Perspective
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Stress-induced ordering evolution of 1D segmented heteronanostructures and their chemical post-transformations
Stress-induced ordering evolution of 1D segmented heteronanostructures and their chemical post-transformations
The formation mechanisms for periodic heterostructures are still poorly understood. Here, the authors propose a versatile approach to synthesize one-dimensional segmented heterostructures and reveal a stress-induced ordering mechanism through phase-field simulations.
- Qing-Xia Chen
- , Yu-Yang Lu
- & Shu-Hong Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Helical-caging enables single-emitted large asymmetric full-color circularly polarized luminescence
Helical-caging enables single-emitted large asymmetric full-color circularly polarized luminescence
Circularly polarised luminescence (CPL) is essential for asymmetric synthetic photochemistry. Here, the authors integrate white quantum dots with chiral nematic liquid crystal or liquid crystal polymer to achieve single-emitted tuneable full-colour or white CPL for enantioselective polymerization.
- Yajie Zhou
- , Yaxin Wang
- & Taotao Zhuang
-
Article
| Open Access Precise solid-phase synthesis of CoFe@FeOx nanoparticles for efficient polysulfide regulation in lithium/sodium-sulfur batteries
Precise solid-phase synthesis of CoFe@FeOx nanoparticles for efficient polysulfide regulation in lithium/sodium-sulfur batteries
Solid-phase synthesis strategy is promising for fabricating desired complex metal nanoparticles on supports. Here, the authors synthesize CoFe@FeOx core-shell nanoparticles as the separator coatings via precise solid-phase method which effectively regulates polysulfides for lithium/ sodium-sulfur batteries.
- Yanping Chen
- , Yu Yao
- & Jian Liu
-
Article
| Open Access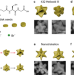 Halide-assisted differential growth of chiral nanoparticles with threefold rotational symmetry
Halide-assisted differential growth of chiral nanoparticles with threefold rotational symmetry
Expanding the library of chiral plasmonic nanoparticles will foster the development of chiroptical applications. Here, the authors apply halide-assisted differential growth to convert Au nanodisks into triskelion-shaped chiral nanoparticles with threefold rotational symmetry.
- Jiapeng Zheng
- , Christina Boukouvala
- & Jianfang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Remodeling nanodroplets into hierarchical mesoporous silica nanoreactors with multiple chambers
Remodeling nanodroplets into hierarchical mesoporous silica nanoreactors with multiple chambers
Multi-chambered structures have attracted great attention due to their ability to create multifunctional partitions in different chambers. Here, the authors prepared mesoporous silica nanoreactors with hierarchical chambers for catalytic cascades.
- Yuzhu Ma
- , Hongjin Zhang
- & Dongyuan Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Coemissive luminescent nanoparticles combining aggregation-induced emission and quenching dyes prepared in continuous flow
Coemissive luminescent nanoparticles combining aggregation-induced emission and quenching dyes prepared in continuous flow
Developing efficient light harvesting systems at low cost is a challenge. Here, the authors synthesized coemissive dyes in a continuous flow microreactor featuring a controlled cascade FRET process combining aggregation-induced emission and quenching.
- Chong Li
- , Qi Liu
- & Shengyang Tao
-
Article
| Open Access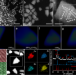 A library of polytypic copper-based quaternary sulfide nanocrystals enables efficient solar-to-hydrogen conversion
A library of polytypic copper-based quaternary sulfide nanocrystals enables efficient solar-to-hydrogen conversion
While polytypic semiconductors are promising for solar-to-fuel applications, preparing homojunction nanomaterials has proven challenging. Here, authors obtain a library of polytypic copper-based quaternary sulfide nanocrystals by selective epitaxial growth of kesterite phase on wurtzite structure.
- Liang Wu
- , Qian Wang
- & Shu-Hong Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Six-photon upconverted excitation energy lock-in for ultraviolet-C enhancement
Six-photon upconverted excitation energy lock-in for ultraviolet-C enhancement
Photon upconversion with near-infrared excitation and ultraviolet emission has many applications, but suffers from low quantum efficiency. Here, the authors report a six-photon upconversion process in nanoparticles with heterogeneous core-multishell structure, that regulate the energy transfer pathway.
