Featured
-
-
Letter |
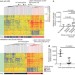 An interferon-inducible neutrophil-driven blood transcriptional signature in human tuberculosis
An interferon-inducible neutrophil-driven blood transcriptional signature in human tuberculosis
Here, the human immune response to infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis has been characterized by transcriptional profiling. The results show that active tuberculosis correlates with a particular transcriptional signature that is dominated by a neutrophil-driven interferon-inducible gene profile. The study provides a broad range of transcriptional biomarkers with potential as diagnostic and prognostic tools to combat the tuberculosis epidemic.
- Matthew P. R. Berry
- , Christine M. Graham
- & Anne O’Garra
-
Letter |
 A mechanically stabilized receptor–ligand flex-bond important in the vasculature
A mechanically stabilized receptor–ligand flex-bond important in the vasculature
Here, a new type of behaviour of receptor–ligand bonds has been identified, by using a new method that links receptor and ligand in a single molecule to measure binding and unbinding. The binding of von Willebrand factor to the glycoprotein Ib α subunit on the surface of platelets is important for coagulation. This receptor–ligand bond is now shown to have two distinct states, one seen at low force and a second that has greater force resistance. This has implications for how increased blood flow activates platelet plug formation.
- Jongseong Kim
- , Cheng-Zhong Zhang
- & Timothy A. Springer
-
Research Highlights |
Immunology: Killer cells help
-
News |
 Attack of the ancient 'zombie' ants
Attack of the ancient 'zombie' ants
Fossil leaf bears the telltale scars of insects infected by parasitic fungus.
- Kate Larkin
-
News |
 Nickel allergy tracked to a single receptor
Nickel allergy tracked to a single receptor
Molecular pathway reveals why allergen triggers reaction in humans but not in mice.
- Alla Katsnelson
-
Article |
 Mesenchymal and haematopoietic stem cells form a unique bone marrow niche
Mesenchymal and haematopoietic stem cells form a unique bone marrow niche
The identity of the cells that form the haematopoietic stem cell (HSC) niche in bone marrow has been unclear. These authors identify nestin-expressing mesenchymal stem cells as niche-forming cells. These nestin-expressing cells show a close physical association with HSCs and express high levels of genes involved in HSC maintenance, and their depletion reduces bone marrow homing of haematopoietic progenitors.
- Simón Méndez-Ferrer
- , Tatyana V. Michurina
- & Paul S. Frenette
-
News |
 Therapeutic HIV vaccines show promise
Therapeutic HIV vaccines show promise
Clinical trials hint that treatment strategy is not a dead end.
- Alison Abbott
-
Research Highlights |
 Virology: HIV spread in 3D
Virology: HIV spread in 3D
-
Research Highlights |
Immunology: HIV in the cross hairs
-
Outlook |
 On high alert
On high alert
HIV keeps the immune system in a hyperactive state, gradually leading to its ruin, reports Emma Marris.
- Emma Marris
-
Outlook |
 Tiny steps towards an HIV vaccine
Tiny steps towards an HIV vaccine
Recent successes are reinvigorating research into a vaccine for HIV, reports Cassandra Willyard.
- Cassandra Willyard
-
Outlook |
 Learning from the elite
Learning from the elite
Researchers hope to unlock the secrets of the select few who rein in, or even resist, HIV infection, says Bijal Trivedi.
- Bijal Trivedi
-
News |
 Japanese monkey deaths puzzle
Japanese monkey deaths puzzle
Researchers claim outbreaks of unknown haemorrhagic illness are no threat to humans.
- David Cyranoski
-
News |
 Souped-up antibody fends off HIV
Souped-up antibody fends off HIV
Targeted search yields proteins that neutralize nearly all HIV strains.
- Heidi Ledford
-
Research Highlights |
Cardiovascular biology: Low B cells, low plaques
-
Letter |
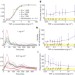 Single-cell NF-κB dynamics reveal digital activation and analogue information processing
Single-cell NF-κB dynamics reveal digital activation and analogue information processing
Multicellular organisms, particularly their immune systems, rely on complex cell-to-cell communication, mediated by signalling molecules that form spatiotemporal concentration gradients. Here, high-throughput microfluidic cell culture and fluorescence microscopy, together with quantitative gene expression analysis and mathematical modelling, have been used to investigate how mammalian cells respond to different levels of TNF-α and signal to NF-κB. Both digital and analogue responses are revealed.
