Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access ATRX, DAXX or MEN1 mutant pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors are a distinct alpha-cell signature subgroup
ATRX, DAXX or MEN1 mutant pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors are a distinct alpha-cell signature subgroup
In pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PanNETs) ATRX, DAXX, and MEN1 are commonly mutated (A-D-M mutant PanNETs). Here, the authors find in a cohort of PanNETS 58% are A-D-M mutant PanNETs, with a worse clinical outcome and differences in gene expression and methylation compared to A-D-M wild type cases- these gene expression differences suggest that A-D-M mutant PanNETs potentially originate from a cell type similar to alpha cells.
- Chang S. Chan
- , Saurabh V. Laddha
- & Laura H. Tang
-
Article
| Open Access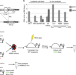 EVI1 overexpression reprograms hematopoiesis via upregulation of Spi1 transcription
EVI1 overexpression reprograms hematopoiesis via upregulation of Spi1 transcription
Chr3q26 rearrangements cause overexpression of EVI1 and associate with myeloid neoplasms, but the mechanism behind this association is unclear. Here, using a novel mouse model they show that EVI1 causes premalignant myeloid expansion with suppression of other lineages through upregulation of Spi1/PU.1.
- Edward Ayoub
- , Michael P. Wilson
- & Archibald S. Perkins
-
Article
| Open Access Metastatic adrenocortical carcinoma displays higher mutation rate and tumor heterogeneity than primary tumors
Metastatic adrenocortical carcinoma displays higher mutation rate and tumor heterogeneity than primary tumors
Adrenocortical cancer (ACC) is a rarely diagnosed and aggressive cancer whose metastatic form has been scarcely studied. Here, the authors study primary and metastatic ACC to investigate genomic heterogeneity, discovering higher mutation rates in metastatic lesions and novel recurrent mutations.
- Sudheer Kumar Gara
- , Justin Lack
- & Electron Kebebew
-
Article
| Open Access A comprehensive overview of genomic imprinting in breast and its deregulation in cancer
A comprehensive overview of genomic imprinting in breast and its deregulation in cancer
In growth and development genomic imprinting is important in regulating gene expression. Here, the authors study loss of imprinting (LOI) in cancer, developing a mixture model to detect monoallelically expressed loci without genotyping data - applying this novel methodology to TCGA breast cancer data they find massive deregulation of imprinting.
- Tine Goovaerts
- , Sandra Steyaert
- & Tim De Meyer
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide discovery of somatic regulatory variants in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Genome-wide discovery of somatic regulatory variants in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
The driver mutations for the two main molecular subgroups of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) are poorly defined. Here, an integrative genomics analysis identifies 3′ UTR NFKBIZ mutations within the activated B-cell DLBCL subgroup and small FCGR2B amplifications in the germinal centre B-cell DLBCL subgroup.
- Sarah E. Arthur
- , Aixiang Jiang
- & Ryan D. Morin
-
Article
| Open Access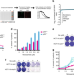 Mitochondrial uncoupling reveals a novel therapeutic opportunity for p53-defective cancers
Mitochondrial uncoupling reveals a novel therapeutic opportunity for p53-defective cancers
Several challenges are involved in direct targeting of mutant p53, while targeting altered fitness of cells with loss of wild type p53 is an alternative approach. Here they identify niclosamide to be selectively toxic to p53 deficient cells through a previously unknown mitochondrial uncoupling mechanism.
- R. Kumar
- , L. Coronel
- & C. F. Cheok
-
Article
| Open Access Acquired cancer resistance to combination immunotherapy from transcriptional loss of class I HLA
Acquired cancer resistance to combination immunotherapy from transcriptional loss of class I HLA
Acquired resistance is a major problem in cancer immunotherapy. Here the authors report a study of two patients with Merkel cell carcinoma under immunotherapy treatment who develop resistance after deep responses for >1 year and identified a novel mechanism of acquired, gene-specific transcriptional suppression of HLAs.
