Featured
-
-
Letter |
 Non-invasive imaging through opaque scattering layers
Non-invasive imaging through opaque scattering layers
The image of a fluorescent object hidden behind an opaque layer can be retrieved non-invasively by exploiting the correlation properties of the speckle pattern produced by illuminating the object through the layer using laser light.
- Jacopo Bertolotti
- , Elbert G. van Putten
- & Allard P. Mosk
-
News |
 A giant bid to etch tiny circuits
A giant bid to etch tiny circuits
Intel invests US$1 billion into extreme-ultraviolet light technology that will quarter the size of transistors.
- Katherine Bourzac
-
-
Letter |
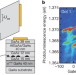 Quantum quench of Kondo correlations in optical absorption
Quantum quench of Kondo correlations in optical absorption
- C. Latta
- , F. Haupt
- & A. Imamoglu
-
Research Highlights |
Achieving spin control
-
Letter |
 Hard-tip, soft-spring lithography
Hard-tip, soft-spring lithography
Scanning probe techniques such as atomic force microscopy can be readily harnessed to prepare nanoscale structures with exquisite resolution, but are not in general suited for high-throughput patterning. Techniques based on contact printing, on the other hand, offer high throughput over large areas, but can't compete on resolution. Now, an approach is described that offers the best of both worlds: by attaching an array of hard, scanning-probe-like silicon tips to a flexible elastomeric substrate (similar to those used in contact printing), it is possible to rapidly create arbitrary patterns with sub-50-nm resolution over centimetre-scale areas.
- Wooyoung Shim
- , Adam B. Braunschweig
- & Chad A. Mirkin
-
Research Highlights |
Optical physics: A peek at a molecule's guts
-
Letter |
 Spectroscopic confirmation of a galaxy at redshift z = 8.6
Spectroscopic confirmation of a galaxy at redshift z = 8.6
Until now, the most distant spectroscopically confirmed galaxies known in the Universe were at redshifts of z = 8.2 and z = 6.96. It is now reported that the galaxy UDFy-38135539 is at a redshift of z = 8.5549 ± 0.0002. The finding has implications for our understanding of the timing, location and nature of the sources responsible for reionization of the Universe after the Big Bang.
- M. D. Lehnert
- , N. P. H. Nesvadba
- & S. Basa
-
Research Highlights |
Microscopy: See through tissue
-
News |
 It's a wrap for bacteria
It's a wrap for bacteria
Atomically thin carbon sheets offer bacteria a protective shell in electron microscopes.
- Geoff Brumfiel

 Giant Sun scope clears final hurdle
Giant Sun scope clears final hurdle