Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Myoglobin-loaded gadolinium nanotexaphyrins for oxygen synergy and imaging-guided radiosensitization therapy
Myoglobin-loaded gadolinium nanotexaphyrins for oxygen synergy and imaging-guided radiosensitization therapy
Researchers have been working on radiosensitizers to improve radiotherapy efficacy. Here the authors generate gadolinium nanotexaphyrins (Gd-NTs) that self-assemble and further load it with myoglobulin to relieve hypoxia, improve radiosensitization effects of Gd-coordinated Texaphyrin, and suppress tumor recurrence.
- Xiaotu Ma
- , Xiaolong Liang
- & Fan Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of a covalent organic framework with hetero-environmental pores and its medicine co-delivery application
Synthesis of a covalent organic framework with hetero-environmental pores and its medicine co-delivery application
The characteristics of the pores are vital for controlling the performance of covalent organic frameworks, but obtaining different chemical environments in different pores is challenging. Here, the authors report the development of covalent organic frameworks with differing pore environments.
- Wenyan Ji
- , Pai Zhang
- & Bao-Hang Han
-
Comment
| Open Access Breaking barriers for glioblastoma with a path to enhanced drug delivery
Breaking barriers for glioblastoma with a path to enhanced drug delivery
Progress in treatment for glioblastoma is hindered by the blood-brain barrier (BBB). In genetic mouse models recapitulating brain invasion and abnormal angiogenesis of human glioblastoma, Cai and colleagues demonstrate that optical modulation of the BBB with nanoparticles boosts intratumoural chemotherapy concentration, prolonging survival. We discuss prospects for clinical translation of exemplary innovative techniques.
- Imran Noorani
- & Jorge de la Rosa
-
Article
| Open Access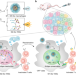 pH-gated nanoparticles selectively regulate lysosomal function of tumour-associated macrophages for cancer immunotherapy
pH-gated nanoparticles selectively regulate lysosomal function of tumour-associated macrophages for cancer immunotherapy
A high abundance of tumour associated macrophages with immunosuppressive properties is associated with inefficient anti-tumour immune responses. Here the authors report the design and characterization of pH-gated nanoparticles selectively targeting and reprogramming M2-like macrophages in the tumour microenvironment, re-sensitizing tumours to immune checkpoint blockade.
- Mingmei Tang
- , Binlong Chen
- & Yiguang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access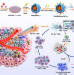 Cell microparticles loaded with tumor antigen and resiquimod reprogram tumor-associated macrophages and promote stem-like CD8+ T cells to boost anti-PD-1 therapy
Cell microparticles loaded with tumor antigen and resiquimod reprogram tumor-associated macrophages and promote stem-like CD8+ T cells to boost anti-PD-1 therapy
Tumor associated macrophages (TAMs) contribute to the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Here the authors show that macrophage-derived microparticles modified with a M2-like macrophage targeting peptide and loaded with the TLR7/8 agonist resiquimod reprogram TAMs from immunosuppressive to inflammatory, promoting anti-tumor immune responses in preclinical HCC models.
- Xiaoqiong Zhang
- , Zhaohan Wei
- & Lu Gan
-
Article
| Open Access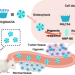 Dual hypoxia-responsive supramolecular complex for cancer target therapy
Dual hypoxia-responsive supramolecular complex for cancer target therapy
The natural product BE-43547A2 (BE) could potentially serve as a template of hypoxia target strategy for treating pancreatic cancer, but the unsatisfactory pharmacokinetics profile and severe toxicity impeded the application of BE or its derivatives. Here the authors report a supramolecular dual hypoxia-responsive BE-based complex for achieving efficient drug delivery within tumors.
- Jian-Shuang Guo
- , Juan-Juan Li
- & Yue Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Hypothermal opto-thermophoretic tweezers
Hypothermal opto-thermophoretic tweezers
Traditional optical tweezers require high laser powers risking photothermal damage of the trapped objects. Here, the authors present hypothermal opto-thermophoretic tweezers (HOTTs), which use environmental cooling to simultaneously enhance thermophoretic trapping force at low laser powers and suppress the thermal damage to trapped objects.