- K. G. Paulson
- , V. Voillet
- & A. G. Chapuis
-
Article
| Open Access LNMAT1 promotes lymphatic metastasis of bladder cancer via CCL2 dependent macrophage recruitment
LNMAT1 promotes lymphatic metastasis of bladder cancer via CCL2 dependent macrophage recruitment
Mechanism of lymph node (LN) metastasis induced by tumor associated macrophages (TAMs) remains unclear. Here they demonstrate that a long noncoding RNA LNMAT1 promotes LN metastasis of bladder cancer via recruitment of TAMs through epigenetic regulation of CCL2 expression.
- Changhao Chen
- , Wang He
- & Tianxin Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Implementation and benchmarking of a novel analytical framework to clinically evaluate tumor-specific fluorescent tracers
Implementation and benchmarking of a novel analytical framework to clinically evaluate tumor-specific fluorescent tracers
Fluorescent tracers are being tested in clinical trials to improve detection of tumor margins, but procedures are not standardised. Here, the authors develop an analytical framework that is compatible with the workflow in the operating theatre, and show that it leads to an 88% increase in intraoperative detection of tumor margins in patients with breast cancer.
- Marjory Koller
- , Si-Qi Qiu
- & Gooitzen M. van Dam
-
Article
| Open Access Recurrent WNT pathway alterations are frequent in relapsed small cell lung cancer
Recurrent WNT pathway alterations are frequent in relapsed small cell lung cancer
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients frequently relapse and become resistant to chemotherapy. Here, the authors analyse the genomic and transcriptomic landscape of primary and relapsed SCLC patients as well as in vitro models, and discover that activation of WNT signalling can drive chemotherapy resistance.
- Alex H. Wagner
- , Siddhartha Devarakonda
- & Ramaswamy Govindan
-
Article
| Open Access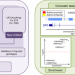 Identification of multiple risk loci and regulatory mechanisms influencing susceptibility to multiple myeloma
Identification of multiple risk loci and regulatory mechanisms influencing susceptibility to multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a cancer of the plasma cells, and the complete aetiology of the disease is still unclear. Here the authors perform an additional GWAS analysis followed by a meta-analysis with existing GWAS and replication genotyping and identify 6 novel risk loci and utilise gene expression, epigenetic profiling and in situ Hi-C data to further our understanding of MM susceptibility.
- Molly Went
- , Amit Sud
- & Stephen N. Thibodeau
-
Article
| Open Access Different patterns of clonal evolution among different sarcoma subtypes followed for up to 25 years
Different patterns of clonal evolution among different sarcoma subtypes followed for up to 25 years
Hofvander and colleagues compare the patterns of clonal evolution in different pathogenetic subgroups of sarcoma. They show that sarcomas driven by gene fusion or amplification display few additional changes over time, whereas sarcomas with complex karyotypes show a gradual increase of nucleotide- and chromosome-level mutations.
- Jakob Hofvander
- , Björn Viklund
- & Fredrik Mertens
-
Article
| Open Access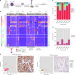 Unravelling subclonal heterogeneity and aggressive disease states in TNBC through single-cell RNA-seq
Unravelling subclonal heterogeneity and aggressive disease states in TNBC through single-cell RNA-seq
Triple-negative breast cancer is highly heterogeneous and aggressive. Here, the authors utilise single-cell RNA sequencing to investigate this heterogeneity, and discover a subpopulation of cells associated with metastasis and treatment resistance signatures, and linked to long term survival outcomes.
- Mihriban Karaayvaz
- , Simona Cristea
- & Leif W. Ellisen
-
Article
| Open Access Ap4 is rate limiting for intestinal tumor formation by controlling the homeostasis of intestinal stem cells
Ap4 is rate limiting for intestinal tumor formation by controlling the homeostasis of intestinal stem cells
The c-MYC oncoprotein has many targets whose actions are not fully understood including TFAP4/AP4. Here, the authors show in a mouse model of inherited colorectal cancer that deletion of AP4 decreased the frequency of c-MYC-driven intestinal adenomas, and reveal Ap4 as a mediator of adenoma initiation and regulator of colonic and intestinal stem cell and Paneth cell homeostasis.