- Qianqian Su
- , Han-Lin Wei
- & Dayong Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmon-driven synthesis of individual metal@semiconductor core@shell nanoparticles
Plasmon-driven synthesis of individual metal@semiconductor core@shell nanoparticles
Light-driven heating of plasmonic metal nanoparticles can activate temperature-sensitive reactions at the nanoscale. Here, the authors exploit such nanoscale plasmonic reactors to drive, control, and spectroscopically track the growth of single metal@semiconductor core@shell nanoparticles.
- Rifat Kamarudheen
- , Gayatri Kumari
- & Andrea Baldi
-
Article
| Open Access A nanomaterials discovery robot for the Darwinian evolution of shape programmable gold nanoparticles
A nanomaterials discovery robot for the Darwinian evolution of shape programmable gold nanoparticles
The ability to discover and optimise the synthesis of inorganic nanomaterials has significant impact on various fields, from sensing to medicine. Here, the authors use a genetic algorithm to drive a robotic platform toward a pre-defined, spectroscopic goal in order to discover and optimise the conditions for several nanoparticle shapes.
- Daniel Salley
- , Graham Keenan
- & Leroy Cronin
-
Comment
| Open Access Paving the path to the future of carbogenic nanodots
Paving the path to the future of carbogenic nanodots
Insufficient purification and incomplete characterization pose a serious problem for attributing photoluminescence properties to carbogenic nanodots, especially those synthesized by bottom-up approaches. Here, we provide a roadmap for the successful future of these nanodots.
- Navneet C. Verma
- , Aditya Yadav
- & Chayan K. Nandi
-
Article
| Open Access On demand synthesis of hollow fullerene nanostructures
On demand synthesis of hollow fullerene nanostructures
At nanoscale, it is synthetically very difficult to increase the structural complexity of hollow structures. Here, the authors use a stepwise liquid templating strategy to build, assemble, and interconnect fullerene hollow nanostructures, just like the synthetic freedom one could have with pottery.
- Fei Han
- , Ruoxu Wang
- & Hongyu Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Pulsed axial epitaxy of colloidal quantum dots in nanowires enables facet-selective passivation
Pulsed axial epitaxy of colloidal quantum dots in nanowires enables facet-selective passivation
The precise control over nanoscale structures is crucial in developing new, functional nanomaterials. Here, authors demonstrate a controllable method to epitaxially stack CdS quantum dots into ZnS nanowires and show improved photocatalytic hydrogen evolution activities.
- Yi Li
- , Tao-Tao Zhuang
- & Shu-Hong Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Deconvolution of octahedral Pt3Ni nanoparticle growth pathway from in situ characterizations
Deconvolution of octahedral Pt3Ni nanoparticle growth pathway from in situ characterizations
Understanding the growth pathway of faceted alloy nanoparticles at the atomic level is crucial to morphology control and property tuning, but remains a challenge. Here, the authors reveal the particle growth and facet formation mechanisms of octahedral Pt3Ni nanoparticles using multiple cutting-edge in situ techniques.
- Xiaochen Shen
- , Changlin Zhang
- & Zhenmeng Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Design principles of chiral carbon nanodots help convey chirality from molecular to nanoscale level
Design principles of chiral carbon nanodots help convey chirality from molecular to nanoscale level
A promising and efficient route to chiral materials involves the transfer of chirality across length scales. Here, the authors use chiral molecular precursors to synthesize chiral carbon nanodots, which in turn can template the formation of chiral supramolecular assemblies.
- Luka Ðorđević
- , Francesca Arcudi
- & Maurizio Prato
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution of thiolate-stabilized Ag nanoclusters from Ag-thiolate cluster intermediates
Evolution of thiolate-stabilized Ag nanoclusters from Ag-thiolate cluster intermediates
Gold nanoclusters are known to grow stepwise from gold-thiolate monomers and oligomers. Here, the authors find that the evolution of silver nanoclusters differs completely from that of gold: rather than following a bottom-up pathway, the clusters evolve from similarly-sized Ag-thiolate cluster intermediates.