- Pavana Siddhartha Kollipara
- , Xiuying Li
- & Yuebing Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access A ferroptosis-targeting ceria anchored halloysite as orally drug delivery system for radiation colitis therapy
A ferroptosis-targeting ceria anchored halloysite as orally drug delivery system for radiation colitis therapy
Radiation colitis is a major side effect for pelvic radiotherapy patients, but there are limited available treatments. Here, the authors use a halloysite clay based material for the alleviation of radiation colitis in mice by inhibiting ferroptosis.
- Yue Feng
- , Xiang Luo
- & Mingxian Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Cholesterol removal improves performance of a model biomimetic system to co-deliver a photothermal agent and a STING agonist for cancer immunotherapy
Cholesterol removal improves performance of a model biomimetic system to co-deliver a photothermal agent and a STING agonist for cancer immunotherapy
Strategies for biological membrane engineering have been proposed to enhance their anti-clearance efficiency and improve their clinical translation potential. Here the authors design nanoparticles coated with low-cholesterol membranes from T cells overexpressing PD1, showing reduced clearance in the blood and improved anti-tumor efficacy when loaded with a STING agonist and a photothermal agent.
- Lin Li
- , Mengxing Zhang
- & Ling Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access CD98hc is a target for brain delivery of biotherapeutics
CD98hc is a target for brain delivery of biotherapeutics
New delivery platforms are needed to allow broader application of biotherapeutics for CNS diseases. Here, the authors show enhanced CNS delivery with a transport vehicle engineered to bind CD98hc, a highly expressed target at the blood-brain barrier.
- Kylie S. Chew
- , Robert C. Wells
- & Mihalis S. Kariolis
-
Article
| Open Access Optical blood-brain-tumor barrier modulation expands therapeutic options for glioblastoma treatment
Optical blood-brain-tumor barrier modulation expands therapeutic options for glioblastoma treatment
Relevant preclinical models and effective drug delivery strategies are important to advance glioblastoma (GBM) therapy. Here, the authors characterise genetically engineered mouse models that recapitulate two important GBM subtypes, and use them to show that picosecond laser stimulation of vascular-targeting gold nanoparticles can modulate blood-brain-tumour barrier permeability and expand therapeutic options for GBM.
- Qi Cai
- , Xiaoqing Li
- & Zhenpeng Qin
-
Article
| Open Access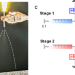 Efficient electrospray deposition of surfaces smaller than the spray plume
Efficient electrospray deposition of surfaces smaller than the spray plume
Electrospray deposition is a promising technique for depositing functional coatings at the micro-/nano-scale. Here, the authors establish the necessary conditions for high efficiency electrospray deposition of small targets, establishing promise as an alternative to other conformal coating methods.
- Sarah H. Park
- , Lin Lei
- & Jonathan P. Singer
-
Article
| Open Access Hyperthermia-triggered biomimetic bubble nanomachines
Hyperthermia-triggered biomimetic bubble nanomachines
Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems have shown potential for treating malignant tumors, however, limited tumor penetration of nanosystems remains a hurdle for effective tumor therapy. Here, the authors report a biomimetic bubble nanomachine with tumor-cell-membrane-derived nanovesicle secretion triggered by near-infrared laser irradiation for enhanced tumor penetration.
- Junbin Gao
- , Hanfeng Qin
- & Yingfeng Tu
-
Article
| Open Access Hyaluronic acid-bilirubin nanomedicine-based combination chemoimmunotherapy
Hyaluronic acid-bilirubin nanomedicine-based combination chemoimmunotherapy
Immunosuppressive tumour immune microenvironments (TME) limit the success of immune checkpoint blockade (ICD). Here, the authors develop a hyaluronic acid-bilirubin nanoparticle (HABN) capable of inducing immunogenic cell death in tumour cells and altering the TME, resulting in increased sensitivity to ICB (anti-PD-L1) in preclinical models of colorectal cancer and breast cancer.
