Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Comment
| Open Access BerkSEL: A scale-invariant laser beyond the Schawlow-Townes two-mirror strategy
BerkSEL: A scale-invariant laser beyond the Schawlow-Townes two-mirror strategy
I argue that a surface emitting laser that remains single mode irrespective of its size, a scale-invariant laser, should of necessity also waste light at the edge. This is a fundamental departure from the Schawlow-Townes two-mirror strategy that keeps light away from mirrors and edges to preserve gain and minimize loss. The strategy was implemented in the recent discovery of the Berkeley Surface Emitting Laser (BerkSEL).
- Boubacar Kanté
-
Article
| Open Access Modulation-free laser stabilization technique using integrated cavity-coupled Mach-Zehnder interferometer
Modulation-free laser stabilization technique using integrated cavity-coupled Mach-Zehnder interferometer
Stable lasers are crucial in many applications like sensing. Here, the authors demonstrate a laser frequency locking method that maintains performance, eliminates modulation, simplifies architecture, and enables miniaturization on a photonic chip.
- Mohamad Hossein Idjadi
- , Kwangwoong Kim
- & Nicolas K. Fontaine
-
Article
| Open Access Antireflective vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser for LiDAR
Antireflective vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser for LiDAR
The authors showcase an innovative anti-reflective vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (AR-VCSEL) that achieves low divergence and maintains a single-mode lasing. The 6-junction AR-VCSEL array demonstrates low divergence from 8° to 16° (D86) and tripled brightness compared to conventional counterparts. The AR-VCSEL offers an excellent avenue for long-distance LiDARs.
- Cheng Zhang
- , Huijie Li
- & Dong Liang
-
Article
| Open Access Spatio-spectral 4D coherent ranging using a flutter-wavelength-swept laser
Spatio-spectral 4D coherent ranging using a flutter-wavelength-swept laser
Solid-state spatio-spectral coherent light detection and ranging system is proposed based on flutter-wavelength-swept laser for real-time four-dimensional coherent imaging over extended measurable distance even in challenging environments.
- Dawoon Jeong
- , Hansol Jang
- & Chang-Seok Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Perovskite quantum dot one-dimensional topological laser
Perovskite quantum dot one-dimensional topological laser
Topological lasers often suffer from low directionality, and/or complex design requirements hindering operation at small wavelengths. Here, by using a few monolayers of perovskite quantum dots, the authors demonstrate a lithography-free, vertical-emitting, single-mode laser emitting in the green.
- Jingyi Tian
- , Qi Ying Tan
- & Cesare Soci
-
Article
| Open Access Photonic Majorana quantum cascade laser with polarization-winding emission
Photonic Majorana quantum cascade laser with polarization-winding emission
THz integrate light sources represent an important building blocks for various applications. Here the authors report an electrically driven topological laser based on photonic Majorana zero mode that can convert electricity directly into THz single-mode laser with topologically nontrivial beams.
- Song Han
- , Yunda Chua
- & Qi Jie Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Self-evolving photonic crystals for ultrafast photonics
Self-evolving photonic crystals for ultrafast photonics
Generation and control of short pulse is desired for ultrafast applications. Here the authors demonstrate ultrafast pulse generation using self-evolving photonic crystal that can transition from high loss to low loss state based on dynamic dispersion compensation.
- Takuya Inoue
- , Ryohei Morita
- & Susumu Noda
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-decoupling of vertical cavity surface-emitting lasers with complete phase modulation using on-chip integrated Jones matrix metasurfaces
Spin-decoupling of vertical cavity surface-emitting lasers with complete phase modulation using on-chip integrated Jones matrix metasurfaces
Here the authors harness the on-chip integration of Jones matrix metasurfaces to demonstrate an ultra-compact approach to access and manipulate the optical spin states of vertical cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs) with previously unattainable phase controllability.
- Pei-Nan Ni
- , Pan Fu
- & Patrice Genevet
-
Article
| Open Access Chip-scale high-peak-power semiconductor/solid-state vertically integrated laser
Chip-scale high-peak-power semiconductor/solid-state vertically integrated laser
Here the authors demonstrate chip-scale high-peak-power lasers by vertical integration of semiconductor and solid state laser gain mediums to reach the same maturity level as existing semiconductor lasers, which are suitable for miniaturization and cost-effective mass production.
