Featured
-
-
Article |
 Effect of pre-intercalation on Li-ion diffusion mapped by topochemical single-crystal transformation and operando investigation
Effect of pre-intercalation on Li-ion diffusion mapped by topochemical single-crystal transformation and operando investigation
Pre-intercalation with alkali-metal ions is attractive for accessing higher reversible capacity and improved rate performance in Li-ion batteries. Topochemical single-crystal transformations in a tunnel-structured positive electrode are used to clarify the effect of pre-intercalation in modifying the host lattice and altering diffusion pathways.
- Yuting Luo
- , Joseph V. Handy
- & Sarbajit Banerjee
-
Article |
 Creep-free polyelectrolyte elastomer for drift-free iontronic sensing
Creep-free polyelectrolyte elastomer for drift-free iontronic sensing
Conventional iontronic pressure sensors suffer from signal drift and inaccuracy owing to creep of soft materials and ion leakage. Here the authors report a leakage-free and creep-free polyelectrolyte-elastomer-based iontronic sensor that achieves a drift rate two to three orders of magnitude lower than those of conventional iontronic sensors.
- Yunfeng He
- , Yu Cheng
- & Chuan Fei Guo
-
Research Briefing |
 Semiconducting black phosphorus nanoribbons grown on insulating substrates
Semiconducting black phosphorus nanoribbons grown on insulating substrates
Single-crystal black phosphorus nanoribbons have been grown through chemical vapour transport, using black phosphorus nanoparticles as seeds. The nanoribbons orient exclusively along the zigzag direction and have good semiconductor properties that render them suitable for use as channel material in field-effect transistors.
-
Article |
 Inverse chirality-induced spin selectivity effect in chiral assemblies of π-conjugated polymers
Inverse chirality-induced spin selectivity effect in chiral assemblies of π-conjugated polymers
The authors report the inverse effect of chiral-induced spin selectivity in an organic material.
- Rui Sun
- , Kyung Sun Park
- & Dali Sun
-
Article |
 Near-room-temperature water-mediated densification of bulk van der Waals materials from their nanosheets
Near-room-temperature water-mediated densification of bulk van der Waals materials from their nanosheets
Strong bulk van der Waals materials are fabricated by the compressive moulding of two-dimensional nanosheets near room temperature through water-mediated densification, providing an energy-efficient way for synthesizing various van der Waals materials and a potential for tailoring compositions.
- Jiuyi Zhu
- , Fei Li
- & Hui-Ming Cheng
-
Article |
 Prediction of DNA origami shape using graph neural network
Prediction of DNA origami shape using graph neural network
Limited datasets hinder the accurate prediction of DNA origami structures. A data-driven and physics-informed approach for model training is presented using a graph neural network to facilitate the rapid virtual prototyping of DNA-based nanostructures.
- Chien Truong-Quoc
- , Jae Young Lee
- & Do-Nyun Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Suppression of Dexter transfer by covalent encapsulation for efficient matrix-free narrowband deep blue hyperfluorescent OLEDs
Suppression of Dexter transfer by covalent encapsulation for efficient matrix-free narrowband deep blue hyperfluorescent OLEDs
Suppressed Dexter transfer is needed to achieve efficient and stable hyperfluorescence, but complex matrices must be involved. A molecular design strategy has been proposed where Dexter transfer can be substantially reduced by an encapsulated terminal emitter, leading to ‘matrix-free’ hyperfluorescence.
- Hwan-Hee Cho
- , Daniel G. Congrave
- & Hugo Bronstein
-
News & Views |
 Mobile ion confinement for better thermoelectrics
Mobile ion confinement for better thermoelectrics
Restricting the directional segregation of mobile ions via strategic local ion confinement allows remarkable thermoelectric performance with better stability.
- Animesh Bhui
- & Kanishka Biswas
-
Article |
 Highly stabilized and efficient thermoelectric copper selenide
Highly stabilized and efficient thermoelectric copper selenide
Cu2Se is of interest for thermoelectrics as it is environmentally sustainable and has a high figure of merit ZT; however, copper ion migration impacts device stability. Here a co-doping strategy that combines steric and electrostatic effects is shown to improve device stability as well as improving ZT to 3.