- Stephanie Jaeckel
- , Markus Kaller
- & Heiko Hermeking
-
Article
| Open Access A feed forward loop enforces YAP/TAZ signaling during tumorigenesis
A feed forward loop enforces YAP/TAZ signaling during tumorigenesis
The Hippo pathway is frequently dysregulated in cancer. Here, the authors identify NUAK2 as negative regulator of the Hippo pathway from a siRNA kinome screen and show that NUAK2 promotes YAP/TAZ nuclear localisation while NUAK2 is a transcriptional target of YAP/TAZ, thus providing a feed forward loop to promote tumorigenesis.
- Mandeep K. Gill
- , Tania Christova
- & Liliana Attisano
-
Perspective
| Open Access Evaluating intrinsic and non-intrinsic cancer risk factors
Evaluating intrinsic and non-intrinsic cancer risk factors
Understanding the contributions of extrinsic and intrinsic factors on cancer risk is fundamental in determining the intervention and prevention strategies to tackle cancer. Here the authors provide a review of the different factors impacting cancer risk and discuss the limitations of different approaches in evaluating the relative contributions of these factors.
- Song Wu
- , Wei Zhu
- & Yusuf A Hannun
-
Article
| Open Access Group I Paks are essential for epithelial- mesenchymal transition in an Apc-driven model of colorectal cancer
Group I Paks are essential for epithelial- mesenchymal transition in an Apc-driven model of colorectal cancer
Group I Paks, like Pak1, are required for the activation of several key oncogenic signaling pathways. Here the authors study an inducible peptide mimicking the auto-inhibitory domain of Pak1 and show promising anti-tumor effects in a mouse model of colorectal cancer.
- H. Y. Chow
- , B. Dong
- & J. Chernoff
-
Article
| Open Access HIF-2α-pVHL complex reveals broad genotype-phenotype correlations in HIF-2α-driven disease
HIF-2α-pVHL complex reveals broad genotype-phenotype correlations in HIF-2α-driven disease
Hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-2α transcription factor is mutated in polycythemia and various neuroendocrine tumors. Here the authors present the crystal structure of a HIF-2α peptide bound to the pVHL-elongin B-elongin C (VBC) heterotrimeric complex and propose a classification scheme for HIF-2α mutations that helps to predict disease phenotype outcome.
- Daniel Tarade
- , Claire M. Robinson
- & Michael Ohh
-
Article
| Open Access Loss of GCNT2/I-branched glycans enhances melanoma growth and survival
Loss of GCNT2/I-branched glycans enhances melanoma growth and survival
Aberrant glycosylation patterns on cancer cells promote several pro-tumorigenic functions, including enhancing tumor cell proliferation. Here the authors provide data that show melanoma cells downregulate GCNT2 with consequent loss of I-branched glycans; this leads to the formation of extended i-linear glycans and enhances melanoma growth via increases, in part, by IGF-1- and extracellular matrix-induced signaling.
- Jenna Geddes Sweeney
- , Jennifer Liang
- & Charles J. Dimitroff
-
Article
| Open Access Inhibition of IRE1 RNase activity modulates the tumor cell secretome and enhances response to chemotherapy
Inhibition of IRE1 RNase activity modulates the tumor cell secretome and enhances response to chemotherapy
IRE1/XBP-1 activation has a major role in Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). Here, the authors show that inhibition of IRE1’s RNase activity attenuates autocrine and paracrine signaling of pro-tumorigenic cytokines and synergizes with paclitaxel to confer potent anti-tumor effects in TNBC.
- Susan E. Logue
- , Eoghan P. McGrath
- & Afshin Samali
-
Article
| Open Access A reliable murine model of bone metastasis by injecting cancer cells through caudal arteries
A reliable murine model of bone metastasis by injecting cancer cells through caudal arteries
Reliably modelling bone metastasis in mice is essential for research. Here, the authors present a new murine model for cancer metastasis based on intra-caudal artery injection that reliably recapitulates bone metastasis.
