Featured
-
-
Article |
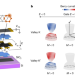 Orbital multiferroicity in pentalayer rhombohedral graphene
Orbital multiferroicity in pentalayer rhombohedral graphene
Orbital multiferroicity reported in pentalayer rhombohedral graphene features ferro-orbital-magnetism and ferro-valleytricity, both of which can be controlled by an electric field.
- Tonghang Han
- , Zhengguang Lu
- & Long Ju
-
Article |
 DNA-based programmable gate arrays for general-purpose DNA computing
DNA-based programmable gate arrays for general-purpose DNA computing
Generic single-stranded oligonucleotides used as a uniform transmission signal can reliably integrate large-scale DNA integrated circuits with minimal leakage and high fidelity for general-purpose computing.
- Hui Lv
- , Nuli Xie
- & Chunhai Fan
-
Article |
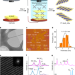 Phase-dependent growth of Pt on MoS2 for highly efficient H2 evolution
Phase-dependent growth of Pt on MoS2 for highly efficient H2 evolution
We report the production of MoS2 nanosheets with high phase purity, showing that the 2H-phase templates facilitate epitaxial growth of Pt nanoparticles, whereas the 1T′ phase supports single-atomically dispersed Pt atoms.
- Zhenyu Shi
- , Xiao Zhang
- & Hua Zhang
-
News & Views |
 Surface interaction propels molecule forwards
Surface interaction propels molecule forwards
The interaction of a molecule with a specific surface has been shown to produce consistent unidirectional motion driven by voltage pulses. The mechanism can even facilitate the transport of molecular cargo.
- Leo Gross
- & Jascha Repp
-
Article |
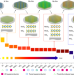 Stack growth of wafer-scale van der Waals superconductor heterostructures
Stack growth of wafer-scale van der Waals superconductor heterostructures
Stacks of van der Waals superconductor heterostructures comprising many layers and several blocks of two-dimensional materials have been grown in a highly controllable manner at a wafer scale using a high-to-low temperature strategy.
- Zhenjia Zhou
- , Fuchen Hou
- & Libo Gao
-
Article |
 Adsorbate motors for unidirectional translation and transport
Adsorbate motors for unidirectional translation and transport
An adsorbate motor that moves unidirectionally on a copper surface is achieved by inducing intramolecular hydrogen transfer in a single molecule.
- Grant J. Simpson
- , Mats Persson
- & Leonhard Grill
-
Article |
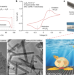 Visualizing interfacial collective reaction behaviour of Li–S batteries
Visualizing interfacial collective reaction behaviour of Li–S batteries
In situ liquid-cell electrochemical transmission electron microscopy allows the direct visualization of the transformation of lithium polysulfides over electrode surfaces at the atomic scale, leading to a new energy-storage mechanism in lithium–sulfur batteries.
- Shiyuan Zhou
- , Jie Shi
- & Hong-Gang Liao
-
News |
 University mourns nanoscientist killed on UNC campus
University mourns nanoscientist killed on UNC campus
Zijie Yan led a laboratory at the University of North Carolina that studied light–matter interactions on the nanometre scale.
- Mariana Lenharo
-
Article
| Open Access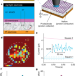 Proton transport through nanoscale corrugations in two-dimensional crystals
Proton transport through nanoscale corrugations in two-dimensional crystals
A study using high-resolution scanning electrochemical cell microscopy attributes proton permeation through defect-free graphene and hexagonal boron nitride to transport across areas of the structure that are under strain.
- O. J. Wahab
- , E. Daviddi
- & P. R. Unwin
-
Article
| Open Access An analog-AI chip for energy-efficient speech recognition and transcription
An analog-AI chip for energy-efficient speech recognition and transcription
A low-power chip that runs AI models using analog rather than digital computation shows comparable accuracy on speech-recognition tasks but is more than 14 times as energy efficient.
- S. Ambrogio
- , P. Narayanan
- & G. W. Burr
-
Perspective |
 The future transistors
The future transistors
The challenges and opportunities for the design of field-effect transistors are discussed and a vision of future transistors and potential innovation opportunities is provided.
- Wei Cao
- , Huiming Bu
- & Kaustav Banerjee
-
Research Highlight |
 DNA origami provides a stout armour for cells
DNA origami provides a stout armour for cells
A double layer of twisted, folded DNA protects cells from mechanical forces while allowing them freedom to assemble.
-
Research Briefing |
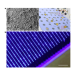 Liquid-based assembly accelerates production of microLED displays
Liquid-based assembly accelerates production of microLED displays
MicroLED displays have advantages over commercially available technologies, but are difficult to put together efficiently. Agitating microLED chiplets and a substrate together in fluid causes them to self‑assemble quickly and with high yield.
