Article |
 Structure of the human 80S ribosome
Structure of the human 80S ribosome
The structure of the human ribosome at high resolution has been solved; by combining single-particle cryo-EM and atomic model building, local resolution of 2.9 Å was achieved within the most stable areas of the structure.
- Heena Khatter
- , Alexander G. Myasnikov
- & Bruno P. Klaholz
-
Letter |
 eIF3 targets cell-proliferation messenger RNAs for translational activation or repression
eIF3 targets cell-proliferation messenger RNAs for translational activation or repression
Eukaryotic initiation factor 3 (eIF3)—the deregulation of which has been linked with diverse cancers—is shown to bind to and direct the specialized translation of a subset of messenger RNAs, primarily involved in cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis, and can exert either translational activation or repression.
- Amy S. Y. Lee
- , Philip J. Kranzusch
- & Jamie H. D. Cate
-
Letter |
 Structure of the E. coli ribosome–EF-Tu complex at <3 Å resolution by Cs-corrected cryo-EM
Structure of the E. coli ribosome–EF-Tu complex at <3 Å resolution by Cs-corrected cryo-EM
A single particle cryo-EM structure of the 70S ribosome in complex with the elongation factor Tu breaks the 3 Å resolution barrier of the technique and locally exceeds the resolution of previous crystallographic studies, revealing all modifications in rRNA and explaining their roles in ribosome function and antibiotic binding.
- Niels Fischer
- , Piotr Neumann
- & Holger Stark
-
Letter |
 NIK1-mediated translation suppression functions as a plant antiviral immunity mechanism
NIK1-mediated translation suppression functions as a plant antiviral immunity mechanism
A new mechanism that plants use to combat begomoviruses—one of the most pathogenic groups of plant viruses, causing severe disease in major crops worldwide—is uncovered: plants inhibit the transcription of genes associated with the translational apparatus, thus causing a general reduction in protein synthesis.
- Cristiane Zorzatto
- , João Paulo B. Machado
- & Elizabeth P. B. Fontes
-
Letter |
 Initiation of translation in bacteria by a structured eukaryotic IRES RNA
Initiation of translation in bacteria by a structured eukaryotic IRES RNA
A eukaryotic viral internal ribosome entry site (IRES) element is described that binds both bacterial and eukaryotic ribosomes and initiates translation in both, demonstrating that RNA structure-based initiation can occur in both these domains of life, although in bacteria the element uses a mechanism that differs from that in eukaryotes.
- Timothy M. Colussi
- , David A. Costantino
- & Jeffrey S. Kieft
-
Article |
 RNA regulons in Hox 5′ UTRs confer ribosome specificity to gene regulation
RNA regulons in Hox 5′ UTRs confer ribosome specificity to gene regulation
Specialized ribosomes (with a particular protein composition) carry out translation of specific transcripts; analysis of Hox mRNA translation in mice reveals that unique RNA structural elements within their 5′ UTRs, including internal ribosome entry sites and translation inhibitory elements, are responsible for this specialized mode of translation.
- Shifeng Xue
- , Siqi Tian
- & Maria Barna
-
Letter |
 mTORC1-mediated translational elongation limits intestinal tumour initiation and growth
mTORC1-mediated translational elongation limits intestinal tumour initiation and growth
The mTORC1 complex has been implicated in tumorigenesis owing partially to its ability to increase protein translation; now, mTORC1 activity in the mouse intestine is shown not to be required for normal homeostasis but to be necessary for the triggering of tumorigenesis by APC mutations, suggesting that it could be a good target for the prevention of colorectal cancer in high-risk patients.
- William J. Faller
- , Thomas J. Jackson
- & Owen J. Sansom
-
Letter |
 The complete structure of the large subunit of the mammalian mitochondrial ribosome
The complete structure of the large subunit of the mammalian mitochondrial ribosome
The structure of the 39S large mitoribosome subunit is solved by cryo-electron microscopy at an impressive 3.4 Å resolution, revealing the location of 50 ribosomal proteins, the peptidyl transferase centre, the tRNAs within this active site, and the nascent peptide chain within the exit tunnel.