- Takahiro Kuchimaru
- , Naoya Kataoka
- & Shinae Kizaka-Kondoh
-
Correspondence
| Open Access Challenging PD-L1 expressing cytotoxic T cells as a predictor for response to immunotherapy in melanoma
Challenging PD-L1 expressing cytotoxic T cells as a predictor for response to immunotherapy in melanoma
- Lieve Brochez
- , Annabel Meireson
- & Vibeke Kruse
-
Article
| Open Access Recurrent homozygous deletion of DROSHA and microduplication of PDE4DIP in pineoblastoma
Recurrent homozygous deletion of DROSHA and microduplication of PDE4DIP in pineoblastoma
Pineoblastoma is a highly aggressive and rare childhood brain cancer, and the genetic drivers of sporadic pineoblastoma are unknown. Here, the authors genomically interrogated pediatric and adult pineoblastomas and found novel variants including recurrent homozygous deletions of DROSHA.
- Matija Snuderl
- , Kasthuri Kannan
- & Matthias A. Karajannis
-
Article
| Open Access Drug capture materials based on genomic DNA-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles
Drug capture materials based on genomic DNA-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles
Chemotherapy agents are prone to producing severe side-effects, and their sequestration prior to their entering of the circulatory system is thus highly desirable. Here, the authors functionalize iron oxide nanoparticles with genomic DNA and achieve sequestration of doxorubicin, cisplatin, and epirubicin from biological solutions.
- Carl M. Blumenfeld
- , Michael D. Schulz
- & Robert H. Grubbs
-
Article
| Open Access Armadillo repeat containing 12 promotes neuroblastoma progression through interaction with retinoblastoma binding protein 4
Armadillo repeat containing 12 promotes neuroblastoma progression through interaction with retinoblastoma binding protein 4
Armadillo (ARM) family proteins can act as oncogenes or tumor suppressors. Here, the authors show that a new ARM protein (ARMC12) is upregulated in neuroblastoma, binds the PRC2 component RBBP4, and inhibits transcription of tumor suppressive genes.
- Dan Li
- , Huajie Song
- & Qiangsong Tong
-
Article
| Open Access Integrative genomic analysis of adult mixed phenotype acute leukemia delineates lineage associated molecular subtypes
Integrative genomic analysis of adult mixed phenotype acute leukemia delineates lineage associated molecular subtypes
Mixed phenotype acute leukemia (MPAL) is a rare leukemia that presents both myeloid and lymphoid markers on blasts. Here the authors perform genomic analysis to show MPAL involves genetic and epigenetic heterogeneity and is genetically distinct from AML, B-ALL, and T-ALL.
- Koichi Takahashi
- , Feng Wang
- & P. Andrew Futreal
-
Article
| Open Access miR-130a and miR-145 reprogram Gr-1+CD11b+ myeloid cells and inhibit tumor metastasis through improved host immunity
miR-130a and miR-145 reprogram Gr-1+CD11b+ myeloid cells and inhibit tumor metastasis through improved host immunity
Tumours produce soluble factors that contribute to the expansion of Gr-1+CD11b+ immature myeloid cells with TGFβ dependent immune suppressive function. Here, the authors show miR-130a and miR-145 target TβRII and reprogram these cells by altering the cytokine microenvironment, improving anti-tumour immunity and inhibiting metastasis in preclinical mouse models.
- Hiroki Ishii
- , Suman K. Vodnala
- & Li Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Prognostic significance of frequent CLDN18-ARHGAP26/6 fusion in gastric signet-ring cell cancer
Prognostic significance of frequent CLDN18-ARHGAP26/6 fusion in gastric signet-ring cell cancer
Signet-ring cell carcinoma (SRCC) is a unique type of gastric cancer with no prognostic features. Here, the authors report a CLDN18-ARHGAP26/6 gene fusion in patients with a high signet-ring cell content, poor survival outcomes, and who experience no benefit from platinum/fluoropyrimidines-based chemotherapy.