- Yonghyun Lee
- , Jongyoon Shinn
- & James J. Moon
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of scaffold proteins for improved endogenous engineering of extracellular vesicles
Identification of scaffold proteins for improved endogenous engineering of extracellular vesicles
Extracellular vesicles are naturally occurring nanoparticles that are gaining ground as delivery modalities for therapeutics. Here, the authors conducted a large-scale screening programme to identify potential scaffold proteins for cargo loading into extracellular vesicles.
- Wenyi Zheng
- , Julia Rädler
- & Samir EL Andaloussi
-
Article
| Open Access Chemically programmed STING-activating nano-liposomal vesicles improve anticancer immunity
Chemically programmed STING-activating nano-liposomal vesicles improve anticancer immunity
Agonists of the cytosolic DNA-sensing STING pathway potently remodel the tumour immune microenvironment to support anti-tumour adaptive immunity, but at the expense of adverse systemic inflammation. Here authors exchange the STING agonist MSA-2 with its prodrugs that are suitable for nano-liposomal delivery and thus achieve increased efficiency and decreased toxicity.
- Xiaona Chen
- , Fanchao Meng
- & Hangxiang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Interventional hydrogel microsphere vaccine as an immune amplifier for activated antitumour immunity after ablation therapy
Interventional hydrogel microsphere vaccine as an immune amplifier for activated antitumour immunity after ablation therapy
Minimally invasive irreversible electroporation shows some therapeutic promise in irresectable pancreatic cancers that are notorious for poor survival. Here authors combine this with administration of a hydrogel microsphere vaccine that augments the antigen presentation T cell response cascade that naturally initiates following ablation.
- Xiaoyu Liu
- , Yaping Zhuang
- & Zhongmin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Multiomics analysis of naturally efficacious lipid nanoparticle coronas reveals high-density lipoprotein is necessary for their function
Multiomics analysis of naturally efficacious lipid nanoparticle coronas reveals high-density lipoprotein is necessary for their function
ApoE is known to be important for lipid nanoparticle function. Here, the authors shows that efficacious coronal ApoE originates from high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles and, enhances hepatic delivery, making HDL a superior biomarker for lipid nanoparticle potency.
- Kai Liu
- , Ralf Nilsson
- & Alan Sabirsh
-
Article
| Open Access Temperature-triggered in situ forming lipid mesophase gel for local treatment of ulcerative colitis
Temperature-triggered in situ forming lipid mesophase gel for local treatment of ulcerative colitis
Treatment of the chronic disease ulcerative colitis is impeded by systemic side effects of orally administered drugs. Here the authors develop a gel that uses the rectal temperature as a mechanism to trigger solidification for localized delivery of colitis therapeutics.
- Marianna Carone
- , Marianne R. Spalinger
- & Simone Aleandri
-
Article
| Open Access Scarless wound healing programmed by core-shell microneedles
Scarless wound healing programmed by core-shell microneedles
Effective reprogramming of chronic wound healing remains challenging due to the limited drug delivery efficacy hindered by physiological barriers, as well as the inappropriate dosing timing in distinct healing stages. Here, the authors report a core-shell structured microneedle array patch with programmed functions which dynamically modulates the wound immune microenvironment according to the varied healing phases
- Ying Zhang
- , Shenqiang Wang
- & Zhen Gu
-
Article
| Open Access An injectable liposome-anchored teriparatide incorporated gallic acid-grafted gelatin hydrogel for osteoarthritis treatment
An injectable liposome-anchored teriparatide incorporated gallic acid-grafted gelatin hydrogel for osteoarthritis treatment
Osteoarthritis is a common disease that causes pain and difficulty moving joints. Here the authors present an injectable gelatin-based hydrogel that slowly releases teriparatide drug to avoid frequent injections, offering a potential solution for patients with osteoarthritis.