- Jianglin Yue
- , Kenji Tanaka
- & Masanao Kamata
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated Pockels laser
Integrated Pockels laser
On-Chip integration of laser systems led to impressive development in many field of application like LIDAR or AR/VR to cite a few. Here the authors harness Pockels effect in an integrated semiconductor platform achieving fast on-chip configurability of a narrow linewidth laser.
- Mingxiao Li
- , Lin Chang
- & Qiang Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial tomography of light resolved in time, spectrum, and polarisation
Spatial tomography of light resolved in time, spectrum, and polarisation
The work harnesses principles of spatial state tomography to fully characterise an optical beam in space, time, spectrum, and polarisation. Analysis of the output of a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser illustrates the technique’s capabilities.
- Martin Plöschner
- , Marcos Maestre Morote
- & Joel Carpenter
-
Article
| Open Access General recipe to realize photonic-crystal surface-emitting lasers with 100-W-to-1-kW single-mode operation
General recipe to realize photonic-crystal surface-emitting lasers with 100-W-to-1-kW single-mode operation
Here, the authors analytically derive the general conditions for 100-W-to-1-kW-class single-mode operation in ultra-large-area (3~10 mm) photonic crystal lasers. Such high power single-mode semiconductor lasers will bring innovation to a wide variety of fields.
- Takuya Inoue
- , Masahiro Yoshida
- & Susumu Noda
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-low threshold lasing through phase front engineering via a metallic circular aperture
Ultra-low threshold lasing through phase front engineering via a metallic circular aperture
Low threshold lasing is widely required, especially for portable systems. Here the authors design a circular subwavelength metallic aperture in a QCL to shape its phase front and control diffraction losses, which in turn allows a lower threshold dissipation power, enabling the fabrication of shorter cavities.
- Zhixin Wang
- , Filippos Kapsalidis
- & Jérôme Faist
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance lasers for fully integrated silicon nitride photonics
High-performance lasers for fully integrated silicon nitride photonics
Achieving high output power and low noise integrated lasers is a major challenge. Here the authors experimentally demonstrate integrated lasers from a Si/SiN heterogeneous platform that shows Hertz-level linewidth, paving the way toward fully integrating low-noise silicon nitride photonics in volume using real devices for lasing.
- Chao Xiang
- , Joel Guo
- & John E. Bowers
-
Article
| Open Access Mode-locked short pulses from an 8 μm wavelength semiconductor laser
Mode-locked short pulses from an 8 μm wavelength semiconductor laser
Producing pulses in the mid-IR often requires bulky sources and has been inaccessible with compact and versatile quantum cascade lasers (QCLs). Here, the authors demonstrate actively mode-locked, mid-IR QCL operation at room temperature.
- Johannes Hillbrand
- , Nikola Opačak
- & Benedikt Schwarz
-
Article
| Open Access Solid cyclooctatetraene-based triplet quencher demonstrating excellent suppression of singlet–triplet annihilation in optical and electrical excitation
Solid cyclooctatetraene-based triplet quencher demonstrating excellent suppression of singlet–triplet annihilation in optical and electrical excitation
Though reducing non-emissive triplet excited-states using quenchers effectively improves organic semiconductor laser diode (OSLD) performance, existing quenchers are not suitable for devices. Here, the authors designed a solid-state triplet quencher for OSLD under optical and electrical excitation.
- Van T. N. Mai
- , Viqar Ahmad
- & Shih-Chun Lo
-
Article
| Open Access Dually modulated photonic crystals enabling high-power high-beam-quality two-dimensional beam scanning lasers
Dually modulated photonic crystals enabling high-power high-beam-quality two-dimensional beam scanning lasers
Beam scanning lasers are required for systems for smart mobility, object recognition, and adaptive illuminations. The authors demonstrate dually modulated photonic crystals, wherein the positions and sizes of the photonic-crystal lattice points are modulated simultaneously, to achieve mechanical-free, 2D beam scanning.