- Yang Shu
- , Weihan Zhang
- & Jiankun Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Combined Rho-kinase inhibition and immunogenic cell death triggers and propagates immunity against cancer
Combined Rho-kinase inhibition and immunogenic cell death triggers and propagates immunity against cancer
Activation of an immune response is critical for the efficacy of cancer therapies. Here, the authors show that combination of ROCK inhibitor with chemotherapeutics that induce immunogenic cell death of cancer cells leads to increased dendritic cells’ maturation and synergistic CD8+ cytotoxic T cell priming and infiltration into the tumours, leading to suppressed tumour growth and improved overall survival in syngeneic and genetically engineered tumour models.
- Gi-Hoon Nam
- , Eun Jung Lee
- & In-San Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Factor XIIIA—expressing inflammatory monocytes promote lung squamous cancer through fibrin cross-linking
Factor XIIIA—expressing inflammatory monocytes promote lung squamous cancer through fibrin cross-linking
Lung squamous carcinomas (LUSC) are poorly molecularly characterized, but sub-populations show promising response to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Here, the authors identify a subset of LUSC characterized by infiltration of inflammatory monocytes, where metastasis is linked to Factor XIIIA promoting fibrin cross-linking.
- Alessandro Porrello
- , Patrick L. Leslie
- & Chad V. Pecot
-
Article
| Open Access MLL-fusion-driven leukemia requires SETD2 to safeguard genomic integrity
MLL-fusion-driven leukemia requires SETD2 to safeguard genomic integrity
In leukemia, diverse fusion proteins involving the MLL gene can drive oncogenic activity. Here, the authors describe a dependency of MLL-leukemia cells on the methyltransferase SETD2 to maintain genomic integrity during leukemia initiation and maintenance.
- Anna Skucha
- , Jessica Ebner
- & Florian Grebien
-
Article
| Open Access Outlier response to anti-PD1 in uveal melanoma reveals germline MBD4 mutations in hypermutated tumors
Outlier response to anti-PD1 in uveal melanoma reveals germline MBD4 mutations in hypermutated tumors
Hypermutated tumors respond more favorably to checkpoint inhibitor-based immune therapy. Here, the authors describe a new hypermutated phenotype due to germline mutations and subsequent somatic loss of heterozygosity of MBD4, and a dramatic response to the PD-1 inhibitor pembrolizumab in a patient with a MBD4-inactivated hypermutated uveal melanoma.
- Manuel Rodrigues
- , Lenha Mobuchon
- & Marc-Henri Stern
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide and high-density CRISPR-Cas9 screens identify point mutations in PARP1 causing PARP inhibitor resistance
Genome-wide and high-density CRISPR-Cas9 screens identify point mutations in PARP1 causing PARP inhibitor resistance
The mechanisms of PARP inhibitor (PARPi) resistance are poorly understood. Here the authors employ a CRISPR mutagenesis approach to identify PARP1 mutants causing PARPi resistance and find that PARP1 mutations are tolerated in BRCA1 mutated cells, suggesting alternative resistance mechanisms.
- Stephen J. Pettitt
- , Dragomir B. Krastev
- & Christopher J. Lord
-
Article
| Open Access The effects of mutational processes and selection on driver mutations across cancer types
The effects of mutational processes and selection on driver mutations across cancer types
A central question in cancer research is how specific driver mutations are acquired and maintained during cancer development. Here Temko et al. use public sequencing data to infer the effect of mutation and selection on a set of driver mutations and suggest that selection frequently dominates.
- Daniel Temko
- , Ian P. M. Tomlinson
- & Trevor A. Graham
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated molecular subtyping defines a curable oligometastatic state in colorectal liver metastasis
Integrated molecular subtyping defines a curable oligometastatic state in colorectal liver metastasis
The oligometastasis hypothesis suggests certain metastases are limited in extent and curable with focal therapies. Here they identify three integrated molecular subtypes of colorectal cancer liver metastasis, which complement clinical risk stratification to distinguish the subset of oligometastatic patients.