-
Research Briefing |
 Nanoscale origami with DNA-wireframe paper
Nanoscale origami with DNA-wireframe paper
Origami — the art of making various shapes from a single piece of paper — has been realized at the nanoscale using DNA. Sheets of ‘DNA wireframe paper’ have been developed that, through folding along crease lines, can be transformed into a range of target shapes in response to external stimuli.
-
Article |
 Harnessing a paper-folding mechanism for reconfigurable DNA origami
Harnessing a paper-folding mechanism for reconfigurable DNA origami
A method is presented to harness the paper-folding mechanism of reconfigurable macroscale systems to create reconfigurable DNA origami structures, in anticipation that it will advance the development of complex molecular systems.
- Myoungseok Kim
- , Chanseok Lee
- & Do-Nyun Kim
-
Article |
 Observation of the orbital Hall effect in a light metal Ti
Observation of the orbital Hall effect in a light metal Ti
The orbital Hall effect is observed in the light metal titanium, confirming the orbital Hall effect and indicating that orbital angular momentum is an important degree of freedom in solids.
- Young-Gwan Choi
- , Daegeun Jo
- & Hyun-Woo Lee
-
Research Briefing |
 Nanoparticles containing diverse elements made using liquid metal
Nanoparticles containing diverse elements made using liquid metal
The synthesis of high-entropy alloy nanoparticles (HEA-NPs) — small particles each containing multiple principal metal elements — typically requires extreme conditions to ensure adequate mixing of constituents. Innovative experiments show that the liquid metal can act as a mixing reservoir to facilitate the synthesis of a diverse range of such nanoparticles in mild conditions.
-
Article |
 Liquid metal for high-entropy alloy nanoparticles synthesis
Liquid metal for high-entropy alloy nanoparticles synthesis
We discovered that liquid metal endowing negative mixing enthalpy with other elements could provide a stable thermodynamic condition and act as a desirable dynamic mixing reservoir, realizing the synthesis of high-entropy alloy nanoparticles.
- Guanghui Cao
- , Jingjing Liang
- & Lei Fu
-
Article |
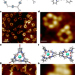 Characterization of just one atom using synchrotron X-rays
Characterization of just one atom using synchrotron X-rays
Using a specialized tip as a detector, the fingerprints of a single atom of iron and terbium are observed in synchrotron X-ray absorption spectra, allowing elemental and chemical characterization one atom at a time.
- Tolulope M. Ajayi
- , Nozomi Shirato
- & Saw-Wai Hla
-
Article |
 Indefinite and bidirectional near-infrared nanocrystal photoswitching
Indefinite and bidirectional near-infrared nanocrystal photoswitching
This study reports unlimited near-infrared photoswitching in inorganic avalanching nanoparticles via a discrete shift of threshold intensity mediated by internal defect-based colour centres.
- Changhwan Lee
- , Emma Z. Xu
- & P. James Schuck
-
Article
| Open Access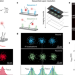 Ångström-resolution fluorescence microscopy
Ångström-resolution fluorescence microscopy
The authors introduce a single-molecule DNA-barcoding method, resolution enhancement by sequential imaging, that improves the resolution of fluorescence microscopy down to the Ångström scale using off-the-shelf fluorescence microscopy hardware and reagents.
- Susanne C. M. Reinhardt
- , Luciano A. Masullo
- & Ralf Jungmann
-
Article |
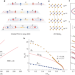 Orbital Fulde–Ferrell–Larkin–Ovchinnikov state in an Ising superconductor
Orbital Fulde–Ferrell–Larkin–Ovchinnikov state in an Ising superconductor
The discovery of an orbital Fulde–Ferrell–Larkin–Ovchinnikov state in the multilayer Ising superconductor 2H-NbSe2, in which the translational and rotational symmetries are broken, enables the preparation of such states in other materials with broken inversion symmetries.
- Puhua Wan
- , Oleksandr Zheliuk
- & Jianting Ye
-
Research Highlight |
 Gut microbes ‘eat’ nanoparticles — leading to microbiome changes
Gut microbes ‘eat’ nanoparticles — leading to microbiome changes
Humans can accidentally ingest nanomaterials in consumer products, with unknown effects.
-
News & Views |
 Bright light coaxed from electrically driven quantum dots
Bright light coaxed from electrically driven quantum dots
Nanocrystals made from a semiconducting material have been shown to emit intense light when excited with an electric current. The technology could be used to build a type of laser that is more versatile than those in general use.
- Thilo Stöferle
- & Rainer F. Mahrt
-
Article |
 Constrained C2 adsorbate orientation enables CO-to-acetate electroreduction
Constrained C2 adsorbate orientation enables CO-to-acetate electroreduction
A study using a copper-in-silver dilute alloy catalyst in a high-pressure gas flow reactor reports highly selective electrosynthesis of acetate from carbon monoxide.
