Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Compact and wideband nanoacoustic pass-band filters for future 5G and 6G cellular radios
Compact and wideband nanoacoustic pass-band filters for future 5G and 6G cellular radios
This work addresses the fundamental challenge of the frequency up-scaling of microacoustic devices. The manuscript presents the first bank of on-chip multi-frequency, low-loss, wideband, and compact passband filters for mobile 5G and 6G applications.
- Gabriel Giribaldi
- , Luca Colombo
- & Matteo Rinaldi
-
Article
| Open Access Frequency-hopping wave engineering with metasurfaces
Frequency-hopping wave engineering with metasurfaces
Metasurfaces show variable scattering with frequency sequence. This frequency-hopping response breaks a conventional linear frequency concept and markedly expands available frequency channels from a linear number to its factorial number.
- Hiroki Takeshita
- , Ashif Aminulloh Fathnan
- & Hiroki Wakatsuchi
-
Article
| Open Access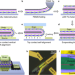 Ultrashort vertical-channel MoS2 transistor using a self-aligned contact
Ultrashort vertical-channel MoS2 transistor using a self-aligned contact
The simultaneous scaling down of the channel length and gate length of 2D transistors remains challenging. Here, the authors report a self-alignment process to fabricate vertical MoS2 transistors with sub-1 nm gate length and sub−50 nm channel length, exhibiting on-off ratios over 105 and on-state currents of 250 μA/μm at 4 V bias.
- Liting Liu
- , Yang Chen
- & Yuan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Bionic artificial skin with a fully implantable wireless tactile sensory system for wound healing and restoring skin tactile function
Bionic artificial skin with a fully implantable wireless tactile sensory system for wound healing and restoring skin tactile function
Although artificial skins can facilitate the healing of damaged skin, the restoration of tactile functions remain a challenge. Here, Kang et al. report an artificial skin with an implantable tactile sensor that can simultaneously replace the tactile function by nerve stimulation and promote skin regeneration.
- Kyowon Kang
- , Seongryeol Ye
- & Youngmee Jung
-
Article
| Open Access Photogating-assisted tunneling boosts the responsivity and speed of heterogeneous WSe2/Ta2NiSe5 photodetectors
Photogating-assisted tunneling boosts the responsivity and speed of heterogeneous WSe2/Ta2NiSe5 photodetectors
Photodetectors based on 2D materials can exhibit high photoresponsivity, but usually at the cost of their response speed. Here, the authors report a strategy based on photogating-assisted tunneling to overcome this trade-off in WSe2/Ta2NiSe5 heterostructures.
- Mingxiu Liu
- , Jingxuan Wei
- & Shaojuan Li
-
Article
| Open Access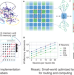 Mosaic: in-memory computing and routing for small-world spike-based neuromorphic systems
Mosaic: in-memory computing and routing for small-world spike-based neuromorphic systems
Designing efficient artificial neural network circuit architectures for optimal information routing remains a challenge. Here, the authors propose “Mosaic", the first demonstration of on-chip in-memory spike routing using memristors, optimized for small-world graphs prevalent in mammalian brains, offering orders of magnitude reduction in routing events compared to current approaches.
- Thomas Dalgaty
- , Filippo Moro
- & Melika Payvand
-
Article
| Open Access Purely self-rectifying memristor-based passive crossbar array for artificial neural network accelerators
Purely self-rectifying memristor-based passive crossbar array for artificial neural network accelerators
Designing memristor-integrated passive crossbar arrays to accelerate artificial neural networks with high reliability remains a challenge. Here, the authors propose a self-rectifying resistive switching device incorporated into a crossbar array with a density of 1 kb whose operational performance is assessed in terms of defected-cell proportion, reading margin, and selection functionality.
- Kanghyeok Jeon
- , Jin Joo Ryu
- & Gun Hwan Kim
-
Article
| Open Access A multi-stable deployable quadrifilar helix antenna with radiation reconfigurability for disaster-prone areas
A multi-stable deployable quadrifilar helix antenna with radiation reconfigurability for disaster-prone areas
Impromptu communications are indispensable for disaster-prone regions with damaged infrastructure. Here, the authors propose a mechanically actuated bi-stable reconfigurable quadrifilar helix antenna suitable for both terrestrial and satellite L-band communications.
