Research Briefing |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Anti-reflection structure for perfect transmission through complex media
Anti-reflection structure for perfect transmission through complex media
An anti-reflection structure is used to eliminate all back scattering of light passing through a diffusive medium.
- Michael Horodynski
- , Matthias Kühmayer
- & Matthieu Davy
-
Article |
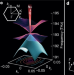 Scalable single-mode surface-emitting laser via open-Dirac singularities
Scalable single-mode surface-emitting laser via open-Dirac singularities
A photonic crystal cavity arranged in a hexagonal pattern shows unconventional losses that allow single-mode lasing operation to be maintained as the cavity is scaled up in size.
- Rushin Contractor
- , Wanwoo Noh
- & Boubacar Kanté
-
Research Highlight |
 These ‘drab’ moths dazzle when the light is right
These ‘drab’ moths dazzle when the light is right
Night-loving insects that look brown by day have bright, species-specific patterns under infrared light.
-
Article |
 Axial Higgs mode detected by quantum pathway interference in RTe3
Axial Higgs mode detected by quantum pathway interference in RTe3
Detection of an axial Higgs mode by quantum pathway interference reveals an unconventional charge density wave phase in RTe3.
- Yiping Wang
- , Ioannis Petrides
- & Kenneth S. Burch
-
Article |
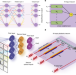 An on-chip photonic deep neural network for image classification
An on-chip photonic deep neural network for image classification
Using a three-layer opto-electronic neural network, direct, clock-less sub-nanosecond image classification on a silicon photonics chip is demonstrated, achieving a classification time comparable with a single clock cycle of state-of-the-art digital implementations.
- Farshid Ashtiani
- , Alexander J. Geers
- & Firooz Aflatouni
-
Article |
 Electrically tunable quantum confinement of neutral excitons
Electrically tunable quantum confinement of neutral excitons
Electrically controlled quantum confinement of excitons to below 10 nm is achieved in a 2D semiconductor by combining in-plane electric fields with interactions between excitons and free charges.
- Deepankur Thureja
- , Atac Imamoglu
- & Puneet A. Murthy
-
Perspective |
 Strongly correlated electron–photon systems
Strongly correlated electron–photon systems
The control of light–matter interactions as a way to manipulate and synthesize strongly correlated quantum matter is discussed, highlighting a field termed ‘strongly correlated electron–photon science’.
- Jacqueline Bloch
- , Andrea Cavalleri
- & Angel Rubio
-
Article
| Open Access Qubit teleportation between non-neighbouring nodes in a quantum network
Qubit teleportation between non-neighbouring nodes in a quantum network
A quantum network formed by three optically connected nodes comprising solid-state qubits demonstrates the teleportation of quantum information between two non-neighbouring nodes, negating the need for a direct connection between them.
- S. L. N. Hermans
- , M. Pompili
- & R. Hanson
-
Article |
 Free-electron lasing with compact beam-driven plasma wakefield accelerator
Free-electron lasing with compact beam-driven plasma wakefield accelerator
Using a compact, particle-beam-driven plasma-based accelerator to accelerate high-quality electron beams that are completely characterized in the six-dimensional phase space, free-electron lasing is observed with narrow-band amplified radiation in the infrared range.
- R. Pompili
- , D. Alesini
- & M. Ferrario
-
Article
| Open Access Microcomb-driven silicon photonic systems
Microcomb-driven silicon photonic systems
A simple and power-efficient microcomb source is used to drive complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor silicon photonic engines, a step towards the next generation of fully integrated photonic systems.
- Haowen Shu
- , Lin Chang
- & John E. Bowers
-
Article |
 Polariton Bose–Einstein condensate from a bound state in the continuum
Polariton Bose–Einstein condensate from a bound state in the continuum
Using a patterned waveguide, a Bose–Einstein condensate of polaritons is realized in a bound state in the continuum, with a low condensation threshold density that occurs at a dispersion saddle point.
- V. Ardizzone
- , F. Riminucci
- & D. Sanvitto
-
Article |
 Light-field control of real and virtual charge carriers
Light-field control of real and virtual charge carriers
Light-field control of real and virtual charge carriers in a gold–graphene–gold heterostructure is demonstrated, and used to create a logic gate for application in lightwave electronics.