- Jian Jin
- , Joshua Wicks
- & Yuanjie Pang
-
Article
| Open Access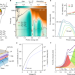 Electrically driven amplified spontaneous emission from colloidal quantum dots
Electrically driven amplified spontaneous emission from colloidal quantum dots
Colloidal quantum dot devices demonstrating electrically pumped amplified spontaneous emission are described, showing strong, broadband optical gain and bright edge emission, opening the path to solution-processable laser diodes.
- Namyoung Ahn
- , Clément Livache
- & Victor I. Klimov
-
Article |
 Tunable electron–flexural phonon interaction in graphene heterostructures
Tunable electron–flexural phonon interaction in graphene heterostructures
Experimental observation and calculations show that broken reflection symmetry in graphene heterostructures allows tunable electron–flexural phonon coupling, providing a way to control quantum matter at the atomic scale.
- Mir Mohammad Sadeghi
- , Yajie Huang
- & Li Shi
-
Article |
 Many-body cavity quantum electrodynamics with driven inhomogeneous emitters
Many-body cavity quantum electrodynamics with driven inhomogeneous emitters
Under strong excitation, inhomogeneously broadened solid-state emitters coupled with high cooperativity to a cavity demonstrate collectively induced transparency and dissipative many-body dynamics, resulting from cavity–ion coupling.
- Mi Lei
- , Rikuto Fukumori
- & Andrei Faraon
-
Article |
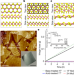 pH-dependent water permeability switching and its memory in MoS2 membranes
pH-dependent water permeability switching and its memory in MoS2 membranes
We demonstrate the memory effects and stimuli-regulated transport of molecules through an intelligent, phase-changing MoS2 membrane in response to external pH, a phenomenon unique to the 1T′ phase of MoS2.
- C. Y. Hu
- , A. Achari
- & R. R. Nair
-
Article
| Open Access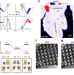 Two-dimensional ferroelectricity in a single-element bismuth monolayer
Two-dimensional ferroelectricity in a single-element bismuth monolayer
A single-element ferroelectric state is observed in a black phosphorus-like bismuth layer, in which the ordered charge transfer and the regular atom distortion between sublattices happen simultaneously and ferroelectric switching is further visualized experimentally.
- Jian Gou
- , Hua Bai
- & Andrew Thye Shen Wee
-
Article |
 2D fin field-effect transistors integrated with epitaxial high-k gate oxide
2D fin field-effect transistors integrated with epitaxial high-k gate oxide
The epitaxial synthesis of high-density, vertically aligned arrays of two-dimensional (2D) fin-oxide heterostructures is described, enabling the fabrication of 2D fin field-effect transistors with high electron mobility and desirable low-power specifications.
- Congwei Tan
- , Mengshi Yu
- & Hailin Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum-well states at the surface of a heavy-fermion superconductor
Quantum-well states at the surface of a heavy-fermion superconductor
By using millikelvin scanning tunnelling microscopy to study atomically flat terraces on U-terminated surfaces of the heavy-fermion superconductor URu2Si2, the two-dimensional heavy fermions are shown to form quantum-well states on the surface.
- Edwin Herrera
- , Isabel Guillamón
- & Hermann Suderow
-
Article |
 Ballistic two-dimensional InSe transistors
Ballistic two-dimensional InSe transistors
A two-dimensional field-effect transistor made of indium selenide is shown to outperform state-of-the-art silicon-based transistors, operating at lower supply voltage and achieving record high transconductance and ballistic ratio.
- Jianfeng Jiang
- , Lin Xu
- & Lian-Mao Peng
-
Where I Work |
 I work in an ultra-clean room on ultra-small chips
I work in an ultra-clean room on ultra-small chips
Luis Fonseca leads research into micro-, nano- and photonic chip technologies that could kill cancer cells, protect the environment and facilitate space research.
- Patricia Maia Noronha
-
News & Views |
 Bow-tie particles boast a tunable twist
Bow-tie particles boast a tunable twist
Particles that self-assemble from nanoribbons into bow-tie-shaped structures can be tailored to change the degree of their twist. A search for how best to quantify this twist homes in on a measure of how the bow ties respond to light.
- Bart Kahr
-
Article |
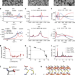 Photonically active bowtie nanoassemblies with chirality continuum
Photonically active bowtie nanoassemblies with chirality continuum
Self-limited assembly of 'imperfect' chiral nanoparticles enables formation of bowtie-shaped microparticles with size monodispersity and continuously variable chirality to be used for printing photonically active metasurfaces.