- Rosette Maria Bichara
- , Joseph Costantine
- & Maria Sakovsky
-
Article
| Open Access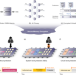 Embedding security into ferroelectric FET array via in situ memory operation
Embedding security into ferroelectric FET array via in situ memory operation
Existing solutions based Advanced Encryption Standard to address the security issues of nonvolatile memories incurs significant performance and power overhead. Here, the authors propose a lightweight XOR-gate based encryption/decryption technique by exploiting in-situ array operations, which achieves significant area/latency/power reduction compared to conventional designs.
- Yixin Xu
- , Yi Xiao
- & Kai Ni
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time photonic blind interference cancellation
Real-time photonic blind interference cancellation
The authors demonstrate real-time blind photonic interference cancellation using FPGA-photonic coordinated processing with zero calibration micro-ring resonator control and sub-second cancellation weight identification.
- Joshua C. Lederman
- , Weipeng Zhang
- & Paul R. Prucnal
-
Article
| Open Access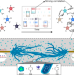 Structural plasticity for neuromorphic networks with electropolymerized dendritic PEDOT connections
Structural plasticity for neuromorphic networks with electropolymerized dendritic PEDOT connections
Neural networks are powerful tools for solving complex problems, but finding the right network topology for a given task remains an open question. Here, the authors propose a bio-inspired artificial neural network hardware able to self-adapt to solve new complex tasks, by autonomously connecting nodes using electropolymerization.
- Kamila Janzakova
- , Ismael Balafrej
- & Fabien Alibart
-
Article
| Open Access Electrical performance of a fully reconfigurable series-parallel photovoltaic module
Electrical performance of a fully reconfigurable series-parallel photovoltaic module
Reconfigurable modules have the potential to increase the energy yield of partially shaded photovoltaic systems. Here, the authors present outdoor test results of a full-scale prototype that can produce over 10% more energy than a module with fixed interconnections and six bypass diodes.
- Andres Calcabrini
- , Mirco Muttillo
- & Olindo Isabella
-
Article
| Open Access Collaborative and privacy-preserving retired battery sorting for profitable direct recycling via federated machine learning
Collaborative and privacy-preserving retired battery sorting for profitable direct recycling via federated machine learning
Unsorted retired batteries pose recycling challenges due to diverse cathodes. Here, the authors propose a privacy-preserving machine learning system that enables accurate sorting with minimal data, important for a sustainable battery recycling industry.
- Shengyu Tao
- , Haizhou Liu
- & Hongbin Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous efficiency elevation of quantum-dot light-emitting diodes induced by operational degradation
Anomalous efficiency elevation of quantum-dot light-emitting diodes induced by operational degradation
Quantum-dot light-emitting diodes may exhibit anomalous efficiency enhancement upon electrical stress, as revealed by the authors, resulting from the continuous deterioration of cathode contacts.
- Siyu He
- , Xiaoqi Tang
- & Yizheng Jin
-
Article
| Open Access A fully integrated, standalone stretchable device platform with in-sensor adaptive machine learning for rehabilitation
A fully integrated, standalone stretchable device platform with in-sensor adaptive machine learning for rehabilitation
Methods for the wireless, continuous monitoring and analysis of activities directly from the throat skin have not been developed. Here, the authors present a stretchable device platform that provides wireless measurements and machine learning-based analysis of vibrations and muscle electrical activities from the throat.
- Hongcheng Xu
- , Weihao Zheng
- & Libo Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Universal selective transfer printing via micro-vacuum force
Universal selective transfer printing via micro-vacuum force
Transfer printing of inorganic semiconductors is essential for high-performance flexible electronics. Here, Park et al. report the micro-vacuum assisted selective transfer to integrate inorganic thin-film semiconductors on unusual substrates.
- Sang Hyun Park
- , Tae Jin Kim
- & Keon Jae Lee
-
Article
| Open Access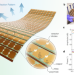 Real-data-driven real-time reconfigurable microwave reflective surface
Real-data-driven real-time reconfigurable microwave reflective surface
The authors demonstrate how flexible metasurfaces powered by artificial neural network can dynamically manipulate the EM scattering behavior from an arbitrary surface - an ultimate ambition for many EM stealth and communication problems.