- Tobias Boolakee
- , Christian Heide
- & Peter Hommelhoff
-
Article |
 Observation of chiral state transfer without encircling an exceptional point
Observation of chiral state transfer without encircling an exceptional point
A study realizes a photonic emulator to probe the temporal evolution of light in a non-Hermitian system, and reports the observation of chiral state transfer without encircling an exceptional point.
- Hadiseh Nasari
- , Gisela Lopez-Galmiche
- & Mercedeh Khajavikhan
-
Article |
 Single electrons on solid neon as a solid-state qubit platform
Single electrons on solid neon as a solid-state qubit platform
A solid-state single-electron qubit platform is demonstrated based on trapping and manipulating isolated single electrons on an ultraclean solid neon surface in vacuum, which performs near the state of the art for a charge qubit.
- Xianjing Zhou
- , Gerwin Koolstra
- & Dafei Jin
-
Article |
 Observation of chiral and slow plasmons in twisted bilayer graphene
Observation of chiral and slow plasmons in twisted bilayer graphene
Two new plasmon modes are observed in macroscopic twisted bilayer graphene with a highly ordered moiré superlattice, the first being the signature of chiral plasmons and the second a slow plasmonic mode around 0.4 electronvolts.
- Tianye Huang
- , Xuecou Tu
- & Xiaomu Wang
-
Research Highlight |
 The nanoparticles that give a famed antique porcelain its dazzle
The nanoparticles that give a famed antique porcelain its dazzle
An iridescent purple glaze on German Meissen ware from the eighteenth century is traced to minute specks of gold.
-
Article
| Open Access Thermophotovoltaic efficiency of 40%
Thermophotovoltaic efficiency of 40%
Two-junction TPV cells with efficiencies of more than 40% are reported, using an emitter with a temperature between 1,900 and 2,400 °C, for integration into a TPV system for thermal energy grid storage.
- Alina LaPotin
- , Kevin L. Schulte
- & Asegun Henry
-
Article |
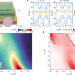 Intelligent infrared sensing enabled by tunable moiré quantum geometry
Intelligent infrared sensing enabled by tunable moiré quantum geometry
Tunable quantum geometric properties of moiré graphene enable the use of a convolutional neural network to simultaneously decipher the light polarization, power and wavelength in a subwavelength-scale smart device.
- Chao Ma
- , Shaofan Yuan
- & Fengnian Xia
-
Article |
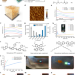 High-brightness all-polymer stretchable LED with charge-trapping dilution
High-brightness all-polymer stretchable LED with charge-trapping dilution
A material design strategy and fabrication process is described to produce all-polymer light-emitting diodes with high brightness, current efficiency and good mechanical stability, with applications in skin electronics and human–machine interfaces.
- Zhitao Zhang
- , Weichen Wang
- & Zhenan Bao
-
Article
| Open Access A large-scale microelectromechanical-systems-based silicon photonics LiDAR
A large-scale microelectromechanical-systems-based silicon photonics LiDAR
A large focal plane switch array is constructed to steer the laser beam of a LiDAR system, leading to 3D imaging with 16,384 pixels, improving the resolution and coverage of solid-state LiDARs.
- Xiaosheng Zhang
- , Kyungmok Kwon
- & Ming C. Wu
-
News & Views |
 Light arrays measure up on a chip the size of a fingertip
Light arrays measure up on a chip the size of a fingertip
An optical device enables high-speed, high-resolution distance measurements to be made over a large field of view. Clever switching gives the integrated design a tiny footprint and keeps its power consumption low.
- H. Y. Fu
- & Qian Li
-
Article |
 Structure of the moiré exciton captured by imaging its electron and hole
Structure of the moiré exciton captured by imaging its electron and hole
Imaging the electron and hole that bind to form interlayer excitons in a 2D moiré material enables direct measurement of its diameter and indicates the localization of its centre of mass.
- Ouri Karni
- , Elyse Barré
- & Keshav M. Dani
-
News & Views |
 Plasmas primed for rapid pulse production
Plasmas primed for rapid pulse production
A plasma-based device is set to challenge particle accelerators that generate high-quality light pulses, with evidence that the cheaper plasma platform can run at competitive repetition rates.