- Haihua Hu
- , Yiwei Ju
- & Jing-Feng Li
-
Article |
 Lyophilized lymph nodes for improved delivery of chimeric antigen receptor T cells
Lyophilized lymph nodes for improved delivery of chimeric antigen receptor T cells
Implants made from patient-derived lyophilized lymph nodes loaded with chimeric antigen receptor T cells improve T cell delivery and inhibit tumour recurrence.
- Jiaqi Shi
- , Wei Wu
- & Zhen Gu
-
News & Views |
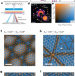 Unveiling the intricate moiré of moiré texture
Unveiling the intricate moiré of moiré texture
The atomic reconstruction and stacking arrangement in twisted trilayer graphene with a range of varying twist angles are elucidated by four-dimensional scanning transmission electron microscopy, revealing the hierarchical moiré of moiré superstructures that govern the structural symmetry at different length scales.
- Ruichun Luo
- & Wu Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Trapped O2 and the origin of voltage fade in layered Li-rich cathodes
Trapped O2 and the origin of voltage fade in layered Li-rich cathodes
Oxygen redox cathodes deliver higher energy densities than those based on transition metal redox but commonly exhibit voltage fade on extended cycling. The loss of O-redox capacity and voltage fade is shown to arise from a reduction in O2−/O2 redox process reversibility and O2 loss.
- John-Joseph Marie
- , Robert A. House
- & Peter G. Bruce
-
Article |
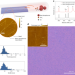 Seeded growth of single-crystal black phosphorus nanoribbons
Seeded growth of single-crystal black phosphorus nanoribbons
Single-crystal black phosphorus nanoribbons are grown uniformly on insulating substrates by chemical vapour transport growth with black phosphorus nanoparticles as seeds, demonstrating potential for application in nanoelectronic devices and the exploration of the exotic physics in black phosphorus.
- Hongya Wang
- , Yichen Song
- & Yuanbo Zhang
-
Article |
 Fibration of powdery materials
Fibration of powdery materials
A universal and non-destructive technique is developed to process diverse types of powder into micro- or nanofibres, providing flexibility for material design and applications based on functional particles.
- Hanwei Wang
- , Cheng Zeng
- & Huiqiao Li
-
Article |
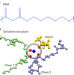 Nanosecond solvation dynamics in a polymer electrolyte for lithium batteries
Nanosecond solvation dynamics in a polymer electrolyte for lithium batteries
Solvation dynamics at picosecond timescales critically affect charge transport in aqueous systems, but conflicting values have been reported for organic electrolytes. Lifetimes on the order of 1 ns for mixtures of organic polymer and lithium salt exhibiting ultraslow dynamics of solvation shell break-up are now reported.
- Neel J. Shah
- , Chao Fang
- & Nitash P. Balsara
-
Article |
 Nanofeather ruthenium nitride electrodes for electrochemical capacitors
Nanofeather ruthenium nitride electrodes for electrochemical capacitors
Fast charging is driving extensive research on enhanced electrodes for high-performance electrochemical capacitors and micro-supercapacitors. Thick ruthenium nitride pseudocapacitive films are shown to exhibit enhanced capacitance with a time constant of less than 6 s.
- Huy Dinh Khac
- , Grace Whang
- & Christophe Lethien
-
Article |
 High-density stable glasses formed on soft substrates
High-density stable glasses formed on soft substrates
Controlling substrate elasticity during physical vapour deposition allows access to high-density stable glasses that would otherwise be formed under prohibitively slow deposition conditions on rigid substrates.
- Peng Luo
- , Sarah E. Wolf
- & Zahra Fakhraai
-
Article |
 Bridging length scales in organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors through internal strain and mesoscale dynamics
Bridging length scales in organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors through internal strain and mesoscale dynamics
Understanding mesoscale structure and dynamics in organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors is crucial. Mesoscale strain kinetics and structural hysteresis have been studied, and they uncover the coupling between charge carrier dynamics and mesoscale order in organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors.
- Ruiheng Wu
- , Dilara Meli
- & Christopher J. Takacs
-
Perspective |
 Creating chirality in the nearly two dimensions
Creating chirality in the nearly two dimensions
Two-dimensional (2D) materials, despite their small thickness, can display chirality that enables prominent asymmetric optical, electrical transport, and magnetic properties. This Perspective discusses the intriguing physics enabled by the structural chirality and the possible ways to create and control chirality in 2D materials.
