Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Light-wave-controlled Haldane model in monolayer hexagonal boron nitride
Light-wave-controlled Haldane model in monolayer hexagonal boron nitride
We introduce strong tailored light-wave-driven time-reversal symmetry breaking in monolayer hexagonal boron nitride, realizing a sub-laser-cycle controllable analogue of the topological model of Haldane and inducing non-resonant valley polarization.
- Sambit Mitra
- , Álvaro Jiménez-Galán
- & Shubhadeep Biswas
-
Article |
 Integrated frequency-modulated optical parametric oscillator
Integrated frequency-modulated optical parametric oscillator
An integrated device that combines optical parametric oscillation and electro-optic modulation in lithium niobate creates a flat-top frequency-comb-like output with low power requirements.
- Hubert S. Stokowski
- , Devin J. Dean
- & Amir H. Safavi-Naeini
-
Article |
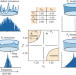 Nozaki–Bekki solitons in semiconductor lasers
Nozaki–Bekki solitons in semiconductor lasers
Free-running stable optical dissipative solitons, called Nozaki–Bekki solitons, are created in a ring semiconductor laser; their spontaneous formation with tuning of laser bias eliminates the need for an external optical pump.
- Nikola Opačak
- , Dmitry Kazakov
- & Benedikt Schwarz
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of interband Berry phase in laser-driven crystals
Observation of interband Berry phase in laser-driven crystals
The Berry phase is resolved in light-driven crystals, via attosecond interferometry, in which the electronic wavefunction accumulates a geometric phase as it interacts with the laser field, mapping its coherence into the emission of high-order harmonics.
- Ayelet J. Uzan-Narovlansky
- , Lior Faeyrman
- & Nirit Dudovich
-
Article |
 Kerr-induced synchronization of a cavity soliton to an optical reference
Kerr-induced synchronization of a cavity soliton to an optical reference
The passive and electronics-free Kerr-induced synchronization of optical-frequency combs could be used in their control and stabilization and to simplify optical clock systems.
- Grégory Moille
- , Jordan Stone
- & Kartik Srinivasan
-
Article
| Open Access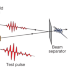 Dynamic optical response of solids following 1-fs-scale photoinjection
Dynamic optical response of solids following 1-fs-scale photoinjection
Petahertz-scale optical-field metrology in a pump-probe setting enables the direct observation of how the optical properties of a medium evolve after 1-fs-scale photoinjection.
- Dmitry A. Zimin
- , Nicholas Karpowicz
- & Vladislav S. Yakovlev
-
Article |
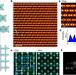 Ultrathin quantum light source with van der Waals NbOCl2 crystal
Ultrathin quantum light source with van der Waals NbOCl2 crystal
A van der Waals crystal, niobium oxide dichloride, with vanishing interlayer electronic coupling and considerable monolayer-like excitonic behaviour in the bulk, as well as strong and scalable second-order optical nonlinearity, is discovered, which enables a high-performance quantum light source.
- Qiangbing Guo
- , Xiao-Zhuo Qi
- & Andrew T. S. Wee
-
Article |
 A photonic integrated continuous-travelling-wave parametric amplifier
A photonic integrated continuous-travelling-wave parametric amplifier
By using Si3N4 photonic integrated circuits on a silicon chip, a continuous-travelling-wave parametric amplifier is shown to yield a parametric gain exceeding both on-chip propagation loss as well as fibre–chip–fibre coupling losses.
- Johann Riemensberger
- , Nikolai Kuznetsov
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
Article |
 Integrated femtosecond pulse generator on thin-film lithium niobate
Integrated femtosecond pulse generator on thin-film lithium niobate
A femtosecond pulse generator is realized using an electro-optic time-lens system integrated on a lithium niobate photonic chip, capable of tunable repetition rates and wavelengths.
- Mengjie Yu
- , David Barton III
- & Marko Lončar
-
Article |
 Femtosecond laser writing of lithium niobate ferroelectric nanodomains
Femtosecond laser writing of lithium niobate ferroelectric nanodomains
We propose and experimentally demonstrate a non-reciprocal near-infrared femtosecond laser-writing technique for reconfigurable three-dimensional nanoscale ferroelectric domain engineering in LiNbO3 crystals.
- Xiaoyi Xu
- , Tianxin Wang
- & Yong Zhang
-
Article |
 Observation of chiral state transfer without encircling an exceptional point
Observation of chiral state transfer without encircling an exceptional point
A study realizes a photonic emulator to probe the temporal evolution of light in a non-Hermitian system, and reports the observation of chiral state transfer without encircling an exceptional point.