- Savaş Tay
- , Jacob J. Hughey
- & Markus W. Covert
-
Letter |
 Subcapsular sinus macrophages prevent CNS invasion on peripheral infection with a neurotropic virus
Subcapsular sinus macrophages prevent CNS invasion on peripheral infection with a neurotropic virus
Macrophages that populate the lymph nodes are known to clear viruses from the lymph and to initiate antiviral humoral immune responses. It is now shown that these macrophages also have another function: they prevent lymph-borne neurotropic viruses from entering the central nervous system. The mechanism is dependent on the production of type I interferon.
- Matteo Iannacone
- , E. Ashley Moseman
- & Ulrich H. von Andrian
-
Letter |
 Sphingosine-1-phosphate is a missing cofactor for the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAF2
Sphingosine-1-phosphate is a missing cofactor for the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAF2
Engagement of the tumour-necrosis factor (TNF) receptor results in the assembly of multi-component signalling complexes by adaptor proteins that include TNF receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2). Genetic evidence indicates that TRAF2 is needed for the polyubiquitination of receptor interacting protein 1 (RIP1), but direct evidence has been lacking. Here it is shown that the lipid sphingosine-1-phosphate is a co-factor needed for this ubiquitination activity of TRAF2.
- Sergio E. Alvarez
- , Kuzhuvelil B. Harikumar
- & Sarah Spiegel
-
News |
 AIDS researcher cleared of misconduct
AIDS researcher cleared of misconduct
Berkeley cites academic freedom and lack of evidence as it wraps up investigation over contentious paper.
- Zoë Corbyn
-
Letter |
 TLR recognition of self nucleic acids hampers glucocorticoid activity in lupus
TLR recognition of self nucleic acids hampers glucocorticoid activity in lupus
Glucocorticoids are widely used to treat patients with autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), but many treatment regimens cannot maintain disease control in SLE patients. Here it is shown that the stimulation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells through toll-like receptors TLR7 and TLR9 can account for the reduced activity of glucocorticoids to inhibit the type I interferon pathway in SLE patients. Thus inhibitors of TLR7 and TLR9 signalling might prove to be effective corticosteroid-sparing drugs.
- Cristiana Guiducci
- , Mei Gong
- & Franck J. Barrat
-
Research Highlights |
Ecology: A watery grave
-
News & Views |
 Immunity takes a heavy Toll
Immunity takes a heavy Toll
Toll receptors trigger immune responses through adaptor proteins and kinase enzymes. Structural studies reveal that hierarchical assembly of these proteins into a helical tower initiates downstream signalling events.
- Steven A. Wasserman
-
News & Views |
When an infection turns lethal
Losses in biodiversity and the emergence of new infectious diseases are among the greatest threats to life on the planet. The declines in amphibian populations lie at the interface between these issues.
- Andrew R. Blaustein
- & Pieter T. J. Johnson
-
Letter |
 Functionally defective germline variants of sialic acid acetylesterase in autoimmunity
Functionally defective germline variants of sialic acid acetylesterase in autoimmunity
Sialic acid acetylesterase (SIAE) is an enzyme that is involved in B-cell activation and is required to maintain immunological tolerance in mice. It is shown here that rare, inherited and functionally defective SIAE variants are associated with a variety of autoimmune diseases in humans. The study provides one of the first examples of the importance of rare genetic variants in complex diseases, such as those involving autoimmunity.
- Ira Surolia
- , Stephan P. Pirnie
- & Shiv Pillai
-
Letter |
 Quiescent haematopoietic stem cells are activated by IFN-γ in response to chronic infection
Quiescent haematopoietic stem cells are activated by IFN-γ in response to chronic infection
Using a mouse model of Mycobacterium avium infection, it is shown here that interferon-γ regulates the proliferation of primitive haematopoietic cells during chronic infection.
- Megan T. Baldridge
- , Katherine Y. King
- & Margaret A. Goodell
-
News |
 Flu experts rebut conflict claims
Flu experts rebut conflict claims
Reports throw unsubstantiated suspicion on scientific advice given to the World Health Organization.
- Declan Butler
-
News |
 Key to psychological disorder may lie in the immune system
Key to psychological disorder may lie in the immune system
Bone-marrow transplants cure obsessive-compulsive behaviour in mice.
- Janelle Weaver
-
Article |
 Helical assembly in the MyD88–IRAK4–IRAK2 complex in TLR/IL-1R signalling
Helical assembly in the MyD88–IRAK4–IRAK2 complex in TLR/IL-1R signalling
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are crucial to innate immunity. Activation of these proteins, and of receptors for the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1 and IL-18, leads to the recruitment of adaptor proteins such as MyD88. These in turn interact with further proteins such as IRAK2 and IRAK4. The crystal structure of the MyD88–IRAK2–IRAK4 death domain complex is now reported, explaining how these three proteins cooperate in TLR/IL-1R signalling.