- Erda Wen
- , Xiaozhen Yang
- & Daniel F. Sievenpiper
-
Article
| Open Access A semiconductor 96-microplate platform for electrical-imaging based high-throughput phenotypic screening
A semiconductor 96-microplate platform for electrical-imaging based high-throughput phenotypic screening
Cell-based phenotypic assays link in vitro discovery to disease pathology. Here, the authors report a semiconductor-based microplate platform to perform high-throughput, high-dimensional “electrical imaging” for label-free assessment of live cell morphology and function.
- Shalaka Chitale
- , Wenxuan Wu
- & Jeffrey Abbott
-
Article
| Open Access Bringing uncertainty quantification to the extreme-edge with memristor-based Bayesian neural networks
Bringing uncertainty quantification to the extreme-edge with memristor-based Bayesian neural networks
Bayesian networks gain importance in safety-critical applications. Authors conducted experiments with a memristor-based Bayesian network trained with variational inference with technological loss, achieving accurate heartbeats classification and prediction certainty.
- Djohan Bonnet
- , Tifenn Hirtzlin
- & Elisa Vianello
-
Article
| Open Access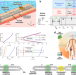 Amphibious epidermal area networks for uninterrupted wireless data and power transfer
Amphibious epidermal area networks for uninterrupted wireless data and power transfer
Body area networks represent a wearable technology suitable for applications like virtual reality and health monitoring. Here, the study presents a wireless battery-free channel that works reliably in harsh environments, including underwater. It utilizes stretchable magneto-inductive metamaterials to enable uninterrupted communication.
- Amirhossein Hajiaghajani
- , Patrick Rwei
- & Peter Tseng
-
Article
| Open Access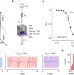 Probabilistic computing with NbOx metal-insulator transition-based self-oscillatory pbit
Probabilistic computing with NbOx metal-insulator transition-based self-oscillatory pbit
Probabilistic computing has recently emerged as a promising energy-based computing system for solving non-deterministic polynomial-time-hard (NP-hard) problems. Here the authors develop a novel pbit unit, using NbOx volatile memristor, in which a self-clocking oscillator harnesses noise-induced metal-insulator transition, enabling high-performance probabilistic computing.
- Hakseung Rhee
- , Gwangmin Kim
- & Kyung Min Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Printed sustainable elastomeric conductor for soft electronics
Printed sustainable elastomeric conductor for soft electronics
Printed stretchable electronics with sustainable elastomers are typically limited by their electro-mechanical performances. Herein, Lv et al. report a sustainable vegetable oil-based polyurethane-enabled printed conductor with high performance enabled by the porous binder and sintering of silver flakes.
- Jian Lv
- , Gurunathan Thangavel
- & Pooi See Lee
-
Article
| Open Access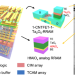 Monolithic three-dimensional integration of RRAM-based hybrid memory architecture for one-shot learning
Monolithic three-dimensional integration of RRAM-based hybrid memory architecture for one-shot learning
Designing efficient 3D artificial neural networks chip remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a M3D-LIME chip with monolithic three-dimensional integration of hybrid memory architecture based on resistive random-access memory, which achieves a high classification accuracy of 96% in one-shot learning task while exhibiting 18.3× higher energy efficiency than GPU.
- Yijun Li
- , Jianshi Tang
- & Huaqiang Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum noise and its evasion in feedback oscillators
Quantum noise and its evasion in feedback oscillators
Feedback oscillators are a fundamental tool in science and engineering. Here, Loughlin and Sudhir provide a generalized Schawlow-Townes-like formula for quantum-limited feedback oscillators, thus giving a general model to study the fundamental output noise of these devices and techniques to reduce their noise further.
- Hudson A. Loughlin
- & Vivishek Sudhir
-
Article
| Open Access Negative capacitors and inductors enabling wideband waveguide metatronics
Negative capacitors and inductors enabling wideband waveguide metatronics
The authors showcase a method to design negative lumped elements by engineering the effective permittivity within the waveguide, which enables realizations of wideband waveguide metatronics and promises performance enhancement in various fields.