- Hadiseh Nasari
- , Gisela Lopez-Galmiche
- & Mercedeh Khajavikhan
-
Article |
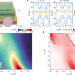 Intelligent infrared sensing enabled by tunable moiré quantum geometry
Intelligent infrared sensing enabled by tunable moiré quantum geometry
Tunable quantum geometric properties of moiré graphene enable the use of a convolutional neural network to simultaneously decipher the light polarization, power and wavelength in a subwavelength-scale smart device.
- Chao Ma
- , Shaofan Yuan
- & Fengnian Xia
-
Article
| Open Access Deep physical neural networks trained with backpropagation
Deep physical neural networks trained with backpropagation
A hybrid algorithm that applies backpropagation is used to train layers of controllable physical systems to carry out calculations like deep neural networks, but accounting for real-world noise and imperfections.
- Logan G. Wright
- , Tatsuhiro Onodera
- & Peter L. McMahon
-
Article |
 Giant modulation of optical nonlinearity by Floquet engineering
Giant modulation of optical nonlinearity by Floquet engineering
Coherent control and giant modulation of optical nonlinearity in a van der Waals layered magnetic insulator is demonstrated using Floquet engineering.
- Jun-Yi Shan
- , M. Ye
- & D. Hsieh
-
Article |
 Optomechanical dissipative solitons
Optomechanical dissipative solitons
Stable, dissipative optomechanical solitons are realized using optical fields in a whispering gallery mode resonator by balancing the optomechanical nonlinearities with a tailored modal dispersion.
- Jing Zhang
- , Bo Peng
- & Lan Yang
-
Article |
 On-chip electro-optic frequency shifters and beam splitters
On-chip electro-optic frequency shifters and beam splitters
Engineering of the coupling between optical modes in a lithium niobate chip enables the realization of tunable, bi-directional and low-loss electro-optic frequency shifters controlled using only continuous and single-tone microwaves.
- Yaowen Hu
- , Mengjie Yu
- & Marko Lončar
-
Article |
 Quantized nonlinear Thouless pumping
Quantized nonlinear Thouless pumping
Nonlinearity is shown to induce quantized topological transport via soliton motion; specifically, we demonstrate nonlinear Thouless pumping of photons in waveguide arrays with a non-uniformly occupied energy band.
- Marius Jürgensen
- , Sebabrata Mukherjee
- & Mikael C. Rechtsman
-
Article |
 Van der Waals heterostructure polaritons with moiré-induced nonlinearity
Van der Waals heterostructure polaritons with moiré-induced nonlinearity
Polaritons formed by moiré excitons in heterobilayers of transition metal dichalcogenides exhibit strong nonlinearity owing to quantum confinement by the tunable moiré lattice potential.
- Long Zhang
- , Fengcheng Wu
- & Hui Deng
-
Article |
 Observation of the exceptional-point-enhanced Sagnac effect
Observation of the exceptional-point-enhanced Sagnac effect
precisely controllable integrated optical gyroscope based on stimulated Brillouin scattering is used to study non-Hermitian physics, revealing a four-fold enhancement of the Sagnac scale factor near exceptional points.
- Yu-Hung Lai
- , Yu-Kun Lu
- & Kerry Vahala
-
Article |
 Non-Hermitian ring laser gyroscopes with enhanced Sagnac sensitivity
Non-Hermitian ring laser gyroscopes with enhanced Sagnac sensitivity
A method based on non-Hermitian singularities, or exceptional points, is established and used to increase the Sagnac scale factor and enhance the sensitivity of ring-laser gyroscopes.
- Mohammad P. Hokmabadi
- , Alexander Schumer
- & Mercedeh Khajavikhan
-
Letter |
 Giant nonreciprocal second-harmonic generation from antiferromagnetic bilayer CrI3
Giant nonreciprocal second-harmonic generation from antiferromagnetic bilayer CrI3
Large second-harmonic generation is observed in antiferromagnetic bilayers of CrI3, providing information about the microscopic origin of layered antiferromagnetism and motivating the use of two-dimensional magnets in nonlinear optical devices.
- Zeyuan Sun
- , Yangfan Yi
- & Shiwei Wu
-
Letter |
 Nonlinear optics in the fractional quantum Hall regime
Nonlinear optics in the fractional quantum Hall regime
Nonlinear optical measurements in a two-dimensional electron system embedded in an optical cavity show enhanced polariton–polariton interactions in the fractional quantum Hall regime.