- Su-Chang Lin
- , Yu-Chih Lo
- & Hao Wu
-
Letter |
 Induction of tumour immunity by targeted inhibition of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay
Induction of tumour immunity by targeted inhibition of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay
The main reason why tumours are not controlled by the immune system is that they do not express potent tumour rejection antigens. Tumour vaccination aims to provoke a response to any antigens that are expressed. Here, a new approach is described: nonsense-mediated messenger RNA decay in tumour cells is inhibited, leading to the expression of new antigens and to significant inhibition of tumour growth in mice.
- Fernando Pastor
- , Despina Kolonias
- & Eli Gilboa
-
News |
 Well-trained immune cells keep HIV in check
Well-trained immune cells keep HIV in check
Differences in T-cell development may explain why some infected people do not develop AIDS.
- Alla Katsnelson
-
Letter |
 Effects of thymic selection of the T-cell repertoire on HLA class I-associated control of HIV infection
Effects of thymic selection of the T-cell repertoire on HLA class I-associated control of HIV infection
'Elite controllers' are rare people who are infected with HIV but maintain low levels of HIV RNA without being treated, making it unlikely that they will develop AIDS. Certain HLA class I alleles, notably HLA-B57, are enriched in elite controllers. Here a model is proposed to explain how such elite controllers generate an effective immune response against HIV. In this model, HLA-B57 binds to fewer self-peptides, resulting in a T-cell repertoire with enhanced cross-reactivity and leading to a more effective T-cell response to the virus.
- Andrej Košmrlj
- , Elizabeth L. Read
- & Arup K. Chakraborty
-
Letter |
 Structural basis of oligomerization in the stalk region of dynamin-like MxA
Structural basis of oligomerization in the stalk region of dynamin-like MxA
Dynamin is a protein that catalyses the scission of clathrin-coated pits at the plasma membrane. The mechanisms of dynamin-catalysed scission remain poorly understood. Here, the structure of the stalk region of human MxA, a dynamin-like protein, is presented. A structural model of MxA oligomerization and stimulated GTP hydrolysis is put forward that has functional implications for all members of the dynamin family.
- Song Gao
- , Alexander von der Malsburg
- & Oliver Daumke
-
Research Highlights |
Immunology: Inflammatory good guys
-
News |
 A shot in the arm for cancer vaccines?
A shot in the arm for cancer vaccines?
Researchers anxiously await a decision by US regulators on a controversial cancer therapy.
- Heidi Ledford
-
Letter |
 Innate lymphoid cells drive interleukin-23-dependent innate intestinal pathology
Innate lymphoid cells drive interleukin-23-dependent innate intestinal pathology
The cytokine interleukin (IL)-23 has inflammatory effects on innate immune cells and can drive colitis, but the cellular and molecular pathways involved are poorly characterized. Here it is shown that bacterial-driven innate colitis involves a previously unknown population of IL-23-responsive innate leukocytes that produce IL-17 and interferon-γ. These cells may represent a target in inflammatory bowel disease.
- Sofia Buonocore
- , Philip P. Ahern
- & Fiona Powrie
-
News & Views |
 Close encounters of the second type
Close encounters of the second type
To combat intestinal worms, mammals rely on adaptive immune responses mediated by T cells. However, it seems that, initially, innate immune cells mimic T-cell activity, while T cells get ready for action.
- Gérard Eberl
-
Research Highlights |
Immunology: Misplaced target
-
Research Highlights |
Evolution: Sex and immunity
-
News & Views |
 Host and microbes in a pickle
Host and microbes in a pickle
Metabolic disorders such as obesity are characterized by long-term, low-grade inflammation. Under certain conditions, the resident microorganisms of the gut might contribute to this inflammation, resulting in disease.
- Ping Li
- & Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
-
Letter |
 IL25 elicits a multipotent progenitor cell population that promotes TH2 cytokine responses
IL25 elicits a multipotent progenitor cell population that promotes TH2 cytokine responses
Several non-haematopoietic-cell-derived cytokines, including interleukin (IL)25, have been implicated in inducing T helper 2 (TH2) cell-dependent inflammation, but their precise role has been unclear. Here, IL25 is shown to promote the accumulation of multipotent progenitor cells in gut-associated lymphoid tissue. These cells can give rise to macrophage or granulocyte lineages that promote the differentiation of TH2 cells and contribute to protective immunity against helminth infections.