- Ryoichi Sakata
- , Kenji Ishizaki
- & Susumu Noda
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-single exciton optical gain threshold in colloidal semiconductor quantum wells with gradient alloy shelling
Sub-single exciton optical gain threshold in colloidal semiconductor quantum wells with gradient alloy shelling
Colloidal quantum wells are highly promising for applications of solution-processed lasers, but their performance is limited by multi-excitonic nature of the materials. Here, the authors demonstrate optical gain in graded alloy core/shell CdSe/CdS@CdZnS quantum wells at less than one exciton per particle resulting in ultralow thresholds.
- Nima Taghipour
- , Savas Delikanli
- & Hilmi Volkan Demir
-
Article
| Open Access Continuous-wave quantum dot photonic crystal lasers grown on on-axis Si (001)
Continuous-wave quantum dot photonic crystal lasers grown on on-axis Si (001)
Fabricating semiconductor photonic lasers based on III-V materials are challenging because of the material mismatch with silicon. Here the authors monolithically grow quantum-dot-based photonic crystal membrane lasers directly on an on-axis silicon substrate.
- Taojie Zhou
- , Mingchu Tang
- & Huiyun Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Lasing in strained germanium microbridges
Lasing in strained germanium microbridges
Germanium (based) lasers are a promising route towards a fully CMOS-compatible light source, key to the further development of silicon photonics. Here, the authors realize lasing from strained germanium microbridges up to 100 K, finding a quantum efficiency close to 100%.
- F. T. Armand Pilon
- , A. Lyasota
- & H. Sigg
-
Article
| Open Access Room temperature terahertz semiconductor frequency comb
Room temperature terahertz semiconductor frequency comb
Terahertz frequency combs are highly desired for applications in precision measurements, sensing, spectroscopy and metrology. Here the authors demonstrate the room-temperature chip-based THz frequency comb using nonlinear frequency generation from a mid-infrared quantum cascade laser comb.
- Quanyong Lu
- , Feihu Wang
- & Manijeh Razeghi
-
Article
| Open Access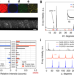 Laser restructuring and photoluminescence of glass-clad GaSb/Si-core optical fibres
Laser restructuring and photoluminescence of glass-clad GaSb/Si-core optical fibres
Semiconductor-core optical fibres are of interest for their non-linear optical and electro-optical properties. Here, GaSb/Si composite-core optical fibres were fabricated and a CO2 laser was used to facilitate controlled GaSb segregation within the silicon. This has implications for embedding light sources in IR-transmitting fibers
- S. Song
- , K. Lønsethagen
- & U. J. Gibson
-
Article
| Open Access Mutual coupling and synchronization of optically coupled quantum-dot micropillar lasers at ultra-low light levels
Mutual coupling and synchronization of optically coupled quantum-dot micropillar lasers at ultra-low light levels
The synchronisation of optical cavities in the quantum regime is still relatively unexplored. Here, Kreinberg et al. investigate the coupling behaviour of two quantum dot microlasers and find that spontaneous emission noise from cavity QED effects plays an important role.
- Sören Kreinberg
- , Xavier Porte
- & Stephan Reitzenstein
-
Article
| Open Access Continuous wave amplified spontaneous emission in phase-stable lead halide perovskites
Continuous wave amplified spontaneous emission in phase-stable lead halide perovskites
In order to develop perovskite-based lasers and LEDs for applications, their potential as room-temperature CW-pumped gain materials has to be established. Here, Brenner et al. demonstrate cw-pumped amplified spontaneous emission up to 120 K from a hybrid organic-inorganic halide perovskite layer.
- Philipp Brenner
- , Ofer Bar-On
- & Uli Lemmer
-
Article
| Open Access Robust lasing modes in coupled colloidal quantum dot microdisk pairs using a non-Hermitian exceptional point
Robust lasing modes in coupled colloidal quantum dot microdisk pairs using a non-Hermitian exceptional point
Pairs of microdisk lasers are one of the most common systems for studying optical PT-symmetry. Here, Lafalce, Zeng et al. study the influence of fabrication imperfections in a disk pair made from colloidal quantum dots and show that the resulting three modes also coalesce at an exceptional point.