- Xu Qin
- , Pengyu Fu
- & Yue Li
-
Article
| Open Access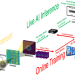 Deep learning at the edge enables real-time streaming ptychographic imaging
Deep learning at the edge enables real-time streaming ptychographic imaging
Next-generation light sources and fast detectors enable unparalleled materials characterization, but increased data rates and compute needs preclude real-time analysis. Here, Babu et al. leverage high-performance computing and AI@Edge to achieve real-time, low-dose imaging on streaming data at 2 KHz.
- Anakha V. Babu
- , Tao Zhou
- & Mathew J. Cherukara
-
Article
| Open Access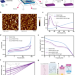 Azobenzene-based optoelectronic transistors for neurohybrid building blocks
Azobenzene-based optoelectronic transistors for neurohybrid building blocks
Designing efficient optoelectronic synaptic devices with advanced light responsive multimodal platforms remains a challenge. Here, the authors report on an organic optoelectronic neuromorphic platform that is based on conductive polymers and light-sensitive molecules that can be used to imitate the retina including visual pathways and typical memory processes of neurons.
- Federica Corrado
- , Ugo Bruno
- & Francesca Santoro
-
Article
| Open Access Wafer-scale organic-on-III-V monolithic heterogeneous integration for active-matrix micro-LED displays
Wafer-scale organic-on-III-V monolithic heterogeneous integration for active-matrix micro-LED displays
The electrical properties of solution deposited organic semiconductor channels are sensitive to substrate surface and processing conditions. Here, authors develop organic-last-integration technology to fabricate multilayer organic thin film transistor material stack onto micro light-emitting diode.
- Lei Han
- , Simon Ogier
- & Xiaojun Guo
-
Article
| Open Access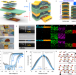 Laterally gated ferroelectric field effect transistor (LG-FeFET) using α-In2Se3 for stacked in-memory computing array
Laterally gated ferroelectric field effect transistor (LG-FeFET) using α-In2Se3 for stacked in-memory computing array
Designing a high-density memory array to effectively manage large data volumes remains a challenge. Here, the authors introduce a stacked ferroelectric memory array comprised of laterally gated ferroelectric field-effect transistors device with high vertical scalability and efficient memory properties, making it suitable for 3D in-memory computing structures.
- Sangyong Park
- , Dongyoung Lee
- & Jin-Hong Park
-
Article
| Open Access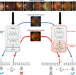 Uncertainty-inspired open set learning for retinal anomaly identification
Uncertainty-inspired open set learning for retinal anomaly identification
Failure to recognize samples from unseen classes is a major limitation of AI recognition and classification of retinal anomalies. Here, the authors present the Uncertainty-inspired Open Set learning model that categorises fundus images into pre-trained categories, and provides an uncertainty score that alerts the need for manual inspection when dealing with out-of-distribution images.
- Meng Wang
- , Tian Lin
- & Huazhu Fu
-
Article
| Open Access Neuro-inspired optical sensor array for high-accuracy static image recognition and dynamic trace extraction
Neuro-inspired optical sensor array for high-accuracy static image recognition and dynamic trace extraction
Neuro-inspired vision systems hold great promise to address the growing demands of mass data processing for edge computing. Here the authors, develop a neuro-inspired optical sensor based on NbS2/MoS2 films that can operate with monolithically integrated functions of static image enhancement and dynamic trajectory registration.
- Pei-Yu Huang
- , Bi-Yi Jiang
- & Cheng-Yan Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Nonlinearity synergy: An elegant strategy for realizing high-sensitivity and wide-linear-range pressure sensing
Nonlinearity synergy: An elegant strategy for realizing high-sensitivity and wide-linear-range pressure sensing
The development of flexible pressure sensors with a wide linear range and high sensitivity is challenging. Chen et al. demonstrate a sensor for robotics and wearable devices, using nonlinear elasticity of an elastic spacer as a stiffness regulator and a microstructured sensing layer with non-linear piezoresistivity.
- Rui Chen
- , Tao Luo
- & Wei Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Remote inspection of adversary-controlled environments
Remote inspection of adversary-controlled environments
Physical unclonable functions (PUFs) normally ensure authentication of small physical objects. Here, instead, the authors observe that also rooms and buildings can serve as PUFs. They apply this insight to monitor the integrity of enclosed environments, such as art galleries, bank vaults, or data centers.
