Featured
-
-
Article |
 Remarkable heat conduction mediated by non-equilibrium phonon polaritons
Remarkable heat conduction mediated by non-equilibrium phonon polaritons
Measurements of thermal transport along 3C-SiC nanowires with and without a gold coating on the end(s) suggest that thermally excited surface phonon polaritons can be used in nanostructures to substantially enhance thermal conductivity.
- Zhiliang Pan
- , Guanyu Lu
- & Deyu Li
-
Article
| Open Access All-analog photoelectronic chip for high-speed vision tasks
All-analog photoelectronic chip for high-speed vision tasks
An all-analog chip combining electronic and light computing achieves systemic energy efficiency of more than three orders of magnitude and a computing speed of more than one order of magnitude compared with state-of-the-art computing processors.
- Yitong Chen
- , Maimaiti Nazhamaiti
- & Qionghai Dai
-
News & Views |
 The compact accelerator that keeps electrons on the straight and narrow
The compact accelerator that keeps electrons on the straight and narrow
A silicon-based device uses laser light to accelerate electrons and simultaneously shape them into a narrow beam. The principle could be used to build microchip accelerators that do away with bulky conventional designs.
- Yelong Wei
-
Article |
 Coherent nanophotonic electron accelerator
Coherent nanophotonic electron accelerator
A scalable nanophotonic electron accelerator with a high particle acceleration gradient and good beam confinement achieves an energy gain of 43%.
- Tomáš Chlouba
- , Roy Shiloh
- & Peter Hommelhoff
-
Article |
 Cavity-mediated thermal control of metal-to-insulator transition in 1T-TaS2
Cavity-mediated thermal control of metal-to-insulator transition in 1T-TaS2
Cavity-mediated thermal control of metal-to-insulator transition is achieved by embedding the charge density wave material 1T-TaS2 into cryogenic tunable terahertz cavities.
- Giacomo Jarc
- , Shahla Yasmin Mathengattil
- & Daniele Fausti
-
News & Views |
 An all-organic laser that is electrically driven
An all-organic laser that is electrically driven
An organic light-emitting diode has been integrated with an optically driven organic laser to produce laser light from electricity. The design bypasses many of the challenges posed by direct electrical input in such devices.
- Stéphane Kéna-Cohen
-
Article
| Open Access Electrically driven organic laser using integrated OLED pumping
Electrically driven organic laser using integrated OLED pumping
An electrically driven organic semiconductor laser is achieved by integrating a device structure that efficiently couples an organic light-emitting diode, with extremely high internal-light generation, with a polymer distributed feedback laser.
- Kou Yoshida
- , Junyi Gong
- & Ifor D. W. Samuel
-
Article
| Open Access Resonant X-ray excitation of the nuclear clock isomer 45Sc
Resonant X-ray excitation of the nuclear clock isomer 45Sc
Resonant X-ray excitation of the 45Sc nuclear isomeric state was achieved by irradiation of a Sc-metal foil with 12.4-keV photon pulses from a state-of-the-art X-ray free-electron laser, allowing a high-precision determination of the transition energy.
- Yuri Shvyd’ko
- , Ralf Röhlsberger
- & Tomasz Kolodziej
-
Research Highlight |
 How lasers detect day-length changes of a few milliseconds
How lasers detect day-length changes of a few milliseconds
Device decades in the making senses very small alterations in Earth’s rotation.
-
News |
 World’s most powerful X-ray laser will ‘film’ chemical reactions in unprecedented detail
World’s most powerful X-ray laser will ‘film’ chemical reactions in unprecedented detail
Upgraded laser in California will produce one million X-ray pulses per second to study ultrafast processes at the atomic level.
- Katherine Bourzac
-
Article |
 Flatband λ-Ti3O5 towards extraordinary solar steam generation
Flatband λ-Ti3O5 towards extraordinary solar steam generation
A route to greatly elevate joint densities of states by introducing a flat-band electronic structure is demonstrated, showing metallic λ-Ti3O5 powders have a high solar absorptivity and offering insights into access to cost-effective solar-to-steam generation.
- Bo Yang
- , Zhiming Zhang
- & Liang Zuo
-
Research Briefing |
 A step closer to repeaters for quantum networks
A step closer to repeaters for quantum networks
Loss of photons over long-distance connections limits the development of quantum networks, necessitating the use of quantum ‘repeater’ systems to boost signals between network nodes. Erbium ions incorporated into calcium tungstate crystals have been found to emit photons in the telecommunications frequency band that are indistinguishable from each other, and thus show promise for use in such repeaters.