- Evan Lafalce
- , Qingji Zeng
- & Z. Valy Vardeny
-
Article
| Open Access How lasing happens in CsPbBr3 perovskite nanowires
How lasing happens in CsPbBr3 perovskite nanowires
Lead-halide perovskite are an interesting material platform for light-emitting devices but the underlying lasing mechanism is still disputed. Here, Schlaus et al. use time-resolved spectroscopy of CsPbBr3 nanowires to show that lasing results from stimulated emission of an electron-hole plasma.
- Andrew P. Schlaus
- , Michael S. Spencer
- & X.-Y. Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access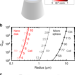 Non-obstructive intracellular nanolasers
Non-obstructive intracellular nanolasers
While the sharp emission lines of microlasers are advantageous for cell tagging, their relatively large size can impede cell migration and behavior. Here, Fikouras et al. develop nano-sized lasers that can readily tag and track various types of cells, including through narrow constrictions.
- Alasdair H. Fikouras
- , Marcel Schubert
- & Malte C. Gather
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast switch-on dynamics of frequency-tuneable semiconductor lasers
Ultrafast switch-on dynamics of frequency-tuneable semiconductor lasers
Single-mode, tuneable monolithic semiconductor lasers are important light sources for integrated photonics. Here, Kundu et al. observe the switch-on dynamics and mode competition of a terahertz quantum cascade laser and explain the behaviour with a carrier and photon transport model.
- Iman Kundu
- , Feihu Wang
- & A. Giles Davies
-
Article
| Open Access An InP-based vortex beam emitter with monolithically integrated laser
An InP-based vortex beam emitter with monolithically integrated laser
Orbital-angular-momentum (OAM) beams have great potential for multiplexing signals in optical communication, but creating a compact source is challenging. The authors integrate a chip-scale optical vortex emitter and DFB laser into a single monolithic device for direct electrically pumped production of OAM beams.
- Juan Zhang
- , Changzheng Sun
- & Siyuan Yu
-
Article
| Open Access High power surface emitting terahertz laser with hybrid second- and fourth-order Bragg gratings
High power surface emitting terahertz laser with hybrid second- and fourth-order Bragg gratings
Proper design of the gratings can enhance the efficiency of distributed-feedback and quantum cascade lasers. Here, Jin et al. use a hybrid grating system that superposes second- and fourth-order Bragg gratings and achieve high radiative efficiency and a single-lobe radiation pattern.
- Yuan Jin
- , Liang Gao
- & Sushil Kumar
-
Article
| Open Access Topological hybrid silicon microlasers
Topological hybrid silicon microlasers
Topological effects, first observed in condensed matter physics, are now also studied in optical systems, extending the scope to active topological devices. Here, Zhao et al. combine topological physics with non-Hermitian photonics, demonstrating a topological microlaser on a silicon platform.
- Han Zhao
- , Pei Miao
- & Liang Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Unusual scaling laws for plasmonic nanolasers beyond the diffraction limit
Unusual scaling laws for plasmonic nanolasers beyond the diffraction limit
Since the first proposal for plasmonic nanolasers there has been a debate about the limitations on performance posed by the inherent losses in metallic systems. Here, the authors compare over 100 plasmonic and photonic laser devices and find sub-wavelength plasmonic lasers to be advantageous.
- Suo Wang
- , Xing-Yuan Wang
- & Ren-Min Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Low-threshold optically pumped lasing in highly strained germanium nanowires
Low-threshold optically pumped lasing in highly strained germanium nanowires
Integrating group IV lasing devices into technologically relevant CMOS architectures has proven challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate low-threshold lasing, which is important for potential electronic and photonic circuits, using strained germanium nanowires as the gain material.
- Shuyu Bao
- , Daeik Kim
- & Donguk Nam
-
Article
| Open Access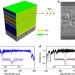 Room-temperature 2D semiconductor activated vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers
Room-temperature 2D semiconductor activated vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers
Two-dimensional materials have recently emerged as interesting materials for optoelectronic applications. Here, Shang et al. demonstrate two-dimensional semiconductor activated vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers where both the gain material and the lasing characteristics are two-dimensional.