- Johannes Tobisch
- , Sébastien Philippe
- & Ulrich Rührmair
-
Article
| Open Access Fast and versatile electrostatic disc microprinting for piezoelectric elements
Fast and versatile electrostatic disc microprinting for piezoelectric elements
In this work, authors demonstrate a fast and versatile microprinting technique to produce high-performance and customizable piezoelectric elements by employing a conductive spiny disc to electrostatically trigger instability to the liquid-air interface of the ink.
- Xuemu Li
- , Zhuomin Zhang
- & Zhengbao Yang
-
Article
| Open Access A low-power vertical dual-gate neurotransistor with short-term memory for high energy-efficient neuromorphic computing
A low-power vertical dual-gate neurotransistor with short-term memory for high energy-efficient neuromorphic computing
Dendritic computing is a promising approach to enhance the processing capability of artificial neural networks. Here, the authors report the development of a neurotransistor based on a vertical dual-gate electrolyte-gated transistor with short-term memory characteristics, a 30 nm channel length, a low read power of ~3.16 fW and read energy of ~30 fJ for dendritic computing.
- Han Xu
- , Dashan Shang
- & Ming Liu
-
Article
| Open Access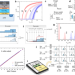 First demonstration of in-memory computing crossbar using multi-level Cell FeFET
First demonstration of in-memory computing crossbar using multi-level Cell FeFET
Designing efficient in-memory-computing architectures remains a challenge. Here the authors develop a multi-level FeFET crossbar for multi-bit MAC operations encoded in activation time and accumulated current with experimental validation at 28nm achieving 96.6% accuracy and high performance of 885 TOPS/W.
- Taha Soliman
- , Swetaki Chatterjee
- & Hussam Amrouch
-
Article
| Open Access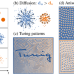 Morphogenetic metasurfaces: unlocking the potential of Turing patterns
Morphogenetic metasurfaces: unlocking the potential of Turing patterns
Inspired by Alan Turing’s last works on morphogenesis, this research introduces a technique for generating metasurfaces through the emergence of anisotropic patterns capable of self-structuring in response to electromagnetic constraints.
- Thomas Fromenteze
- , Okan Yurduseven
- & Cyril Decroze
-
Article
| Open Access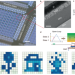 Open-loop analog programmable electrochemical memory array
Open-loop analog programmable electrochemical memory array
Memory devices with open-loop analog programmability are highly desired in training tasks. Here, the authors developed an electrochemical memory array that can be accurately programmed without any feedback, offering unique capabilities for training.
- Peng Chen
- , Fenghao Liu
- & Gang Pan
-
Article
| Open Access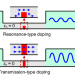 Transmission-type photonic doping for high-efficiency epsilon-near-zero supercoupling
Transmission-type photonic doping for high-efficiency epsilon-near-zero supercoupling
The authors present a transmission-type doping approach to reduce resonant losses in photonic doping. Assisted by the approach, proximate ideal epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) supercoupling with neartotal energy transmission and zero-phase advance is achieved in experiments.
- Wendi Yan
- , Ziheng Zhou
- & Yue Li
-
Article
| Open Access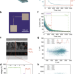 Generative complex networks within a dynamic memristor with intrinsic variability
Generative complex networks within a dynamic memristor with intrinsic variability
Designing efficient AI hardware capable of creating artificial general intelligence remains a challenge. Here, the authors present an approach for the on-demand generation of complex networks within a single memristor by harnessing device dynamics with intrinsic cycle-to-cycle variability and demonstrate the effectiveness of memristive complex network-based reservoirs.
- Yunpeng Guo
- , Wenrui Duan
- & Huanglong Li
-
Article
| Open Access Modulation of perovskite degradation with multiple-barrier for light-heat stable perovskite solar cells
Modulation of perovskite degradation with multiple-barrier for light-heat stable perovskite solar cells
The long-term stability of perovskite solar cells remains a critical challenge for the commercialization of the technology. Here, the authors adopt a non-noble metal/metal oxide/polymer multiple-barrier to suppress device degradation, achieving long-term stability in encapsulated p-i-n devices.