- Hanyu Zhu
- & Boris I. Yakobson
-
Article
| Open Access Spatially reconfigurable antiferromagnetic states in topologically rich free-standing nanomembranes
Spatially reconfigurable antiferromagnetic states in topologically rich free-standing nanomembranes
Topological antiferromagnetic states are generated and spatially reconfigured in free-standing crystalline membranes of haematite through strain design.
- Hariom Jani
- , Jack Harrison
- & Paolo G. Radaelli
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid oxide coatings generate stable Cu catalysts for CO2 electroreduction
Hybrid oxide coatings generate stable Cu catalysts for CO2 electroreduction
Active and stable catalysts to accelerate the transition from fossil fuel to renewable feedstocks, reduce energy consumption and minimize environmental footprints are needed. Electrocatalysts based on copper nanocrystals encapsulated in hybrid alumina shells stable against structural reconstruction during CO2 electroreduction are reported.
- Petru P. Albertini
- , Mark A. Newton
- & Raffaella Buonsanti
-
Article |
 Room temperature optically detected magnetic resonance of single spins in GaN
Room temperature optically detected magnetic resonance of single spins in GaN
Optically detected magnetic resonance (ODMR) is an efficient mechanism for quantum sensors and has been discovered in a few systems, but all have technological limitations. Here the authors report room temperature ODMR in single defects in GaN, promising for integrated quantum sensing applications.
- Jialun Luo
- , Yifei Geng
- & Gregory D. Fuchs
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial-goosebump-driven microactuation
Artificial-goosebump-driven microactuation
Light-induced artificial goosebumps on liquid crystal elastomer skin are used to precisely manipulate passive microstructures, achieving a localized and controllable system for programmable micromachines.
- Mingchao Zhang
- , Aniket Pal
- & Metin Sitti
-
Article |
 High-quality nanocavities through multimodal confinement of hyperbolic polaritons in hexagonal boron nitride
High-quality nanocavities through multimodal confinement of hyperbolic polaritons in hexagonal boron nitride
Exploiting optical multimodal confinement, the deep-subwavelength confinement of hyperbolic phonon polaritons is demonstrated in isotopically pure hexagonal boron nitride, enabling nanoscale polariton manipulation.
- Hanan Herzig Sheinfux
- , Lorenzo Orsini
- & Frank H. L. Koppens
-
Article |
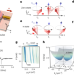 Persistent magnetic coherence in magnets
Persistent magnetic coherence in magnets
Precession phase of a magnetic material is shown to be recalled over timescales far exceeding that of Gilbert damping.
- T. Makiuchi
- , T. Hioki
- & E. Saitoh
-
Article |
 High-temperature Josephson diode
High-temperature Josephson diode
A large Josephson diode effect has been reported at liquid-nitrogen temperatures in twisted flakes of Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+δ.
- Sanat Ghosh
- , Vilas Patil
- & Mandar M. Deshmukh
-
Article |
 Photochemical tuning of dynamic defects for high-performance atomically dispersed catalysts
Photochemical tuning of dynamic defects for high-performance atomically dispersed catalysts
Developing active and stable atomically dispersed catalysts is challenging because of weak non-specific interactions between catalytically active metal atoms and supports. A general method for synthesizing these catalysts via photochemical defect tuning for controlling oxygen-vacancy dynamics is proposed.
- Chan Woo Lee
- , Byoung-Hoon Lee
- & Taeghwan Hyeon
-
News & Views |
 Chromogenic identification of breakdown
Chromogenic identification of breakdown
Early detection of electrical degradation can be identified by colour change due to the chromogenic response of blended molecules in dielectric polymers.
- Gregory A. Sotzing
- & Pritish S. Aklujkar
-
Correspondence |
 Advanced materials provide solutions towards a sustainable world
Advanced materials provide solutions towards a sustainable world
- Lars Hultman
- , Sara Mazur
- & Magnus Berggren
-
News & Views |
 A moiré proximity effect
A moiré proximity effect
Electronic moiré patterns can be imprinted remotely onto a target quantum material, inducing exotic interacting behaviour.
- Arpit Arora
- & Justin C. W. Song
-
News & Views |
 Stronger together
Stronger together
Considering responsive materials as transient collective assemblies rather than individual shape-changing objects allows for emergent functionalities that cannot be derived from the properties of single objects but are driven by interactions between them.