- Jingzhi Shang
- , Chunxiao Cong
- & Ting Yu
-
Article
| Open Access A room temperature continuous-wave nanolaser using colloidal quantum wells
A room temperature continuous-wave nanolaser using colloidal quantum wells
Colloidal nanocrystals are a promising material for easy-to-fabricate nanolasers, but suffer from high threshold powers. Here, the authors combine colloidal quantum wells with a photonic-crystal cavity into a stable, continuous-wave room-temperature nanolaser with a threshold below one microwatt
- Zhili Yang
- , Matthew Pelton
- & Edo Waks
-
Article
| Open Access An integrated parity-time symmetric wavelength-tunable single-mode microring laser
An integrated parity-time symmetric wavelength-tunable single-mode microring laser
The breaking of parity-time symmetric gain and loss profiles can be used to achieve single-mode lasing in coupled microring resonators. Here, Liuet al. show that this effect can be electrically controlled with a tunable lasing wavelength and strong sidemode suppression.
- Weilin Liu
- , Ming Li
- & Jianping Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated plasmonic circuitry on a vertical-cavity surface-emitting semiconductor laser platform
Integrated plasmonic circuitry on a vertical-cavity surface-emitting semiconductor laser platform
Integrated plasmonic sources are crucial in the development of plasmonic circuitry. Here, McPolin et al. show that vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers can be employed as an on-chip, electrically pumped source or detector of plasmonic signals and also demonstrate waveguiding and frequency conversion on this platform.
- Cillian P. T. McPolin
- , Jean-Sebastien Bouillard
- & Anatoly V. Zayats
-
Article
| Open Access Laser chimeras as a paradigm for multistable patterns in complex systems
Laser chimeras as a paradigm for multistable patterns in complex systems
Chimera states are a class of self-organized solutions of high-dimensional networks with non-local and symmetry breaking coupling. Here the authors study the chimera patterns generated in a non-linear optical setup and uncover the transition between chimera orders as a pattern across clusters of chaoticity.
- Laurent Larger
- , Bogdan Penkovsky
- & Yuri Maistrenko
-
Article
| Open Access Ultralow noise miniature external cavity semiconductor laser
Ultralow noise miniature external cavity semiconductor laser
Optical metrology applications require lasers with high spectral purity but on-chip devices with sub-100 Hz linewidth are yet to be realized. Here, Liang et al.present a heterogeneously integrated, chip-scale semiconductor laser with 30 Hz integral linewidth and sub-Hz instantaneous linewidth.
- W. Liang
- , V. S. Ilchenko
- & L. Maleki
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamical properties induced by state-dependent delays in photonic systems
Dynamical properties induced by state-dependent delays in photonic systems
Time delays in feedback loops and connections in dynamical systems and complex networks can depend on the state of the system, but these state-dependent delays are poorly understood. Here, the authors use a photonic system to characterize the switching between two loops with different delay times.
- Jade Martínez-Llinàs
- , Xavier Porte
- & Ingo Fischer
-
Article |
 A borane laser
A borane laser
Solution-processed blue lasers are used in many applications such as spectroscopy or material processing. Here, the authors demonstrate a borane solution-based blue laser that offers a high efficiency and a photostability that is superior to commercial laser dyes.
- Luis Cerdán
- , Jakub Braborec
- & Michael G. S. Londesborough
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum coherence induces pulse shape modification in a semiconductor optical amplifier at room temperature
Quantum coherence induces pulse shape modification in a semiconductor optical amplifier at room temperature
Quantum coherence effects are often only visible at low temperatures, where dephasing times are not too short. Here Kolarczik et al. show that quantum coherence effects can appear in the reshaping of ultrafast laser pulses passing through quantum dots even at room temperature.
- Mirco Kolarczik
- , Nina Owschimikow
- & Ulrike Woggon
-
Article |
 Efficient power extraction in surface-emitting semiconductor lasers using graded photonic heterostructures
Efficient power extraction in surface-emitting semiconductor lasers using graded photonic heterostructures
Photonic crystal semiconductor lasers normally operate in a non-radiative mode, characterized by reduced losses but also low surface emission. Using graded photonic heterostructures, Xuet al. boost power extraction by forcing laser emission in a mode with higher radiation efficiency.
- Gangyi Xu
- , Raffaele Colombelli
- & David A. Ritchie

 Electrically empowered microcomb laser
Electrically empowered microcomb laser