- Guoqing Li
- , Su Liu
- & Hui Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Rectifying disorder of extracellular matrix to suppress urethral stricture by protein nanofilm-controlled drug delivery from urinary catheter
Rectifying disorder of extracellular matrix to suppress urethral stricture by protein nanofilm-controlled drug delivery from urinary catheter
Various anti-fibrotic drugs have been applied to urethral stricture by irrigation or submucosal injection, but their clinical feasibility and effectiveness are limited. Here, the authors design a protein-based nanofilm-controlled drug delivery system with anti-biofilm properties that can be assembled on a catheter.
- Juanhua Tian
- , Delai Fu
- & Peng Yang
-
Article
| Open Access GalNAc-Lipid nanoparticles enable non-LDLR dependent hepatic delivery of a CRISPR base editing therapy
GalNAc-Lipid nanoparticles enable non-LDLR dependent hepatic delivery of a CRISPR base editing therapy
Kasiewicz et al. describe a structure-guided rational design approach to optimize a new GalNAc-Lipid nanoparticle that enables delivery of a base editing therapy in both low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient and wild-type nonclinical models.
- Lisa N. Kasiewicz
- , Souvik Biswas
- & Andrew M. Bellinger
-
Article
| Open Access Restoration of lysosomal acidification rescues autophagy and metabolic dysfunction in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Restoration of lysosomal acidification rescues autophagy and metabolic dysfunction in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
In NAFLD, high levels of fatty acids in the liver impair lysosomal acidification. Here, the authors report the synthesis of novel biodegradable acid-activated acidifying nanoparticles that re-acidify lysosomes, restore autophagy, and reverse fasting hyperglycemia and hepatic steatosis in fat mice.
- Jialiu Zeng
- , Rebeca Acin-Perez
- & Mark W. Grinstaff
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning-driven multifunctional peptide engineering for sustained ocular drug delivery
Machine learning-driven multifunctional peptide engineering for sustained ocular drug delivery
Sustained drug delivery is critical for patient adherence to chronic disease treatments. Here the authors apply machine learning to engineer multifunctional peptides with high melanin binding, high cell-penetration, and low cytotoxicity, enhancing the duration and efficacy of peptide-drug conjugates for sustained ocular delivery.
- Henry T. Hsueh
- , Renee Ti Chou
- & Laura M. Ensign
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoparticle-mediated TRPV1 channel blockade amplifies cancer thermo-immunotherapy via heat shock factor 1 modulation
Nanoparticle-mediated TRPV1 channel blockade amplifies cancer thermo-immunotherapy via heat shock factor 1 modulation
TRPV1 has been associated with proliferation and survival of tumors, and can be activated by heat and other stimuli. Here, the authors block TRPV1 using photothermal nanoparticles encapsulating a TRPV1 antagonist in different cancer types, which can enhance thermo-immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer models.
- Ting Li
- , Shuhui Jiang
- & Huabing Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Cargo-free particles divert neutrophil-platelet aggregates to reduce thromboinflammation
Cargo-free particles divert neutrophil-platelet aggregates to reduce thromboinflammation
Platelet-neutrophil aggregates are a hallmark of thromboinflamation. Here, the authors use cargo-free particles to block platelet-neutrophil aggregates’ vascular wall adhesion, which could become an effective thromboinflammation therapy, regardless of disease cause.
- Alison L. Banka
- , M. Valentina Guevara
- & Omolola Eniola-Adefeso
-
Article
| Open Access An aptamer-based depot system for sustained release of small molecule therapeutics
An aptamer-based depot system for sustained release of small molecule therapeutics
Controlled delivery of small molecule therapeutics is challenging. Here the authors report a simple and effective aptamer-based depot system where the formation of aptamer/drug complexes leads to sustained release, and using this approach demonstrate improved in vivo delivery of channel blockers.