- Arri Priimagi
-
Research Briefing |
 Mechanism of plastic deformation in metal monochalcogenides
Mechanism of plastic deformation in metal monochalcogenides
Metal monochalcogenides — a class of van der Waals layered semiconductors — can exhibit ultrahigh plasticity. Investigation of the deformation mechanism reveals that on mechanical loading, these materials undergo local phase transitions that, coupled with the concurrent generation of a microcrack network, give rise to the ultrahigh plasticity.
-
Article
| Open Access Unlocking Li superionic conductivity in face-centred cubic oxides via face-sharing configurations
Unlocking Li superionic conductivity in face-centred cubic oxides via face-sharing configurations
Oxides with a face-centred cubic anion sublattice are generally not considered as solid-state electrolytes. Li superionic conductivity in face-centred cubic oxides with face-sharing Li configurations have now been created through cation over-stoichiometry in rocksalt-type lattices via excess Li.
- Yu Chen
- , Zhengyan Lun
- & Gerbrand Ceder
-
Article
| Open Access Quenched lattice fluctuations in optically driven SrTiO3
Quenched lattice fluctuations in optically driven SrTiO3
Intense light pulses can induce symmetry breaking, as for the generation of ferroelectricity in SrTiO3. Using ultrafast X-ray diffuse scattering at a free-electron laser, nonlinear phonon interactions that occur on such mid-IR excitation are observed, with a theory for the dynamics presented.
- M. Fechner
- , M. Först
- & A. Cavalleri
-
Article |
 Self-assembled soft alloy with Frank–Kasper phases beyond metals
Self-assembled soft alloy with Frank–Kasper phases beyond metals
Soft building blocks tend to be near spherical, limiting their packing structures to those found in metallic systems. Here the authors report the spontaneous generation of highly deformed mesoatoms using molecular pentagons and observe Frank–Kasper phases not found in metal alloys.
- Xian-You Liu
- , Xiao-Yun Yan
- & Stephen Z. D. Cheng
-
Article |
 General room-temperature Suzuki–Miyaura polymerization for organic electronics
General room-temperature Suzuki–Miyaura polymerization for organic electronics
A general process for a room-temperature, homogeneous Suzuki–Miyaura-type polymerization is reported, demonstrating a route for the scalable production of device-quality conjugated polymers.
- Haigen Xiong
- , Qijie Lin
- & Hui Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Chemo-mechanical failure mechanisms of the silicon anode in solid-state batteries
Chemo-mechanical failure mechanisms of the silicon anode in solid-state batteries
Although silicon anodes are promising for solid-state batteries, they still suffer from poor electrochemical performance. Chemo-mechanical failure mechanisms of composite Si|Li6PS5Cl and solid-electrolyte-free silicon anodes are now revealed and should help in designing improved electrodes.
- Hanyu Huo
- , Ming Jiang
- & Jürgen Janek
-
Article
| Open Access Absence of 3a0 charge density wave order in the infinite-layer nickelate NdNiO2
Absence of 3a0 charge density wave order in the infinite-layer nickelate NdNiO2
Samples of NdNiO2+x are prepared with meticulous control of the oxygen content. Their X-ray scattering and spectroscopy measurements then reveal that the previously reported charge density wave in undoped infinite-layer nickelates is, in fact, a spurious effect.
- C. T. Parzyck
- , N. K. Gupta
- & K. M. Shen
-
Article |
 Field-free switching of perpendicular magnetization by two-dimensional PtTe2/WTe2 van der Waals heterostructures with high spin Hall conductivity
Field-free switching of perpendicular magnetization by two-dimensional PtTe2/WTe2 van der Waals heterostructures with high spin Hall conductivity
The authors demonstrate field-free magnetization switching in van der Waals heterostructures.
- Fei Wang
- , Guoyi Shi
- & Hyunsoo Yang
-
Article |
 Highly anisotropic spin transport in ultrathin black phosphorus
Highly anisotropic spin transport in ultrathin black phosphorus
The authors study spin transport anisotropy in a 5.5 nm black phosphorus ribbon encapsulated by boron nitride.
- Luke Cording
- , Jiawei Liu
- & Barbaros Özyilmaz
-
Article |
 Fe–Ni-based alloys as highly active and low-cost oxygen evolution reaction catalyst in alkaline media
Fe–Ni-based alloys as highly active and low-cost oxygen evolution reaction catalyst in alkaline media
NiFe-based oxo-hydroxides are active for the oxygen evolution reaction but suffer from complex synthesis and durability when deposited. Easily processable Fe–Ni alloys with a highly active oxo-hydroxide surface are now shown to pave the way for oxygen-evolving electrodes for alkaline water electrolysers.