- Sean P. Pitroda
- , Nikolai N. Khodarev
- & Ralph R. Weichselbaum
-
Article
| Open Access Chemically triggered drug release from an antibody-drug conjugate leads to potent antitumour activity in mice
Chemically triggered drug release from an antibody-drug conjugate leads to potent antitumour activity in mice
Current antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) target internalising receptors on cancer cells. Here, the authors report the development and in vivo validation of a non-internalising ADC with the capacity to target cancer cells and release its therapeutic cargo extracellularly via a chemical trigger.
- Raffaella Rossin
- , Ron M. Versteegen
- & Marc S. Robillard
-
Article
| Open Access The senescence-associated secretory phenotype is potentiated by feedforward regulatory mechanisms involving Zscan4 and TAK1
The senescence-associated secretory phenotype is potentiated by feedforward regulatory mechanisms involving Zscan4 and TAK1
In cancer the side effects of therapeutic agents can provoke senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP), which can drive cancer resistance. During the DNA damage response, transcription factor Zscan4 expression is elevated by an ATM-TRAF6-TAK1 axis leading to long term SASP in human stromal cells.
- Boyi Zhang
- , Da Fu
- & Yu Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Epigenetic landscape influences the liver cancer genome architecture
Epigenetic landscape influences the liver cancer genome architecture
Genomic aberrations contribute to the development of cancer; however, their interdependence remains poorly understood. Here the authors analyze liver cancer samples to find correlation between epigenetic features and genetic aberrations including somatic substitutions, mutation signatures, and HBV integration sites.
- Natsuko Hama
- , Yasushi Totoki
- & Tatsuhiro Shibata
-
Article
| Open Access Tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells are resistant to DNA-damaging chemotherapy because of upregulated BARD1 and BRCA1
Tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells are resistant to DNA-damaging chemotherapy because of upregulated BARD1 and BRCA1
Most breast cancer patients are estrogen receptor positive and thus benefit from treatments that inhibit estrogen production; however, one third of tamoxifen-treated patients develops resistance and relapse. Here the authors show that tamoxifen resistant cells are resistant to chemotherapy because of BARD1 and BRCA1 upregulation.
- Yinghua Zhu
- , Yujie Liu
- & Qiang Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Motion model ultrasound localization microscopy for preclinical and clinical multiparametric tumor characterization
Motion model ultrasound localization microscopy for preclinical and clinical multiparametric tumor characterization
The vascular structure of tumors impacts diagnosis, prognosis and drug response; however, imaging methods to analyse this important feature have been hindered by spatial resolution limitations. Here the authors present a tool called motion model ultrasound localization microscopy to morphologically and functionally characterize fine vascular networks in tumors at super-resolution.
- Tatjana Opacic
- , Stefanie Dencks
- & Fabian Kiessling
-
Article
| Open Access Pharmacodynamics of mutant-IDH1 inhibitors in glioma patients probed by in vivo 3D MRS imaging of 2-hydroxyglutarate
Pharmacodynamics of mutant-IDH1 inhibitors in glioma patients probed by in vivo 3D MRS imaging of 2-hydroxyglutarate
Inhibitors of mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) entered recently clinical trials for treatment of gliomas. Here, the authors apply a MRS imaging method for 2HG detection and assessement of the pharmacodynamic effects of the mutant IDH1 inhibitor (IDH305) in 8 mutant IDH1 glioma patients.
- Ovidiu C. Andronesi
- , Isabel C. Arrillaga-Romany
- & Tracy T. Batchelor
-
Article
| Open Access USP52 acts as a deubiquitinase and promotes histone chaperone ASF1A stabilization
USP52 acts as a deubiquitinase and promotes histone chaperone ASF1A stabilization
Histone chaperone ASF1A is often dysregulated in cancers, however the regulation of its abundance is unclear. Here, the authors show that USP52 promotes ASF1A stability through deubiquitination while impairment of this stability reduces breast tumorigenesis and confers sensitivity to DNA damage.