- Patrick Knüppel
- , Sylvain Ravets
- & Atac Imamoglu
-
Letter |
 Resonant electro-optic frequency comb
Resonant electro-optic frequency comb
A low-power, fixed microwave signal in combination with an optical-pump signal generates an optical frequency comb that spans the whole wavelength range of the telecommunications C-band, with possible applications ranging from spectroscopy to optical communications.
- Alfredo Rueda
- , Florian Sedlmeir
- & Harald G. L. Schwefel
-
Letter |
 Electric field correlation measurements on the electromagnetic vacuum state
Electric field correlation measurements on the electromagnetic vacuum state
Electro-optic detection in a nonlinear crystal is used to measure coherence properties of vacuum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field and deduce the spectrum of the ground state of electromagnetic radiation.
- Ileana-Cristina Benea-Chelmus
- , Francesca Fabiana Settembrini
- & Jérôme Faist
-
Letter |
 An ultrafast symmetry switch in a Weyl semimetal
An ultrafast symmetry switch in a Weyl semimetal
Terahertz light pulses induce transitions between a topological and a trivial phase in the Weyl semimetal WTe2 through an interlayer shear strain.
- Edbert J. Sie
- , Clara M. Nyby
- & Aaron M. Lindenberg
-
Letter |
 Battery-operated integrated frequency comb generator
Battery-operated integrated frequency comb generator
Integrating an optical Kerr frequency comb source with an electronically excited laser pump produces a battery-powered comb generator that does not require external lasers, moveable optics or laboratory set-ups.
- Brian Stern
- , Xingchen Ji
- & Michal Lipson
-
Letter |
 Magnetoelectric inversion of domain patterns
Magnetoelectric inversion of domain patterns
The magnetization or polarization of domain states in multiferroics can be reversed while retaining the overall domain pattern, owing to the inherent versatility in coupling the large number of multiferroic order parameters.
- N. Leo
- , V. Carolus
- & M. Fiebig
-
Letter |
 Flying couplers above spinning resonators generate irreversible refraction
Flying couplers above spinning resonators generate irreversible refraction
One-way propagation of light through a standard telecommunications fibre is demonstrated by coupling the fibre to a rapidly rotating silica-glass sphere.
- Shai Maayani
- , Raphael Dahan
- & Tal Carmon
-
Letter |
 An optical-frequency synthesizer using integrated photonics
An optical-frequency synthesizer using integrated photonics
An optical-frequency synthesizer based on stabilized frequency combs has been developed utilizing chip-scale devices as key components, in a move towards using integrated photonics technology for ultrafast science and metrology.
- Daryl T. Spencer
- , Tara Drake
- & Scott B. Papp
-
Letter |
 Attosecond nonlinear polarization and light–matter energy transfer in solids
Attosecond nonlinear polarization and light–matter energy transfer in solids
Petahertz-bandwidth metrology is demonstrated in the measurement of nonlinear polarization in silica.
- A. Sommer
- , E. M. Bothschafter
- & F. Krausz
-
Letter |
 Optical attosecond pulses and tracking the nonlinear response of bound electrons
Optical attosecond pulses and tracking the nonlinear response of bound electrons
Intense light pulses in the visible and adjacent spectral ranges with their energy mostly confined to a half wave cycle—optical attosecond pulses—are synthesized and used to measure the time it takes electrons to respond to light.
- M. Th. Hassan
- , T. T. Luu
- & E. Goulielmakis
-
Letter |
 Linking high harmonics from gases and solids
Linking high harmonics from gases and solids
High-harmonic generation in zinc oxide illuminated by an intense, pulsed, mid-infrared laser is found to involve a recollision effect in which electrons recollide with holes causing harmonics to be emitted, a process similar to that which occurs in atomic systems.
- G. Vampa
- , T. J. Hammond
- & P. B. Corkum
-
Letter |
 Four-wave mixing experiments with extreme ultraviolet transient gratings
Four-wave mixing experiments with extreme ultraviolet transient gratings
Four-wave mixing processes are achieved at suboptical wavelengths by using a free-electron laser as a source to generate extreme ultraviolet pulses that produce transient gratings.
- F. Bencivenga
- , R. Cucini
- & C. Masciovecchio
-
Letter |
 Probing excitonic dark states in single-layer tungsten disulphide
Probing excitonic dark states in single-layer tungsten disulphide
A series of long-lived excitons in a monolayer of tungsten disulphide are found to have strong binding energy and an energy dependence on orbital momentum that significantly deviates from conventional, three-dimensional, behaviour.