- Basil J. Greber
- , Daniel Boehringer
- & Nenad Ban
-
Article |
 Structural basis for the inhibition of the eukaryotic ribosome
Structural basis for the inhibition of the eukaryotic ribosome
Whereas previous structural investigation of ribosome inhibitors has been done using the prokaryotic ribosome, this work presents X-ray crystal structures of the yeast ribosome in complex with 16 inhibitors including eukaryotic-specific inhibitors; the inhibitors all bind the mRNA or tRNA binding sites, larger molecules appear to target specifically the first elongation cycle.
- Nicolas Garreau de Loubresse
- , Irina Prokhorova
- & Marat Yusupov
-
Letter |
 Structural basis for the assembly of the Sxl–Unr translation regulatory complex
Structural basis for the assembly of the Sxl–Unr translation regulatory complex
The crystal structure of the RNA binding domains of Sxl and Unr with msl2 RNA shows that interwoven interactions establish cooperative assembly of the ternary complex, highlighting how binding of relatively general RNA binding domains to RNA can result in a unique and specific protein–RNA architecture.
- Janosch Hennig
- , Cristina Militti
- & Michael Sattler
-
Letter |
 Promoter sequences direct cytoplasmic localization and translation of mRNAs during starvation in yeast
Promoter sequences direct cytoplasmic localization and translation of mRNAs during starvation in yeast
Transcription and translation are generally thought of as disconnected processes in eukaryotes; however, under starvation conditions in yeast, the promoter sequence influences not only messenger RNA levels but also several processes downstream of transcription, including the localization of mRNA within the cytoplasm and the translation rate of mRNA.
- Brian M. Zid
- & Erin K. O’Shea
-
Letter |
 DENR–MCT-1 promotes translation re-initiation downstream of uORFs to control tissue growth
DENR–MCT-1 promotes translation re-initiation downstream of uORFs to control tissue growth
This study identifies the DENR–MCT-1 complex as the first factors in animals specific for translation re-initiation downstream of upstream Open Reading Frames (uORFs).
- Sibylle Schleich
- , Katrin Strassburger
- & Aurelio A. Teleman
-
Letter |
 Dynamic pathways of −1 translational frameshifting
Dynamic pathways of −1 translational frameshifting
To investigate the mechanism of frameshifting during messenger RNA translation, a technique was developed to monitor translation of single molecules in real time using Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET); ribosomes were revealed to pause tenfold longer than usual during elongation at the frameshifting sites.
- Jin Chen
- , Alexey Petrov
- & Joseph D. Puglisi
-
Article |
 The selective tRNA aminoacylation mechanism based on a single G•U pair
The selective tRNA aminoacylation mechanism based on a single G•U pair
X-ray crystal structures of a tRNA synthetase bound to wild-type and mutant alanine tRNAs reveal the structural basis for selectivity.
- Masahiro Naganuma
- , Shun-ichi Sekine
- & Shigeyuki Yokoyama
-
Letter |
 Analysis of orthologous groups reveals archease and DDX1 as tRNA splicing factors
Analysis of orthologous groups reveals archease and DDX1 as tRNA splicing factors
Using a phylogenetic approach, the protein archease is identified as being a subunit of the human transfer RNA splicing ligase, and found to be necessary for full ligase activity, in cooperation with DDX1.
- Johannes Popow
- , Jennifer Jurkin
- & Javier Martinez
-
Article |
 Structural basis of the non-coding RNA RsmZ acting as a protein sponge
Structural basis of the non-coding RNA RsmZ acting as a protein sponge
A novel combined NMR and EPR spectroscopy approach reveals the structure and assembly mechanism of a 70-kDa bacterial ribonucleoprotein complex acting as a protein sponge in translational regulation.
- Olivier Duss
- , Erich Michel
- & Frédéric H.-T. Allain
-
Article |
 Poly(A)-tail profiling reveals an embryonic switch in translational control
Poly(A)-tail profiling reveals an embryonic switch in translational control
A new high-throughput sequencing method to determine mRNA poly(A)-tail length enabled studies of individual RNAs across species and developmental stages to investigate the role of poly(A) length in translational regulation; the relationship between poly(A) length and translational efficiency shown in early embryo systems does not occur later in development, a finding that explains different regulatory consequences of microRNAs acting at different developmental times.
- Alexander O. Subtelny
- , Stephen W. Eichhorn
- & David P. Bartel

 ANKRD16 prevents neuron loss caused by an editing-defective tRNA synthetase
ANKRD16 prevents neuron loss caused by an editing-defective tRNA synthetase