- Michael Litos
-
Article
| Open Access Hyperbolic shear polaritons in low-symmetry crystals
Hyperbolic shear polaritons in low-symmetry crystals
Shear phenomena in the infrared dielectric response of a monoclinic crystal are shown to unveil a new polariton class termed hyperbolic shear polariton that can emerge in any low-symmetry monoclinic or triclinic system.
- Nikolai C. Passler
- , Xiang Ni
- & Alexander Paarmann
-
Research Highlight |
 Retina-like sensors give machines better vision
Retina-like sensors give machines better vision
Semiconductor-based devices that adapt to a wide range of light intensities could prove useful in self-driving vehicles and assembly lines.
-
Article |
 Polarized phonons carry angular momentum in ultrafast demagnetization
Polarized phonons carry angular momentum in ultrafast demagnetization
Ultrafast electron diffraction is used here to reveal in nickel an almost instantaneous, long-lasting population of anisotropic phonons with angular momentum.
- S. R. Tauchert
- , M. Volkov
- & P. Baum
-
Article
| Open Access Deep physical neural networks trained with backpropagation
Deep physical neural networks trained with backpropagation
A hybrid algorithm that applies backpropagation is used to train layers of controllable physical systems to carry out calculations like deep neural networks, but accounting for real-world noise and imperfections.
- Logan G. Wright
- , Tatsuhiro Onodera
- & Peter L. McMahon
-
Research Highlight |
 Light that never ‘sees’ items takes their picture
Light that never ‘sees’ items takes their picture
Photons of different wavelengths go their separate ways to capture images.
-
Article
| Open Access Topological triple phase transition in non-Hermitian Floquet quasicrystals
Topological triple phase transition in non-Hermitian Floquet quasicrystals
A triple phase transition, where changing a single parameter simultaneously gives rise to metal–insulator, topological and a parity–time symmetry-breaking phase transitions, is observed in non-Hermitian Floquet quasicrystals.
- Sebastian Weidemann
- , Mark Kremer
- & Alexander Szameit
-
News & Views |
 Low-power light modifies electron microscopy
Low-power light modifies electron microscopy
An optical device designed to control the properties of electron waves inside an electron microscope demonstrates that clever platforms for integrated photonics need not be powered by expensive laser systems.
- Martin Kozák
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated photonics enables continuous-beam electron phase modulation
Integrated photonics enables continuous-beam electron phase modulation
A silicon nitride microresonator is used for coherent phase modulation of a transmission electron microscope beam, with future applications in combining high-resolution microscopy with spectroscopy, holography and metrology.
- Jan-Wilke Henke
- , Arslan Sajid Raja
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Direct limits for scalar field dark matter from a gravitational-wave detector
Direct limits for scalar field dark matter from a gravitational-wave detector
Using a gravitational-wave detector to listen for dark matter signatures, a direct search for scalar field dark matter was conducted and new upper limits are set on the coupling constants.
- Sander M. Vermeulen
- , Philip Relton
- & Holger Wittel
-
Article |
 Optomechanical dissipative solitons
Optomechanical dissipative solitons
Stable, dissipative optomechanical solitons are realized using optical fields in a whispering gallery mode resonator by balancing the optomechanical nonlinearities with a tailored modal dispersion.
- Jing Zhang
- , Bo Peng
- & Lan Yang
-
Article |
 Multiview confocal super-resolution microscopy
Multiview confocal super-resolution microscopy
A combination of multiview imaging, structured illumination, reconstruction algorithms and deep-learning predictions realizes spatial- and temporal-resolution improvements in fluorescence microscopy to produce super-resolution images from diffraction-limited input images.
- Yicong Wu
- , Xiaofei Han
- & Hari Shroff
-
Article |
 On-chip electro-optic frequency shifters and beam splitters
On-chip electro-optic frequency shifters and beam splitters
Engineering of the coupling between optical modes in a lithium niobate chip enables the realization of tunable, bi-directional and low-loss electro-optic frequency shifters controlled using only continuous and single-tone microwaves.