- Dali Wang
- , Yang Li
- & Christopher B. Weldon
-
Article
| Open Access Exploiting synergistic effect of CO/NO gases for soft tissue transplantation using a hydrogel patch
Exploiting synergistic effect of CO/NO gases for soft tissue transplantation using a hydrogel patch
Autologous skin flap transplantation is a common method to repair complex soft tissue defects. Here the authors develop a hydrogel patch that releases carbon monoxide and nitric oxide gases on demand, to afford a timely blood supply for skin flap transplantation during surgery, just improving the incidence of distal necrosis of the flap and reducing long-term functional loss.
- Xiaoduo Tang
- , Jingyan Ren
- & Bai Yang
-
Review Article
| Open Access Engineering protein-based therapeutics through structural and chemical design
Engineering protein-based therapeutics through structural and chemical design
Ebrahimi and Samanta review the key advances in the chemical and structural modification of proteins that have enabled their rise as indispensable tools in medicine and outline emerging protein engineering strategies that can potentially unlock structures with improved therapeutic properties.
- Sasha B. Ebrahimi
- & Devleena Samanta
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo bioluminescence imaging of natural bacteria within deep tissues via ATP-binding cassette sugar transporter
In vivo bioluminescence imaging of natural bacteria within deep tissues via ATP-binding cassette sugar transporter
Bioluminescent imaging of bacteria in vivo generally requires the use of engineered bacteria. Here the authors take advantage of bacteria specific ATP-binding cassette sugar transporters to enable selective delivery of bioluminescent nanoprobes into bacteria for visualisation, including in deep tissues.
- Qian Zhang
- , Bin Song
- & Yao He
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering tumor-specific gene nanomedicine to recruit and activate T cells for enhanced immunotherapy
Engineering tumor-specific gene nanomedicine to recruit and activate T cells for enhanced immunotherapy
Intratumoral abundance of chemokines, such as CXCL9, is an important driver of T cell infiltration in tumors. Here the authors describe the design of a tumor-specific expression strategy to drive secretion of CXCL9 and an anti-PD-L1 scFv (αPD-L1) in the tumor microenvironment, promoting T cell recruitment and anti-tumor immune response in preclinical cancer models.
- Yue Wang
- , Shi-Kun Zhou
- & Jun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Localized nuclear reaction breaks boron drug capsules loaded with immune adjuvants for cancer immunotherapy
Localized nuclear reaction breaks boron drug capsules loaded with immune adjuvants for cancer immunotherapy
Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) is a type of radiotherapy that induces cell damage through a localized nuclear reaction. Here the authors describe the design of a carborane-based covalent organic framework as a boron capsule loaded with immune adjuvants for concurrent BNCT and immunotherapy, promoting anti-tumour immune responses in preclinical cancer models.
- Yaxin Shi
- , Zhibin Guo
- & Zhibo Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Continuous Spatiotemporal Therapy of A Full-API Nanodrug via Multi-Step Tandem Endogenous Biosynthesis
Continuous Spatiotemporal Therapy of A Full-API Nanodrug via Multi-Step Tandem Endogenous Biosynthesis
Nanomedicine is important in cancer therapy, but loading, drug release, and therapeutic effectiveness issues limit the translation to the clinic. Here, authors report a full-API nanodrug with an ideal API content and pH-responsive release for continuous spatiotemporal cancer therapy based on PpIX-heme-CO/Fe2+/BV-BR metabolic pathway.
- Fang Fang
- , Sa Wang
- & Jinfeng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Acoustic metamaterials-driven transdermal drug delivery for rapid and on-demand management of acute disease
Acoustic metamaterials-driven transdermal drug delivery for rapid and on-demand management of acute disease
Treating acute disease like anaphylaxis is challenging due to the inability to administer therapeutics in a timely manner and regulate pharmacokinetics precisely within a short time window. Here the authors develop active acoustic metamaterials-driven transdermal drug delivery for rapid and on-demand acute disease management.