- Yitao Cao
- , Jiahao Guo
- & Tierui Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Spontaneous formation of gold nanostructures in aqueous microdroplets
Spontaneous formation of gold nanostructures in aqueous microdroplets
Reactions in aqueous microdroplets can significantly differ from those in bulk. Here, the authors report microdroplets that not only accelerate gold nanoparticle formation by several orders of magnitude but also promote spontaneous nanostructure formation with no reducing agents or template.
- Jae Kyoo Lee
- , Devleena Samanta
- & Richard N. Zare
-
Article
| Open Access Au@Nb@H
x
K1-xNbO3 nanopeapods with near-infrared active plasmonic hot-electron injection for water splitting
Au@Nb@H
x
K1-xNbO3 nanopeapods with near-infrared active plasmonic hot-electron injection for water splitting
Although near-infrared light makes up a large portion of the solar spectrum, harvesting it for photocatalytic applications remains challenging. Here the authors deposit unidirectional Au@Nb core-shell nanoparticles into tubular H x K1–xNbO3 nanoscrolls and report cooperative full solar spectrum absorption.
- Ying-Chu Chen
- , Yu-Kuei Hsu
- & Claus Feldmann
-
Article
| Open Access Uncovering active precursors in colloidal quantum dot synthesis
Uncovering active precursors in colloidal quantum dot synthesis
Little is understood about the chemical evolution of precursors to quantum dots. Here, the authors find that under the high temperature conditions typical of CdSe quantum dot synthesis, precursors decompose into highly reactive species in a critical first step before forming monomers and finally nanocrystals.
- Leah C. Frenette
- & Todd D. Krauss
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic-level molybdenum oxide nanorings with full-spectrum absorption and photoresponsive properties
Atomic-level molybdenum oxide nanorings with full-spectrum absorption and photoresponsive properties
Nanostructures with atomic-level thicknesses have the potential to exhibit unique size-dependent properties. Here the authors fabricate sulfur-doped molybdenum oxide architectures with tunable ring-in-ring morphologies and strong visible- and IR-light absorption, endowing them with a range of photoresponsive properties.
- Yong Yang
- , Yang Yang
- & Xun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Precise control of alloying sites of bimetallic nanoclusters via surface motif exchange reaction
Precise control of alloying sites of bimetallic nanoclusters via surface motif exchange reaction
Doping metal nanoclusters at specific sites is a powerful strategy for tuning their properties. Here, the authors precisely control the alloying sites of bimetallic nanoclusters by replacing entire surface motifs with structurally similar heteroatom motifs, tuning the surface composition motif-by-motif rather than atom-by-atom.
- Qiaofeng Yao
- , Yan Feng
- & Jianping Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Atomically-precise colloidal nanoparticles of cerium dioxide
Atomically-precise colloidal nanoparticles of cerium dioxide
Control over nanoparticle atomicity has not yet been extended to metal oxides. Here, the authors present the synthesis and X-ray crystal structures of a family of atomically precise ceria nanoclusters, a pivotal step for understanding the relationship between their atomic structure and reactivity.
- Kylie J. Mitchell
- , Khalil A. Abboud
- & George Christou
-
Article
| Open Access Inflating hollow nanocrystals through a repeated Kirkendall cavitation process
Inflating hollow nanocrystals through a repeated Kirkendall cavitation process
Owing to their unique properties, hollow metal nanocrystals demonstrate greater catalytic promise than their solid counterparts. Here the authors produce hollow and inflated palladium nanocrystals with thin shells via a repeated Kirkendall cavitation process, and demonstrate their activity for formic acid oxidation.
- He Tianou
- , Weicong Wang
- & Yadong Yin
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of the nanoscale Kirkendall effect during galvanic replacement reactions
Direct observation of the nanoscale Kirkendall effect during galvanic replacement reactions
Hollow nanoparticles can be synthesized by galvanic replacement or the Kirkendall effect, which are generally regarded as two separate processes. Here, the authors use liquid TEM to follow the entire galvanic replacement of Ag nanocubes, finding experimental evidence that the Kirkendall effect is a key intermediate stage during hollowing.