-
Article |
 Indistinguishable telecom band photons from a single Er ion in the solid state
Indistinguishable telecom band photons from a single Er ion in the solid state
Er3+ is implanted into CaWO4, a material with non-polar site symmetry free of background rare earth ions, to realize reduced optical spectral diffusion in nanophotonic devices, representing a step towards making telecom band quantum repeater networks with single ions.
- Salim Ourari
- , Łukasz Dusanowski
- & Jeff D. Thompson
-
News & Views |
 From the archive: colour constancy, and an atomic romance
From the archive: colour constancy, and an atomic romance
Snippets from Nature’s past.
-
Research Highlight |
 A rainbow of LEDs adorns objects at the stroke of a pen
A rainbow of LEDs adorns objects at the stroke of a pen
Ordinary ballpoint pens loaded with conductive inks ‘write’ LEDs onto textiles, packaging and more.
-
Article |
 Magneto-optics in a van der Waals magnet tuned by self-hybridized polaritons
Magneto-optics in a van der Waals magnet tuned by self-hybridized polaritons
In the layered magnetic semiconductor CrSBr, emergent light–matter hybrids (polaritons) increase the spectral bandwidth of correlations between the magnetic, electronic and optical properties, enabling largely tunable optical responses to applied magnetic fields and magnons.
- Florian Dirnberger
- , Jiamin Quan
- & Vinod M. Menon
-
Article |
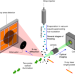 Microstructure and crystal order during freezing of supercooled water drops
Microstructure and crystal order during freezing of supercooled water drops
Optical microscopy and X-ray diffraction are used to study the freezing of water droplets in vacuum, leading to the development of a seven-stage model of freezing and the mapping of ice structures and crystal order.
- Armin Kalita
- , Maximillian Mrozek-McCourt
- & Claudiu A. Stan
-
Article |
 Tautomeric mixture coordination enables efficient lead-free perovskite LEDs
Tautomeric mixture coordination enables efficient lead-free perovskite LEDs
Lead-free perovskite light-emitting diodes (LEDs) prepared using tautomeric mixture coordination provide improved ordering in the crystal structure, reduced recombination and enhanced exciton binding energy compared with lead-containing perovskite-based LEDs.
- Dongyuan Han
- , Jie Wang
- & Ning Wang
-
Article
| Open Access 3D integration enables ultralow-noise isolator-free lasers in silicon photonics
3D integration enables ultralow-noise isolator-free lasers in silicon photonics
Three-dimensional integration of distributed-feedback lasers and ultralow-loss silicon nitride waveguides results in ultralow-noise lasers without the need for optical isolators.
- Chao Xiang
- , Warren Jin
- & John E. Bowers
-
Research Briefing |
 Sources of seismic activity imaged using telecom fibre cables
Sources of seismic activity imaged using telecom fibre cables
A telecommunications fibre cable was used to capture signals of seismic activity during a moderate-sized earthquake in California in 2021. The signals revealed sources of high-frequency seismic activity and, together with simulations, suggest that these sources arise from breaks in asperities: patches where friction usually locks two sides of a fault together.
-
Article |
 The break of earthquake asperities imaged by distributed acoustic sensing
The break of earthquake asperities imaged by distributed acoustic sensing
Distributed acoustic sensing technology is utilized to image four high-frequency rupture subevents of the 2021 Antelope Valley, California, earthquake; the results indicate that the subevents are due to the breaking of fault asperities.
- Jiaxuan Li
- , Taeho Kim
- & Zhongwen Zhan
-
Article |
 Heat-assisted detection and ranging
Heat-assisted detection and ranging
Heat-assisted detection and ranging is experimentally shown to see texture and depth through darkness as if it were day, and also perceives decluttered physical attributes beyond RGB or thermal vision.
- Fanglin Bao
- , Xueji Wang
- & Zubin Jacob
-
Research Briefing |
 Liquid-based assembly accelerates production of microLED displays
Liquid-based assembly accelerates production of microLED displays
MicroLED displays have advantages over commercially available technologies, but are difficult to put together efficiently. Agitating microLED chiplets and a substrate together in fluid causes them to self‑assemble quickly and with high yield.
-
Article |
 Fluidic self-assembly for MicroLED displays by controlled viscosity
Fluidic self-assembly for MicroLED displays by controlled viscosity
A MicroLED lighting panel, assembled in 60 s by a surface-tension-driven fluidic self-assembly technique, gave a yield as high as 99.90% through the addition of a small amount of poloxamer to the assembly solution.
- Daewon Lee
- , Seongkyu Cho
- & Sunghoon Kwon
-
Article |
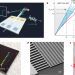 Frequency–angular resolving LiDAR using chip-scale acousto-optic beam steering
Frequency–angular resolving LiDAR using chip-scale acousto-optic beam steering
Three-dimensional imaging using a frequency–angular resolving and frequency-modulated continuous-wave LiDAR enabled by a chip-scale acousto-optic beam-steering device has been demonstrated, with the simplicity and low cost of the device making this a promising technology.