- Steven A. Saenz
- , Mark C. Siracusa
- & David Artis
-
Letter |
 Nuocytes represent a new innate effector leukocyte that mediates type-2 immunity
Nuocytes represent a new innate effector leukocyte that mediates type-2 immunity
Here, a new type of innate effector leukocyte cell — the nuocyte — is described and characterized. It is shown that interleukin (IL)25 and IL33 drive the expansion of the nuocyte population, that these cells secrete IL13, and that they are required for protection against helminth infection.
- Daniel R. Neill
- , See Heng Wong
- & Andrew N. J. McKenzie
-
Letter |
 IκBζ regulates TH17 development by cooperating with ROR nuclear receptors
IκBζ regulates TH17 development by cooperating with ROR nuclear receptors
Interleukin-17-producing helper T (TH17) cells are a distinct T-cell subset characterized by its role in autoimmune disease. Here it is shown that the development of TH17 cells requires the transcription factor IκBζ, as well as nuclear receptors of the ROR family. Mice lacking IκBζ have a defect in TH17 development and are resistant to the induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. The study points to some new potential molecular targets for drugs to treat autoimmune disease.
- Kazuo Okamoto
- , Yoshiko Iwai
- & Hiroshi Takayanagi
-
Letter |
 NLRP3 inflammasomes are required for atherogenesis and activated by cholesterol crystals
NLRP3 inflammasomes are required for atherogenesis and activated by cholesterol crystals
During atherosclerosis, crystals of cholesterol accumulate in atherosclerotic plaques. But are they a consequence or a cause of the inflammation associated with the disease? Here it is shown that small cholesterol crystals appear early in the development of atherosclerosis, and that they act as an endogenous danger signal, causing inflammation by activating the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Cholesterol crystals thus seem to be an early cause, rather than a late consequence, of inflammation.
- Peter Duewell
- , Hajime Kono
- & Eicke Latz
-
Correspondence |
Public database for HIV drug resistance in southern Africa
- Tulio de Oliveira
- , Robert W. Shafer
- & Christopher Seebregts
-
Letter |
 The kinetics of two-dimensional TCR and pMHC interactions determine T-cell responsiveness
The kinetics of two-dimensional TCR and pMHC interactions determine T-cell responsiveness
Quantification of the interaction of T-cell receptors with their peptide–MHC ligands in two–dimensional membranes is shown to yield larger dissociation rate constants than previous assays where one of the interacting partners was in solution.
- Jun Huang
- , Veronika I. Zarnitsyna
- & Cheng Zhu
-
News |
 How 1918 flu antibodies fend off swine flu
How 1918 flu antibodies fend off swine flu
Structural similarities reveal why some elderly people were spared in the recent pandemic.
- Heidi Ledford
-
News |
 Cash crisis looms for vaccine drive
Cash crisis looms for vaccine drive
Rising demand for immunization programmes in developing countries could outstrip funding.
- Declan Butler
-
Letter |
 B-cell-derived lymphotoxin promotes castration-resistant prostate cancer
B-cell-derived lymphotoxin promotes castration-resistant prostate cancer
In a mouse model of prostate cancer it is shown that infiltrating B cells promote tumorigenesis by secreting lymphotoxin. Lymphotoxin accelerates the emergence of castration-resistant prostate tumours in this model. Interfering with this pathway may offer therapeutic strategies for androgen-independent prostate cancer.
- Massimo Ammirante
- , Jun-Li Luo
- & Michael Karin
-
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Adaptive immunity
- Antigen processing and presentation
- Antimicrobial responses
- Applied immunology
- Autoimmunity
- Bone marrow transplantation
- Cell death and immune response
- Chemokines
- Coagulation system
- Complement cascade
- Cytokines
- Gene regulation in immune cells
- Haematopoiesis
- Imaging the immune system
- Immune cell death
- Immune evasion
- Immunogenetics
- Immunological disorders
- Immunotherapy
- Infection
- Infectious diseases
- Inflammation
- Innate immune cells
- Innate immunity
- Lymphatic system
- Lymphocytes
- Lymphoid tissues
- Mucosal immunology
- Neuroimmunology
- Osteoimmunology
- Plant immunology
- Signal transduction
- Translational immunology
- Transplant immunology
- Tumour immunology
- Vaccines

 Microenvironmental reprogramming of thymic epithelial cells to skin multipotent stem cells
Microenvironmental reprogramming of thymic epithelial cells to skin multipotent stem cells Immunology and the elusive AIDS vaccine
Immunology and the elusive AIDS vaccine