- Yaowen Hu
- , Mengjie Yu
- & Marko Lončar
-
Article |
 Distribution control enables efficient reduced-dimensional perovskite LEDs
Distribution control enables efficient reduced-dimensional perovskite LEDs
The efficiency and operating lifetimes of perovskite light-emitting diodes is improved by using a fluorinated triphenylphosphine oxide additive to control the cation diffusion during film deposition and passivate the surface.
- Dongxin Ma
- , Kebin Lin
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Research Highlight |
 Weird crystal makes beetle a living jewel
Weird crystal makes beetle a living jewel
An insect owes its bright green covering to an unusual type of ‘photonic crystal’.
-
Article |
 Reconstruction of Bloch wavefunctions of holes in a semiconductor
Reconstruction of Bloch wavefunctions of holes in a semiconductor
Bloch wavefunctions of two types of hole in gallium arsenide are reconstructed by measuring the polarization of light emitted by collisions of electrons and holes accelerated by a terahertz laser.
- J. B. Costello
- , S. D. O’Hara
- & M. S. Sherwin
-
Outlook |
 Optics shine a light on dental imaging
Optics shine a light on dental imaging
Light can outperform X-rays in tooth examinations and avoids the use of ionizing radiation.
- Neil Savage
-
Article |
 Topological complex-energy braiding of non-Hermitian bands
Topological complex-energy braiding of non-Hermitian bands
Experiments using two coupled optical ring resonators and based on the concept of synthetic dimension reveal non-Hermitian energy band structures exhibiting topologically non-trivial knots and links.
- Kai Wang
- , Avik Dutt
- & Shanhui Fan
-
Article |
 Colorimetric histology using plasmonically active microscope slides
Colorimetric histology using plasmonically active microscope slides
Colour contrast is added to unstained histological samples by using surface plasmon polaritons whose properties depend on the sample’s dielectric constant.
- Eugeniu Balaur
- , Sandra O’ Toole
- & Brian Abbey
-
Article |
 The role of charge recombination to triplet excitons in organic solar cells
The role of charge recombination to triplet excitons in organic solar cells
A substantial pathway for energy loss in organic solar cells may be suppressed by engineering hybridization between non-fullerene acceptor triplet excitons and spin-triplet charge transfer excitons.
- Alexander J. Gillett
- , Alberto Privitera
- & Richard H. Friend
-
Research Highlight |
 Thirty lasers act as one to shine a powerful light
Thirty lasers act as one to shine a powerful light
Cluster of tiny tube-shaped devices creates an intense, focused light source.
-
News & Views |
 Light detection nears its quantum limit
Light detection nears its quantum limit
Organic molecules are increasingly crucial in quantum-optics technologies. An experiment shows how the strong coupling between confined organic molecules and light can improve photon detection at room temperature.
- Sebastian Klembt
-
News |
 COVID in kids and fossil-fuel limits — the week in infographics
COVID in kids and fossil-fuel limits — the week in infographics
Nature highlights three key infographics from the week in science and research.
-
News |
 COVID advances win US$3-million Breakthrough prizes
COVID advances win US$3-million Breakthrough prizes
Pioneers of mRNA vaccines and next-generation sequencing techniques are among the winners of science’s most lucrative awards.
- Zeeya Merali
-
News & Views |
 Hybrid light–matter states formed in self-assembling cavities
Hybrid light–matter states formed in self-assembling cavities
Tiny flakes of metal suspended in a solution have been observed to self-assemble into pairs separated by a narrow gap — offering a tunable system for studying combinations of light and matter known as polaritons.
- Johannes Feist
-
Review Article |
 Interface nano-optics with van der Waals polaritons
Interface nano-optics with van der Waals polaritons
This Review discusses the state of the art of interface optics—including refractive optics, meta-optics and moiré engineering—for the control of van der Waals polaritons.
- Qing Zhang
- , Guangwei Hu
- & Cheng-Wei Qiu
-
Article |
 Tunable self-assembled Casimir microcavities and polaritons
Tunable self-assembled Casimir microcavities and polaritons
Gold nanoflake pairs form by self-assembly in an aqueous ligand solution and offer stable and tunable microcavities by virtue of equilibrium between attractive Casimir forces and repulsive electrostatic forces.
- Battulga Munkhbat
- , Adriana Canales
- & Timur O. Shegai

 The knotty problem of tuning an instrument
The knotty problem of tuning an instrument