- Bingzhao Li
- , Qixuan Lin
- & Mo Li
-
News & Views |
 Clocks synchronized at the quantum limit
Clocks synchronized at the quantum limit
Time signals have been transmitted across 300 kilometres with an accuracy and precision limited only by the quantum nature of photons. The feat promises to revolutionize high-precision science using satellites.
- David Gozzard
-
Article |
 Quantum-limited optical time transfer for future geosynchronous links
Quantum-limited optical time transfer for future geosynchronous links
Laser-based time transfer with near quantum-limited acquisition and timing is demonstrated that can support femtosecond precision over 102 dB link loss, more than sufficient for future time transfer to geosynchronous orbits for future optical clock networks.
- Emily D. Caldwell
- , Jean-Daniel Deschenes
- & Laura C. Sinclair
-
Article
| Open Access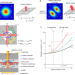 High-brightness scalable continuous-wave single-mode photonic-crystal laser
High-brightness scalable continuous-wave single-mode photonic-crystal laser
We developed large-scale photonic-crystal surface-emitting lasers with controlled Hermitian and non-Hermitian couplings inside the photonic crystal and a pre-installed spatial distribution of the lattice constant, which leads to the realization of a continuous-wave brightness of 1 GW cm−2 sr−1.
- Masahiro Yoshida
- , Shumpei Katsuno
- & Susumu Noda
-
Article |
 Attosecond electron microscopy of sub-cycle optical dynamics
Attosecond electron microscopy of sub-cycle optical dynamics
The cycles of laser light have been used to advance transmission electron microscopy to attosecond time resolution, revealing the interactions between light and matter in terms of their fundamental dimensions in space and time.
- David Nabben
- , Joel Kuttruff
- & Peter Baum
-
Article |
 Indefinite and bidirectional near-infrared nanocrystal photoswitching
Indefinite and bidirectional near-infrared nanocrystal photoswitching
This study reports unlimited near-infrared photoswitching in inorganic avalanching nanoparticles via a discrete shift of threshold intensity mediated by internal defect-based colour centres.
- Changhwan Lee
- , Emma Z. Xu
- & P. James Schuck
-
Research Highlight |
 Camera that could fit on a penny captures vivid colour photos
Camera that could fit on a penny captures vivid colour photos
A ‘meta-lens’ and corrective algorithms allow a tiny device to produce high-resolution images.
-
Article
| Open Access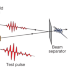 Dynamic optical response of solids following 1-fs-scale photoinjection
Dynamic optical response of solids following 1-fs-scale photoinjection
Petahertz-scale optical-field metrology in a pump-probe setting enables the direct observation of how the optical properties of a medium evolve after 1-fs-scale photoinjection.
- Dmitry A. Zimin
- , Nicholas Karpowicz
- & Vladislav S. Yakovlev
-
Outlook |
 How to lower carbon levels using light
How to lower carbon levels using light
Photocatalysis using light-emitting diodes could reduce the amount of carbon dioxide emitted by industrial chemical processes.
- Neil Savage
-
News & Views |
 Photon lights a path towards a nuclear clock
Photon lights a path towards a nuclear clock
A long-sought photon that is emitted by the nucleus of a thorium isotope has now been observed. The feat is a key step in efforts to build a nuclear clock, a device that is precise enough to probe the Universe’s best-kept secrets.
- Adriana Pálffy
-
Article
| Open Access Density-wave ordering in a unitary Fermi gas with photon-mediated interactions
Density-wave ordering in a unitary Fermi gas with photon-mediated interactions
An experiment with atoms and photons provides a fully tunable and microscopically controllable platform for the experimental study of the interplay of superfluidity and density-wave order.
- Victor Helson
- , Timo Zwettler
- & Jean-Philippe Brantut
-
Article |
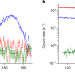 Observation of the radiative decay of the 229Th nuclear clock isomer
Observation of the radiative decay of the 229Th nuclear clock isomer
The authors report on the radiative decay of a low-energy isomer in thorium-229 (229mTh), which has consequences for the design of a future nuclear clock and eases the search for direct laser excitation of the atomic nucleus.
- Sandro Kraemer
- , Janni Moens
- & Ulrich Wahl
-
News & Views |
 Ink that mimics the colour of incoming light
Ink that mimics the colour of incoming light
Light-sensitive particles have been shown to stratify in solution in a way that changes the colour of the whole suspension. The system forms a colour-changing ink that could make electronic paper a viable technology.