- Junhua Xu
- , Hongwei Cai
- & Feng Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Controlled sequential in situ self-assembly and disassembly of a fluorogenic cisplatin prodrug for cancer theranostics
Controlled sequential in situ self-assembly and disassembly of a fluorogenic cisplatin prodrug for cancer theranostics
Manipulating molecular self-assembly and disassembly in vivo may permit temporal control of drug delivery and release. Here, the authors report a fluorogenic cisplatin prodrug for cancer theranostics by leveraging stimuli-triggered in situ self-assembly and intracellular disassembly processes.
- Xidan Wen
- , Rui Zhang
- & Deju Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-long-acting in-situ forming implants with cabotegravir protect female macaques against rectal SHIV infection
Ultra-long-acting in-situ forming implants with cabotegravir protect female macaques against rectal SHIV infection
In this study, the authors developed an ultra-long-acting injectable, biodegradable, and removable in-situ forming implant delivering cabotegravir (CAB ISFI). CAB ISFI was well tolerated and protected against multiple rectal SHIV challenges in female macaques.
- Isabella C. Young
- , Ivana Massud
- & S. Rahima Benhabbour
-
Article
| Open Access Reprogramming systemic and local immune function to empower immunotherapy against glioblastoma
Reprogramming systemic and local immune function to empower immunotherapy against glioblastoma
Glioblastoma (GBM) is characterized by local and systemic immunosuppression, showing limited responses to immunotherapies. Here the authors describe the design of a nanoplatform composed of the lymphopenia alleviating agent cannabidiol and the lymphocyte recruiting cytokine LIGHT, promoting anti-tumor immune responses in GBM preclinical models.
- Songlei Zhou
- , Yukun Huang
- & Jun Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Stem cell–nanomedicine system as a theranostic bio-gadolinium agent for targeted neutron capture cancer therapy
Stem cell–nanomedicine system as a theranostic bio-gadolinium agent for targeted neutron capture cancer therapy
Gadolinium-neutron capture therapy (Gd-NCT) in glioblastoma shows promise but is limited by toxicity and short-half life in the brain. Here, the authors present a magnetised stem cell-nanoparticle system to facilitate brain penetrance of Gd-NCT and demonstrate its utility in an orthotopic rat glioblastoma model.
- Yen-Ho Lai
- , Chia-Yu Su
- & San-Yuan Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Endosomal sorting results in a selective separation of the protein corona from nanoparticles
Endosomal sorting results in a selective separation of the protein corona from nanoparticles
Protein corona formation on nanoparticles and the resultant effects on cellular interactions is well documented, where less is known about the fate of the corona in the cell. Here, the authors track the protein corona and nanoparticles in cells and describe the separation and different processing within different cellular compartments.
- Shen Han
- , Richard da Costa Marques
- & Ingo Lieberwirth
-
Article
| Open Access An integrated Mg battery-powered iontophoresis patch for efficient and controllable transdermal drug delivery
An integrated Mg battery-powered iontophoresis patch for efficient and controllable transdermal drug delivery
Wearable transdermal iontophoresis offers advantages for patient-comfort when deploying epidermal diseases treatments but current self-powered iontophoresis based on energy harvesters is limited in the support of efficient long-term operation therapeutic administration. Here, the authors propose a simplified wearable iontophoresis patch with a built-in Mg battery for efficient and controllable transdermal delivery.
- Yan Zhou
- , Xiaoteng Jia
- & Gordon Wallace
-
Article
| Open Access Molecularly self‐fueled nano-penetrator for nonpharmaceutical treatment of thrombosis and ischemic stroke
Molecularly self‐fueled nano-penetrator for nonpharmaceutical treatment of thrombosis and ischemic stroke
Thrombotic cerebro-cardiovascular diseases are the leading causes of disability and death worldwide but current drug therapeutics show important limitations. Here, the authors exploit a selfpropelling nano-penetrator with high fuel loading and controllable motion which is molecularly co-assembled using a photothermal photosensitizer and a photothermal-activable NO donor.