- Ziliang Ye
- , Ting Cao
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Letter |
 Giant nonlinear response from plasmonic metasurfaces coupled to intersubband transitions
Giant nonlinear response from plasmonic metasurfaces coupled to intersubband transitions
Multiple-quantum-well semiconductors can provide one of the largest known nonlinear material responses, which is, however, geometrically limited to light beams polarized perpendicular to the semiconductor layers; by coupling a plasmonic metasurface to the semiconductor heterostructure, this limitation can be lifted, opening a new path towards ultrathin planarized components with large nonlinear response.
- Jongwon Lee
- , Mykhailo Tymchenko
- & Mikhail A. Belkin
-
Letter |
 A quantum gate between a flying optical photon and a single trapped atom
A quantum gate between a flying optical photon and a single trapped atom
Quantum gates — in which stationary quantum bits are combined with ‘flying’ quantum bits, that is, photons — will be essential in quantum networks; such a gate, between a laser-trapped atomic quantum bit and a single photon, is now reported.
- Andreas Reiserer
- , Norbert Kalb
- & Stephan Ritter
-
Letter |
 Attractive photons in a quantum nonlinear medium
Attractive photons in a quantum nonlinear medium
By coupling light to strongly interacting atomic Rydberg states in a dispersive regime, it is possible to induce individual photons to travel as massive particles with strong mutual attraction, such that the propagation of photon pairs is dominated by a two-photon bound state.
- Ofer Firstenberg
- , Thibault Peyronel
- & Vladan Vuletić
-
Letter |
 A micrometre-scale Raman silicon laser with a microwatt threshold
A micrometre-scale Raman silicon laser with a microwatt threshold
A continuous-wave Raman silicon laser with a photonic-crystal nanocavity less than ten micrometres in size and an unprecedentedly low lasing threshold of one microwatt is demonstrated, showing that the integration of all-silicon devices into photonic circuits may be possible.
- Yasushi Takahashi
- , Yoshitaka Inui
- & Susumu Noda
-
News & Views |
 Brighter images with no added noise
Brighter images with no added noise
A special type of optical amplifier based on a vapour of rubidium has been demonstrated that makes faint images brighter without adding noise. This concept could find use in biological imaging and image processing.
- Stéphane Clemmen
- & Alexander Gaeta
-
News & Views |
 Mixing waves in a diamond
Mixing waves in a diamond
Use of an ultra-high-intensity X-ray laser has allowed X-ray and optical waves to be mixed in a diamond sample. The effect paves the way to studying the microscopic optical response of materials on an atomic scale. See Article p.603
- Nina Rohringer
-
Letter |
 Non-classical light generated by quantum-noise-driven cavity optomechanics
Non-classical light generated by quantum-noise-driven cavity optomechanics
The effect of quantum radiation-pressure fluctuations on the collective motion of ultracold atoms is observed in a cavity-optomechanical system, and the back-action of this motion on the cavity light field is shown to produce sub-shot-noise optical squeezing.
- Daniel W. C. Brooks
- , Thierry Botter
- & Dan M. Stamper-Kurn
-
Letter |
 Quantum nonlinear optics with single photons enabled by strongly interacting atoms
Quantum nonlinear optics with single photons enabled by strongly interacting atoms
A cold, dense atomic gas is found to be optically nonlinear at the level of individual quanta, thereby opening possibilities for quantum-by-quantum control of light fields, including single-photon switching and deterministic quantum logic.
- Thibault Peyronel
- , Ofer Firstenberg
- & Vladan Vuletić
-
Letter |
 Direct generation of photon triplets using cascaded photon-pair sources
Direct generation of photon triplets using cascaded photon-pair sources
Non-classical states of light, such as entangled photon states, form an essential quantum resource. Entangled photon pairs can be created by spontaneous parametric down-conversion of laser light, but so far it has not been possible to produce photon triplets in this way. These authors report the generation of quantum-correlated photon triplets by cascaded down-conversion of a single pump photon. This should find widespread use in optical quantum technologies.
- Hannes Hübel
- , Deny R. Hamel
- & Thomas Jennewein
-
News & Views |
Single-atom transistor for light
A subtle quantum-interference effect has been used to control the optical response of a single atom confined in a cavity. It could offer a means to develop logic gates for an optical quantum computer.
- Scott Parkins
-
News & Views |
 Chaotic billiard lasers
Chaotic billiard lasers
The chaotic motion of light rays gives microlasers surprising emission properties, enhancing quantum tunnelling by many orders of magnitude and producing highly directional output beams.
- A. Douglas Stone

 Optical clocks at sea
Optical clocks at sea