- Hector Lopez-Rios
- & Monica Olvera de la Cruz
-
Article
| Open Access Photochromism from wavelength-selective colloidal phase segregation
Photochromism from wavelength-selective colloidal phase segregation
A simple spectral selective active colloidal system is designed in which TiO2 colloidal species are coded with dyes to form a photochromic swarm that adapts the appearance of incident light due to layered phase segregation.
- Jing Zheng
- , Jingyuan Chen
- & Jinyao Tang
-
Research Highlight |
 How light makes nearby particles do the twist
How light makes nearby particles do the twist
Light travelling through a fibre can impart a twist to glass spheres if the light itself is not twisting.
-
Research Briefing |
 Detectors that encode angles of incoming light as colour
Detectors that encode angles of incoming light as colour
Most light-field sensors — devices that detect the angles of incoming light rays to reconstruct 3D scenes — can detect light only in the ultraviolet and visible wavelength ranges. A newly developed light-field sensor comprising perovskite nanocrystals encodes the angles of incoming visible-light beams and X-rays as different colours.
-
Article
| Open Access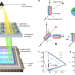 X-ray-to-visible light-field detection through pixelated colour conversion
X-ray-to-visible light-field detection through pixelated colour conversion
Lithographically patterned perovskite nanocrystal arrays were used to determine radiation vectors from X-rays to visible light and the emission colours of the nanoparticles was used to create images of three-dimensional objects and for phase-contrast imaging.
- Luying Yi
- , Bo Hou
- & Xiaogang Liu
-
News & Views |
 Bright light coaxed from electrically driven quantum dots
Bright light coaxed from electrically driven quantum dots
Nanocrystals made from a semiconducting material have been shown to emit intense light when excited with an electric current. The technology could be used to build a type of laser that is more versatile than those in general use.
- Thilo Stöferle
- & Rainer F. Mahrt
-
Article
| Open Access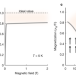 Photo-induced high-temperature ferromagnetism in YTiO3
Photo-induced high-temperature ferromagnetism in YTiO3
All-optical, mode-selective manipulation of the crystal lattice can be used to enhance and stabilize ferromagnetism in YTiO3 well above its equilibrium ordering temperature and for many nanoseconds, enabling dynamic engineering of practically useful non-equilibrium functionalities in fluctuating electronic systems.
- A. S. Disa
- , J. Curtis
- & A. Cavalleri
-
Article |
 Concurrent self-assembly of RGB microLEDs for next-generation displays
Concurrent self-assembly of RGB microLEDs for next-generation displays
A new transfer method for microLEDs fabrication based on fluidic self-assembly technology combining magnetic and dielectrophoresis forces is described, achieving a very high simultaneous RGB LED transfer yield and over large areas.
- Wonjae Chang
- , Jungsub Kim
- & Jeong Soo Lee
-
Article
| Open Access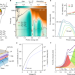 Electrically driven amplified spontaneous emission from colloidal quantum dots
Electrically driven amplified spontaneous emission from colloidal quantum dots
Colloidal quantum dot devices demonstrating electrically pumped amplified spontaneous emission are described, showing strong, broadband optical gain and bright edge emission, opening the path to solution-processable laser diodes.
- Namyoung Ahn
- , Clément Livache
- & Victor I. Klimov
-
Research Highlight |
 How this shrimp gets its brilliant white stripe
How this shrimp gets its brilliant white stripe
Extremely white pigment stems from a peculiar arrangement of reflective molecules.
-
News & Views |
 From the archive: how several artists’ works mimic impressions made on the eye’s retina, and the curious effects of blue glass on colour
From the archive: how several artists’ works mimic impressions made on the eye’s retina, and the curious effects of blue glass on colour
Snippets from Nature’s past.
-
Article |
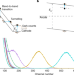 Self-powered perovskite photon-counting detectors
Self-powered perovskite photon-counting detectors
Suppression of shallow traps responsible for dark count rates in polycrystalline methylammonium lead triiodide using diphenyl sulfide enables the production of metal-halide perovskite photon-counting detectors that allow sensitive detection of γ-ray spectra.
- Ying Zhou
- , Chengbin Fei
- & Jinsong Huang
-
Article |
 Separating single- from multi-particle dynamics in nonlinear spectroscopy
Separating single- from multi-particle dynamics in nonlinear spectroscopy
Transient absorption with N prescribed excitation intensities allows isolation of N increasingly nonlinear responses, enabling separation of single- and multiple-exciton dynamics.
- Pavel Malý
- , Julian Lüttig
- & Tobias Brixner

 A superconducting nanowire single-photon camera with 400,000 pixels
A superconducting nanowire single-photon camera with 400,000 pixels