- See Wee Chee
- , Shu Fen Tan
- & Utkur Mirsaidov
-
Article
| Open Access Growth mechanism of strongly emitting CH3NH3PbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals with a tunable bandgap
Growth mechanism of strongly emitting CH3NH3PbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals with a tunable bandgap
The development of perovskite nanocrystals is limited by poor mechanistic understanding of their growth. Here, the authors systematically study the ligand-assisted reprecipitation synthesis of CH3NH3PbBr3 nanocrystals, revealing the effect of precursor and ligand concentrations on bandgap tunability.
- He Huang
- , Johannes Raith
- & Andrey L. Rogach
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding seed-mediated growth of gold nanoclusters at molecular level
Understanding seed-mediated growth of gold nanoclusters at molecular level
Synthetic nanochemistry currently lacks the molecular step-by-step routes afforded to organic chemistry by total synthesis. Here, the authors track the seeded growth of atom-precise gold nanoclusters using mass spectrometry, revealing that the clusters evolve through a series of intermediates in two-electron steps.
- Qiaofeng Yao
- , Xun Yuan
- & Jianping Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Binary temporal upconversion codes of Mn2+-activated nanoparticles for multilevel anti-counterfeiting
Binary temporal upconversion codes of Mn2+-activated nanoparticles for multilevel anti-counterfeiting
Luminescent materials that are capable of binary temporal coding are desirable for multilevel anti-counterfeiting. Here, the authors engineer nanoparticles that produce binary color codes on different timescales by combining the long-lived luminescence of Mn2+ with the relatively short-lived emission of lanthanides.
- Xiaowang Liu
- , Yu Wang
- & Xiaogang Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Shuttling single metal atom into and out of a metal nanoparticle
Shuttling single metal atom into and out of a metal nanoparticle
Doping a metal nanocluster with heteroatoms dramatically changes its properties, but it remains difficult to dope with single-atom control. Here, the authors devise a strategy to dope single atoms of Ag or Cu into hollow Au nanoclusters, creating precise alloy nanoparticles atom-by-atom.
- Shuxin Wang
- , Hadi Abroshan
- & Rongchao Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Using shape to turn off blinking for two-colour multiexciton emission in CdSe/CdS tetrapods
Using shape to turn off blinking for two-colour multiexciton emission in CdSe/CdS tetrapods
CdSe/CdS tetrapods exhibit the unusual trait of two-colour multiexcitonic emission. Here Mishraet al. study this type of dual emission at the single-nanocrystal level. By tuning arm diameter and length they seek to understand shape-dependent evolution of the emission and of blinking behaviour.
- Nimai Mishra
- , Noah J. Orfield
- & Jennifer A. Hollingsworth
-
Article
| Open Access Precise localization of metal nanoparticles in dendrimer nanosnakes or inner periphery and consequences in catalysis
Precise localization of metal nanoparticles in dendrimer nanosnakes or inner periphery and consequences in catalysis
Organic supports are often employed for encapsulation of metal nanoparticles. Here the authors report a method for the precise localisation of gold, silver and copper nanoparticles within a dendrimer support and show how this localisation influences catalytic performance.
- Xiang Liu
- , Danijela Gregurec
- & Didier Astruc
-
Article
| Open Access Gram-scale synthesis of coordination polymer nanodots with renal clearance properties for cancer theranostic applications
Gram-scale synthesis of coordination polymer nanodots with renal clearance properties for cancer theranostic applications
Coordination polymers are promising drug delivery nanomaterials as their structural properties can be easily controlled. Here, Wang et al. prepare coordination nanodots that integrate cancer imaging and therapeutic functions with beneficial renal clearance.
- Fuyao Liu
- , Xiuxia He
- & Zhenxin Wang

 Emerging trends in chiral inorganic nanomaterials for enantioselective catalysis
Emerging trends in chiral inorganic nanomaterials for enantioselective catalysis