- Lucile Magnier
- , Garance Cossard
- & Marian Chatenet
-
Article |
 Two-dimensional few-atom noble gas clusters in a graphene sandwich
Two-dimensional few-atom noble gas clusters in a graphene sandwich
Direct observation of noble gas structures has been achieved at room temperature using electron microscopy. This was enabled by trapping them between two layers of graphene, where they form two-dimensional clusters.
- Manuel Längle
- , Kenichiro Mizohata
- & Jani Kotakoski
-
Article
| Open Access Shallow defects and variable photoluminescence decay times up to 280 µs in triple-cation perovskites
Shallow defects and variable photoluminescence decay times up to 280 µs in triple-cation perovskites
Quantifying recombination in halide perovskites is crucial, but quantitative analysis remains rare. Here the authors observe a long-lived and continuously changing photoluminescence decay time due to the high density of shallow defects and substantial rates of charge carrier trapping.
- Ye Yuan
- , Genghua Yan
- & Thomas Kirchartz
-
Article
| Open Access Electrochemical and chemical cycle for high-efficiency decoupled water splitting in a near-neutral electrolyte
Electrochemical and chemical cycle for high-efficiency decoupled water splitting in a near-neutral electrolyte
Hydrogen produced by water splitting using renewable electricity is key to achieve net-zero carbon emissions. Decoupling hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions during electrolysis is attractive but efficiency and operational challenges remain. A process producing hydrogen and oxygen in separate cells and supporting continuous operation in a membraneless system is now proposed.
- Ilya Slobodkin
- , Elena Davydova
- & Avner Rothschild
-
Article |
 Local atomic stacking and symmetry in twisted graphene trilayers
Local atomic stacking and symmetry in twisted graphene trilayers
The local layer alignment in a wide range of trilayer graphene structures has been extracted by interferometric four-dimensional scanning transmission electron microscopy, uncovering the complex picture of lattice reconstruction in twisted trilayers.
- Isaac M. Craig
- , Madeline Van Winkle
- & D. Kwabena Bediako
-
Article |
 Compensating losses in polariton propagation with synthesized complex frequency excitation
Compensating losses in polariton propagation with synthesized complex frequency excitation
Propagation losses have limited the practical use of polaritons in photonic applications. Here the authors demonstrate a substantial enhancement in the propagation distance of phonon polaritons, employing synthetic optical excitation of complex frequency with virtual gain synthesized by combining multiple real frequency measurements.
- Fuxin Guan
- , Xiangdong Guo
- & Shuang Zhang
-
Article |
 Deciphering the ultra-high plasticity in metal monochalcogenides
Deciphering the ultra-high plasticity in metal monochalcogenides
The metal monochalcogenides are a group of van der Waals layered semiconductors with ultra-high plasticity. It is now revealed that their plasticity is attributed to the ability to transform their stacking order or phases, coupled with the concurrent generation of a micro-crack network.
- Lok Wing Wong
- , Ke Yang
- & Jiong Zhao
-
Article |
 Fast cycling of lithium metal in solid-state batteries by constriction-susceptible anode materials
Fast cycling of lithium metal in solid-state batteries by constriction-susceptible anode materials
Interfacial reactions between lithium and anodes are not well understood in an all-solid environment. For the silicon anode we now demonstrate that, rather than strong Li–Si alloying at the conventional solid–liquid interface, the lithiation reaction of micrometre-sized Si can be greatly constricted at the solid–solid interface.
- Luhan Ye
- , Yang Lu
- & Xin Li
-
Article |
 All-optical multilevel physical unclonable functions
All-optical multilevel physical unclonable functions
Employing light-transformable polymers, multiple physical unclonable functions are demonstrated within a single device with all-optical reversible reconfigurability. Such devices may enable quantum secure authentication and nonlinear cryptographic key generation applications.
- Sara Nocentini
- , Ulrich Rührmair
- & Francesco Riboli

 Highly reversible extrinsic electrocaloric effects over a wide temperature range in epitaxially strained SrTiO3 films
Highly reversible extrinsic electrocaloric effects over a wide temperature range in epitaxially strained SrTiO3 films