- Hongyuan Zhang
- , Zhiqiang Zhao
- & Cong Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Ligand-tethered lipid nanoparticles for targeted RNA delivery to treat liver fibrosis
Ligand-tethered lipid nanoparticles for targeted RNA delivery to treat liver fibrosis
Gene delivery to fibroblasts for liver fibrosis treatment remains challenging. Here the authors develop a combinatorial library of ligand-tethered lipidoids via a modular synthetic method and adopt a 2-round screening strategy to identify lipidoids for potent and selective gene delivery to fibroblasts.
- Xuexiang Han
- , Ningqiang Gong
- & Michael J. Mitchell
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic assembly of DNA-ceria nanocomplex in living cells generates artificial peroxisome
Dynamic assembly of DNA-ceria nanocomplex in living cells generates artificial peroxisome
Artificial organelles can potentially be used support cellular functions, but there is a trade-off between cellular uptake and cellular retention. Here, the authors report the dynamic assembly of DNA-ceria-based artificial peroxisomes in cells, and show they can be used to reduce intracellular ROS.
- Chi Yao
- , Yuwei Xu
- & Dayong Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered Lactococcus lactis secreting Flt3L and OX40 ligand for in situ vaccination-based cancer immunotherapy
Engineered Lactococcus lactis secreting Flt3L and OX40 ligand for in situ vaccination-based cancer immunotherapy
The probiotic Lactococcus lactis has been used for the delivery of therapeutic molecules. Here the authors engineer Lactococcus lactis to express a fusion protein of Flt3L and OX40 ligand, eliciting anti-tumor immune response in preclinical cancer models.
- Junmeng Zhu
- , Yaohua Ke
- & Baorui Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Self-cleaving guide RNAs enable pharmacological selection of precise gene editing events in vivo
Self-cleaving guide RNAs enable pharmacological selection of precise gene editing events in vivo
Here, authors show that precise integration of an rAAV vector into a chromosomal target locus results in expression of a self-cleaving guide RNA. This recombination event creates genetic resistance to a hepatotoxic compound and enables in vivo expansion of gene-edited hepatocytes using a selection drug.
- Amita Tiyaboonchai
- , Anne Vonada
- & Markus Grompe
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid chalcogen bonds in prodrug nanoassemblies provides dual redox-responsivity in the tumor microenvironment
Hybrid chalcogen bonds in prodrug nanoassemblies provides dual redox-responsivity in the tumor microenvironment
While homodimeric prodrug assemblies can improve drug loading and limit toxicity in cancer therapy, bioactivation within the target site is limited. Here, the authors introduce a hybrid chalcogen bond linker to a docetaxel dimeric prodrug nanoassembly and demonstrate its improved selfassembly, redox-responsivity and antitumor efficacy.
- Tian Liu
- , Lingxiao Li
- & Jin Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Functionally integrating nanoparticles alleviate deep vein thrombosis in pregnancy and rescue intrauterine growth restriction
Functionally integrating nanoparticles alleviate deep vein thrombosis in pregnancy and rescue intrauterine growth restriction
There is still an unmet need for effective and safe drugs to treat deep vein thrombosis during pregnancy, a life-threatening condition for the mother and fetus. Here, the authors show that engineered multifunctional nanoparticles can site-specifically dissolve thrombi and reverse deep vein thrombosis-mediated intrauterine growth restriction and delayed development of fetuses in pregnant rats.
- Juan Cheng
- , Siqi Zhang
- & Jianxiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic electrodynamic nanoparticles comprising ginger-derived extracellular vesicles for synergistic anti-infective therapy
Biomimetic electrodynamic nanoparticles comprising ginger-derived extracellular vesicles for synergistic anti-infective therapy
Antibacterial materials often suffer from issues around safety and application in complex in vivo environments. Here the authors report on the conjugation of electro-driven catalytic Pd-Pt nanosheets on ginger-derived extracellular vesicles for bacterial uptake and synergistic antibacterial therapy.
- Zhuangzhuang Qiao
- , Kai Zhang
- & Fu-Jian Xu

 Lipid nanoparticles with PEG-variant surface modifications mediate genome editing in the mouse retina
Lipid nanoparticles with PEG-variant surface modifications mediate genome editing in the mouse retina