- Shangda Yang
- , Ling Liu
- & Lei Shi
-
Article
| Open Access RNA cytosine methylation and methyltransferases mediate chromatin organization and 5-azacytidine response and resistance in leukaemia
RNA cytosine methylation and methyltransferases mediate chromatin organization and 5-azacytidine response and resistance in leukaemia
Resistance to chemotherapy is a serious issue that can be influenced by RNA epigenetics and chromatin structure. Here, the authors show in leukaemia cells that RNA 5-methylcytosine (RNA:m5C) and RNA:m5C methyltransferases (RCMTs) mediate chromatin structures that can modulate 5-Azacitidine response and resistance.
- Jason X. Cheng
- , Li Chen
- & James W. Vardiman
-
Article
| Open Access Integrative proteomics in prostate cancer uncovers robustness against genomic and transcriptomic aberrations during disease progression
Integrative proteomics in prostate cancer uncovers robustness against genomic and transcriptomic aberrations during disease progression
Understanding of molecular events in cancer requires proteome-level characterisation. Here, proteome profiling of patient samples representing primary and progressed prostate cancer enables the authors to identify pathway alterations that are not reflected at the genomic and transcriptomic levels.
- Leena Latonen
- , Ebrahim Afyounian
- & Tapio Visakorpi
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated genomics and functional validation identifies malignant cell specific dependencies in triple negative breast cancer
Integrated genomics and functional validation identifies malignant cell specific dependencies in triple negative breast cancer
Triple negative breast cancers harbor multiple copy number aberrations driving gene expression changes thought to underpin their malignant phenotypes. Here the authors integrate these features, finding and functionally validating 37 gene addictions among which they identify the mechanism of addiction to KIFC1, a potential selective drug target.
- Nirmesh Patel
- , Daniel Weekes
- & Andrew N. J. Tutt
-
Article
| Open Access Eya3 partners with PP2A to induce c-Myc stabilization and tumor progression
Eya3 partners with PP2A to induce c-Myc stabilization and tumor progression
Eya proteins are characterised by phosphatase activity associated with both the evolutionary conserved region and the less conserved N-terminal domain (NTD). Here the authors show that NTD mediates the interaction with PP2A and regulates c-Myc phosphorylation and stability, potentially switching PP2A from a tumour suppressor to an oncogene.
- Lingdi Zhang
- , Hengbo Zhou
- & Heide L Ford
-
Article
| Open Access Adoptive cancer immunotherapy using DNA-demethylated T helper cells as antigen-presenting cells
Adoptive cancer immunotherapy using DNA-demethylated T helper cells as antigen-presenting cells
A critical determinant of tumor eradication by adoptive immunotherapy is the tumor associated antigen recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Here the authors generate ex vivo autologous cytotoxic T lymphocytes by exposure to antigens induced by DNA demethylation and report the results of a phase 1 trial of 25 patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme with tumor regression in three patients.
- Alexei F. Kirkin
- , Karine N. Dzhandzhugazyan
- & Walter Fischer
-
Article
| Open Access Early circulating tumor DNA dynamics and clonal selection with palbociclib and fulvestrant for breast cancer
Early circulating tumor DNA dynamics and clonal selection with palbociclib and fulvestrant for breast cancer
Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) may provide a prediction of treatment response, but could be impacted by tumor heterogeneity. Here, the authors investigate ctDNA in CDK4/6 inhibitor treatment in advanced breast cancer, finding ctDNA levels predict progression-free survival and anticipate clonal selection.
- Ben O’Leary
- , Sarah Hrebien
- & Nicholas C. Turner
-
Article
| Open Access Whole-exome sequencing reveals the origin and evolution of hepato-cholangiocarcinoma
Whole-exome sequencing reveals the origin and evolution of hepato-cholangiocarcinoma
Hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma (H-ChC) is a rare subtype of liver cancer with features of hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Here, the authors utilize whole exome sequencing to highlight the monoclonal origin and stemness of H-ChC, as well as substantial intratumoral heterogeneity.
- Anqiang Wang
- , Liangcai Wu
- & Haitao Zhao

 Targeting SPINK1 in the damaged tumour microenvironment alleviates therapeutic resistance
Targeting SPINK1 in the damaged tumour microenvironment alleviates therapeutic resistance