- Jing Zhou
- , Zonghao Liu
- & Wei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access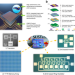 CMOS backend-of-line compatible memory array and logic circuitries enabled by high performance atomic layer deposited ZnO thin-film transistor
CMOS backend-of-line compatible memory array and logic circuitries enabled by high performance atomic layer deposited ZnO thin-film transistor
The progress of high-performance oxide-based transistors is essential for seamlessly integrating monolithic 3-D circuits into the CMOS backend. The authors propose using atomic layer deposition for ZnO due to its compatibility with low-temperature backend integration. They also successfully integrated ZnO TFTs with HfO2 RRAM in a 1 kbit 1T1R array, showcasing RRAM switching capabilities.
- Wenhui Wang
- , Ke Li
- & Yida Li
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient optimization with higher-order Ising machines
Efficient optimization with higher-order Ising machines
Combinatorial optimization problems can be solved on parallel hardware called Ising machines. Most studies have focused on the use of second-order Ising machines. Compared to second-order Ising machines, the authors show that higher-order Ising machines realized with coupled-oscillator networks can be more resource-efficient and provide superior solutions for constraint satisfaction problems.
- Connor Bybee
- , Denis Kleyko
- & Friedrich T. Sommer
-
Article
| Open Access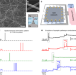 Tomography of memory engrams in self-organizing nanowire connectomes
Tomography of memory engrams in self-organizing nanowire connectomes
Hardware architectures based on self-organized memristive networks of nano objects have attracted a growing attention. Here, nanowire connectomes are experimentally proved to translate spatially correlated short-term plasticity effects into long-lasting topological changes, thus emulating both information encoding and memory consolidation of human brain.
- Gianluca Milano
- , Alessandro Cultrera
- & Carlo Ricciardi
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance cost efficient simultaneous wireless information and power transfers deploying jointly modulated amplifying programmable metasurface
High-performance cost efficient simultaneous wireless information and power transfers deploying jointly modulated amplifying programmable metasurface
In this work, the authors demonstrate a ‘jointly modulated’ amplifying programmable metasurface (APM) for simultaneous wireless information and power transmission (SWIPT). Their technique outperforms existing methods, significantly improving power transmission and adaptability for conveying energy and data across various domains, including wireless implants, 6 G networks, and IoT systems.
- Xin Wang
- , Jia Qi Han
- & Tie Jun Cui
-
Article
| Open Access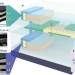 Monolithic 3D integration of 2D transistors and vertical RRAMs in 1T–4R structure for high-density memory
Monolithic 3D integration of 2D transistors and vertical RRAMs in 1T–4R structure for high-density memory
Designing a monolithic 3D structure with interleaved logic and high-density memory layers has been difficult to achieve due to challenges in managing the thermal budget. Here, the authors demonstrate a 3D integration of monolayer MoS2 transistors with 3D vertical RRAMs through a low-temperature fabrication process whose 1T–nR structure shows high promise for low-power and high-density memory applications.
- Maosong Xie
- , Yueyang Jia
- & Rui Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient combinatorial optimization by quantum-inspired parallel annealing in analogue memristor crossbar
Efficient combinatorial optimization by quantum-inspired parallel annealing in analogue memristor crossbar
Combinatorial optimization problems have various important applications but are notoriously difficult to solve. Here, the authors propose a quantum inspired algorithm and apply it to classical analog memristor hardware, demonstrating an efficient solution for intricate problems.
- Mingrui Jiang
- , Keyi Shan
- & Can Li
-
Article
| Open Access Creating speech zones with self-distributing acoustic swarms
Creating speech zones with self-distributing acoustic swarms
Want to mute or focus on speech from a specific region in a crowded room? Here, the authors built an acoustic swarm that, along with neural networks, separates and localizes concurrent speakers in the 2D space with high precision.
- Malek Itani
- , Tuochao Chen
- & Shyamnath Gollakota
-
Article
| Open Access Light-enhanced molecular polarity enabling multispectral color-cognitive memristor for neuromorphic visual system
Light-enhanced molecular polarity enabling multispectral color-cognitive memristor for neuromorphic visual system
Designing optoelectronic synapses having a multispectral color-discriminating ability is crucial for neuromorphic visual system. Here, the authors propose an strategy to introduce RGB color-discriminating synaptic functionality into a 2-terminals memristor regardless of switching medium and design a color image-recognizing CNN and light-programmable reservoir computing.
- Jongmin Lee
- , Bum Ho Jeong
- & Hui Joon Park

 Moving event detection from LiDAR point streams
Moving event detection from LiDAR point streams