- Prashant Kumar
- , Thi Vo
- & Nicholas A. Kotov
-
Research Briefing |
 Stretchy electronic devices assembled in a Lego-like way
Stretchy electronic devices assembled in a Lego-like way
In current stretchable electronic devices, connection points between modules are made using commercially available pastes and break easily under mechanical deformation. An innovative connection interface has been developed to enable robust stretchable devices to be reliably assembled in a Lego‑like manner by simply pressing the interfaces of two modules together without pastes.
-
Nature Podcast |
 How ‘metadevices’ could make electronics faster
How ‘metadevices’ could make electronics faster
Getting electronics into super-fast terahertz speeds, and how cognitive changes could alter social media’s effects on young people.
- Nick Petrić Howe
- & Shamini Bundell
-
Article |
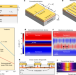 Electronic metadevices for terahertz applications
Electronic metadevices for terahertz applications
Through microscopic manipulation of radiofrequency fields, a new class of compact terahertz devices is proposed, setting the stage for next-generation ultrafast semiconductor electronics.
- Mohammad Samizadeh Nikoo
- & Elison Matioli
-
Research Briefing |
 Designer silicon nanowires produce hydrogen from water and light
Designer silicon nanowires produce hydrogen from water and light
Silicon nanowires that can convert light into electricity were engineered to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. When integrated with co-catalysts and suspended in water, these light-activated nanoreactors produced hydrogen gas under visible and infrared light.
-
Article |
 Water splitting with silicon p–i–n superlattices suspended in solution
Water splitting with silicon p–i–n superlattices suspended in solution
The simplicity of particle suspension reactors and the precise synthetic control afforded by silicon nanowire growth are used to develop a system that can produce hydrogen fuel by splitting water with sunlight.
- Taylor S. Teitsworth
- , David J. Hill
- & James F. Cahoon
-
Article
| Open Access Attosecond field emission
Attosecond field emission
By using sub-cycle light transients to induce optical field emission of electron pulses from tungsten nanotips and a weak replica of the same transient, investigation of attosecond emission dynamics in real time is demonstrated.
- H. Y. Kim
- , M. Garg
- & E. Goulielmakis
-
Article |
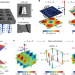 Observation of intrinsic chiral bound states in the continuum
Observation of intrinsic chiral bound states in the continuum
Chiral metasurfaces have been produced, with experimental observation of intrinsic chiral bound states in the continuum, which may lead to applications in chiral light sources and detectors, chiral sensing, valleytronics and asymmetric photocatalysis.
- Yang Chen
- , Huachun Deng
- & Cheng-Wei Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access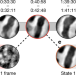 Coherent correlation imaging for resolving fluctuating states of matter
Coherent correlation imaging for resolving fluctuating states of matter
Nanoscale magnetic fluctuations are spatiotemporally resolved beyond conventional resolution limits using coherent correlation imaging, in which frames in Fourier space are recorded and analysed using an iterative hierarchical clustering algorithm.
- Christopher Klose
- , Felix Büttner
- & Bastian Pfau
-
Article |
 Non-epitaxial single-crystal 2D material growth by geometric confinement
Non-epitaxial single-crystal 2D material growth by geometric confinement
Geometric confinement on arbitrary substrates promotes, without epitaxial seeding, the layer-by-layer growth of two-dimensional single-crystal monolayers and bilayers of transition metal dichalcogenides.
- Ki Seok Kim
- , Doyoon Lee
- & Jeehwan Kim
-
Research Briefing |
 An artificial molecular motor powered by electricity
An artificial molecular motor powered by electricity
Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical motion. A molecular motor has been designed in which electricity drives redox reaction cycles that lead to the movement of two small rings around a large circular loop. The small rings make one full revolution around the loop for every two redox cycles.
-
Article
| Open Access An electric molecular motor
An electric molecular motor
An electrically driven motor on the molecular scale based on [3]catenane is described, in which two cyclobis(paraquat-p-phenylene) rings operate by means of redox reactions, demonstrating highly unidirectional movement around a circular loop.
- Long Zhang
- , Yunyan Qiu
- & J. Fraser Stoddart
-
Article |
 Approaching the quantum limit in two-dimensional semiconductor contacts
Approaching the quantum limit in two-dimensional semiconductor contacts
The electrical contact of two-dimensional transistors is pushed close to the quantum limit by hybridization of the energy bands with antimony; the contacts have low contact resistance and excellent stability.
- Weisheng Li
- , Xiaoshu Gong
- & Xinran Wang
-
Article |
 Long-range ordered porous carbons produced from C60
Long-range ordered porous carbons produced from C60
A new type of carbon, long-range ordered porous carbon, is synthesized from carbon fullerenes at the gram scale and under ambient pressure.
- Fei Pan
- , Kun Ni
- & Yanwu Zhu

 Meet the unsung scientists behind the Nobel for quantum dots
Meet the unsung scientists behind the Nobel for quantum dots